1.5 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
1.5a - Windows Command Line Tools: Professor Messer
Navigation
cd/chdir

cd/chdir: Allows users to change the directory they’re working in/their current directory.cd ..: Variant of thecdcommand that allows users to navigate one directory above the current working directory.
dir

dir: Displays a list of files and folders (directories) in a directory. Can be used for the current directory, but you can use a specific path to view another directory (e.g.,C:\Users\currentuser\Downloads).
Disk management
chkdsk
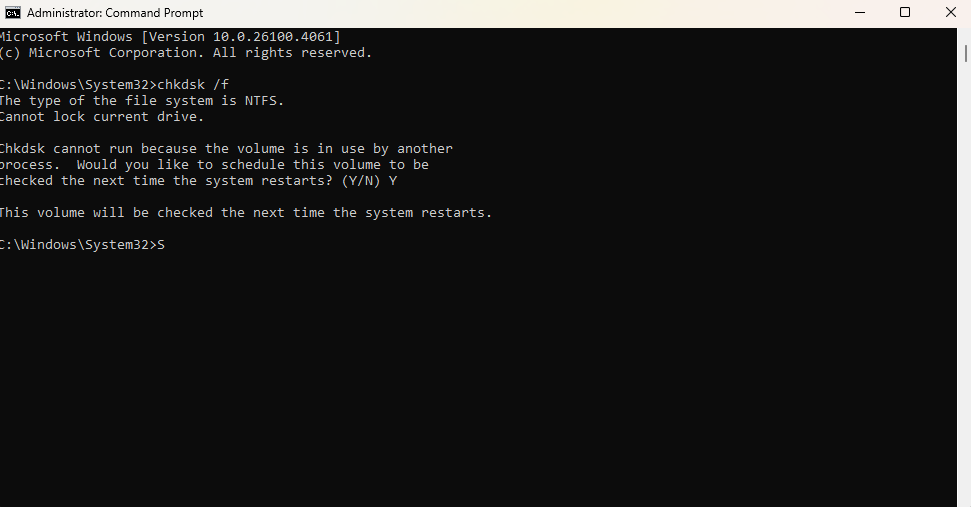
chkdsk: Command used to check the filesystem on a disk.chkdsk /f: Command used to check a disk’s filesystem and fix logical errors present on a disk.chkdsk /r: Command used to locate bad drive sectors and recover readable information - use of/rimplies/f.
format
format: Command used to format a disk for use within Windows (i.e., initializes a filesystem and prepares to write files to a storage drive). BE CAREFUL WITH DRIVE ADMINISTRATION (USE BACKUPS) - YOU CAN LOSE DATA!
diskpart
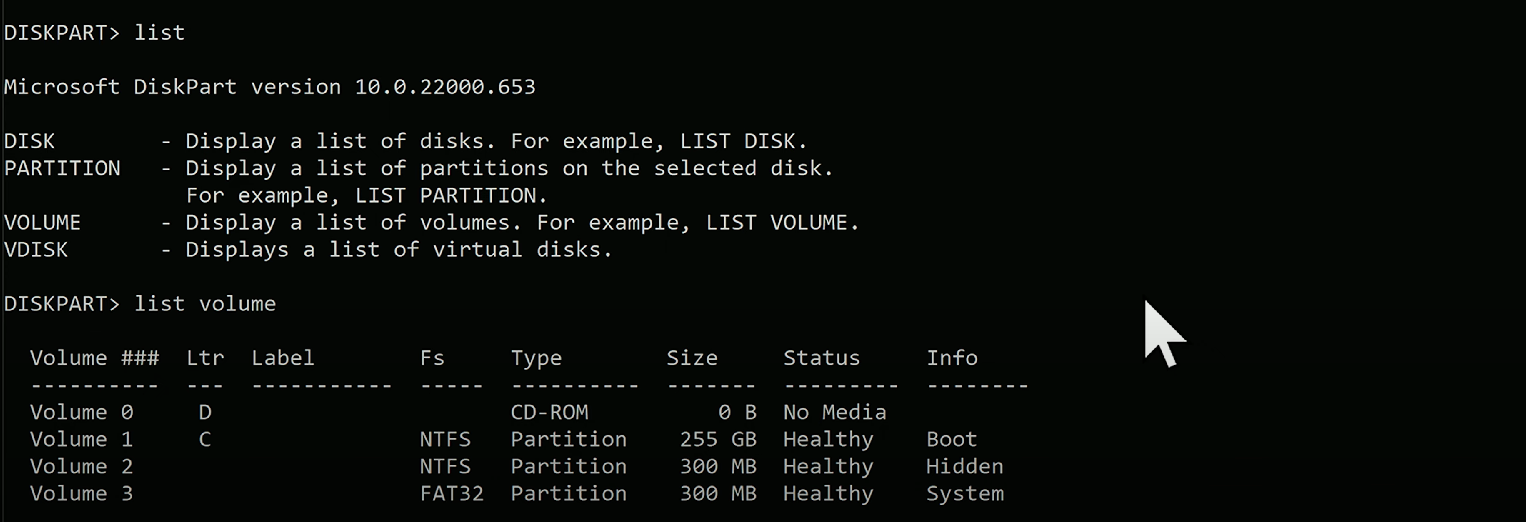
diskpart: Command used to create and manage disk partitions (which are then formatted usingformat). BE CAREFUL AND HAVE BACKUPS - YOU CAN LOSE DATA.
File management
md/mkdir
md/mkdir: Command used to create a new directory in the specified path.
rd/rmdir
rd/rmdir: Command used to remove a directory.
del/erase
del/erase: Command used to remove files.
robocopy
robocopy: Command used to copy files and directories while retaining attributes and permissions. Uses syntaxrobocopy <source> <destination> <file> \[parameters].
copy
copy: Command used to copy files from one location to another. Uses syntaxcopy \[parameters] <source> \[parameters] <destination>.copy \v: Variant of thecopycommand that verifies copies are written correctly (i.e., uses a prompt).copy \y: Variant of thecopycommand that suppresses confirmation prompts (used when you want to overwrite an existing destination file).
Informational
hostname
hostname: Command used to display or set the name of the selected Windows Device.
net user
net user: Command used to manage user accounts on a Windows Device, allowing the creation, modification, or deletion of users.
winver
winverCommand used to display the “About Windows” dialog - used to check the version of Windows running on a machine.
whoami
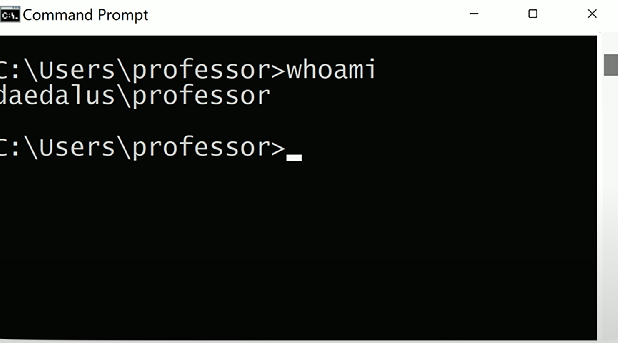
whoami: Command used to find user/group information for a Windows machine (i.e., who you’re logged in as).whoami /all: Variant of thewhoamicommand that provides detailed information about the user. Shows the username, SID, group information, and attributes/privileges associated with the user’s group(s).
[command name] /? or help [command name]
[command name] /?orhelp [command name]: Used to check a command and its parameters for proper usage.
OS management
Windows workstations (for business/large-scale environments) are administered via Group Policy. This is used to control settings on individual user/individual group workstations.
gpupdate
gpupdate: Command used to update a Group Policy for a specific user or account. Uses syntaxgpupdate /target:{computer|user}orgpupdate /target:user.gpupdate /force: Command used to force a Group Policy update for a specific user. Uses syntaxgpupdate /target:{computer|user} /forceorgpupdate /target:user /force.
gpresult
gpresult: Used to verify Group Policy Settings for a computer or user. Uses the/rparameter to check for GPO settings currently running
sfc
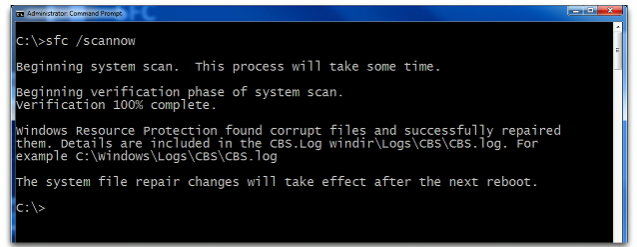
sfc: System File Checker - Windows utility that allows users to scan for and restore corrupted Windows operating system files.
1.5b - The Windows Network Command Line: Professor Messer
Network
ipconfig
ipconfig: A command used to display and manage the network configurations of a Windows computer, including IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, TCP/IP and network adapters, and DNS/DHCP servers.
ping

ping: Command used to test reachability - if an IP address exists/is reachable on a network. Determines round-trip time using Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). Primary network troubleshooting tools.
netstat
netstat: Command used to analyze network communications - what devices are communicating with this device on a local/external network.netstat -a: Variation of thenetstatcommand used to check all active connections to a Windows machine.netstat -b: Variation of thenetstatcommand used to check what Windows binaries (applications) are being used for communication. Requires elevated/Admin privileges to run.netstat -n: Variation of thenetstatcommand that prevents netstat from performing DNS name resolutions.
nslookup
nslookup: Command used to find information for nameservers/DNS servers (FQDNs, IP addresses, etc.).
net user
net user: Command used to connect, disconnect and display information about shared network resources, allowing users to map network drives.
tracert
tracert: Command used to check the route a packet takes to its destination. The TTL value given refers to the number of hops (i.e., connections), rather than seconds/minutes (TTL=1 is the first connection, TTL=2 is the second).Mechanics of tracert:
A packet is sent across network
Packet encounters a router, which decreases the TTL value by 1
If a packet receives a TTL value of zero, this produces a “TTL exceeded” error
The IP address of the router (network hop) and the traceroute TTL value (e.g., 1 for the first hop, 2 for the second hop) are sent back to the original machine
The original machine keeps sending traceroute TTL packets (with incrementing TTL values), until the TTL packets reach their destination, where the receiving machine’s IP is recorded as the last hop.
pathping
pathping: A command that combines the functionalities of ping and tracert, by first running a traceroute, then measuring round-trip time/packet loss at each hop (ping).