
AP GoPo Chapter 4
Founders intended presidents to have limited powers, but presidents utilize the expressed, implied, or delegated powers
requirements to be president: natural born citizen, at least 35 years old, have lived in the US for at least 14 years
there was first no limit to how many terms a president could serve until F. Roosevelt’s election to a fourth term in 1944, and with 22nd amendment now you can only serve 2 terms
The president can be impeached for conviction of treason, bribery, or other high crimes. In this case or in the case of death, resignation, or temporary disability, the vice president shall become president.
The president plays the chief executive, legislative leader, chief diplomat, political party and public opinion leader, and military commander
expressed powers: powers that are specifically outlined in the Constitution
implied powers: powers that are not expressly stated, but have been interpreted by the presidents as necessary to faithfully execute the law
delegated powers: powers that are delegated to the president by Congress in order to implement legislation
president has executive power
federal bureaucracy - The departments, agencies, bureaus, and offices of the executive branch of government that are characterized by hierarchical organization and the assignment of specific job responsibilities to employees.
The president has expressed power to establish federal departments in the executive branch
cabinet - The president’s closest advisors, consisting of each of the department secretaries as well as other discretionary officials, such as the vice president.
The president has the implied power to reorganize the federal bureaucracy
The president is like a CEO
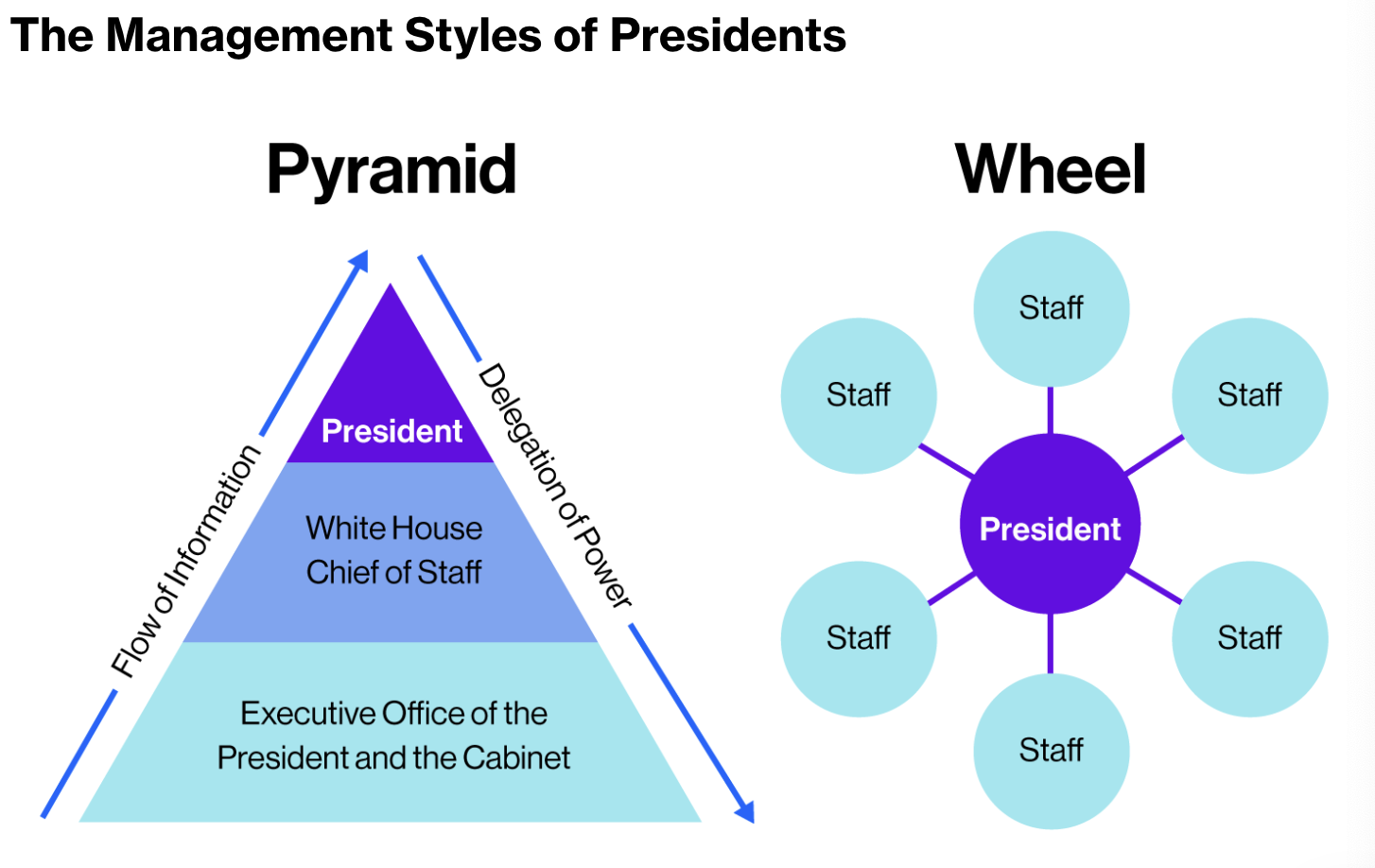
constitution implies that the president has the power to establish offices necessary to faithfully execute the law
Executive Power Clause - The portion of Article II, sec. 1, of the Constitution that grants the president the authority to carry out all laws passed by Congress. The vague language of this clause has been used by presidents to significantly expand the powers of the office.
executive orders - Declarations issued by a president that relate to the organization of the federal bureaucracy, the execution of federal legislation, and the enforcement of federal court decisions that do not require the approval of Congress.
executive privilege - The act of withholding information from congressional, judicial, or public scrutiny.
Executive orders are declarations issued by the president that relate to the organization of the federal bureaucracy, the execution of federal legislation, and the enforcement of federal court decisions.
Executive orders do not extend to legislative or judicial responsibilities, must only be used under the umbrella of executive power, and can be ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court.
In times of divided partisanship and congressional gridlock, presidents often turn to executive orders to advance their policy agenda during their first 100 days in office.
Executive privilege is an implied power that enables the president to withhold certain communications from public disclosure, primarily to protect sensitive information.
Claiming executive privilege, President Nixon attempted to withhold audio tapes related to his involvement in the Watergate scandal from evidence, but the Supreme Court dismissed his claim.
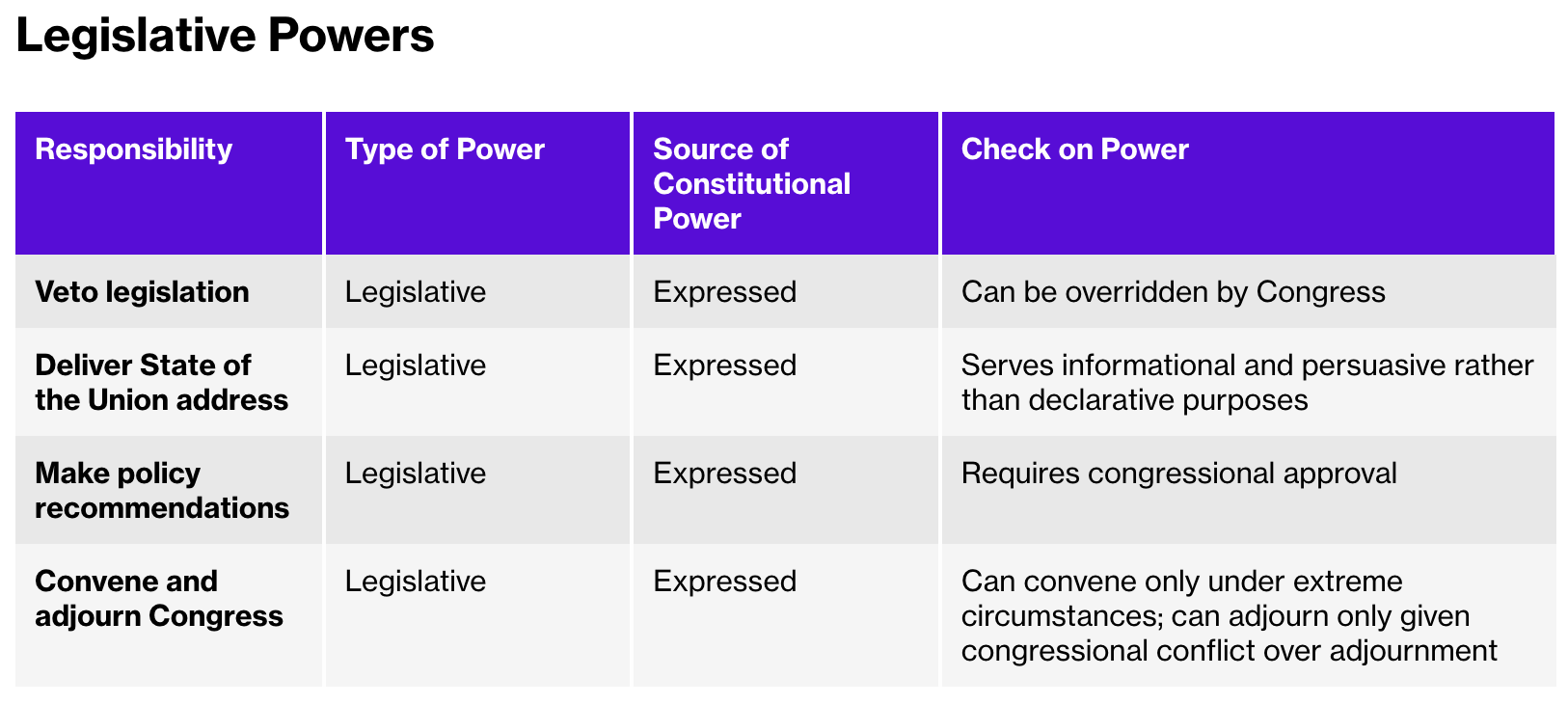
veto - The constitutional right to reject legislation, an expressed power
The president’s veto power is derived from Article I of the Constitution, which outlines the powers and responsibilities of Congress, including the legislative process and the presidential veto.
The legislative powers granted to the president by the Constitution include delivering the State of the Union address and vetoing legislation.
The Constitution grants the vice president the power to serve as the president of the Senate and cast a vote in the event of a tie.
clemency - A process by which an executive in government can grant a pardon or reduce a criminal sentence.
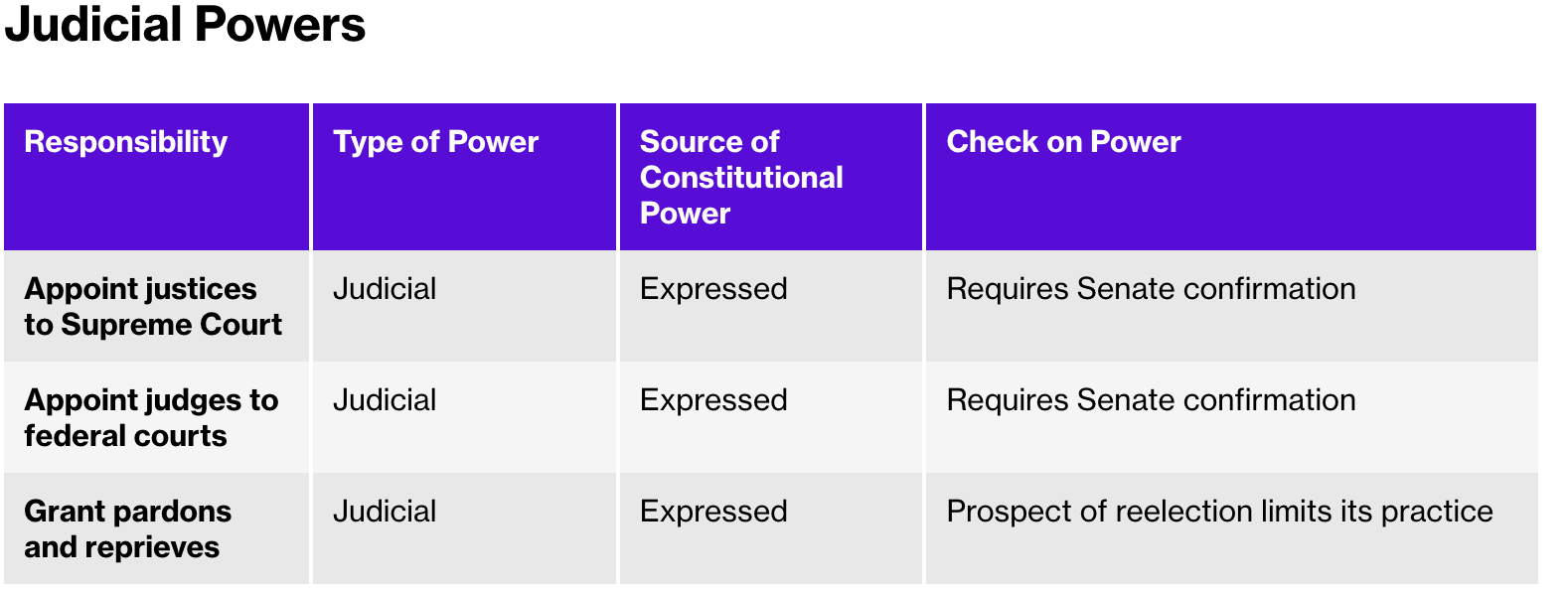
Senate confirmation - The approval of a presidential nominee by two-thirds of the senators present.
The president’s power allows them to nominate federal judges, which can shape the ideology of the judicial branch and the decisions they make.
The Constitution grants the president the power to nominate justices to the Supreme Court, but the Senate plays a crucial role in the process by confirming or rejecting these nominations through a majority vote.
Judges serve lifetime terms and their decisions influence political and legal outcomes for many years, so their appointments have long-lasting effects on politics.
pardons - The exoneration of a person from both a crime and its associated penalty.
reprieves - The exoneration of a person from the penalty associated with a crime, but not the crime itself.
amnesty - A pardon that is issued to a group of people who are not in compliance with the law.
Amnesty is a type of pardon that is issued to a group of people to exonerate them of the crime and the penalty, whereas reprieves only release an individual from the penalty.
diplomatic - The management of relationships between countries.
executive agreements - An international agreement established by the president without congressional approval.
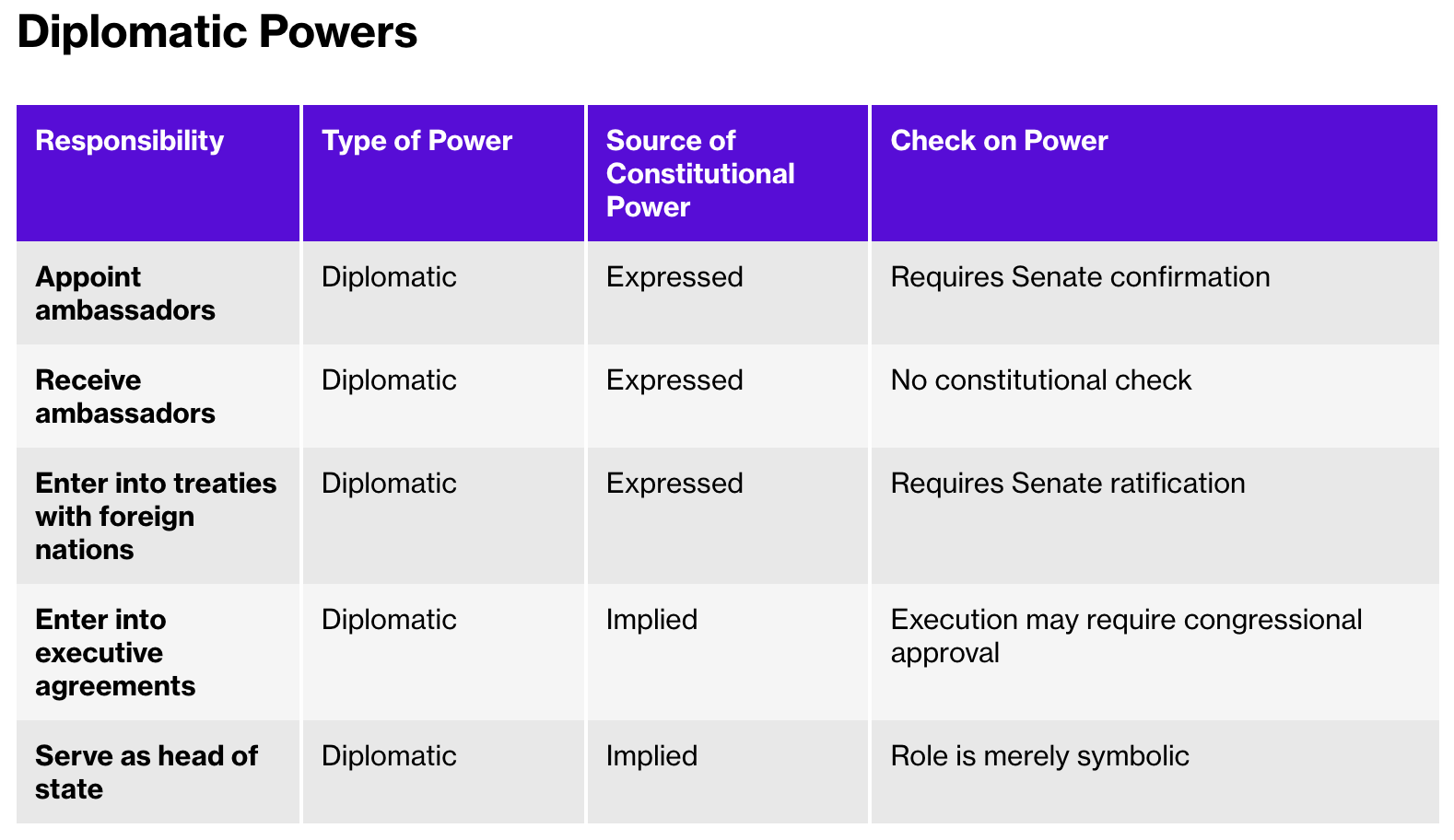
A treaty requires at least two-thirds of the Senate to support the president’s proposal
An executive agreement is an international agreement established by the president without congressional approval.
Presidents often use their role as symbolic head of state by participating in state visits, international summits, and diplomatic ceremonies, where their presence and actions symbolize the U.S. government’s commitment to diplomacy and international cooperation.
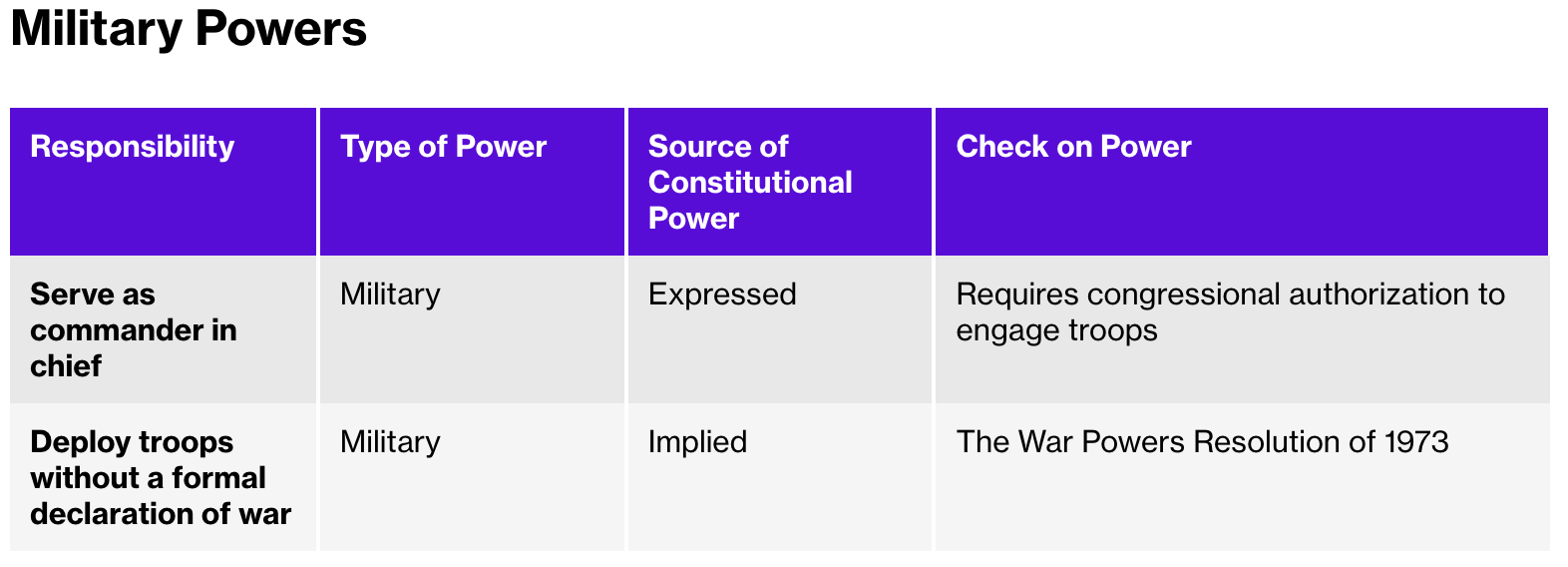
The Constitution grants Congress the authority to declare war (an expressed power), while the president is the commander in chief, which has been interpreted to mean having the power to deploy troops.
Congress has only declared war 5 times in the past 200 years, but the president has deployed troops to fight even without Congress declaring war because their expressed power as commander of chief has been interpreted to meant that they can mobilize troops as long as it is in the interest of protecting and preserving the Constitution
The War Powers Resolution (1973) was designed to limit the president’s ability to deploy the military without the consent of Congress.
The Constitution appoints the president as the commander in chief of the military who communicates directly with the top civilian and military leaders of the Department of Defense.
Presidents have interpreted their power as commander in chief to mean that they can mobilize troops without a formal declaration of war from Congress if it is in the interest of protecting and preserving the Constitution.
When George Washington was president, there were only three executive departments: State, Treasury, and War. As of 2023, there are 15 executive departments.
The physical growth in the size of the federal bureaucracy over the last 200 years is evidence of the expansion of presidential power.
The expansion of presidential power is the result of several factors, including the delegation of greater authority by Congress, the development of political parties and mass media, and the growth in the number of public policies and programs.
Commerce Clause - The enumerated power from Article I, section 8, of the Constitution that grants Congress the authority to regulate commerce. The Commerce Clause has provided the basis for expanded national power through federal legislation on a broad array of issues.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation was one of the key programs added to the federal bureaucracy as a result of the New Deal. It was established in response to the banking crisis that contributed to the Great Depression. Other New Deal programs include Social Security and the National Labor Relations Board.
During the Great Depression, the national government expanded its role significantly by implementing various social and economic policies to address the widespread unemployment and economic hardship.
By adding the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), Congress increased both presidential authority and administrative responsibility.
The sheer volume of programs and policies that the president must administer has led to the expansion of presidential power due to the increased responsibilities and decision-making authority.
The mutually beneficial relationship between the president and their political party stems from the president’s ability to enact the party’s agenda while the party engages voters.
The mutually beneficial relationship between a president and their own political party plays a crucial role in advancing the president’s policy objectives and can strengthen the president’s ability to influence the legislative process.
“Going public” in politics refers to politicians engaging and communicating with the general public through different forms of mass media to gain support for their policies, initiatives, or political goals.
habeas corpus - The right to be brought before a judge before being illegally imprisoned.
The presidential oath of office sets the parameters for presidential power by emphasizing the president’s commitment to uphold the Constitution and serve the American people within the boundaries of the law. Presidents have expanded their power over time by loosely interpreting the responsibilities suggested by the presidential oath of office.
Delegating authority can expand presidential power by allowing the president to make decisions or take actions authorized by Congress.
The Reorganization Act of 1939 act expanded the office by allowing Roosevelt six additional staff members to support his presidency.
Dickerson argues that voters want divisive candidates who talk about change. This leads to electing candidates who may not have the attributes needed for the job.
According to Dickerson, the presidency has grown too much for one person to be able to work reasonably in the office.
Although executive orders do not require the approval of Congress, they can be ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court or repealed by subsequent administrations.
Judicial review limits presidential power by enabling the courts to assess the constitutionality of presidential actions and potentially declare them unconstitutional.
One limitation on the president’s ability to veto legislation is that Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
The Constitution limits the power of the president in various ways, such as requiring Supreme Court nominations to be confirmed by senators, declarations of war to be signed by Congress, and the Senate’s approval of foreign treaties.
impeachment - The process by which the House of Representatives or another legislative body initiates charges against a government official for misconduct.
indictment - A formal, written accusation submitted to a court by a grand jury alleging that a specific person has committed a specific crime, usually a felony. An indictment is a way of charging someone with committing one or more offenses and stating that there are sufficient grounds for the court to proceed with a trial.
impeached presidents: Andrew Johnson (1868 for high crimes and misdemeanors), Bill Clinton (1998 for perjury and obstruction of justice), Donald Trump (2019 for abuse of power and obstruction of Congress, 2021 for incitement of insurrection); All were later acquitted by the Senate and none were removed from the office
Nixon was on the brink of impeachment before he resigned from office
House of Representatives has the power to impeach (Article 1, Section 2)
Article 2, Section 4: The President ... shall be removed from Office on Impeachment for, and Conviction of, Treason, Bribery, or other high Crimes and Misdemeanors.

Nixon resigned in 1974 after audio tapes were released incriminating him of wrongdoing
The impeachments of presidents Clinton and Trump revealed close party-line votes in Congress, which suggests political polarization influences the impeachment process and restricts Congress’s ability to remove an executive.
Removal from office requires a two-thirds majority vote in the Senate, so if the president’s party has a majority in the Senate, senators may prevent removal even after impeachment
According to Neustadt, a president’s performance is directly related to their ability to persuade and influence others within the political system.
LBJ (Lyndon Baines Johnson) was sworn into office on an Air Force 1 two hours after the assassination of JFK.
He was obsessed with the telephone (always calling people) and he began recording his conversations soon after he became president (around 9,000 of his conversations were recorded) which he made his secretaries transcribe
Arthur Goldberg was a Supreme Court Justice and supporter of LBJ
AP GoPo Chapter 4
Founders intended presidents to have limited powers, but presidents utilize the expressed, implied, or delegated powers
requirements to be president: natural born citizen, at least 35 years old, have lived in the US for at least 14 years
there was first no limit to how many terms a president could serve until F. Roosevelt’s election to a fourth term in 1944, and with 22nd amendment now you can only serve 2 terms
The president can be impeached for conviction of treason, bribery, or other high crimes. In this case or in the case of death, resignation, or temporary disability, the vice president shall become president.
The president plays the chief executive, legislative leader, chief diplomat, political party and public opinion leader, and military commander
expressed powers: powers that are specifically outlined in the Constitution
implied powers: powers that are not expressly stated, but have been interpreted by the presidents as necessary to faithfully execute the law
delegated powers: powers that are delegated to the president by Congress in order to implement legislation
president has executive power
federal bureaucracy - The departments, agencies, bureaus, and offices of the executive branch of government that are characterized by hierarchical organization and the assignment of specific job responsibilities to employees.
The president has expressed power to establish federal departments in the executive branch
cabinet - The president’s closest advisors, consisting of each of the department secretaries as well as other discretionary officials, such as the vice president.
The president has the implied power to reorganize the federal bureaucracy
The president is like a CEO

constitution implies that the president has the power to establish offices necessary to faithfully execute the law
Executive Power Clause - The portion of Article II, sec. 1, of the Constitution that grants the president the authority to carry out all laws passed by Congress. The vague language of this clause has been used by presidents to significantly expand the powers of the office.
executive orders - Declarations issued by a president that relate to the organization of the federal bureaucracy, the execution of federal legislation, and the enforcement of federal court decisions that do not require the approval of Congress.
executive privilege - The act of withholding information from congressional, judicial, or public scrutiny.
Executive orders are declarations issued by the president that relate to the organization of the federal bureaucracy, the execution of federal legislation, and the enforcement of federal court decisions.
Executive orders do not extend to legislative or judicial responsibilities, must only be used under the umbrella of executive power, and can be ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court.
In times of divided partisanship and congressional gridlock, presidents often turn to executive orders to advance their policy agenda during their first 100 days in office.
Executive privilege is an implied power that enables the president to withhold certain communications from public disclosure, primarily to protect sensitive information.
Claiming executive privilege, President Nixon attempted to withhold audio tapes related to his involvement in the Watergate scandal from evidence, but the Supreme Court dismissed his claim.

veto - The constitutional right to reject legislation, an expressed power
The president’s veto power is derived from Article I of the Constitution, which outlines the powers and responsibilities of Congress, including the legislative process and the presidential veto.
The legislative powers granted to the president by the Constitution include delivering the State of the Union address and vetoing legislation.
The Constitution grants the vice president the power to serve as the president of the Senate and cast a vote in the event of a tie.
clemency - A process by which an executive in government can grant a pardon or reduce a criminal sentence.

Senate confirmation - The approval of a presidential nominee by two-thirds of the senators present.
The president’s power allows them to nominate federal judges, which can shape the ideology of the judicial branch and the decisions they make.
The Constitution grants the president the power to nominate justices to the Supreme Court, but the Senate plays a crucial role in the process by confirming or rejecting these nominations through a majority vote.
Judges serve lifetime terms and their decisions influence political and legal outcomes for many years, so their appointments have long-lasting effects on politics.
pardons - The exoneration of a person from both a crime and its associated penalty.
reprieves - The exoneration of a person from the penalty associated with a crime, but not the crime itself.
amnesty - A pardon that is issued to a group of people who are not in compliance with the law.
Amnesty is a type of pardon that is issued to a group of people to exonerate them of the crime and the penalty, whereas reprieves only release an individual from the penalty.
diplomatic - The management of relationships between countries.
executive agreements - An international agreement established by the president without congressional approval.

A treaty requires at least two-thirds of the Senate to support the president’s proposal
An executive agreement is an international agreement established by the president without congressional approval.
Presidents often use their role as symbolic head of state by participating in state visits, international summits, and diplomatic ceremonies, where their presence and actions symbolize the U.S. government’s commitment to diplomacy and international cooperation.

The Constitution grants Congress the authority to declare war (an expressed power), while the president is the commander in chief, which has been interpreted to mean having the power to deploy troops.
Congress has only declared war 5 times in the past 200 years, but the president has deployed troops to fight even without Congress declaring war because their expressed power as commander of chief has been interpreted to meant that they can mobilize troops as long as it is in the interest of protecting and preserving the Constitution
The War Powers Resolution (1973) was designed to limit the president’s ability to deploy the military without the consent of Congress.
The Constitution appoints the president as the commander in chief of the military who communicates directly with the top civilian and military leaders of the Department of Defense.
Presidents have interpreted their power as commander in chief to mean that they can mobilize troops without a formal declaration of war from Congress if it is in the interest of protecting and preserving the Constitution.
When George Washington was president, there were only three executive departments: State, Treasury, and War. As of 2023, there are 15 executive departments.
The physical growth in the size of the federal bureaucracy over the last 200 years is evidence of the expansion of presidential power.
The expansion of presidential power is the result of several factors, including the delegation of greater authority by Congress, the development of political parties and mass media, and the growth in the number of public policies and programs.
Commerce Clause - The enumerated power from Article I, section 8, of the Constitution that grants Congress the authority to regulate commerce. The Commerce Clause has provided the basis for expanded national power through federal legislation on a broad array of issues.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation was one of the key programs added to the federal bureaucracy as a result of the New Deal. It was established in response to the banking crisis that contributed to the Great Depression. Other New Deal programs include Social Security and the National Labor Relations Board.
During the Great Depression, the national government expanded its role significantly by implementing various social and economic policies to address the widespread unemployment and economic hardship.
By adding the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), Congress increased both presidential authority and administrative responsibility.
The sheer volume of programs and policies that the president must administer has led to the expansion of presidential power due to the increased responsibilities and decision-making authority.
The mutually beneficial relationship between the president and their political party stems from the president’s ability to enact the party’s agenda while the party engages voters.
The mutually beneficial relationship between a president and their own political party plays a crucial role in advancing the president’s policy objectives and can strengthen the president’s ability to influence the legislative process.
“Going public” in politics refers to politicians engaging and communicating with the general public through different forms of mass media to gain support for their policies, initiatives, or political goals.
habeas corpus - The right to be brought before a judge before being illegally imprisoned.
The presidential oath of office sets the parameters for presidential power by emphasizing the president’s commitment to uphold the Constitution and serve the American people within the boundaries of the law. Presidents have expanded their power over time by loosely interpreting the responsibilities suggested by the presidential oath of office.
Delegating authority can expand presidential power by allowing the president to make decisions or take actions authorized by Congress.
The Reorganization Act of 1939 act expanded the office by allowing Roosevelt six additional staff members to support his presidency.
Dickerson argues that voters want divisive candidates who talk about change. This leads to electing candidates who may not have the attributes needed for the job.
According to Dickerson, the presidency has grown too much for one person to be able to work reasonably in the office.
Although executive orders do not require the approval of Congress, they can be ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court or repealed by subsequent administrations.
Judicial review limits presidential power by enabling the courts to assess the constitutionality of presidential actions and potentially declare them unconstitutional.
One limitation on the president’s ability to veto legislation is that Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
The Constitution limits the power of the president in various ways, such as requiring Supreme Court nominations to be confirmed by senators, declarations of war to be signed by Congress, and the Senate’s approval of foreign treaties.
impeachment - The process by which the House of Representatives or another legislative body initiates charges against a government official for misconduct.
indictment - A formal, written accusation submitted to a court by a grand jury alleging that a specific person has committed a specific crime, usually a felony. An indictment is a way of charging someone with committing one or more offenses and stating that there are sufficient grounds for the court to proceed with a trial.
impeached presidents: Andrew Johnson (1868 for high crimes and misdemeanors), Bill Clinton (1998 for perjury and obstruction of justice), Donald Trump (2019 for abuse of power and obstruction of Congress, 2021 for incitement of insurrection); All were later acquitted by the Senate and none were removed from the office
Nixon was on the brink of impeachment before he resigned from office
House of Representatives has the power to impeach (Article 1, Section 2)
Article 2, Section 4: The President ... shall be removed from Office on Impeachment for, and Conviction of, Treason, Bribery, or other high Crimes and Misdemeanors.

Nixon resigned in 1974 after audio tapes were released incriminating him of wrongdoing
The impeachments of presidents Clinton and Trump revealed close party-line votes in Congress, which suggests political polarization influences the impeachment process and restricts Congress’s ability to remove an executive.
Removal from office requires a two-thirds majority vote in the Senate, so if the president’s party has a majority in the Senate, senators may prevent removal even after impeachment
According to Neustadt, a president’s performance is directly related to their ability to persuade and influence others within the political system.

LBJ (Lyndon Baines Johnson) was sworn into office on an Air Force 1 two hours after the assassination of JFK.
He was obsessed with the telephone (always calling people) and he began recording his conversations soon after he became president (around 9,000 of his conversations were recorded) which he made his secretaries transcribe
Arthur Goldberg was a Supreme Court Justice and supporter of LBJ
 Knowt
Knowt