Copy of 10.2 The Endocrine Glands.docx
10.2 The Endocrine Glands
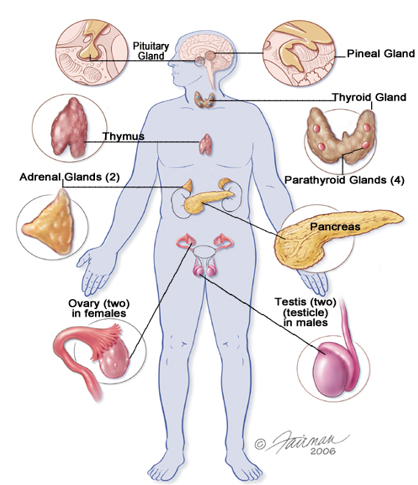
Control of Hormone Secretion
-hormones are released in short bursts, with little or no secretion between bursts
- When increasingly stimulated, endocrine glands release hormones in more frequent bursts
- When there is little stimulation, the frequency of bursts decreases
- Hormone secretion is regulated by:
- Signals from the nervous system
- Chemical changes in the body
- Other hormones
The Hypothalamus
- Small region of the brain that controls the pituitary gland
- Major link between the nervous system and the endocrine system
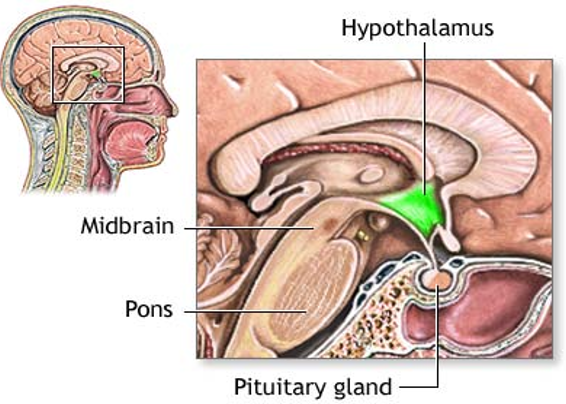
The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
Together they regulate virtually all aspects of growth, development, metabolism, and homeostasis.
- Hypothalamus secretes 9 different hormones
- Pituitary gland secretes 7 different hormones and is divided into two lobes (anterior and posterior pituitary gland)
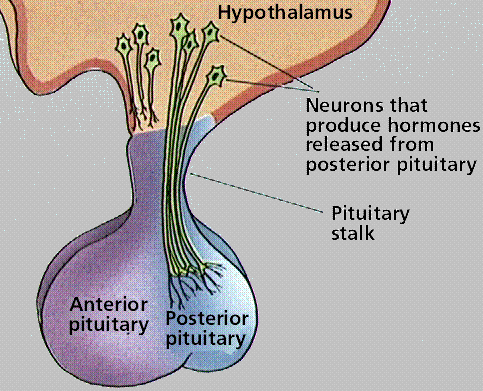
Anterior pituitary | Posterior pituitary |
Hormones produced and released: | Hormones released: |
|
|
Growth hormone is essential for growth. Cells under the action of GH increase in size and number. Too little or too much GH can cause dwarfism or gigantism.
Thyroid- stimulating hormone (TSH) is involved in regulating metabolic rates and body temperature.
Gonadotropins (FSH & LH) affect the gonads by stimulating gamete formation and production of sex hormones. Prolactin is secreted near the end of pregnancy and prepares the breasts for milk production.
Posterior Pituitary Gland
Does not synthesize hormones but rather stores and releases two hormones (listed above). These hormones are produced in the cells of the hypothalamus and packed into vesicles which are then transported to and stored in the posterior pituitary gland.