Atoms, Molecules and Ions
Atoms are the smallest particle of any element
Sub-atomic particle | Proton(p) | Neutron(n) | Electron(e) |
|---|---|---|---|
Relative Mass | 1 | 1 | 1/1840 |
Relative Charge | +1 | 0 | 1 |
Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus which is positively charged and contains most of the mass
Mass of electrons too small to be counted as part of the mass
atom is electrically neutral as the number of positively charged protons is equal to the number of negatively charged electrons
Periodic Table
Contains metals, non-metals and metalloids-have properties of both metals and non-metals
Atoms(Noble gases) in group 18 are stable due to having a Completely Filled Outermost Electron Shell (CFOES) and are inert and exist as single atoms
Have a duplet(2) or octet(8) electronic configuration
Will share, lose or gain valence electrons for atoms to attain a stable noble gas electronic configuration
Therefore, atoms may need to lose or gain electrons to become stable in which they become charged particles called ions
Gains valence electrons>negative ions (anions)
Loses valence electrons>positive ions (cations)
Chemical Compound of Ions
Positive ions attracts negative ions in which an ionic compound is formed and an ionic bond exists between them>electrostatic forces of attraction
Ions formed through transfer of valence electrons from metals to non-metals
Example:
Name of Ion | Name of atom before the ion is formed | Charge of Ion | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
Hydrogen | Hydrogen | +1 | H+ |
Oxide | Oxygen | -2 | O2- |
Chloride | Chlorine | -1 | Cl- |
Transition Metals
Name of Ion | Name of atom before the ion is formed | Charge of ion | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
Copper(I) | Copper | +1 | Cu+ |
Iron(II) | Iron | +2 | Fe2+ |
Iron (III) | Iron | +3 | Fe3+ |
Finding the Chemical Formula
Sodium Chloride
Formula of ions | Na+ | Cl- |
|---|---|---|
Charge | +1 | -1 |
Simplest Ratio | 1 | 1 |
Chemical Formula: NaCl
Magnesium Chloride
Formula of Ions | Mg2+ | Cl- |
|---|---|---|
Charge | +2 | -1 |
Simplest ratio | 2 | 2 |
Chemical Formula: MgCl 2
*To find the chemical formula, you criss-cross the formula of the ions and the simplest ratio of the combining ions
Polyatomic Ions
Two or more atoms chemically combined to form an ion
Example:
Name | Number of each type of atom | Charge | Formula of Ion |
|---|---|---|---|
Hydroxide ion | 1 oxygen atom and 1 hydrogen atom | -1 | OH- |
Sulfate ion | 1 sulfur atom and 4 oxygen atoms | -2 | SO4 2- |
Ammonium ion | 1 nitrogen atom and 4 hydrogen atoms | +1 | NH4+ |
Molecules
Two or more elements chemically combined together
Molecule of an element is made up of the same type of atoms
Molecules of a compound is made up of two or more different types of atoms
Examples:
Molecule of an Element
Element | Chemical Formula | Number of atoms in molecule |
|---|---|---|
Hydrogen (H) | H2 | 2 |
Oxygen (O) | O2 | 2 |
Nitrogen (N) | N2 | 2 |
Sulfur (S) | S8 or S | 2 |
Fluorine (F) | F2 | 8 |
Chlorine (Cl) | Cl2 | 2 |
Bromine (Br) | Br2 | 2 |
Molecule of Compounds
Chemical Name | Number of each type of atom | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|
Water | 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom | H2O |
Carbon dioxide | 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms | CO2 |
Nitrogen dioxide | 1 nitrogen atom and 2 oxygen atoms | NO2 |
Sulfur dioxide | 1 sulfur atom and 2 oxygen atoms | SO2 |
Chemical Equations
Must be balanced
Number of atoms of each element before and after the reaction must be equal
Mass is conserved during a chemical reaction
Tips from a wise woman
Use numbers like 2 and 3
Always try to make odd numbers even
Balance ‘H’ and ‘O’ last
Go for LCM (lowest common multiple)
Always check answer
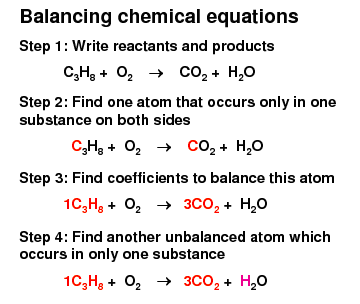
Image by By Ansaroo
 Knowt
Knowt
