Cumulative AP Psych Vocab
Chapter 1 terminology:
Psychology
the science of behavior and mental processes
Wilhelm Wundt
“Father” of psychology
Founded the first psychological laboratory in Leipzig, Germany in 1897.
Established psychology as a science
Stanley Hall
Helped found the American Psychological Association (APA)
Created first psychology laboratory in the US
Founded the first psychology research journal
Structuralism- Edward Titchner
the whole can be understood by examining its parts
Sought to understand the human mind by breaking it down into its most basic components (structures)
Sensations
Mental images
Feelings, etc
Examined how these elements combine to form more complex experiences
Functionalism
Examined the function of the human mind
Was concerned with how the mind allows us to adapt and survive
Focused on the mind’s purpose, not its parts
William James
Wrote the first psychology textbook called Principles of Psychology
Was critical of structuralism
Established school of functionalism
Introspection
Process of looking inward, observing one’s mental experiences/sensations, and reporting them back to the researcher
What sensations, images, or feelings are you experiencing?
Unreliable because the results are subjective and inconsistent
Mary Whiton Calkins
Student of William James
First female to complete all PhD requirements at Harvard
Was denied degree because she was a woman
First female president of the American Psychological Association
Margaret Floy Washburn
First female to earn PhD in psychology
Studied animal behavior and wrote a book called The Animal Mind
Second female president of the American Psychological Association
Dorthea Dix
American activist on behalf of the severely mentally ill
Lobbied Congress to create first generation of mental asylums
Leta Stetter Hollingworth
Psychoanalysis- Sigmund Freud, Carl Jung,
First approach developed outside of a university setting.
Focused on the cause, development, and treatment of abnormal behavior.
Emphasized the role of the unconscious mind: the memories, feelings, and drives that are outside of our awareness.
Believed that early childhood experiences influence personality and behavior.
Believed that we are driven primarily by unconscious desires and feelings.
Criticized as being unscientific since the unconscious mind cannot be studied objectively.
Sigmund Freud
Austrian neurologist
Believed psychological illness was different than physical illness and could be cured with “talking therapy.”
Founder of psychoanalysis
Unconscious
Behaviorism- John Watson, BF Skinner
Said psychology should only be concerned with what can be objectively observed and measured
Redefined psychology as the scientific study of observable behavior
Not concerned with things that cannot be directly observed, such as thoughts, feelings, and the unconscious mind.
Believes behavior is learned (conditioned by environmental factors)
Focuses on how behaviors are learned and modified
John Watson
One of the founders of the behavioral approach
Believed psychology should only focus on what could be objectively measured
Conducted infamous Little Albert experiment
Behavior
Humanism- Carl Rogers, Abraham Maslow
Addressed perceived flaws in both the psychoanalytic and behavioral approaches
Focuses on people’s potential and their drive to be their best
Has a more positive outlook on people than the behavioral or psychoanalytic approaches
Emphasizes a person’s positive qualities
Emphasizes the capacity for human growth/reaching one’s potential
Emphasizes the freedom to choose one’s destiny
Cognitive perspective- Jean Piaget, Noam Chomsky, Herbert Simon
COGNITION = thinking / information-processing
Studies how thinking and perception influence behavior.
How we direct our attention
Memory
Thinking
Problem solving
Decision-making
In the cognitive view, an individual’s mental processes are in control of behavior through memories, perceptions, images, and thinking.
Biological perspective- James Olds, Roger Sperry, David Hubel, Torsten Wiesel
Focuses on how genetics, the nervous system, hormones, and brain structures influence a person’s thinking and behavior
Is concerned with the biological causes of human thought and behavior
Is interested in how biological treatments (medicine, surgery, etc.) may improve certain psychological conditions
Evolutionary perspective- David Buss
Began with Charles Darwin
Emphasizes how evolution influences thinking and behavior.
Looks for aspects of human thought and behavior that help us and our genes survive over time.
Focuses on humans as a species; does not focus on specific individuals
Gestalt psychology
Clinical psychology
Psychologist who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders
Provides counseling/therapy (does NOT prescribe medication)
Works in hospitals, clinics, rehabilitation centers, and private practices
Positive psychology- Martin Seligman
The scientific study of human flourishing
Goal is to discover and promote the strengths and virtues that help individuals and communities thrive
Focuses on both individual and societal well-being
APA
Developmental psychology
Studies how people change and develop over their lifespan.
Cognitive and motor development, language acquisition, emotional development
Social psychology
Studies how we think about, influence, and relate to other people
Educational psychology
Researches how people learn and remember information
Helps develop more effective curriculum, testing procedures, classroom structures, etc.
Does not focus on individual students like a school psychologist
Health psychology
Examines how biological, social, and psychological factors influence health and illness.
Designs conducts, or evaluates programs that help people live healthier lives (quitting smoking, improving sleep, managing pain, etc.)
Physiological/Biological psychology
Forensic psychology
Experimental psychology
Using experiments to study human thought and behavior
Cognitive Neuroscience
Studies the biological processes that enable cognition (thinking, perceiving, memory, etc.).
Brain structures
Neural networks
Psychometrics
Focuses on the construction of assessment tools, measurement instruments, and formal models that help study and observe human thoughts and behavior.
These would be used in research studies and clinical settings
Personality
Studies people’s characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling, and acting
Psychiatry
Medical doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of mental illness.
Typically prescribes medication to treat mental illness
Works in hospitals, clinics, rehabilitation centers, and private practices
Counseling psychology
Assists people with personal problems (often related to school, work, relationships, etc.)
Provides counseling/therapy
Most commonly works in private practices or clinics
Applied psychology
Research that is undertaken to solve a particular problem, not just to learn something new
Industrial-Organizational Psychology (I-O Psych)
Uses psychological training in the workplace
Helps companies select and train employees, boost morale and productivity, design products, and implement systems
School psychology
Tests students for learning and emotional struggles
Helps create individualized education plans for students with learning and emotional struggles
Occasionally provides counseling, but not often
Empiricism
The idea that knowledge comes from experience, and that observation and experimentation allow us to gain scientific knowledge
Theory
Culture
Ethnocentrism
Nature v. Nurture
Chapter 2 terminology:
Hypothesis
Expresses a relationship between two variables.
A variable is anything that can vary among participants in a study
Theory
Operational definition
Explain what you mean in your hypothesis.
How will the variables be measured in “real life” terms.
How you operationalize the variables will tell us if the study is valid and reliable
Participants/subjects
Data collection techniques
Journal
Experiment
Independent variable
Whatever is being manipulated in the experiment.
Hopefully the independent variable brings about change
Dependent variable
Whatever is being measured in the experiment.
It is dependent on the independent variable.
Experimental group
Control group
Extraneous/confounding variables
Placebo effect
Random assignment
Once you have a random sample, randomly assigning them into two groups helps control for confounding variables.
Experimental Group v. Control Group.
Group Matching (1 to 1 comparison)
Random sampling
allows us to obtain a sample representative of the population
So that results of the study can be generalized to the population
Descriptive/correlational research
Positive correlation
The variables go in the SAME direction
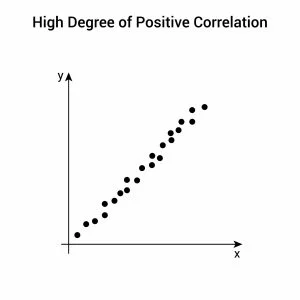
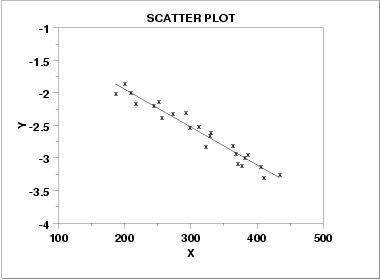
Negative correlation
The variables go in opposite directions
Correlation coefficient
A number that measures the strength of a relationship.
Range is from -1 to +1
The relationship gets weaker the closer you get to zero.
Illusory Correlation
Third variable
Naturalistic observation
Watch subjects in their natural environment.
Do not manipulate the environment.
never really show cause and effect
Reactivity
even the control group may experience changes.
Just the fact that you know you are in an experiment can cause change
Case study
A detailed picture of one or a few subjects.
Tells us a great story…but is just descriptive research.
Does not even give us correlation data
Self fulfilling prophecy
Survey
Most common type of study in psychology
Measures correlation
Cheap and fast
Need a good random sample
Low-response rate
Questionnaires
Replication
Meta-analysis
Sampling bias
Population
Social desirability bias
Halo effect
Experimenter bias
Another confounding variable.
Not a conscious act.
Double-blind procedure
participants AND researchers do not know which group they are in/treatment they receive
APA ethical guidelines
Anecdotal evidence
Appendix B terminology(back of textbook p. A-21):
Statistics
Recording the results from our studies.
Must use a common language so we all know what we are talking about.
Frequency distribution
Histogram
Frequency polygon
Descriptive statistics
Just describes sets of data.
You might create a frequency distribution.
Frequency polygons or histograms.
Central tendency: Median, mean, mode
Negatively skewed distribution
If a group has a low outlier, the curve has a negative skew (contains more high scores)
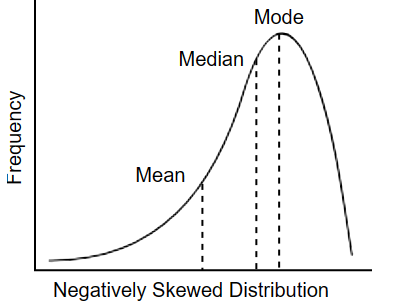
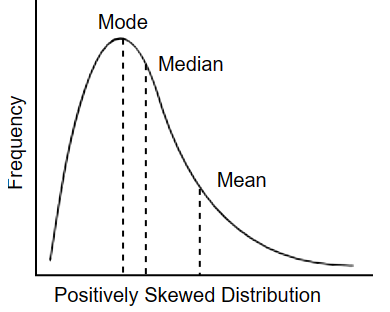
Positively skewed distribution
If group has one high score, the curve has a positive skew (contains more low scores)
mode is the high point, median is in the middle, mean is the biggest number
Variability
Range
distance from highest to lowest scores.
Standard deviation
the variance of scores around the mean
The higher the variance or SD, the more spread out the distribution is.
1 SD is 34% 2 sd is 13.6% 3 SD is 2.1%
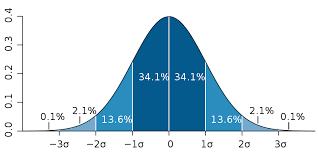
Normal distribution (bell curve)
the mean, median and mode are all the same
Percentile score
Scatter diagram/ scatter plot
Coefficient of determination
Percentage of variation in one variable that can be predicted based on the other variable
To get this number, multiply the correlation coefficient by itself
Coefficient of determination goes up as the strength of a correlation increases
Inferential statistics
The purpose is to discover whether the finding can be applied to the larger population from which the sample was collected.
P-value= .05 for statistical significance.
At 5% or less, less likely the results are due to chance
Null hypothesis
Is the observed correlation large enough to support our hypothesis or might a correlation of the size have occurred by chance?
Do our result REJECT the null hypothesis?
Statistical significance
It is said to exist when the probability that the observed findings are due to chance is very low, usually less than 5 chances in 100 (p value = .05 or less)
When we reject our null hypothesis we conclude that our results were statistically significant.
P-value
Type I v. Type II error
Type I Error- said IV had an effect but it didn’t (False alarm)
Type II Error- don’t believe the IV had an effect but it really does
Ch 3: Vocabulary to Know
Neurons- know all parts soma, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, terminal buttons, synaptic vesicles, synapse/synaptic cleft
neurotransmitters
resting potential
action potential
absolute refractory period
all-or-none law
presynaptic & postsynaptic neuron
postsynaptic potential (PSP)
inhibitory v. excitatory PSP
reuptake
synaptic pruning
acetylcholine
dopamine
norepinephrine
serotonin
GABA
endorphins
agonist
antagonist
central nervous system
peripheral nervous system
autonomic nervous system
somatic nervous system
sympathetic v. parasympathetic division
fight-flight response
afferent nerves
efferent nerves
spinal cord
ventricles
cerebrospinal fluid
lesioning
ESB
James Olds’ research on pleasure centers
EEG
CT
PET
MRI
fMRI
brainstem
hindbrain: medulla, pons, cerebellum
midbrain: reticular formation
forebrain: cerebrum, cerebral cortex
thalamus
hypothalamus
limbic system
hippocampus
amygdala
occipital lobe- visual cortex
parietal lobe- somatosensory cortex
temporal lobe- auditory cortex
frontal lobe- prefrontal & motor cortex
homunculus brain map
mirror neurons
brain plasticity
neurogenesis
broca’s area
wernicke’s area
left hemisphere
right hemisphere
corpus callosum
Roger Sperry & Michael Gazzaniga’s split brain research
endocrine system
hormones
pituitary gland
oxytocin
pineal gland
thyroid gland
liver
adrenal glands
pancreas
gonads (ovary, testis)
chromosomes
genes
polygenic traits
family studies
twin studies
monozygotic v. dizygotic twins
adoption studies
genetic mapping
epigenetics
Charles Darwin & natural selection
evolutionary psychology
fitness
adaptation
critical period
Chapter 5 (you do not have to do pg. 165-168)
Consciousness
Brian waves: beta, alpha, theta, delta
Biological rhythms
Circadian rhythms
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
Pineal gland- melatonin
Jet lag
EMG, EOG, & EKG
Stages of sleep
REM sleep
Sleep deprivation
Insomnia
Benzodiazepine sedatives and nonbenzodiazepine
Narcolepsy
Sleep apnea
Somnambulism
REM sleep behavior disorder
Content & culture of dreams
Sigmund Freud’s wish fulfillment theory
Manifest v latent content of dreams
Rosalind Cartwright’s theory of problem-solving/mood-regulation view
Hobson & McCarley’s activation-synthesis model
Psychoactive drugs
Narcotics
Sedatives
Stimulants
Hallucinogens
Cannabis
Alcohol
Multifactorial causation
Tolerance
Physical dependence
Psychological dependence
Withdrawal
Mesolimbic dopamine pathway- Nucleus accumbens
Ch.4
Sensation
Perception
Visual agnosia
Light & its physical properties
transduction
Parts of the eye- cornea, pupil, iris, lens, retina, fovea, optic nerve, optic disk (blind spot)
Lens accommodation
Nearsightedness
Farsightedness
Visual receptor cells: rods and cones
Bipolar and ganglion cells
Dark & light adaptation
Receptive field
Visual pathways of the brain: optic chiasm, thalamus, LGN, superior colliculus, visual cortex
Ventral stream & Dorsal stream
Hubel & Wiesel’s research on the visual cortex
Feature detectors
Subtractive v. additive color mixing
Trichromatic theory of color
Color blindness
Dichromats v. monochromats
Opponent processing theory
Reversible figure
Perceptual set
Inattentional blindness
Feature analysis
Top down processing
Bottom down processing
Phi phenomenon
Gestalt principles: figure-ground, proximity, closure, similarity, simplicity, continuity
Perceptual hypothesis
Depth perception
Binocular depth cues: retinal disparity
Monocular depth cues
Pictorial depth cues: linear perspective, texture gradient, interposition, relative size, height in plane, light and shadow
Perceptual constancy
Visual illusions: Muller-Lyer, Ames room, ponzo, moon
Physical properties of sound waves
Frequency
Hertz
Volley principle
External ear: pinna & auditory canal
Middle ear: ear drum, ossicles (hammer, anvil, stir-up)
Inner ear: cochlea, basilar membrane, auditory receptors (hair cells)
Place theory
Frequency theory
Vestibular sense: semicircular canals
Auditory (sound) localization
Taste: gustatory system- taste buds
Primary & fifth tastes
Supertasters and nontasters
Sensory adaptation
Olfactory system- olfactory cilia & olfactory bulb
Receptive fields
Tactile system: Touch
Fast v slow pathway
Gate-control theory
Part of the unit but not in the textbook:
Absolute threshold
Just noticeable difference/difference threshold
Signal detection theory
Gustav Fechner- Fechner’s law
Ernst Weber- Weber’s Law
Stroop Effect
Synesthesia
Kinesthesis
Subliminal message
Selective attention
Cocktail party phenomenon
Change blindness
Afterimage
Complementary colors
Motion parallax & relative motion
Prosopagnosia- face blindness
Vocabulary to Know
Learning
Classical Conditioning
Unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
Unconditioned response (UCR)
Neutral stimulus
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
Conditioned response (CR)
Conditioned reflex
Elicit
Trial
Evaluative conditioning
Acquisition
Stimulus contiguity
Extinction
Spontaneous recovery
Renewal effect
Stimulus generalization
Stimulus discrimination
Schedules of reinforcement
Higher-order conditioning
Operant conditioning/instrumental learning
Consequences
Reinforcement
Operant chamber
Emit
Shaping
Fixed-interval/ Fixed-Ratio
Variable-interval/ Variable-Ratio
Positive reinforcement
Negative reinforcement
Escape learning
Instinctive drift
Sauce béarnaise syndrome
Conditioned taste-aversion
Reinforcement contingencies
Cumulative recorder
Discriminative Stimuli
Primary & Secondary reinforcers
Phobias
Resistance to extinction
Intermittent/Partial reinforcement
Continuous Reinforcement
Patterns of response
Punishment
Observational Learning
Modeling
Behavior modification
Behavioral contract
Biofeedback
People to Know
John Watson- Baby Albert experiment
Edward Thorndike & law of effect
BF Skinner- Operant Conditioning
John Garcia- taste aversion experiment
Martin Seligman- learned helplessness experiment
Robert Rescorla- role of cognitive processes in classical conditioning
Albert Bandura- Bobo the doll experiment (relational v. instrumental aggression)
Edward Tolman- latent learning & cognitive maps experiments
Wolfgang Kohler- Insight learning
Ivan Pavlov- classical conditioning experiment
People to Know (Ch. 7):
Elizabeth Loftus
Endel Tulving
Baddeley’s model of working memory
Hermann Ebbinghaus
Vocabulary to Know (Ch.7)
Tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
Attention
Structural encoding
Phonemic encoding
Semantic encoding
Levels-of-processing theory
Elaboration
Imagery
Dual-coding theory
Information processing theories
Pseudoforgetting
Sensory memory
Decay theory
Short-term memory
Interference theory
Long-term memory
Retroactive interference
Maintenance Rehearsal
Proactive interference
Interference
Schema
Chunk
Repression
Flashbulb memories
Retrograde amnesia
Connectionist/PDP models
Anterograde amnesia
Recognition measure of retention
Consolidation
Anatomy of memory 52. Memory trace
Implicit memory
Encoding Specificity Principle
Semantic network
Explicit memory
Declarative memory
Source monitoring
Misinformation effect
Non-declarative/Procedural memory
Semantic memory
Forgetting curve
Source monitoring error
Episodic memory
Mnemonic devices
Recall measure of retention
Retention
Overlearning
Serial-position effect (primacy & recency)
Hindsight bias
The tendency to believe, after learning the outcome, that you knew it all along
Reality monitoring
Self-referent encoding
Conceptual hierarchy
Transfer-appropriate processing
Destination memory 64. Long term potentiation
Prospective memory 65. Retrospective memory
Method of loci 66. Link method
Chapter 8 Part 1: Problem Solving and Cognition
1. Cognition
22. Problem solving
2. Language
23. Functional fixedness
3. Phonemes
24. Mental set
4. Schema
5. Morphemes
25. Insight
6. Semantics
26. Problem space
7. Syntax
27. Trial and error
8. Milestones in language development
28. algorithms
9. Receptive vocabulary
29. heuristic
10. Productive vocabulary
Incubation effect
Fast mapping
Holistic cognitive style
Overextension
Analytical cognitive style
Underextension
Decision making
Telegraphic speech
Simon’s theory of bounded rationality
Overregularizations
Additive strategy
Metalinguistic awareness
Risky decision making
Bilingualism
Availability heuristic
Behaviorist theories of language (Skinner)
Representative heuristic
Nativist theories of language (Chomsky)
Conjunction fallacy
Language acquisition device (LAD)
Gambler’s fallacy
Interactionist theories
Confirmation bias
Whorf’s linguistic relativity hypothesis
Framing
Semantic slanting
Chapter 8 (Part 2: IQ and testing)
Psychological test
Intelligence test
Aptitude test
Achievement test
Personality test
Standardization
Test norms
Percentile score
Reliability
Test-retest reliability
Validity
Content validity
Criterion-related validity
Construct validity
Mental age
Intelligence quotient
Stanford-Binet test
Factor analysis
Fluid intelligence
Crystallized intelligence
Normal distribution
Deviation IQ scores
Verbal, practical, & social intelligence
Mental retardation
Down syndrome
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Hydrocephaly
Gifted Children
3 rings of Eminence
Heritability ratio
Cumulative deprivation hypothesis
Flynn effect
Reaction range
Creativity
Divergent thinking
Convergent thinking
Sir Francis Galton
Alfred Binet
Lewis Terman
David Wechsler
Charles Spearman’s “g”
Arthur Jensen & The Bell Curve
Claude Steele’s Stereotype threat
Robert Sternberg’s theory of intelligence: practical, analytical, creative
Howard Gardner’s multiple intelligence theory
Not in text but required by collegeboard: Research on your own and know for class
deep v. shallow processing
metacognition
state dependent learning
echoic & iconic memory
contributions of George A. Miller
predictable-world bias
linguistic determinism
sunk-cost fallacy
anchoring and adjustment heuristic/the anchoring effect
optimistic/pessimistic explanatory styles
cognitive dissonance
CHAPTER 10
Development
Prenatal period
Zygote
Germinal stage
Placenta
Embryonic stage
Fetal stage
Teratogens
Age of viability
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Motor development-Gross & Fine Motor Skills
Cephalocaudal trend
Proximodistal trend
Maturation
Developmental Norms
Reflexes
Imprinting
Temperament (know different types)
Longitudinal study
Cross-Sectional study
Attachment
Harry Harlow’s research on attachment
Cohort Effects
Separation anxiety
Secure attachment
Mary Ainsworth’s Strange Situation Procedure
Anxious-Ambivalent attachment
Avoidant attachment
Disorganized-Disoriented attachment
Stage Theory
Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development
Erik Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory (know all stages)
Continuous v. Discontinuous development
Sensorimotor period
Object permanence
Preoperational period
Conservation
Centration
Irreversibility
Egocentrism
Animism
Accommodation & Assimilation
Concrete operational period
Formal operational period
Lev Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory
Lawrence Kohlberg’s moral dev theory
Carol Gilligan’s care orientation
Pubescence
Secondary Sex Characteristics
Puberty
Primary sex characteristics
Menarche
Spermarch
Prefrontal cortex in adolescence
James Marcia’s identity statuses (know all)
Empty nest
Midlife crisis
Menopause
Dementia
Fluid Intelligence
Crystallized Intelligence
Parenting Styles: Authoritarian, Authoritative, Permissive
Elisabeth Kubler-Ross’ Stages of Accepting Death
Gender differences
Gender stereotypes
Gender roles
Socialization
Visual Cliff experiment
death deferral theory
habituation
theory of mind
spotlight effect
Chapter 9: Motivation, Emotion and Social Needs
Homeostasis
Drive
Drive reduction theory
Incentive theory
Evolutionary theories
Biological v. social motives
Hunger & the hypothalamus: LH, VMH, arcuate nucleus, & PVN
Glucostatic theory
Insulin
Leptin
Environmental factors influencing hunger
Obesity
BMI
Set point
Excitement phase & vasocongestion
Plateau Phase
Orgasm Phase
Resolution Phase
Sex v. gender
Gender Differences in Sexual Activity
Gender Differences in Mate Preference
Sexual orientation: heterosexual, homosexual, bisexual
Achievement motive
Projective test
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
3 parts of emotion
Affective forecasting
Galvanic skin response (GSR)
Polygraph
Brain areas influencing emotions
Facial feedback hypothesis
6 fundamental emotions
Display rules
James-Lange theory
Cannon-Bard theory
Schachter’s 2 Factor theory
Evolutionary theory of emotions
Walter Cannon
Master & Johnson’s Human Sexual Response
Robert Triver’s parental investment theory
David Buss
Alfred Kinsey’s 7 point scale
David McClelland
John Atkinson’s 3 determinants of achievement behavior
Overjustification Effect
Yerkes-Dodson Law (Arousal Theory)
Chapter 11: Personality
Personality
McCrae & Costa’s Five-Factor Model
Personality Trait
Psychoanalytic/psychodynamic Theory
Sigmund Freud
Id, Ego, Superego
Pleasure Principle
Reality Principle
Conscious, Preconscious, Unconscious
Carl Jung’s Analytical Psychology
Collective Unconscious
Personal Unconscious
Archetypes
Defense Mechanisms: Repression, Projection, Displacement, Sublimation, Reaction Formation, Regression, Rationalization, Identification
Psychosexual Stages: Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, Genital
Fixation
Libido
Oedipus & Electra Complex
Alfred Adler’s Individual Psychology
Striving for superiority
Compensation
Birth Order
Behaviorism perspective
BF Skinner’s views on personality (determinism & response tendencies)
Albert Bandura- reciprocal determinism
Self-efficacy
Walter Mischel & person-situation controversy
Humanism perspective
Carl Roger’s person centered theory
self-concept
incongruence
Abraham Maslow’s theory of self actualization
Chapter 13: Stress, Coping, & Health Vocabulary
Stress
Primary appraisal
Secondary appraisal
Frustration
Conflict
Approach-approach
approach -avoidance
Avoidance-avoidance
Change
Holmes & Rahe’s Social Readjustment Rating
Pressure
Broaden-and-build theory of emotions
inverted-U hypothesis/Arousal Theory(Yerkes Dodson law)
Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome (know all 3 phases)
ACTH
Adrenal medulla & cortex
Corticosteroids
Catecholamines
Coping
Aggression
Catastrophic thinking
Self indulgence
Internet addiction
Defense mechanisms
Constructive coping
Coronary heart disease relation to stress
Type A & type B personality
Depressive disorders relation to heart disease
Immune response
Social support
Optimism
Internal & external locus of control (not in text)
Positive effects of stress
Ellis’ Rational-emotive behavior therapy
Ch 12 Social Psychology Vocabulary to Know
Social psychology
Person perception
Stereotypes
Illusory correlation
Ingroup/outgroup
Attribution
actor-observer bias
Internal v. external attributions
Weiner’s model
Fundamental attribution error
self serving bias
5 factors of attraction
Defensive attribution (just world phenomenon)
Individualism
Collectivism
Interpersonal attraction
Matching hypothesis
Sternberg’s triangular theory of love (not in text)
Passionate v. companionate love
Adult attachment styles
Attitudes
Explicit v implicit attitudes
Persuasion: source, receiver, message, channel
Mere exposure effect
Leon Festinger’s cognitive dissonance
Elaboration likelihood model: central & peripheral routes of persuasion
Conformity
Solomon Asch’s conformity studies
Normative influence
Informational influence
Obedience
Stanley Milgram’s authority study
Philip Zimbardo’s prison study
Social roles
Group
Bystander effect & Diffusion of responsibility
Social loafing
Group polarization
Groupthink
Group cohesiveness
Prejudice
Discrimination
Foot-in-the-door technique
Door-in-the-face technique*
Reciprocity norm
Lowball technique
Social facilitation*
Deindividuation*
out-group homogeneity bias*
altruism*
Frustration-aggression principle*
Instrumental aggression*
False consensus effect*
Prisoner’s dilemma/social trap*
Scapegoat theory*
Chapter 14: Psychological disorders
Medical model
Criteria of abnormal behavior
Diagnosis
Prognosis
Etiology
DSM
Comorbidity
Prevalence
Anxiety disorders
Generalized anxiety disorder
Phobic disorder
Panic disorder
Agoraphobia
OCD
PTSD
Concordance rate
Dissociative disorders
Dissociative amnesia
Dissociative fugue
Dissociative identity disorder
Depressive disorders
Major depressive disorder
Anhedonia
Bipolar disorders
Schizophrenia
Delusions
Hallucinations
Schizophrenia
Positive v. negative symptoms
Expressed emotion
Somatization disorders:illness anxiety disorder, somatoform, conversion disorder
Personality disorders (antisocial, narcissistic, histrionic, dependent, borderline, schizoid)
Insanity
Involuntary commitment
Culture-bound disorders
Eating disorders: anorexia nervosa, bulimia, binge-eating
Chapter 15
Insight therapies
Behavioral therapies
Biomedical therapies
Clinical psychologist
Counseling psychologist
Psychiatrists
Psychoanalysis
Free association
Dream analysis
Interpretation
Resistance
Transference
Carl Roger’s Client-centered therapy
Positive psychology
Group therapy
Couples/marriage therapy
Family therapy
Spontaneous remission
Systematic desensitization
Exposure therapies
Aversion therapy
Social skills training
Aaron Beck’s Cognitive-behavioral treatment
Cognitive therapy
Albert Ellis’ Rational-emotive behavior therapy
Psychopharmacotherapy
Antianxiety drugs
Antipsychotic drugs
Tardive dyskinesia
Antidepressant drugs
Mood stabilizers (lithium)
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Mental hospital
Dorothea Dix
Deinstitutionalization