Unit 5 Part 2: Intro to Lophotrochozoans, Phylum Platyhelminthes, Phylum Nematoda
Lophotrochozoan Phyla:
General Characteristics of Lophotrochozoans:
- Bilaterally symmetrical
- Triploblastic
- Protostome: blastopore develops into the anus
Function of Lophophore Structure:
- A horseshoe shaped feeding structure that is a common evolutionary link between members of the phyla. Each member will have this structure at one point in their lives
- Shows evolutionary relationship
==Phylum Platyhelminthes:==
How many species?
- 34,000 species
==Characteristics:==
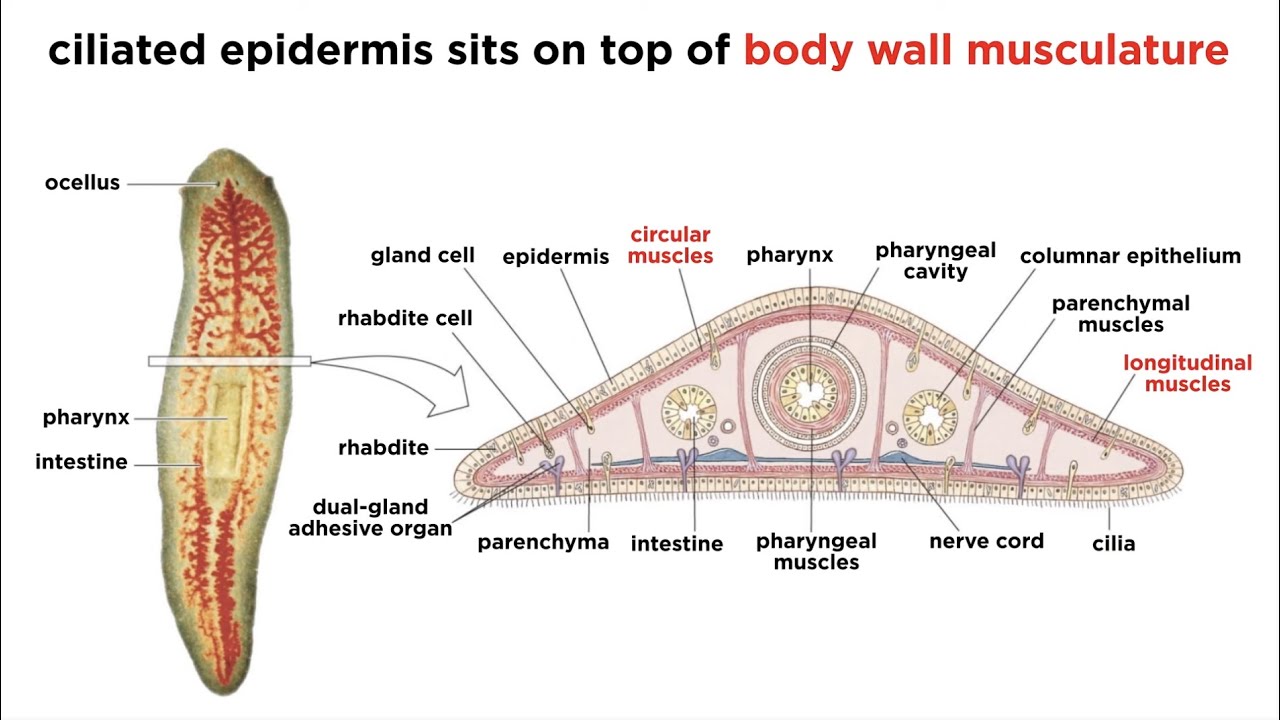
- Flattened
- ==Triploblastic:== has three tissue layers
- ==Acoelomate== (has no coelom/no body cavity/no organs or organ systems)
- ==Bilaterally symmetrical==
- Unsegmented worms
==Classes of Platyhelminthes (4):==
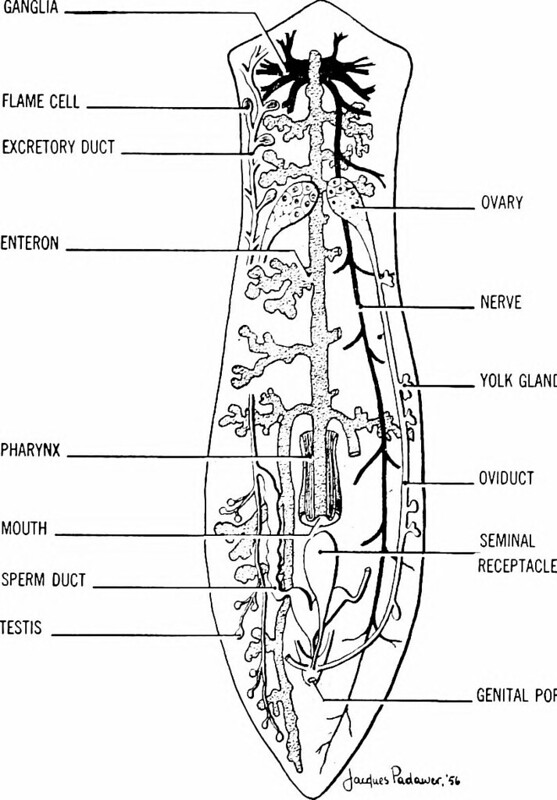
- ==Class Turbellaria (Planarians!!!!!!)==:
- Free-living and aquatic
- Can be both freshwater and marine
- Predators and scavengers (first true hunters!)
- 1 cm-60 cm
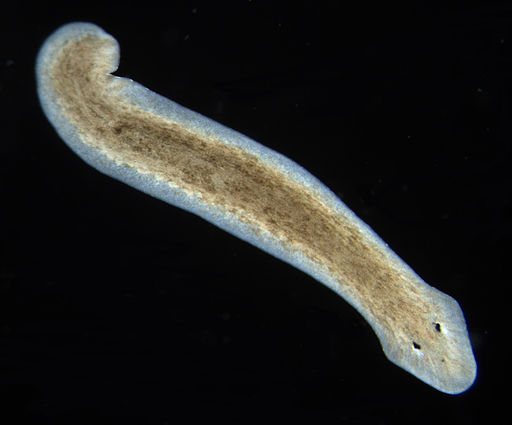
==Locomotion:==
- They are bottom dwellers
- They move using cillia and muscular contractions
- They can free swim sometimes
==Digestions:==
- They have an incomplete digestive tract: they only have a mouth but they don’t have an anus
- Branched digestive systems allows for diffusion of nutrients
- No circulatory system
- They have a Pharynx: muscular ingestion organ that is located on their underbelly and attaches to their mouth
- Chemo receptors on their head that help them find prey
- ==Chemo receptors==: structures/cells that can sense chemicals/heat in the water to find prey
==Exchanges in the Environment:==
- No respiratory organs
- Gases are exchanged, nitrogenous waste (chemical waste/cellular waste) is eliminated through diffusion through body wall and flame cells
- ==Flame Cells==: a specialized excretory cell (they operate like kidneys)
==Nervous and Sensory Function:==
- Central ganglia: cluster of neurons located in the head region
- Platyhelminthes can detect touch, water current, and chemicals
- ==Auricles:== projections on the side of the head; help locate food by using chemoreceptors
- ==Ocelli:== “eye spots” that orient the animal towards light
- Most platyhelminthes (turbeliina) are negatively photoreceptive (meaning they move away from the light)
==Reproduction and Development:==
Asexually by transverse fission
- ==Transverse Fission==: They can pinch their bodies together horizontally and make two halfs called zooids. These half each grow the part that they need to become a new turbellina that being either a tail or a head.
Sexually: ==monoecious== (both male and female reproductive organs in one body)
==Reciprocal sperm exchange between individuals==
Fertilized eggs are laid in capsule called coccoon
==Summer capsules==: hatch in a fast time, 2 to 3 weeks and immature animals emerge
==Autumn capsules==: thick walls that resist freezing and drying out; hatch after winter when conditions are favorable
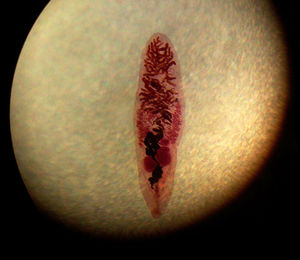
==Class Trematoda:==
- These are called ==flukes==
- Wide, flat shape
- 10,000 species; that are all parasitic
- They feed on host cells and cell fragments
==Class Monogenea:==
- External parasites of ==fishes==
- Attach to gill filaments
==Class Cestiodea:==
- This class includes ==tapeworms==
- They lack a mouth and simple digestive systems
- Instead these cestiodea absorb nutrition from host through cell wall
- ==Proglottids:== long, repeating sections that each contains a set of reproductive structures
^^Phylum Nematoda:^^
Main Characteristics:
- ^^Triploblastic^^
- ^^Bilateral^^
- Unsegmented
- ^^Pseudocoelomate (fake body cavity)^^
- ^^Cuticle^^: outer body covering of nematodes that is made of the collagen protein
- Covers body
- Digestive System:
- ^^Complete digestive tract^^: mouth and anus
- Mouth surrounded by lip bearing sense organs
- Located on the head
Nematode Parasites of Humans:
^^Ascaris lumbricodes^^: Affects dogs and cats normally
- ^^Intestinal roundworm^^
- 800 million people infected
- Live in small intestines
- Eggs exist in the feces that the dog and cats excrete
- Eggs ingested and move to intestinal tract
^^Enterobius vermicularis^^
- ^^Human pinworms^^
- Most common roundworms in US
- Live in lower region of large intestine
- Females carry eggs out of rectum, deposit them, then die
- Eggs are swallowed and move to intestines
^^Necator americanus^^
- The New World Hookworm
- Found in Southern US
- Live in small intestine
- Eggs pass out in feces and hatch
- Larva penetrate the skin, makes way to the intestines
^^Trichenella spiralis (pork worm)^^
- The pork worm
- Live in small intestines of all carnivores and omnivores
- Females give birth to live larvae that migrate to muscle tissue
- Remain infective for years (trichinosis)
- Transmission: Another animal eats muscle, migrates to that animal’s small intestines
^^Wucheria species^^
- The filarial worms
- Live in lymphatic system of humans
- Causes fluids to accumulate in appendages (elephantiasis)
- Produce larvae: microfilariae
- Circulates in bloodstream, carried by mosquitoes to next person (intermediate host)