P4
Developing the model of the atom
John Dalton- Agreed with Democritus meaning:
Atom were tiny spheres that couldn’t be broken down any further
100 Years later JJ Thompson discovered electrons could be remove from atoms hence the PLUM PUDDING MODELLL:
This suggested that atoms were spheres of positive charge with tiny negative spheres stuck in them.
The charges cancelled each other out making the entire atom of neutral charge
Problems
How does the nucleus not collapse due to electro static attraction
Geiger Marsden experiment (Alpha particle scattering experiment)
knowledge:
They believed the plum pudding model was correct
They knew that opposite charges attract and like charges repel
What they expected
Because the plum pudding model suggested an atom that had no overall charge as the positive sphere and negative electrons cancelled each other out
Meaning that the positive alpha particles could pass straight through
Results
Most alpha particles went straight through
But a small number were deflected
And around 1 in 10,000 were deflected by more than 90°
Conclusions
Most of the atom is just empty space
Because the majority just passed through
Most of the mass is focused in a positively charged nucleus
Because the alpha particles must have been repelled by a like charge.
Electrons orbit the nucleus
In order to not be drawn into the nucleus by electrostatic attraction
Bohr
Said that electrons orbit at fixed distances
The further away the more energy it has
When electron go down a level they lose energy and emit EM radiation
When electrons go up a level they absorb EM radiation- gaining energy
Isotopes and Nuclear radiation
These are atoms With the same Atomic number, different Mass number
Some isotopes are unstable and decay into other material giving out radiation in order to become more stable
Radioactive decay- An unstable nucleus can become more stable over time by randomly (spontaneously) emitting ionising radiation
Radioactive substances- Spit out one or more types or radiation
Ionising power- How easily radiation can knock electrons off atoms making them positive ions
Penetration power- The ability of radiation to pass through matter
The random nature of radiation- You can’t predict when a radioactive nucleus will decay or which nucleus will decay next
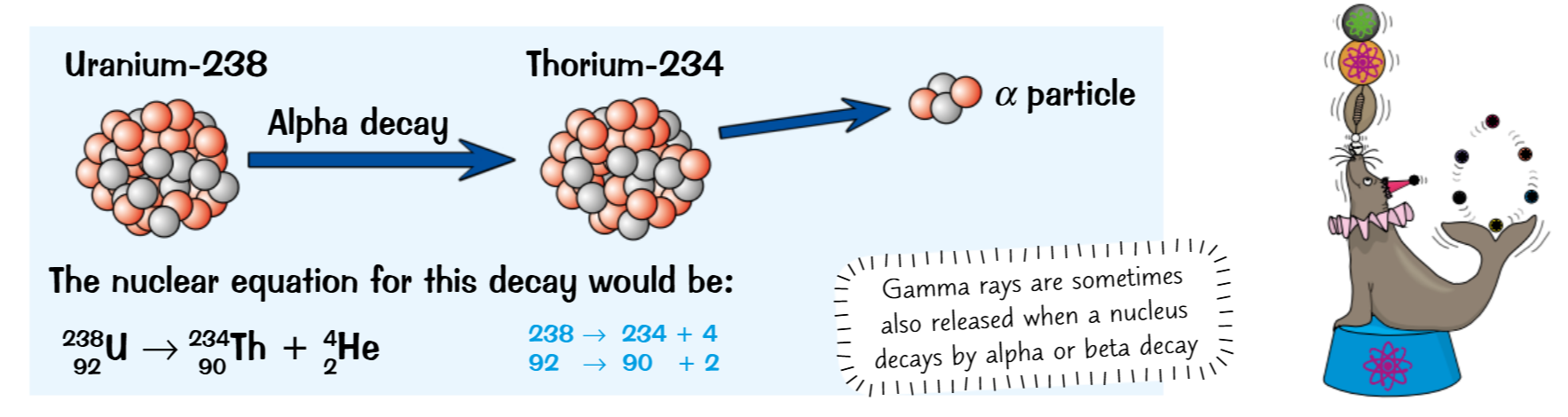
Alpha
What is it- A helium nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutron)
Penetration- Stopped by paper pr a few cm of air
Ionising- Very strong
Extra- When emitted the element changes as it loses 2 protons and 2 neutrons,
Mass decreases by 4 charge decreases by 2
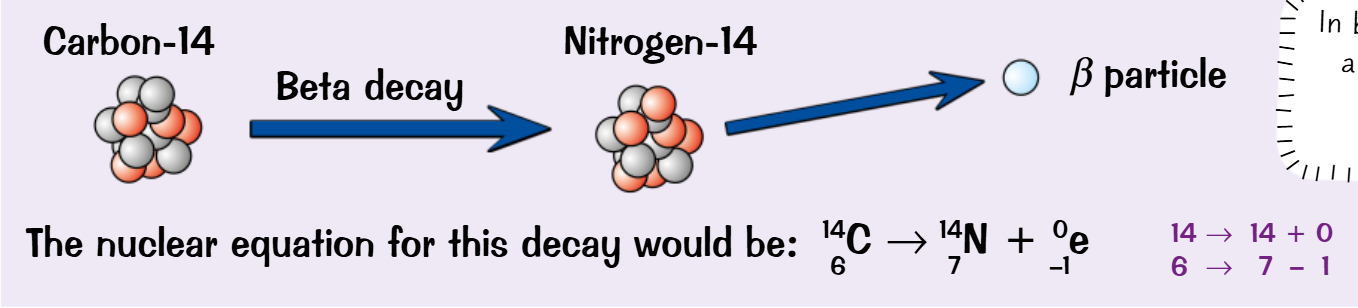
Beta
What is it- a fast moving electron
Penetration- stopped by aluminium foil
Ionising- Mid
Extra~ Every beta radiation emitted causes a neutron in the nucleus to turn into a proton, changing the element altogether, as it Gains a proton
~ Charge increases by 1
~A Neutron turns into a fast moving electron that runs away and a proton that stays
~Mass remains unchanged
Gamma Rays
What is it- A wave of energy
Penetration- Partially stopped by thick lead/ meters of concrete
Ionising- weak
Extra~ No change in mass or charge, just a release of energy
Nuclear equations
Shows the process of nuclear decay in the form:
Atom before decay → Atom after decay + radiation emitted
The total mass and atomic numbers have to be equal on both sides
Now taking into account the factors from the aforementioned extras you apply this the nuclear equations:
Half life
Each time a radioactive nucleus decays to become stable its radioactivity decrease. Some sources take a few hours to decay whilst others take millions of years to decay, But eventually the radioactivity will drop off.
Half life~ the time it takes for the amount for the number of radioactive nuclei to halve
It is measured in becquerels, Bq 1Bq = 1 decay per second
Background radiation and contamination
This is the ever present amount of constant radiation in the background at all times.
Subtract this from radiation results whenever you can
Radioactivity naturally occurs in:
Cosmic rays
Fallout from past nuclear explosions or waste or melt downs
Radiation dose measures the risk of harm to body tissue due to exposure:
It is measured in sieverts and millisieverts
When an object is exposed to radiation it is IRRADIATED, This is the one to do with sieverts
When an object is contaminated: Radioactive atoms get onto or inside the object
Outside the body: (So commonly irradiation wise)
beta and gamma radiation are the most dangerous as the can penetrate the skin and damage organs
Whereas alpha is stopped by skin and air
Inside the body: (So commonly contamination wise)
Alpha is most dangerous due to the high ionising power
Beta as it is absorbed over a wider area or passes out the body all together its less dangerous
Gamma is least dangerous as it passes out the body completely hand has the lowest ionising power

Fission
This is nuclear the radiation that we are used to:
It usually starts when a nucleus absorbs a neutron,
then it decays into to lighter elements and another fast moving neutron
This fast moving neutron is absorbed by another nucleus
Which repeats the process causing a chain reaction
During this reaction lots of energy is released through gamma rays and kinetic energy
Which can generate heat which heats water to make steam to turn a turbine
Which makes nuclear energy
Fission in a reactor is controlled and slowed using rods which absorb neutrons
In order to stop a nuclear melt down
Uncontrolled fission chain reactions can lead to a nuclear weapon
Fusion
This is the joining of small nuclei at high speeds e.g. Hydrogen
These nuclei fuse to grate a larger nucleus (e.g. helium)
Some of the mass of the smaller nuclei turns to energy, producing a stupid amount of energy
However the conditions to create a fusion reactor are Hard as hell to make they require insane pressures and temperatures
YES FINALY UUUGHGHTTT P4 FINISHED