Paper 2: The Cold War - Superpower Tensions and Rivalries
Origins
What is the Cold War?
→ Period of hostility and high tension due to ideological conflicts between the USA and the USSR which emerged following the defeat of Nazi Germany.
Factors which lead to mutual suspicion:
Bolshevik Revolution in 1917
establishment of the first Communist state
ideas threatened the basis of Western Society
Intervention of the West in the Russian Civil War 1918-22 supporting the whites in their attempt to overthrow the Bolshevik government.
the USSR did not receive diplomatic recognition nor join the League of Nations until the 1930s.
Appeasement of Hitler and the Nazis in the 1930s by the West was partly motivated by fear of Communism
Non-Aggression Pact allowed Hitler to attack the West
increased suspicion
Reasons for the USA and USSR to emerge as superpowers in 1945:
Military Reasons
defeating Germany made the USA the number one navy force and the USSR the number one land force
France and Britain became second rank powers
USSR became the main regional power
Economic Reasons
USA economy was strengthened by the war → committed to open trade
USA used strength to return economic stability in Europe
USSR became a strong neighbour in Eastern Europe
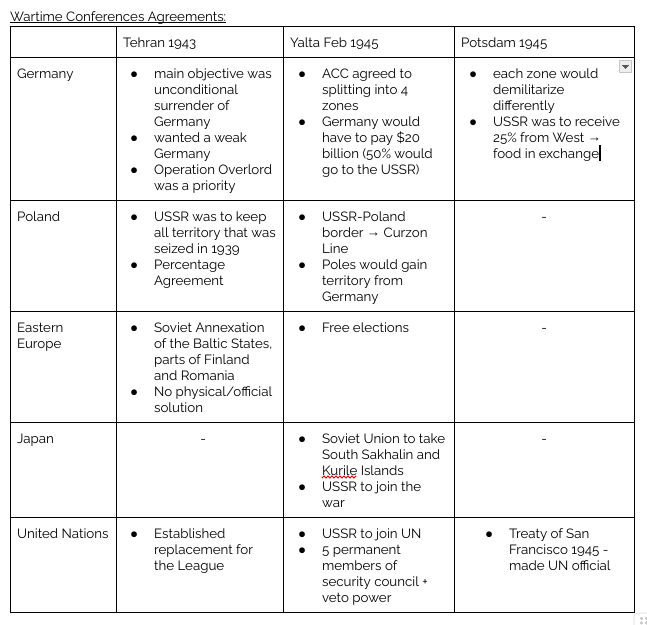
Key Developments 1946-47:
Salami Tactics - USSR
Soviets supervised the organization of governments in the Eastern European states establishing a broad alliance of anti-fascists
Each of the parties was sliced off one after the other
Communist core was left
Poland
Free elections did not occur until 1947
before elections there was murder, censorship and intimidation
Polish Peasant Party → 246 candidates were disqualified, 149 were arrested
one million votes were taken off the official register
Iran
USSR left 30000 troops in the North → encouraged a communist uprising
UN forced USSR to pull out
Greece and Turkey
anti-imperialist rebellions → Churchill felt betrayed
Italy and France
Communist parties increased in membership
West feared that these countries could be weak-links in anti-communist western europe
Kennan's Long Telegram 1946:
Key idea: USSR system was buoyed by the threat of a hostile world outside its borders and that the USSR was fanatically and implacably hostile to the west. Strong resistance was encouraged
USSR view of the world was one of insecurity
Soviets wanted to advanced Stalinist ideology
Soviet regime was cruel and repressive
Telegram helped harden attitudes in the US → key role in the development of containment
Iron Curtain Speech:
By 1946, Soviet dominated Communist governments were set up in Poland, Hungary, Romania and Bulgaria.
despite agreement of free elections at Yalta
Red Army was also present in countries liberated from Germany by the Russians
Soviet reaction to the speech was one of outrage
Churchill was compared to Hitler
Soviets withdrew from the IMF
Stepped up intensity on anti-Western propaganda
Initiated a new 5-year plan of self-strengthening
Truman Doctrine (1947):
“USA had the obligation to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures”
Radical change in US policy (from isolationism)
Doctrine was in response to the unstable conditions in Turkey and in particular Greece
US sent money to Europe in the hope of aiding recovery
USSR saw this as evidence of determination of the US to expand its sphere of influence
Marshall Plan:
Marshall believed that the economies of Western Europe needed immediate help from the USA
Economic extension of the Truman Doctrine
USA invited the USSR to join the Marshall Plan and claimed that this aid was not directed against any country
Aims:
revive European working economies so that the political and social stability could ensue
safeguard the future of the US economy
Soviets rejected Marshall Aid → USA had asked to see their financial records
Soviets felt the USA was establishing an European Empire
saw this as dollar imperialism
in response developed the Molotov Plan → creation of the COMECON 1949
linked Eastern bloc countries to Moscow → designed to stimulate and control their economic development
Red Army Occupation of Eastern Europe 1945-47:
Creation of a satellite empire
Soviet military power
Salami tactics
state policy + spy networks
control through COMECON
By 1948, satellite states were economically and militarily under the control of the USSR
West felt that the USSR went back on their agreement at Yalta
Czechoslovak Coup Feb 1948:
Czechoslovakia expressed interest in the Marshall Plan
pity from the West due to Munich Agreement in 1938
USSR forced CZK to vote against → threatened with an armed intervention
Truman used the coup to implement the Marshall Plan
Berlin Crisis 1948:
Berlin was the only place where soldiers came in direct contact
British wanted to revive the economy while the Soviets wanted to weaken Germany
contrast in aims
Allies decided to join the regions → bizonia
USSR saw this as a threat
Currency reform in the joined zones → new deutschmark
USSR wanted the West out of Berlin
Blockade was an attempt to kick them out
West reacted with the Berlin airlift → Operation pickles
2k Tonnes of supplies per day
sent B29 Bombers
Counter-blockade of coal, steel and machines
Blockade caused a lack of food for the winter, electricity only 4 hours a day
USSR failed to drive the West out of Berlin → Stalin called it quits
Berlin Blockade triggered the creation of the German Democratic Republic
East and West Germany were officially established
NATO was formed → symbolized military division of Europe
No solution for Germany → aims were not met
The Shift to Global Conflict
US Foreign Policy 1949-50:
With the establishment of NATO, the US was optimistic about containment in Europe
NATO’s power rested in the atomic bomb
did not invest large sums of money into developing conventional forces in Western Europe
the US had demobilized their fighting men
1949 - USSR developed their own nuclear bomb and China fell to Communism
bomb was tested successfully → much more quickly than the USA had anticipated
The Red Scare + McCarthyism:
anti-communism
“USSR had conspiracy to place communist sympathisers into key positions in American life
accusation led to purges and show trials
1950 → anti-red → developed anti-communist public opinion
saw China as completely subserved to the Moscow regime
domestic impacts
development of american propaganda
Big Lie
Investigated Hollywood “Secret Actors Guild”
Hollywood 10 wouldn’t cooperate → imprisoned and black listed
USA feared that communism would undermine their freedom
Crusade against communism paved the way for the republicans
Rosenberg Trial → high point of hysteria
Communist treason stayed in American democracy for decades
foreign policy impacts
initiated Crusade for Freedom
funded by the CIA
beginning of spy network and espionage
NSC-68 “Total Commitment”
NSC-68 was a report produced by the US National Security Council
warned how all communist activity everywhere could lead to Moscow
warned of an indefinite period of tension and danger → monolithic communism
military spent $35-50 billion
encouraged giving money to any country perceived by the USA to be resisting communism
economic and military aid
has been criticized as an excuse for US expansionism
Korean War 1950-53:
Until 1945 the Japanese were in charge of Korea, following their loss, it was split into 2, North Korea and South Korea.
The entire region is politically unstable, resulting in war on the 25th of June 1950 between the two sides.
USA was supporting the South Koreans with troops and overall expertise.
All leaders had different motivations for getting involved in Korea
Kim Il Sung
wanted to unify Korea - asked for Soviet help
told Mao that Stalin supported the invasion
Mao
only agreed because he believed that Stalin supported Kim
hoped Stalin would support the invasion of Taiwan
feared an American invasion of China
Stalin
approved the North invasion
sent advisors to North Korea
opportunism due to the events in Japan - saw it as a safe gamble
Truman
policy of containment
fear of monolithic communism
pressured the UN to get involved to support the South
domino theory
Countries were affected differently due to the events in Korea
USA
NSC-68 tripled the defense budget
Germany was rearmed and became part of NATO
Greece and Turkey became part of NATO
Condemned China as being an aggressor
Treaty of San Francisco was signed with Japan in 1952
Seventh Fleet was sent to Taiwan
Involvement in Vietnam and Philippines
Korea
All hope for reunification was lost
China
No longer relied on Soviet help
Became major superpower in the Asian region
USSR
Tensions with the West greatly increased
South East Asia
SEATO was formed - anti communist bloc
Containment in Asia:
Japan
USA occupied Japan in 1945 - objective was to create a weak and pacifist country
demilitarized and introduced a new constitution
1950 - introduced the Reverse Course because they needed a strong anti-communist country (established a self defense force of 75000 men)
USA achieved their aim and Japan’s economy increased rapidly and there was no threat of communism spreading
Taiwan
When North Korea attacked South Korea, US 7th fleet was sent to Taiwan to keep peace between the Nationalists and Communists
Taiwan was recognized as the only official Chinese state (given military and economic aid)
1953 - US withdrew troops to unleash Chiang Kaishek
Formosa Resolution - any and all military action would be taken in order to save Taiwan (brinkmanship and massive retaliation)
Taiwan managed to maintain independence
Vietnam
Domino effect - US failed to contain communism in Indochina
America’s biggest failure → indirectly fostered the growth of communist regimes in Cambodia and Laos
New Leaders, New Ideas - increased tensions in the 1950s:
Roll Back -liberation of countries currently held by the Soviets in Eastern Europe
New Look - preventing the extension of Soviet Communism outside of the areas where it was already established in the belief that without any opportunity to expand the Soviet system would collapse on itself
Brinkmanship - using threats of massive retaliation as an instrument of Containment. Involved threatening nuclear war to intimidate the aggressor into backing down
Coexistence - meant that capitalism and communism should accept the continuing existence of one another rather than using force
Berlin Crisis 1958-61:
East Germany and West Germany were incredibly different from an economic and political standpoint
East Germany
forced collectivization and socialisation
hardship + bad living conditions
authoritarian state (stalinism)
riots 1953 - first major rebellion in the sphere of influence
no free elections
West Germany
great industrial output
received Marshall Aid
democracy
capitalism + political freedom
40000 people a day were fleeing to the West, Khrushchev pushed Kennedy to get out of Berlin
Kennedy did not get out of Berlin and increased military spending
Khrushchev was forced to build a wall to stop people from crossing the border and fleeing
Significance of Wall’s construction
Khrushchev - wall was a defeat (admission that communist propaganda failed)
Ulbricht - did not get peace treaty he wanted but consolidated communist control in East Berlin
Citizens - horrifying experience as families were cut off from each other
Cold War - Germany issue was settled and USA was relieved that war was averted. Moved Cold War focus away from Europe
Cuban Missile Crisis 1960-63:
Historiography
Orthodox
Kennedy’s finest hour → avoided nuclear brinkmanship to preserve world peace
Blockade exerted maximum pressure on the Soviet union while incurring the minimum risk of war
Kennedy remained calm and did not attempt to humiliate Khrushchev - acted statesmanlike
Revisionist
Kennedy unnecessarily raised the cuban episode to a crisis and thus subjected the world to nuclear danger
Kennedy made the crisis public
Acted in self-interest
Post Revisionist
Kennedy did act in a statesmanlike way and was prepared to compromise
ExComm meetings showed him pushing for compromise
Cuba/Turkey trade off was a good call
Effects on the Cold War
USA
Kennedy’s personal prestige increased
showed US into realizing the fragility of its own security
increased the US focus on building military strength
USSR
crisis humiliated Khrushchev
contributed to his eventual fall from power in 1964
Cuba
Castro remained in power
pursued foreign policy independent of Moscow
China
relationship with the USSR deteriorated
still developed nuclear weapons independently
International
world was made a safer (more secular) place
hotline was established between USSR and USA
Test-Ban Treaty 1964
Nuclear non-proliferation Treaty of 1968
Sino-Soviet Relations 1945-1982:
Stalin and Mao 1945-53
Stalin felt that Mao’s interpretation of Marxism was not genuine and disagreed with using peasants
feared each other as rivals in the communist world
did not want the Cold War to spread to Asia
Stalin underestimated the CCP and believed the GMD was the stronger party
Mao was convinced Stalin wanted a weak and divided China
Sino-Soviet Treaty of Alliance
Korean War - USSR demanded that China pay for all weapons and materials
Khrushchev and Mao 1956-64
Secret Speech 1956 - Mao saw it as an attack on his own leadership
Crushing of the Hungarian uprising - Mao saw it as a failure by the USSR to contain reactionary forces
Doctrine of Peaceful Coexistence with the West
Mao believed the USSR was dominated by Revisionists
Cuban Missile Crisis 1962
Brezhnev and Mao 1968-82
Brezhnev followed Stalinist foreign policy
Mao condemned his use of force in CZK - 1968 Prague Spring
Sino-Soviet border war in 1969
Brezhnev criticized the Cultural Revolution
USSR refused to assist China in building nuclear weapons
SEA conflict - Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia
Detente 1970s:
Why did the following want detente?
USA
wanted troops out of Vietnam (30k were killed by 1969)
political pressure at home and protests were developing
improve relations with USSR and get Chinese to negotiate
USSR
had poor relations with China so they did not want to have poor relations with the USA as well
there was no formal treaty recognizing East Germany and they wanted one
China
did not want to be isolated by the West
How did detente lead to an improvement in European relations?
East Germany was recognized as an actual state
Ostpolitik - open relations
Cracks were allowed in the German wall - separated families could see each other
USA allowed China to take a seat in the Security Council
What were the main agreements made under detente?
Moscow Treaty 1970 - recognized borders of Germany and Polish-Western border
Moscow Summit 1972 - restrictions on offensive weapons (mutually agreed restraint)
Helsinki Treaty 1975 - issue of human rights
recognized European borders
encouraged cooperation in space race
SALT 1 1972 - ABM Treaty, Interim Treaty, Basic Principles Agreement
SALT 2 1979
Basic Treaty 1972 - West Germany now recognized East Germany
Why did detente collapse?
Soviets invaded Afghanistan in 1979
USA was convinced the USSR only wanted to spread their influence
The Americans began providing arms to the Afghan rebels whom turned out to be radicals.
USA didn’t sign SALT 2, stopped electronic exports, forbade athletes from attending the 1980 Moscow Olympics
Carter Doctrine - committed the US to intervention if the USSR threatened Western interests in the Persian Gulf
Soviet involvement in Africa and Latin America
Yom Kippur War - USA believed the USSR knew about the Egyptian attack on Israel before it happened
USA felt the USSR benefited from the Helsinki agreement on arms development