L13 Gout "Disease of Kings"
Objectives
Identify Risk Factors
Understand how Purine Metabolism and Uric Acid Elimination contribute to Gout formation
Overproducers and Underexcretors
Factors and Process that predispose Acute Gouty Arthritis in Peripheral Joints of Lower Extremities
Understand Clinical Manifestations of Acute Gouty Arthritis, Tophaceous Gout, and Uric Acid Nephrolithiasis
Notes
What is a possible indicator of Gout
Hyperuricemia (excessive uric acid)
decline in urinary excretion of uric acid below the rate of production
Uric Acid is a byproduct (waste) of what
Purine Metabolism
mostly endogenous, some dietary (red meats, seafood, alcohol, etc)
What are the diagnostic factors of Hyperuricemia
< 7 mg/dL → < 1% risk
> 10 mg/dL → 30% risk
What can happen when there is excess uric acid in the blood
Uric Acid and Monosodium Urate can precipitate into crystal deposition → arthritis
T/F: The body uses Uricases to breakdown Uric Acid
False, converts into Allantoin to solubilize
What is Urate
anionic uric acid (more soluble)
Where is most of urate filtered through?
Kidney’s glomerulus
however, 90% is reabsorbed
What causes excess uric acid
Overproduction or Underexcretion
What are risk factors of Goat
Age
associated with decreased Kidney function
Elevated Serum Urate
Male
Postmenopausal Women
SCr, BUN
Obesity
Alcohol intake
High Purine intake (meat/fish)
What are key players mentioned within the Purine Metabolism Pathway
Ribose 5-Phosphate → PRPP Synthetase → PRPP → + Glutamine → Inosinic Acid → Hypoxanthine → Xanthine Oxidase → Xanthine → Xanthine Oxidase → Uric Acid → Renal Resorption or Excretion
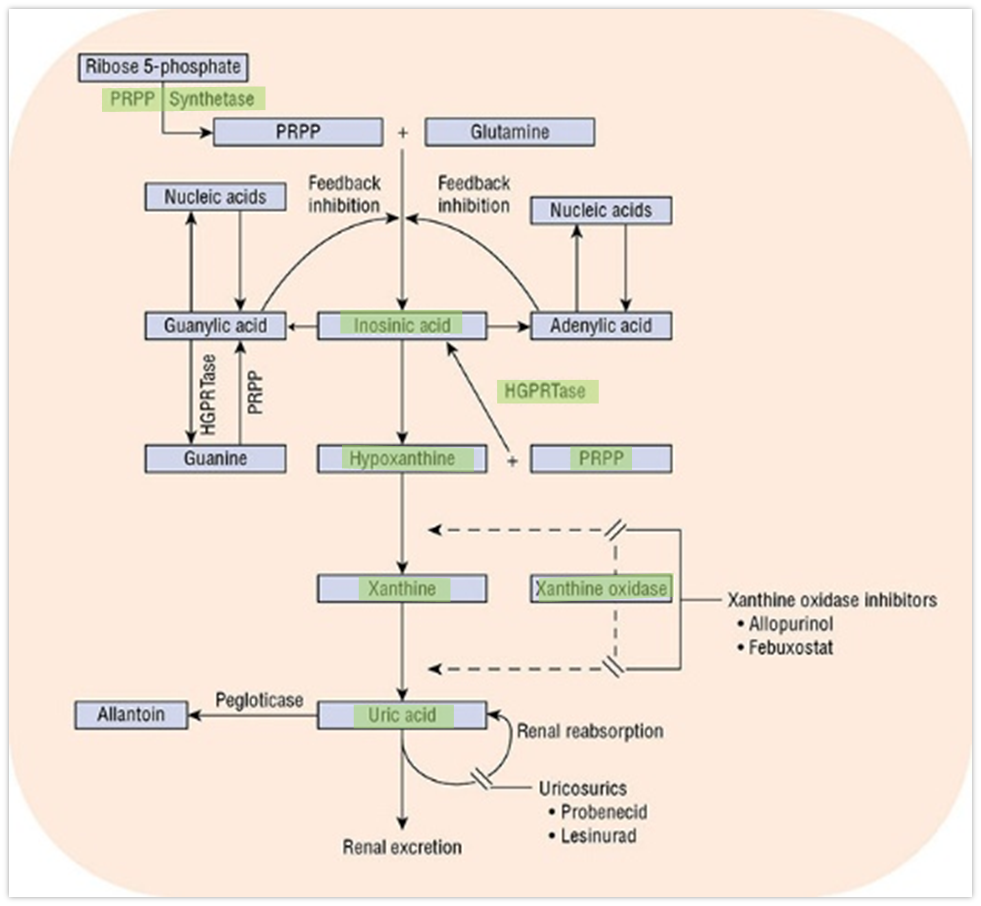
What are Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors used for
Prevents the formation of uric acid, likely to avoid excess production
Why is it important to keep a balance between uric acid production and excretion
Normal Levels are already near the limits of Urate Solubility
Is overproduction or underproduction of uric acid more common in goat?
Underproduction (90%)
What is categorized as overproduction
excrete > 600 mg on purine-free diet (> 1000 mg on a regular diet)
What is categorized as underproduction
excrete < 600 mg on a purine-free diet (< 1000 mg on a regular diet)
What can cause increased tissue breakdown and cell turnover → uric acid overproduction
Cytotoxic Meds
Hemolytic Anemia
Psoriasis
What enzymes can cause uric acid overproduction
Increased PRPP Synthase
Decreased HGPRT
What are possible causes of Underexcretion
Organic acids competing with urate for expression
Decreased kidney function
Medications
List the medications that decrease renal clearance
Diuretics, Ethanol
Nicotinic Acid, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol, Testosterone, Salicylates, Cyclosporine, Cytotoxic meds
How is overproduction or underexcretion
24 hour urine screening
What is Acute Gouty Arthritis
Rapid onset of pain, swelling, and inflammation often the big toe
Insteps (top of foot), Ankles, Heels, Knees, Wrists, Fingers, Elbows
Typically Monoarticular
What is Acute Gouty Arthritis a predisposition to?
Peripheral Joints in Lower Extremities
due to low temp and/or synovial fluid is a poor solvent
urate crystals are less soluble < 37 degrees C
When does AGA pain typically occurs
begins at night
synovial effusions (fluid accumulation) occur for a short period (transiently) during the day with routine activity
water is reabsorbed during the night
supersaturated solution of monosodium urate
What inflammatory responses are cause by Acute Gouty Arthritis Crystal Deposits
Vasodilation
increased Vascular Permeability
Complement Activation
Chemotactic activity
What are causes of AGA
Stress,
Trauma
Alcohol
Infection
Surgery
Rapid lowering of uric acid
Meds
How is AGA diagnose
Aspirate Synovial Fluid
not typically done but is best method
Clinical Triad
Inflammatory Monoarthritis
Elevated Serum Uric Acid Levels
Response to Colchicine
What are the criteria for clinical diagnosis
One or more episodes of swelling, pain, tenderness
Monosodium Urate Crystals
aspiration of joint
Additional Criteria
Ankle or midfoot (monoarticular or oligoarticular)
First metatarsophalangeal joint (monoarticular or oligoarticular)
Redness over affected joint
Cannot bear to touch or put pressure on affected joint
Great difficulty walking or inability to use affected joint
Time to maximal pain < 24 hours
Resolution of symptoms ≤ 14 days
Complete resolution between episodes
Tophus
Hyperuricemia
Synovial fluid analysis
Imaging evidence of urate deposition
Imaging evidence of gout-related joint damage
What is Interval Gout
Asymptomatic periods between attacks
What is Tophaceous Gout
Urate deposits in soft tissue
What are complications of Tophaceous Gout
Soft tissue dmg
Deformity
Joint destruction
Nerve Compression Syndromes
What is Gouty Nephropathy
ACUTE renal failure → blocked urine flow → uric acid crystals in collecting ducts and ureters
Myeloproliferation or Lymphoproliferation
CHRONIC Urate Nephropathy → long-term urate crystal deposits in renal parenchyma
What is Uric Acid Nephrolithiasis
Uric acid Kidney stones
pH of 5 → 15 mg/dL uric acid level
pH of 7 → 200 mg/dL
Do stones form in more basic or acidic conditions?
acidic
What pH do most patients have for spontaneous precipitation (formation) of stones to occur
pH < 6