math revision T05 - pranaya
TOPIC 5: MEASUREMENT
W1AB: CAS Skills Part 1
Simple calculations:
Click the grey calculator icon to create a new document. Then, just type the expression you want to solve, and solve it.
Solving equations with a CAS:
To solve equations on the CAS,
Press ‘menu’
Press ‘3: Algebra’
Press ‘1: Solve’
Type the equation in the bracket, and put a comma, then the pronumeral to solve for next to it.
e.g. solve(x+2=5,x)
NOTE: you can also type ‘solve’ in the calculator, but this might take a long time, since the keyboard layout is not QWERTY.
Solving inequalities on the CAS:
To solve inequalities, do the same thing that you would do for equations, but use the inequality signs (ctrl + =)
e.g. solve(9–2*x<25,x)
NOTE: you need to put 2*x if you want to do 2x in the CAS.
W2AB: Length, Perimeter and Circumference
If units are in the question, you MUST put them in the answer. You don’t have to include units if the unit isn’t specified.
PERIMETER OF A CIRCLE = 2πr or πd (r = radius, d = diameter).
SECTORS: A sector is a fraction of a circle. The fraction can be found by θ/360 (θ = angle of the sector)
PERIMETER OF A SECTOR: θ/360 × πd + 2r
NOTE: if the question doesn’t specify the number of decimal places the final answer needs to be rounded off, then put the answer in terms of pi.
W3AB: Area of 2D shapes:
AREA OF A TRIANGLE = 1/2 x b x h (b = base, h = height)
AREA OF A SQUARE = l² (l = length)
AREA OF A CIRCLE = πr² (r = radius)
AREA OF A RECTANGLE = l x w (l = length, w = width)
AREA OF A TRAPEZIUM = 1/2 (a+b)h (a = top length, b = bottom length, h = height)
AREA OF A KITE/RHOMBUS = xy/2 (x = horizontal length, y = vertical length)
AREA OF A PARALLELOGRAM: = b x h (b = base, h = height)
Composite shapes:
To find areas of composite shapes, you need to break them down into simpler shapes, and find the area of the shapes.
W4AB: Total Surface Area
Total surface area:
The total surface area of a 3D shape can be found by adding up the area of all the sides of the shape.
TSA of a cuboid = 2(wl)+2(wh)+2(lh)
TSA of a cylinder = 2πr²+2πrh
TSA of a cube = 6l²
Composite solids:
Composite solids are basically like composite shapes, but with 3D shapes. You find the total surface area of them by eliminating common faces.
e.g. if there is a cylinder on top of a cuboid, you have to subtract the area of the circular face of the cylinder from the area of the top face of the cuboid.
W5AB: Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
What are prisms?
Prisms are solids that have a constant cross section
AREA OF A PRISM = cross section x length
What are cylinders?
Cylinders are solids with a constant circular cross section.
AREA OF A CYLINDER = same as area of a prism
What is a cross section?
A cross section is a two-dimensional shape that results from cutting a solid.
Why is it important for us to identify the cross-section before calculating the volume of prisms and cylinders?
Finding the cross section is important, because finding the area of it will help find the volume of the prism/cylinder.
Do pyramids have a cross section?
No, it does not, since the cross-section is inconsistent.
VOLUME OF A PRISM = cross section x height
VOLUME OF A CYLINDER = πr²h (r = radius)
VOLUME OF A CONE = πr²h/3 (r = radius, h = height)
W6AB: Unit Conversions
Linear unit conversions:
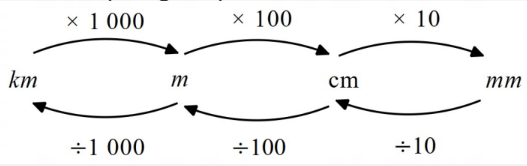
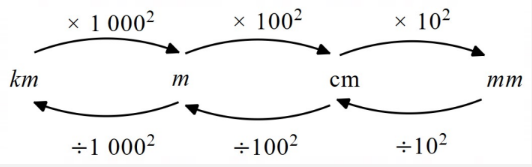
Square unit (area) conversions:
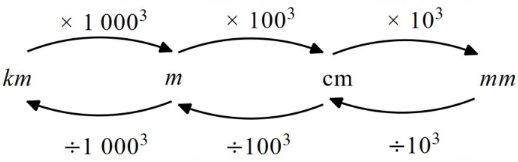
Cubic units (volume) conversions:
Liquid conversion:
1cm³ = 1mL
1m³ = 1kL
W7AB: CAS skills Part 2
Factorising with the CAS:
To factorise an expression, you need to do the following steps:
Click ‘menu’, then ‘3: Algebra’ and ‘2: Factorise’
Put the expression in the brackets, followed by ‘,x’
Press ‘enter’
NOTE: The function won’t work if you don’t put ‘,x’ next to the expression.
You can also type out ‘factor’, but it will take a while.
Expanding with the CAS:
To expand an expression, you need to do the following steps:
Click ‘menu’, then ‘3: Algebra’ and ‘3: Expand’
Put the expression in the brackets
NOTE: You need to put * between each bracket
W8AB: Transposing Formulae
Transposing with a CAS:
To transpose an equation, use the solve function, and the pronumeral that you need to make the subject next to the comma.
e.g. d = s*t (make s the subject)
solve(d=s*t,s)
