DSA Week 6: Nervous System
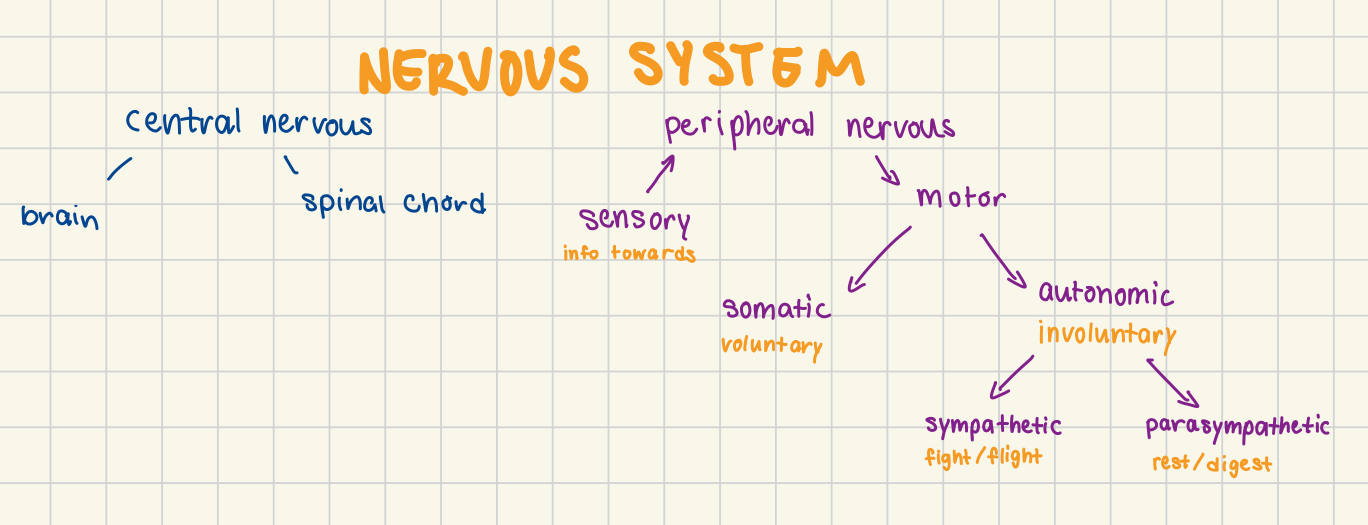
Topic 1: Divisions of the Nervous System
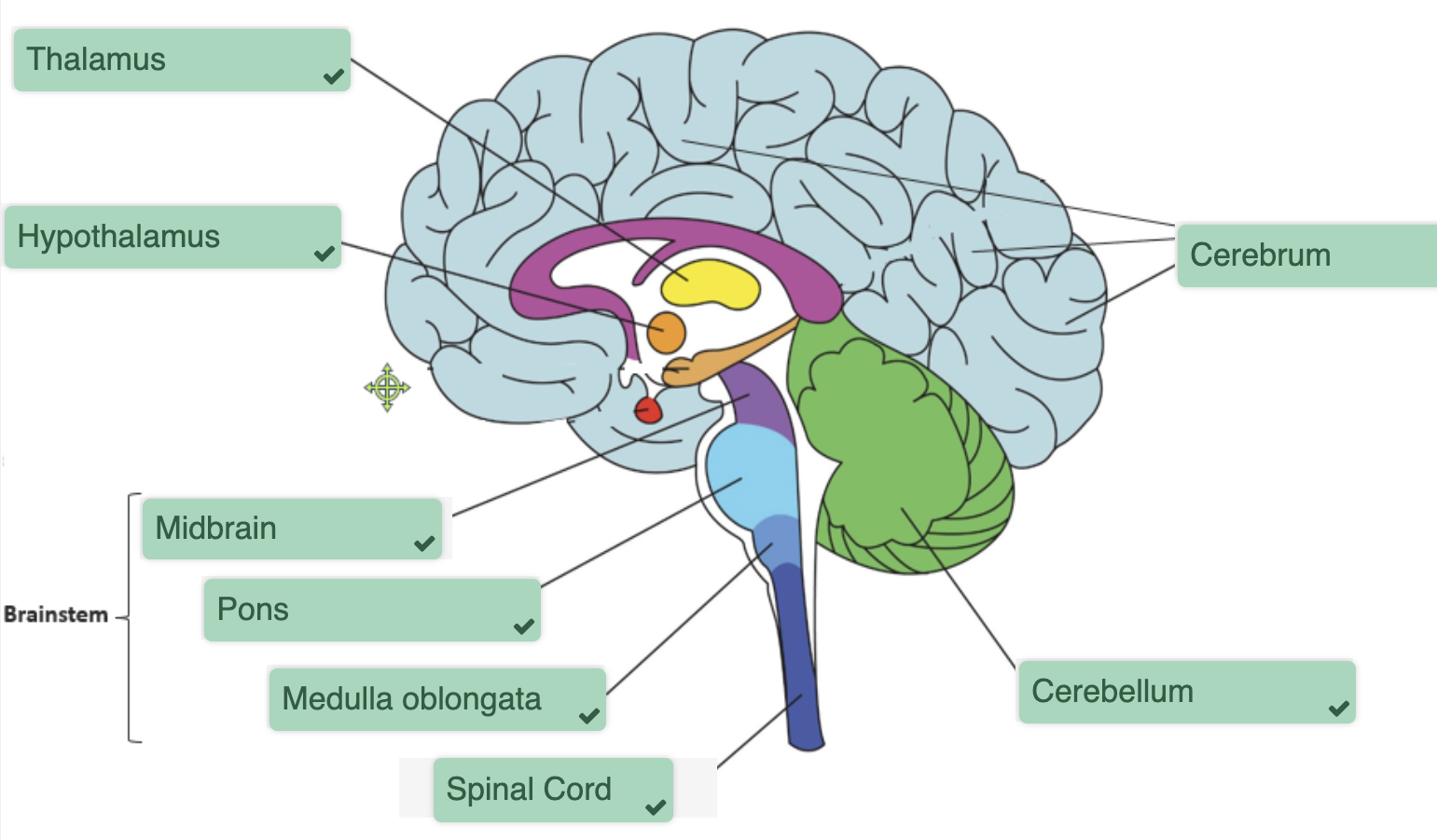
Topic 2: Central Nervous System
The Brain
THE BRAIN STEM:
controls involuntary functions (breathing, heart rate, etc.)
connects cerebrum + cerebellum to the spinal chord
cranial nerves originate in brainstem
Thalamus
relays info from the body to other areas of the brain
from sensory nerves in the skin to the cortex
mail room
Hypothalamus
master cotrol of autonomic system
controls pituitary gland
hunger, thirst, sleep + sex
Limbic System
emotional control
emotional behaviour from
amygdala (anger)
hippocampus (memories)
hypothalamus (regulates emotion)
Cerebrum
contains the cerebrum
cerebral cortex: grey matter (nerve cell bodies) + white matter (nerve fibres)
conscious mind
aware of self + sensation
communicate
remember
understand
intitiate voluntary movement
Cerebellum
coordinate muscle movement
coordination + balance
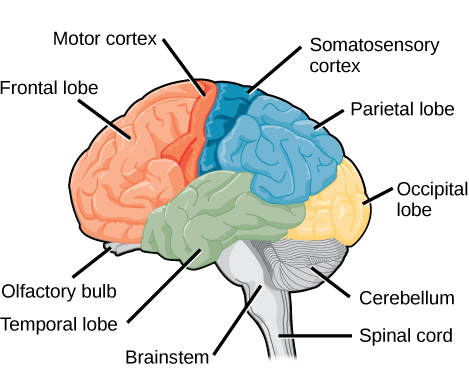
Cerebral Cortex + Lobes
Frontal Lobe
movement
problem solving, reasoning
personality
language
Parietal Lobe
processing somatosensory input
integrates visual + auditory information
Temporal Lobe
hearing
language comprehension
memory
Occipital Lobe
visual processing, perception, memory
Functional Areas of Cerebral Cortex
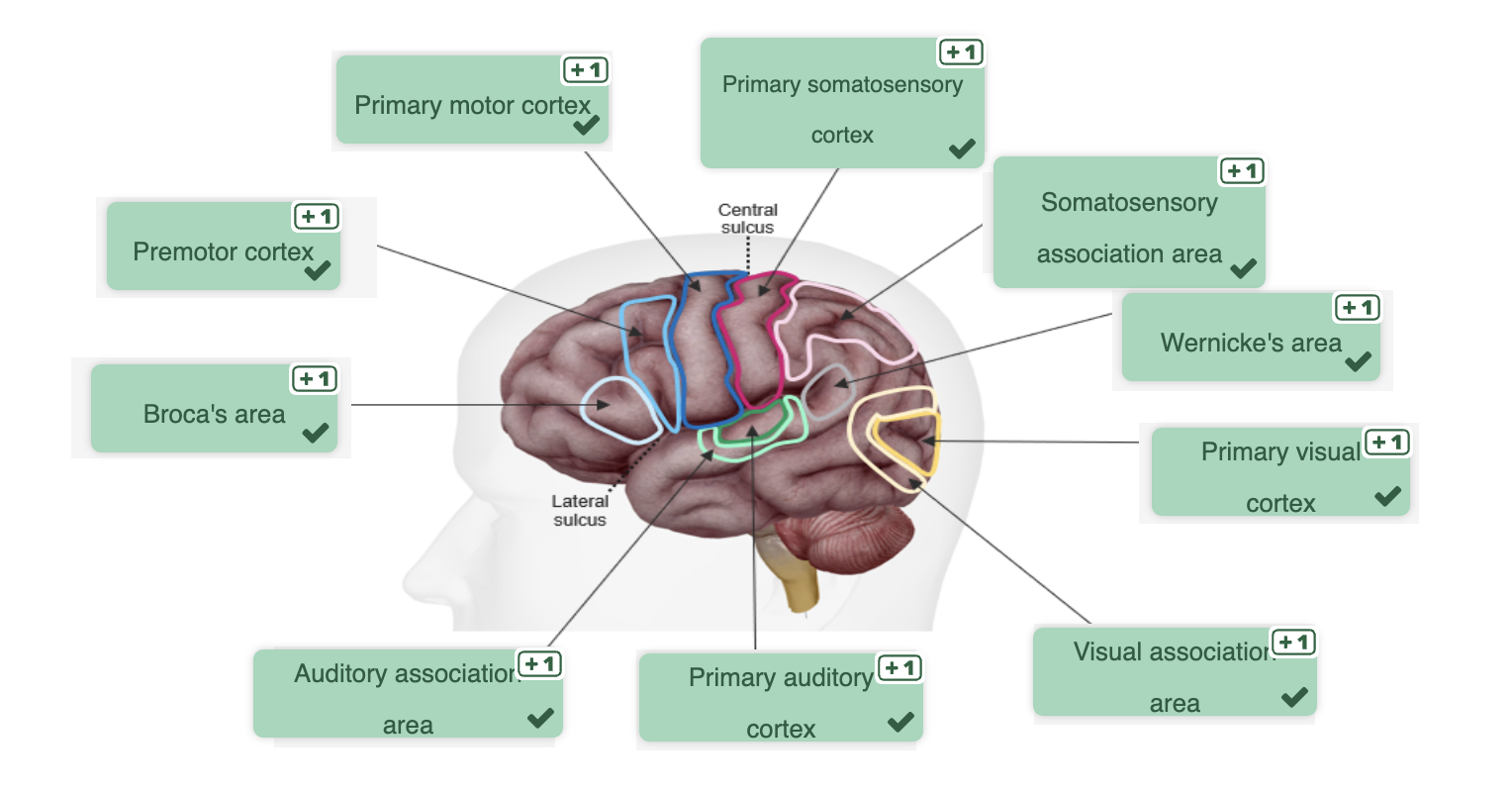
Frontal Lobe
Primary motor cortex
relays motor commands to motor neurons → skeletal muscles
basically motor homunculus (weird looking guy diagram)
Premotor cortex
plans the movement
Broca’s area
language processing + speech
Parietal Lobe
Primary somatosensory cortex
processes touch, temperature, pain, sensory info
sensory homunculus
Somatosensory association cortex
analyses sensory information + sends to understanding area
Temporal Lobe
Primary auditory cortex
processes auditory information
Auditory association cortex
interprets auditory information
associates auditory input with other sensory input
Wernicke’s Area
comprehension of written + spoken language
Occipital Lobe
Primary vision cortex
receives visual stimuli
Vision association cortex
interprets visual stimuli on past experiences
Spinal Chord
Train of nervous tissue + support cells that goes between brain + rest of body
Top: Medulla Oblongata
Bottom: Lumbar region of vertebral column
vertebrae protect the spinal chord
26 vertebrae
vertebrae are disks made up of hyaline cartilage
Spinal Nerves:
pairs
spinal nerves come from the psinal chord
through spaces between vertebrae
named based on which section of the vertebral column
Spinal nerves are bunches of nerves (both motor + sensory)
ventral roots contain motor neurons
dorsal roots contain sensory neurons
dorsal rooot ganglion contain sensory neuron bodies
White matter in the spinal chord:
gray matter in the center is shaped like a butterfly
white matter made up of bundles of neuronal axons
white matter is where action potentials pass between different areas of grey matter
bundle of axons is called a column (dorsal column + ventral column)
Dorsal Column:
towards the back
Ventral Column:
towards the front
Lateral Column:
towards the side
Gray Matter in the spinal chord:
made up of cell bodies, axon terminals, dendrites
receives info + sorts info out
divided into horns (each horn is divided in 1/2)
Dorsal horn:
posterior
cell bodies of interneurons
sensory input
Ventral horn:
anterior
cell bodies of motor neurons
Lateral horn:
situated laterally
contain cell bodies of preganglionic neurons (contribute to autonomic system)
Neuronal pathways:
descending = motor
cerebral cortex to skeletal muscles
brainstem to automatic movement
ascending = sensory
from peripheral nerves to the cerebral cortex
Topic 3: Peripheral Nervous System + Reflexes
Receptors of the Sensory Nervous System
Types of Receptors:
mechanoreceptor
touch + pressure + vibration + stretch
thermoreceptor
temperature change
chemoreceptor
respond to chemicals (smell, taste, changes in blood)
nociceptor
pain receptor
photoreceptor
light (eyes)
Mechanoreceptors:
embedded in the skin
touch changes the shape of the receptor
this triggers ion channels = action potentials
Tactile Sense Localisation:
precision of tactile stimuli is different for different parts of the body
assessed using the 2-point discrimination test
sensitivity is different based on parts of the body
Most sensitive = lips, fingers, palms, soles of feet
The greater receptor density = greater tactile precision
more neurons in the area
Receptive Feild:
area if stimulated leade to activity in the neuron
if receptive feild is small = high density of neurons
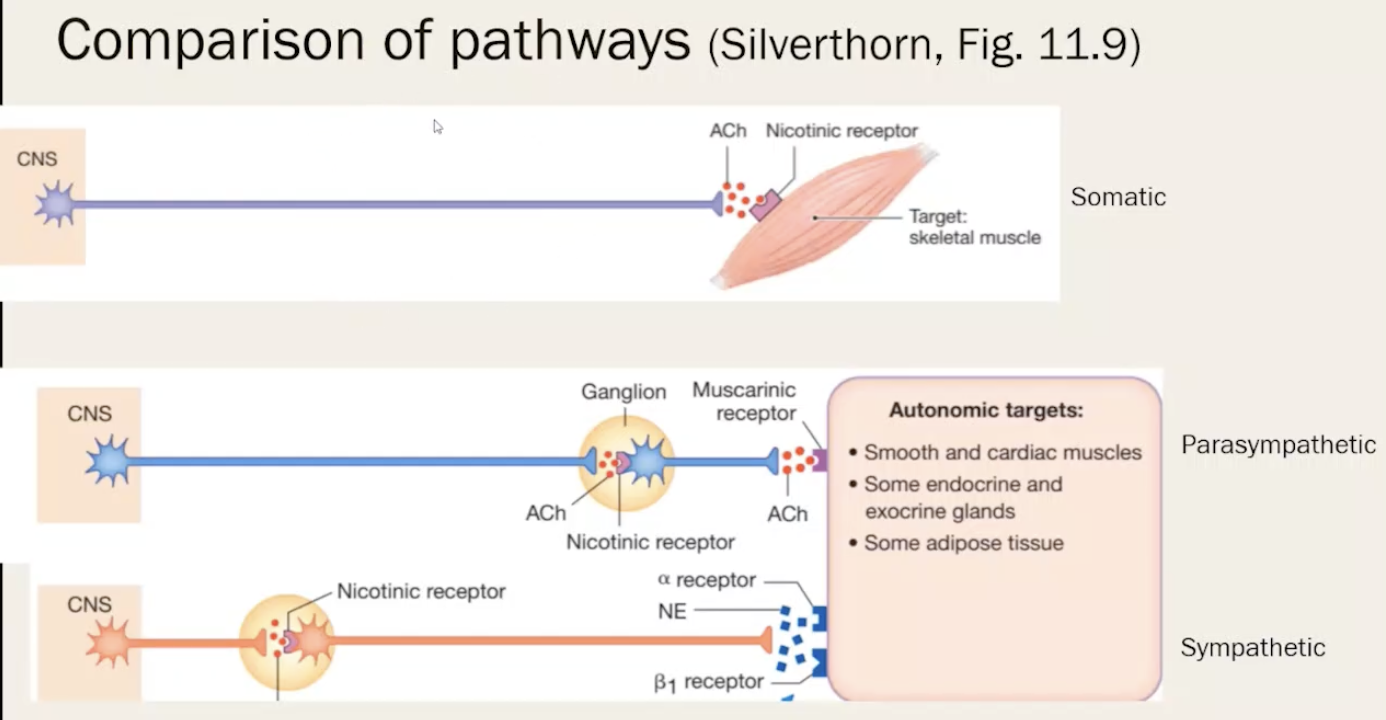
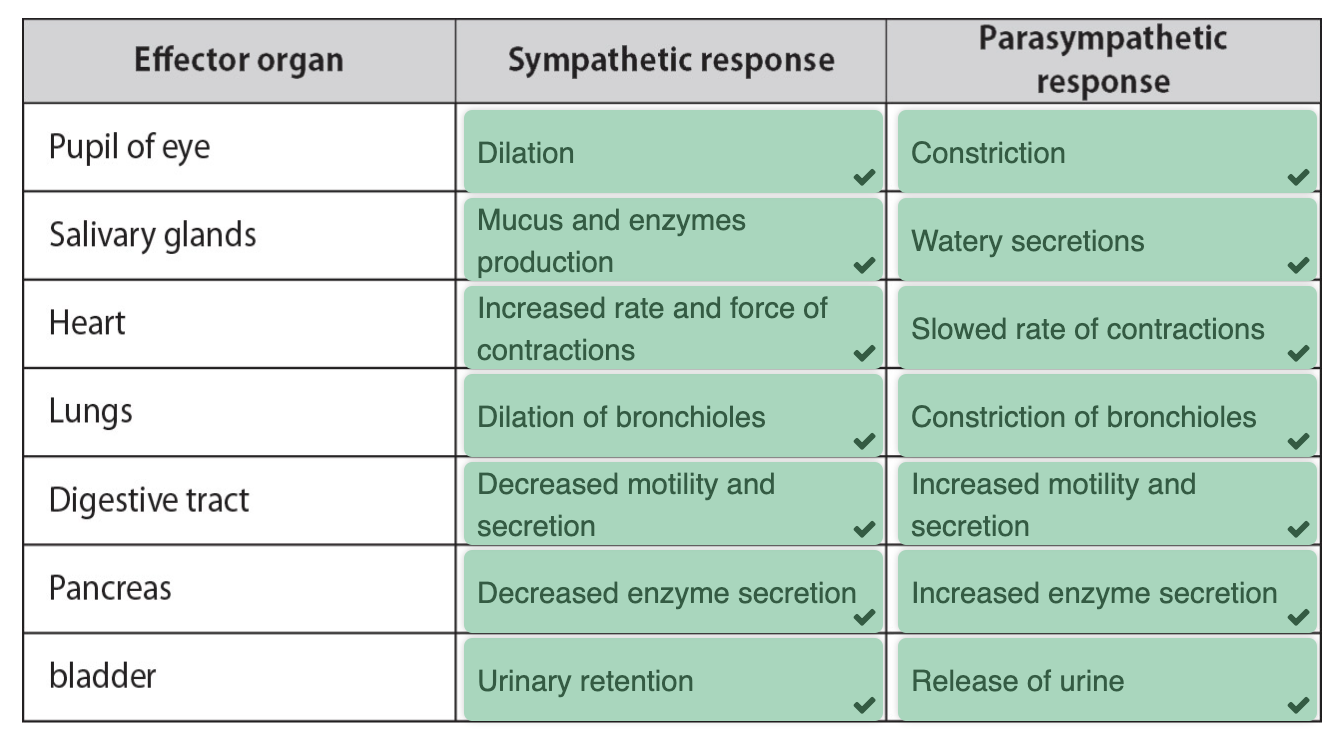
Autonomic Nervous System
Role of autonomic:
involuntary system
controls smooth muscles + organ funtions
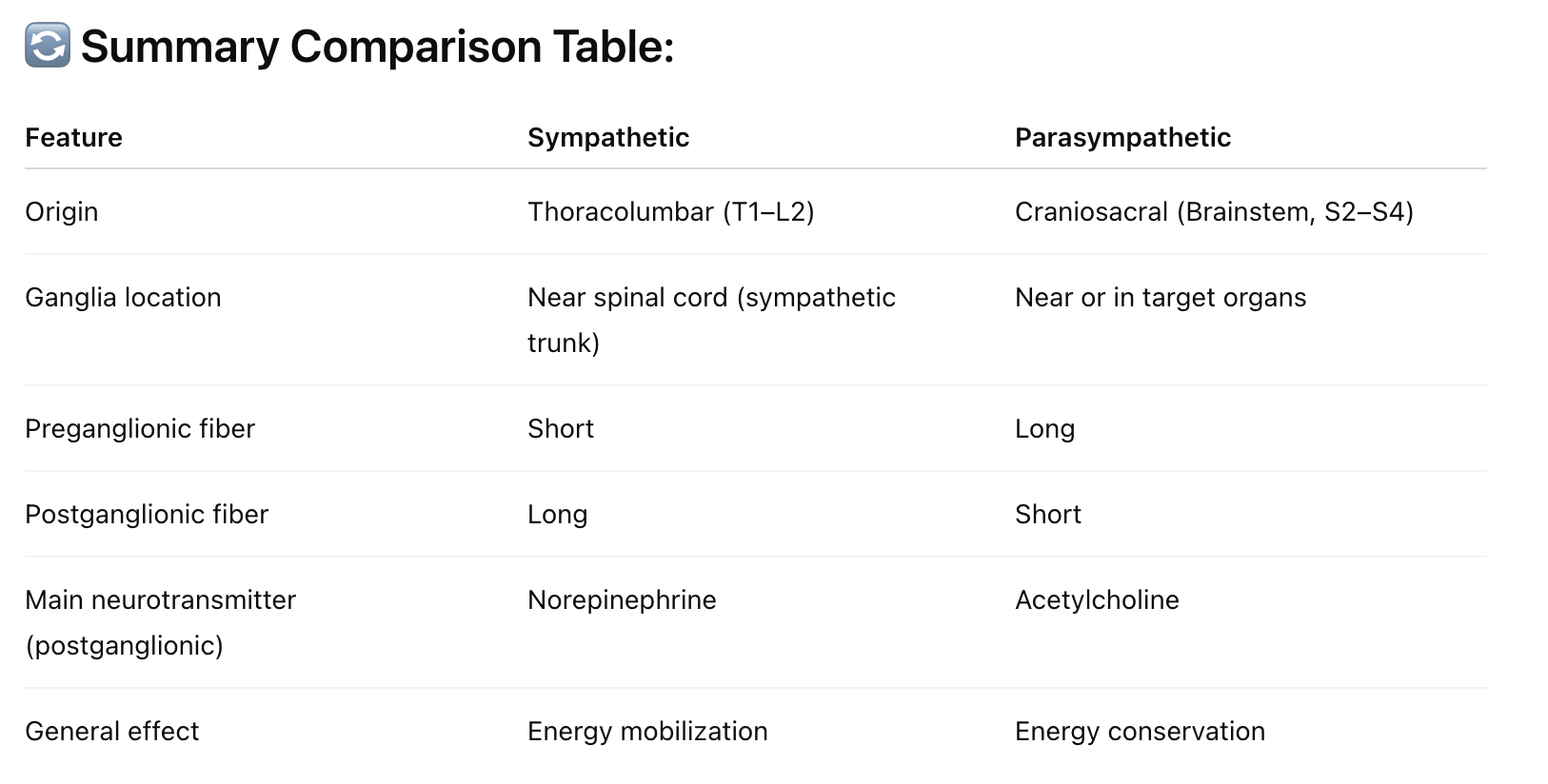
Sympathetic: flight/flight responses
originates in lumbar + thoracic area
ganglia located close to spinal column
short preganglionic neuron
long postganglionic neuron
produce norepinephrine (neurotransmitter) for the adrenergenic receptors
Parasympathetic: rest/digest
originates in the brain + sacrum area
long preganglionic neuron
short postganglionic neuron
produce acetylcholine (ACh - neurotransmitters) for muscarinic receptors
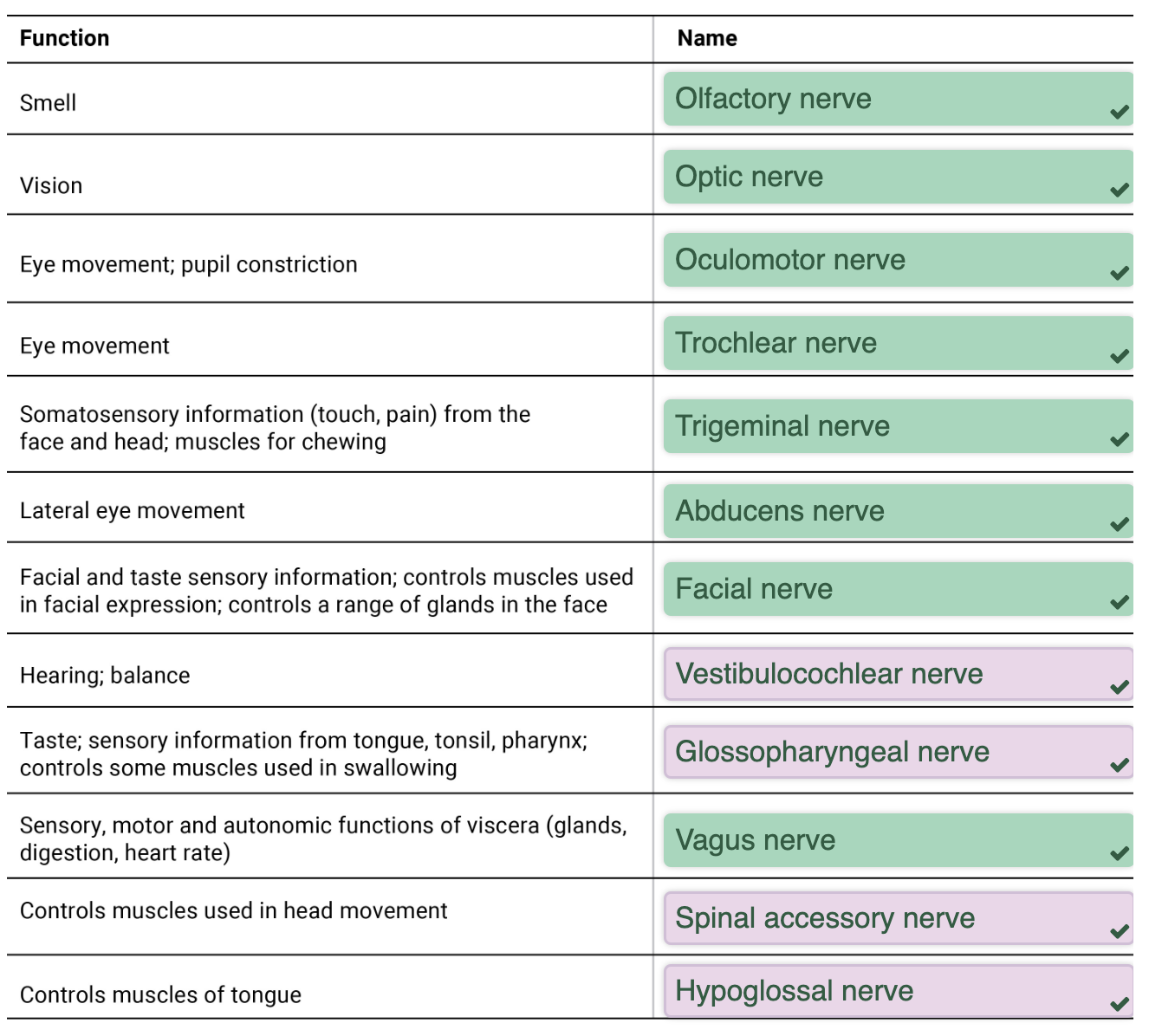
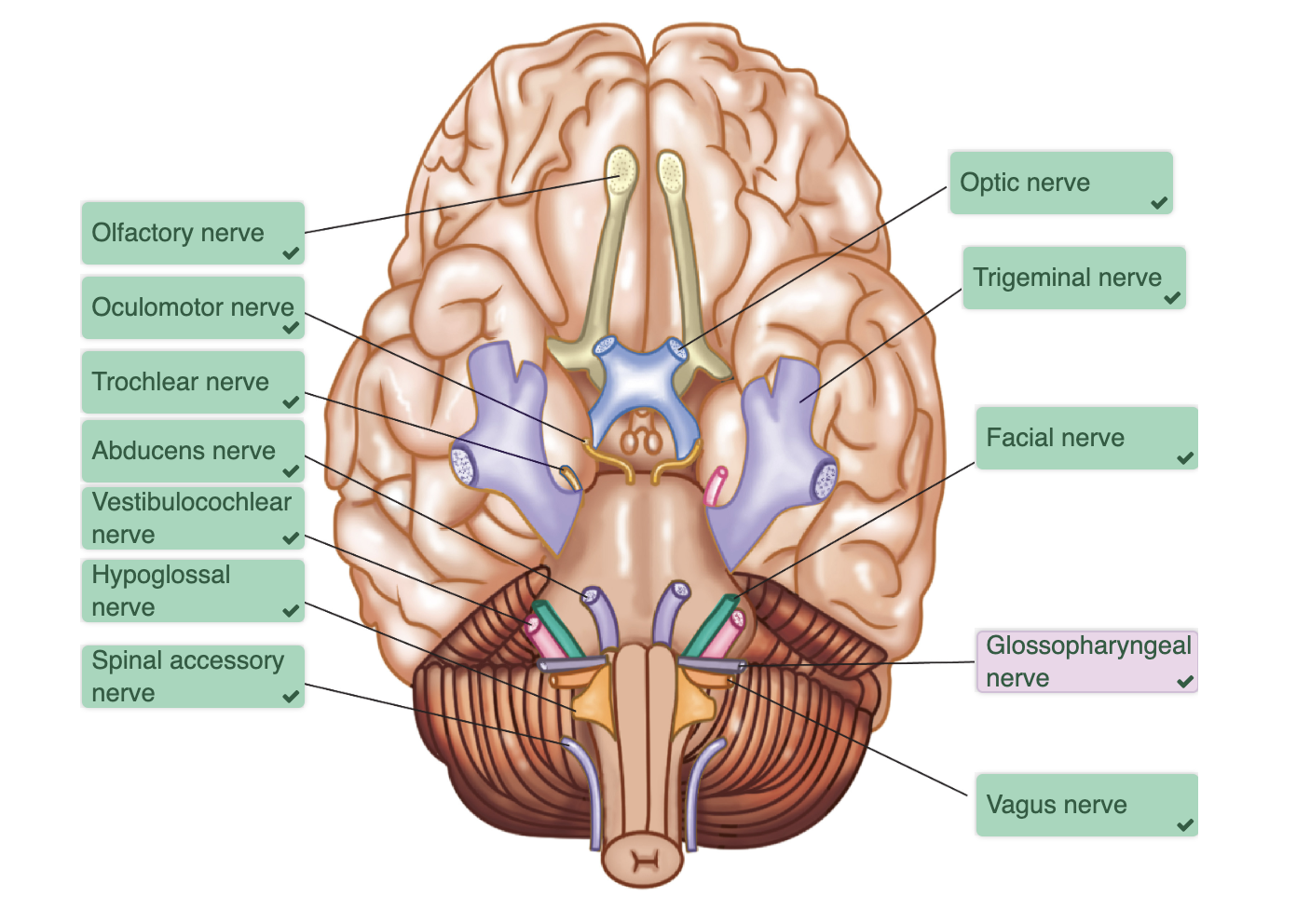
Cranial Nerves
set of 12 paired nerves from the cerebrum
trigger different organs in head + neck
most are sensory fibres but some are motor neurons
Olafactory I:
receptors in nasal mucosa
sensory fibres synapse with olafactory bulb
doesnt enter brain stem
Optic II:
receptors in the retina form the optic nerve
nerves form the optic chiasma
synapse in the thalamus
Oculamotor III:
moves the eye
parasympathetic fibres dilate/constrict the pupil
focus lens
Trochlear IV:
pulley
motor fibres + sensory receptors connect to eye muscle
moves the eyeball up + down
Trigeminal V:
three branches
opthalmic
maxillary
mandibular
sensory: touch (temp + pain)
chewing muscles
Abducens VI:
moves eye from side to side
Facial VII:
facial muscles
sensory nerves for taste
stimulates glands: salivary, nasal, tears
Vestibulocochlear VIII:
sensory ibres from vibration receptors in the cochlear
equilibrium receptors canals and vestibule
Glossopharyngeal IX:
controls tongue + pharynx
motor fibres for swallowing
sensory fibres for taste + sensation
carotid body:
sensory fibres from chemoreceptors monitor oxygen + carbon dioxide levels
sensory fibres for baroreceptors monitor blood pressure
Vagus X:
wanderer - only cranial nerve beyond the head
contains sensory + parasympathetoc fibres
Spinal Accessory XI:
accessory part of the vagus nerve
motor + proprioreceptors signals from 2 large muscles in the neck
Hypoglossal XII:
below the tongue
controls tongue (chewing, speech, swallowing)
Reflexes
rapid motor response to stimulus
survival mechanisms
Simple Reflex Arc:
sensory brings info to spinal chord (interneuron in the spinal chord)
spinal chord sends out response to motor
Stretch reflex:
stimulus: tap stretches the tendons + muscles
spindles detect muscle length
effector: causes quadricep muscles to contract
Gag Reflex:
involuntary reaction clears up the airways
stimulus: oropharynx is touched (glossopharyngeal nerve)
effector: soft palate rises + contraction of palatal + pharyngeal muslces
Topic 4: Neural Pathways
Sensory + Neural Pathways
neural pathways are made up of chains of neurons
Sensory (ascending): from receptors in the periphery to the CNS
First order neurons: from receptors to CNS
cell body located in dorsal root ganglion/cranial nerve ganglion
Second order neurons: transmits signal from spinal chord to thalamus
many decussate
located in spinal chord/brainstem
Third order neurons: conduct impulses from thalamus to other area of the brain
Motor (descending) pathways: from the CNS to the periphery
Upper motor neurons
cell bodies + axons lie within CNS
controls LMN
Lower motor neurons (LMN)
cell bodies located in the ventral horn of the spinal chord
send axons to activate skeletal muscles
Characteristics:
decussation:
cross from one side of the CNS to the other (decussate) at some point
relay:
most consist of a chain of 2/3 neurons
somatopy:
Somatotopy is like a map in your brain that shows which parts of the brain control or feel different parts of your body
Symmetry:
all pathways are paired symmetrically