Chapter Four - Unemployment and Inflation
What is Unemployment?
It applies to labor, land and capital, occurring when some of these factors are idle
Labour unemployment is when someone who is actively seeking employment can't get a job
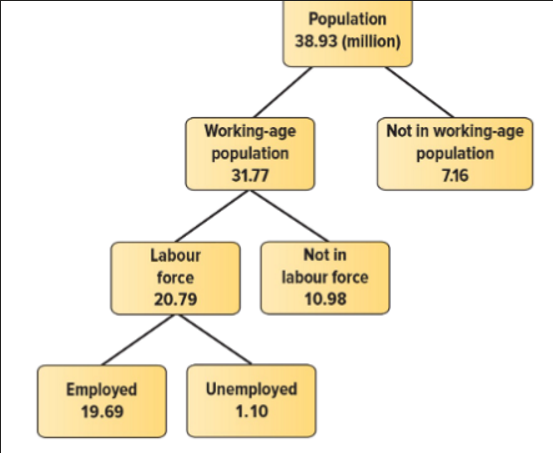
Measuring Unemployment
The working-age population is the country's total population excluding: under 15 years old, those in the 3 territories, on Aboriginal reserves, full-time residents of mental or penal institutions, hospitals or armed forces
Labour Force
Members of the working-age population, who are employed or unemployed. Full-time or part-time
Unemployed plus employed is the labour force
Employed.
Working
Unemployed
In the labor force and actively seeking employment but does not hold paid employment. Not discouraged workers
Type of Unemployment
Frictional Unemployment
Unemployment related to the time between jobs or finding first job.
Time between ending school and finding a full-time job
Structural Unemployment
Results from a mismatch in the skills or location between jobs available and the people looking to work
Possibility leaving a closed industry, re-learn or obtain education and move into new industry
Cyclical Unemployment
Occurs as a result of the recessionary phase of the business cycle
At peak of the business cycle, at or near full employment

Natural Rate of Unemployment
No cyclical unemployment, occurs when there is full employment
Number of people who are unemployed, mostly frictional and always have some natural rate of unemployment
Can change over time as a result of changes in:
Employment insurance benefit, average job search time, labor-force participation rate increasing
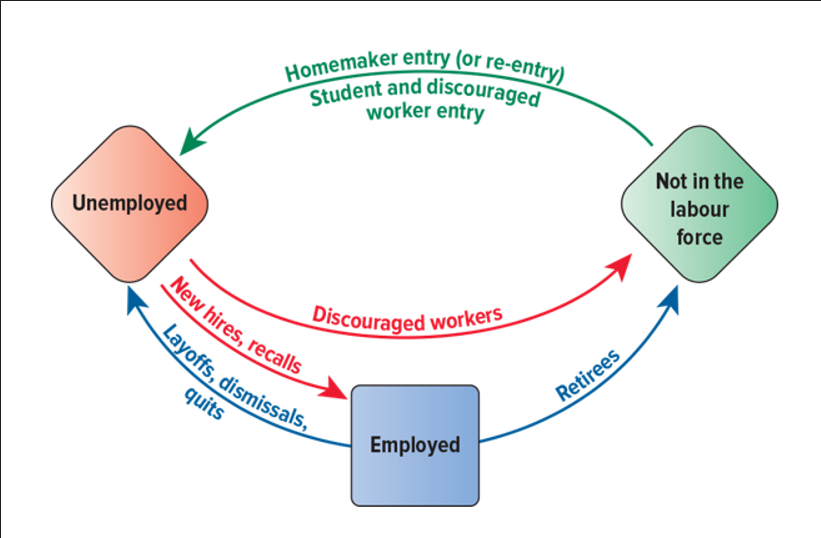
Understand the picture below
Criticisms of the Official Rate of Unemployment
The reported unemployment rate may be:
Understated because part-timers are included as full-timers
Understated because it excludes discouraged workers (people who want to work but not seeking)
Overstated because of false information from EI recipients
Overstated because of false information from those working in the underground economy
Costs of Unemployment
GDP Gap

Actual GDP is real or nominal
What is the cost of unemployment if the economy is functioning at seemingly full capacity? (potential question)
Okun's Law
For every 1% of cyclical unemployment, an economy's GDP is 2.5% below its potential

Inflation – increase in the general level of prices sustained over a period in an economy
Measured using a price index
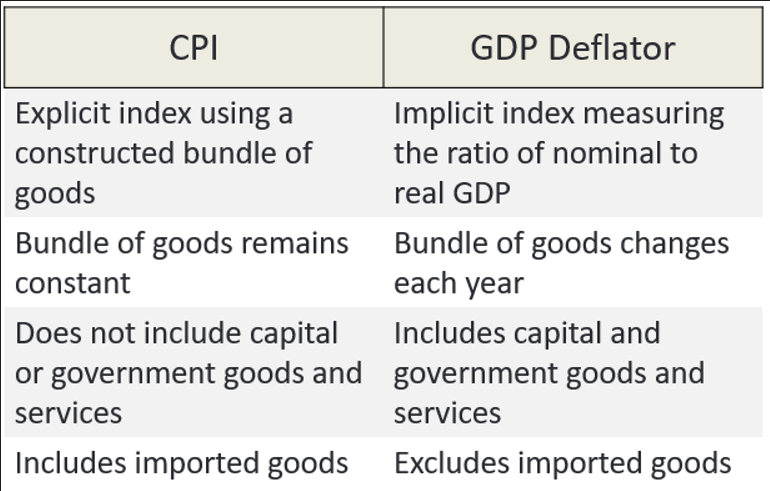
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Base year could be last year or any year given (nominal and real GDP is the same)

Core CPI
Excludes items with highly volatile prices (fruits, vegetables, gas, fuel oil, mortgage interest rates, tobacco)
This gives a better indication of underlying long-term inflation rate
GDP Deflator
Need to know above

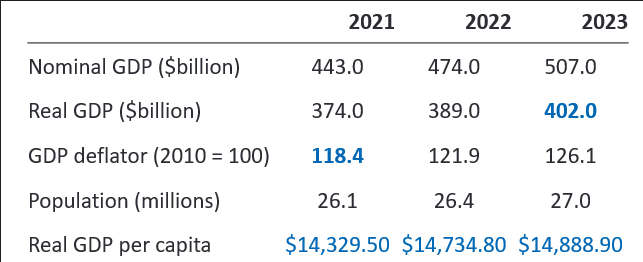
test question
Measuring the Past
Benefits of using a Price Index
Enables us to compare values from past to present if all calculated using the same methods
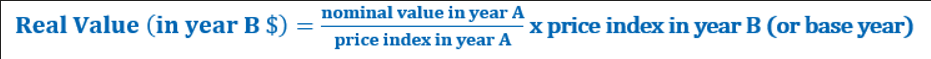
Nominal Income
The present dollar-value of income
Real Income
The purchasing power of income
Nominal income divided by the price level
Rule of 70
Estimated that the time it will take for a figure to double in value given a certain percentage of growth rate (time value of money)
Costs of Inflation
Redistributive Costs
Shifts income from the economically weak to the economically strong
Shifts income from lenders to borrowers
Check textbook for better explanation
Output Costs
Reduces the level of investments and economic growth
Increase menu costs (always having to re-list prices with inflation)
Reduces export and increases imports
Real Interest Rates
The rate of interest measured in constant dollars OR the interest rate when inflation is zero
Causes of Inflation
Demand-side Inflation (Demand Pull)
When the demand for goods and service in the whole economy exceeds its capital to produce them, pulling prices up
Aggregate Demand is more than the economy's capable of producing, even at full employment
Demand is pulling the prices up because demand Is higher then supply
Supply-side Inflation (Cost Push)
Caused by increase in production cost due to: union pushing nominal wage rate, increase in firms profit margins (price gouging), supply chain disruptions
Galloping Inflation or Hyperinflation (high rates of inflation in extreme cases)