Inflammatory and Immunologic Concepts
Terminologies
1. Communicable Disease
Illness caused by an infectious agent of its toxins
2. Infection
Implantation and successful replication of an organism within the body causing immunologic response
3. Contact
the state or condition of physical touching
4. Carrier
a person or thing that carries or holds something
5. Contagious Disease
Disease that is easily transmitted
6. Infectious Disease
Requires direct inoculation through a break on the skin or mucous membrane
7. Host
where a parasite or commensal organism lives
8. Reservoir
chronically infested with the causative agent of a disease and can act as a source of further infection
9. Disinfection
Destruction of pathogens outside the body by physical or chemical mean
10. Concurrent Disinfection
When patient is still the cause of infection
11. Terminal Disinfection
Patient is no longer the source of infection
12. Isolation
Separation of person with communicable disease
13. Reverse Isolation
Separation of immunocompromised person at risk of communicable disease
14. Quarantine
Limitation of freedom within the longest incubation period of the disease
Epidemiology
Epidemiologic Triangle
Agent
Host
Environment
Patterns of Occurrence and Distribution
Endemic - occurring within an area or community
Sporadic - occurring at irregular intervals or only in a few places; scattered or isolated
Epidemic - a rapid spread of disease to a specific region or population
Pandemic - a global outbreak
Agents
Bacteria
Viruses
Fungi
Protozoa
Prions
Helminths
Chain of Infection
Causative Agent
Reservoir
Portal of Entry
Mode of Transmission
Portal of Exit
Susceptible Host
Agent factors
Infectivity
Ability to invade and replicate
Virulence
Strength of the agent to cause a disease
Pathogenicity
Ability to cause a disease
Antigenicity
Ability to stimulate antibody production
Invasiveness
Ability to live outside the body
Mode of Transmission
Direct Contact
Indirect Contact
Droplet Spread
Air-borne Transmission
Vehicle-borne Transmission
Vector-borne Transmission
Acquisition
Community acquired
Nosocomial
Iatrogenic
Stages of Infection
Incubation
Infection - 1st s/sx
Prodromal
1st s/sx - Pathognomonic signs (obvious signs)
Illness or Fastigial
All s/sx
Convalescence or Defervescence
Subsiding s/sx and recovery
Immunity
Natural Immunity
Active
Passive
Artificial Immunity (vaccines)
Active - injection of dead or weakened pathogen
Passive - You receive an injection of antibodies that were generated by another person or animal, or artificially in a lab. These antibody-containing preparations are called antisera and are used to treat infections.
Types of Antigens:
Inactivated (dead or altered pathogen)
Not long lasting
Multiple doses
Booster needed
eg. rabies, hepa a, flu, ipv
Attenuated (weakened pathogen)
Single dose only
Long lasting immunity
eg. measles, mumps, and rubella (mmr), bcg, opv, influenza,
Isolation
Strict Isolation
Contact Isolation
Respiratory Isolation
Enteric Isolation
Drainage/Secretion Precaution
Universal Precaution:

Integumentary Diseases
1. Chicken Pox
Agent: HHV3 or Varicella-Zoster Virus
MOT
Airborne
Direct Contact
Contact with contaminated fomites
Incubation Period: 11 to 21 Days
Period of Communicability: 5 days before onset of rash and 5 days after first crop of vesicles
Signs and Symptoms
Itchy maculovesiculopapular lesions
Earliest complication: Encephalitis
Late complication: Herpes Zoster
Dx
Tszank Smear: A diagnostic test used to identify the presence of viral infections, particularly herpes simplex virus, by examining cells collected from lesions.
Lesion: Center to Periphery
Management
Strict Isolation
Fever: NO ASPIRIN
Pruritus
Calamine Lotion
Oatmeal bath
Cornstarch bath
Antihistamine
Cut nails or use mittens
DOC: Acyclovir/Zovirax
2. Rubeola (measles)
Measles, 1st Disease, English Disease, 7 day rash
Agent: Paramyxoviridae
MOT:
Airborne
Direct Contact
Indirect Contact
Incubation Period: 7-14 days
Period of Communicability: Just before the prodrome until 4 days after the rash appears
Koplik’s Spots (ENANTHEM) – pathognomonic sign
Pre-eruptive Stage
Fever
Catarrhal symptoms - inflammation
Stimson’s line - characterized by transverse line of inflammation along the eyelid margin
Eruptive Stage
Maculo-papular rash (EXANTHEM or widespread rash)
High grade fever
Anorexia and Irritability
Convalescence Stage
Rashes fade away
Fever subsides
Desquamation begins
Symptoms subsides
Management
Supportive and Symptomatic
Fever – Tepid Sponge Bathing
Koplik Spots – Gentian violet, water and salt
Vitamin A
<1 yr – 100,000 IU
>1yr – 200,000 IU
Pregnant – 10,000 IU
Dim light and use Shades
Complication: Bronchopneumonia
Prevention: Immunization
Anti-measles: 9 months
MMR
1st dose at 15 months
2nd dose at 12 years old
No to ASPIRIN - may lead to reye syndrome which affects brain and liver
3. Rubella
German measles, 3 Day Rash
Agent: Togaviridae
MOT
Droplet
Direct contact of respiratory secretions
Transplacental Transmission
Incubation period: 2 to 3 days
Prodromal Period
Low grade fever
Headache
Malaise
Mild coryza - inflammation of mucous membranes
Conjunctivitis - redness and inflammation of eye
Cervical lymphadenopathy
Eruptive period
Forchheimer’s Spot – Pathognomonic (small, red spots that appear on the soft palate of the mouth)
Rash – last for 1 to 5 days
Orchitis - testicle bumps
Transient polyarthritis
Congenital Rubella
IUGR - Intrauterine Growth Restriction
IUFD - Intrauterine Fetal Demise
Cleft palate
Cardiac Defects
Eye defects
Ear defects
Mental retardation
Prevention
MMR: 2 doses
Rubella titer <1:8 – Not immune
Immune serum globulin within one week after exposure
4. Scabies
The Itch
Agent: Sarcoptes scabiei
MOT
Direct inoculation
Skin to skin contact
Indirect contact with fomites
IP: 4 to 6 weeks
Signs and Symptoms
Linear burrow
Anaphylactic reaction
Acropustulosis
Pustules
Blisters
Ulceration
Management
Permethrin (5%) - head to toe and left for 8-14hrs and reapplied a week later
Kwell lotion (Gamma benzene hexachloride)
Crotamiton (Eurax)
DOC: IVERMECTIN: Single dose
Prevention
Good personal hygiene
Avoid direct contact with infected persons
All members of the household should be treated
Neurologic Diseases
1. Rabies
Hydrophobia, Lyssa
Agent: Rhabdovirus
All warm blooded animals are susceptible
MOT
Bite or scratch of rabid animal
Transplant of infected organ
Incubation Period: 9 days to 7 years
Signs and Symptoms
Numbness at site
Salivation
Fever
Headache
Malaise
Hydrophobia/Aerophobia
Hallucination
Confusion or Restlessness
Respiratory paralysis
Dx: Flourescent Antibody Test
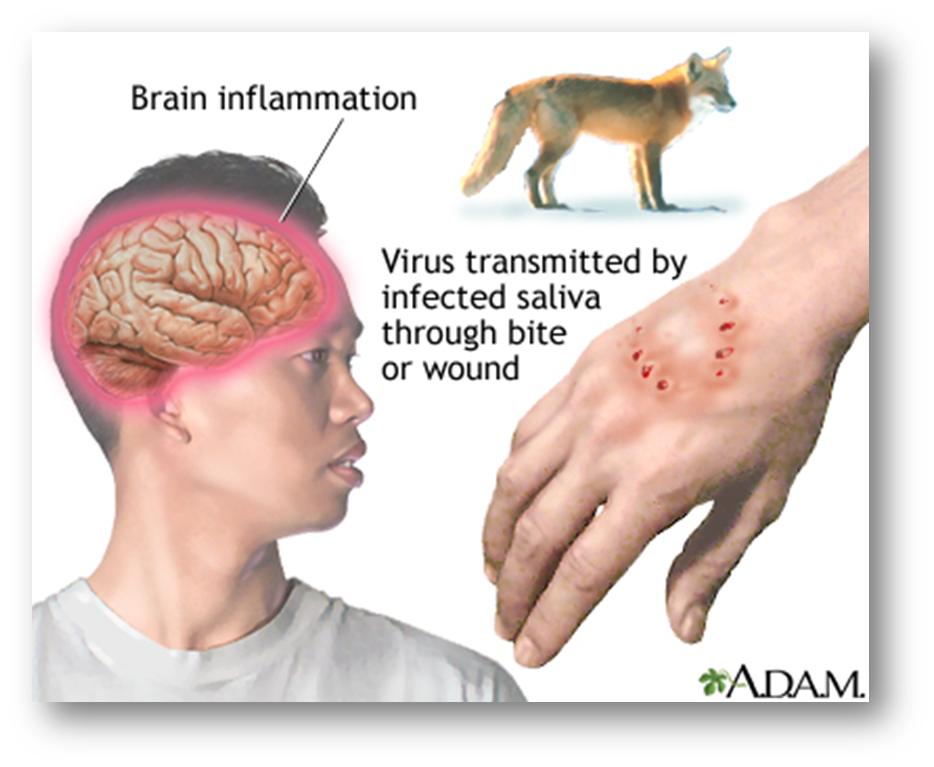
Management
Wash wound for 5 minutes
Observe the dog for 10 to 14 days
Do not rub garlic on wound
Hospital: assess for
Severity
Site (Proximity)
Numbness
Duration
Give Tetanus Immunoglobulin
Rabies Immunoglobulin
Bayrab
Verorab
Rabipur
Imogam
Human Diploid Cell vaccine (HDCV)
Imovax
When symptoms are already present
IVF – cover
Sedation
Restraint
Prevention
Responsible pet ownership
2. Leprosy
Lepra, Hansenosis, Hansen’s Disease
Mycobacterium leprae
MOT
Droplet
Skin to skin contact
Distinct Forms
Lepromatous leprosy
Tuberculoid leprosy
Borderline leprosy
Lepromatous
Multibacillary
Lepromin (-)
Large amount of bacilli in skin lesion
24-30 months treatment
Rifampicin, Dapsone, Lamprene (Clofazimine)
Tuberculoid
Paucibacillary
Lepromin (+)
Organism rarely isolated on skin lesion
6-9 months treatment
Rifampicin, Dapsone
Early Signs and Symptoms
Change in skin color
Loss of sensation
Decreased/absent sweating and hair growth
Thickened or painful nerves
Muscle weakness or paralysis
Nasal obstruction
Pain or redness of eyes
Non healing ulcer
Late Signs and Symptoms
Gynecomastia - enlargement of chest in male
Madarosis - a condition that causes the loss of eyelashes and/or eyebrows
Lagophthalmos - prevents a person from fully closing their eyelids
Leonine facies - causes facial features to resemble a lion
Contractures
Clawing
Sinking nose bridge
Chronic ulceration
Dx: Slit Skin Smear
Prevention
Report all cases and suspects of leprosy
BCG vaccine
Health education
3. Tetanus
Lock jaw
Agent: Clostridium tetani
MOT: Direct Inoculation
IP: 3 to 21 days
Signs and Symptoms
Hemolysis – Tetanolysin
Spasms – Tetanospasmin
Opisthostonus - causes a person to arch their back and neck into a rigid
Trismus - limits the ability to open the mouth
Risus sardonicus - fixed smile
Management
Wash wound area
Hospital: Antitetanus Serum (ATS)
Spasms
Dilantin
Diazepam
DOC
Metronidazole
Penicillin (GABA Antagonist)
Prevention:
Tetanus Toxoid: 5 doses
DPT
4. Meningitis
Agent: Bacteria or Fungi
common in dorm or prison
MOT: Droplet
Signs and Symptoms
Increased ICP
Brudzinki’s Sign *occipital pain
Kernig’s Sign *knee extension
Photophobia
Dx
Lumbar Tap - lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure that involves inserting a needle into the lower back to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Bacterial meningitis (worse)
Cloudy
Yellowish
Decreased glucose
Increased protein
(+) gram stain
Viral meningitis
Clear
Normal glucose
(-) gram stain
Pediatric - High pitched cry and bulging fontanelles
Management
Clue: It’s raining men (meningitis need droplet precaution)
Respiratory Isolation
N95 mask
DOC:
Penicillin G
Mannitol
Steroids – cerebral edema
Prevention: Avoid contact with infected person
5. Poliomyelitis
Infantile paralysis, Acute flaccid paralysis (AFP)
Agent:
Poliovirus 1,2,3
Legio Debilitans
Type I. Brunhilde
Type II. Lansing
Type III. Leon
MOT: Fecal-oral transmission
Signs and Symptoms
Poker Spine – destruction of anterior horn cells of spine caused by ankylosing spondylitis (AS)
Hoyne’s Sign or Tripod Sign - sign of meningeal irritation
Muscle tenderness, weakness, and spasms
Asymmetrical Paralysis of the extremities
Loss of superficial and deep reflexes
Dx: Pandy’s Test - normal protein values 0.20 to 0.45 g/liter
Management
Enteric isolation
ROM exercises
Trochanter rolls and foot board are indicated
Physical Therapy
Prevention
SALK: Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV)
SABIN: Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV)
Vector-Borne Diseases
1. Dengue
H Fever, Dandy’s Fever, Breakbone fever, Infectious Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Agents
Dengue virus 1,2,3,4
Arbovirus
Chikungunya virus
MOT: Vector-borne: Aedes Egypti mosquito
Grade 1
Dengue fever
Fever: 39 degrees Celsius
Abdominal Pain and vomiting
Petechial rash
Grade 2
Dengue hemorrhagic fever
Bleeding
Grade 3
Circulatory collapse
Grade 4
Shock, coma, and death
Dx: Presumptive
Tourniquet test, Rumple-lead test, or Capillary fragility test - The presence of 20 or more petechiae per square inch indicates increased capillary fragility,
Dx: Confirmatory
CBC
Platelet count (150,000 and 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood)
Management
Supportive and symptomatic
Fever: Analgesics, NO ASPIRIN
Increase fluid intake
Oresol
IVF
Blood transfusion
Prevention
Sanitation
Treated mosquito nets
On-stream seeding
On-stream clearing
Wear covered clothing
Planting Neem trees
Zooprophylaxis
2. Malaria
Marsh Fever, Ague
Agents:
Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium vivax
Plasmodium malariae
Plasmoidium ovale
MOT
Vector: Anopheles mosquito (female)
Blood transfusion
Transplacental
Signs and Symptoms
Paroxysms with shaking chills
Rapid rising fever with severe headache
Profuse sweating
Myalgia
Splenomegaly
Hepatomegaly
Dx: Malarial Smear
Management
Chemoprophylaxis: Chloroquine
DOC
Artemether
Quinine
Primaquine
Prevention
Sanitation
Treated mosquito nets
On-stream seeding
On-stream clearing
Wear covered clothing
Planting Neem trees
Zooprophylaxis
Avoid outdoor night activities (9PM to 3AM)
3. Filariasis
Elephantiasis
Agent:
Wuchereria bancrofti
Brugia malayi
Brugia timori
MOT:
Vector:
Aedes Poecellus
Culex quinquefasciatus
Anopheles Minimus
Signs and Symptoms
Acute
Inflammation
Lymphadenitis
Lympharyngitis
Epidydimitis
Chronic
Lymphedema
Hydrocele
Elephantiasis
Dx:
Nocturnal Blood Smear (8PM above)
Immunochromatographic Test
Bentonite Flocculation Test
DOC:
DEC (Diethyl Carbamazipine Citrate)
Hetrazan/Beltrazan
Prevention:
Fumigation/Fogging
Proper garbage disposal
Avoid over hanging of clothes
Seeding: larva eating fishes
Cleaning: exposure to sunlight
Zooprophylaxis
Plant: Neem Trees (sampaguita)
Stock: cover/put salt
Respiratory Diseases
1. Diphtheria
Agent
Klebs-Loeffler Bacillus
Corynebacterium Diphtheria
MOT
Droplet
Signs and Symptoms
Nasal – Foul smelling nasal discharge
Pharyngeal – Pseudomembrane, bull-neck
Laryngeal – Stridor
Dx:
Confirmatory: Nasal and Throat Swab
Schick’s Test – Susceptibility
Maloney’s Test - Hypersensitivity
Management
Do not remove the pseudomembrane
Anti-Diphteria Serum
Tracheostomy set at bedside
DOC:
Penicillin
Erythromycin
2. Pertussis
Whooping cough
Agent:
Bordotella pertussis
Haemophilus pertussis
Bordet-Gengou Bacillus
MOT:
Droplet
Direct contact of respiratory discharges
Signs and Symptoms
A. Catarrhal Stage - Highly communicable
Cough
Sneezing
Teary eyes
Fever
B. Paroxysmal Stage - Frequent coughing ending in inspiratory whoop.
Dx:
Nasal and Throat Swab
Management
DOC: Erythromycin
Supportive Therapy
Fluid and Electrolytes replacement
Adequate nutrition
Oxygen therapy
3. Pneumonia
Figure:
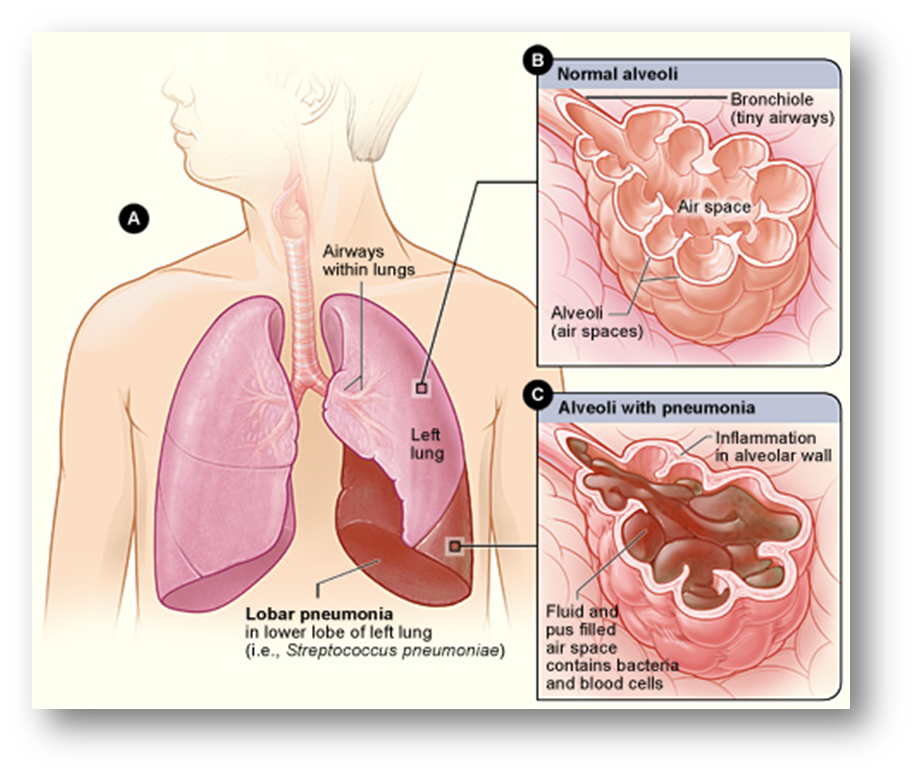
Most common test is impaired gas exchange
Signs and Symptoms
Altered mental status (agitation and restlessness)
yellow sputum
crackles
pleuritic chest pain or pleural friction rub
Consolidation of the lungs
Agent:
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
MOT:
Droplet
Signs and Symptoms
Rusty Sputum
DOC:
1st Amoxicillin
2nd Cotrimoxazole (Hepatotoxic)
4. Tuberculosis
Figure:
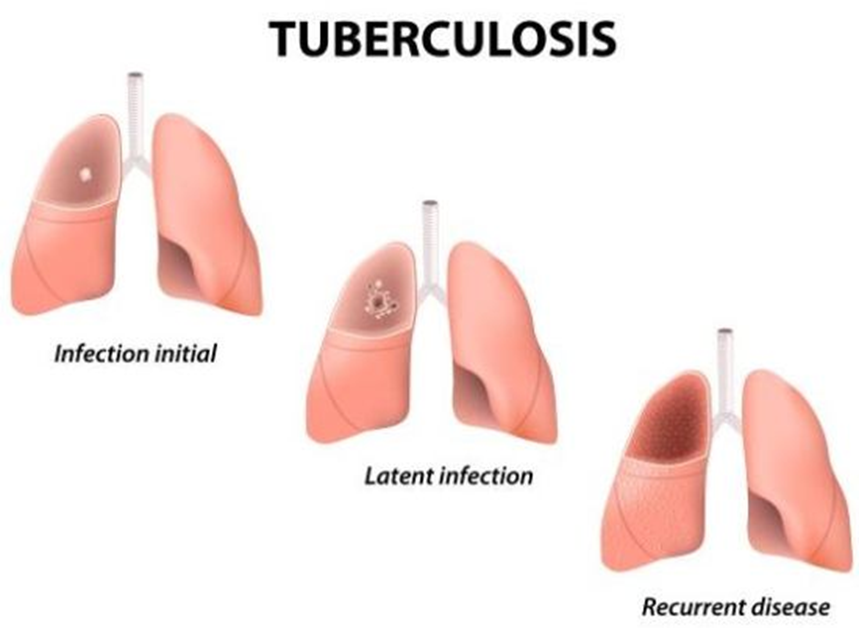
Consumption disease/ Poor Man’s Disease/ Phi
Agent:
M. Tuberculosis
M. Africanum
M. Bovis
MOT:
Airborne
Incubation period: 6-8 weeks
Signs and Symptoms
Cough for 2 weeks or more
Afternoon fever
Night sweats
Chest pain, back pain
Anorexia
Weight loss
Fatigue
Dx:
Presumptive:
Mantoux Test, Tuberculin, or PPD test
Incubation period: 48-72
Induration:
Immunocompromise: >5mm
With risk: >10mm
Without risk: >15mm
DSSM (Direct Sputum Smear Microscopy):
Sputum Test
AF Bacilli Test
Chest X-ray
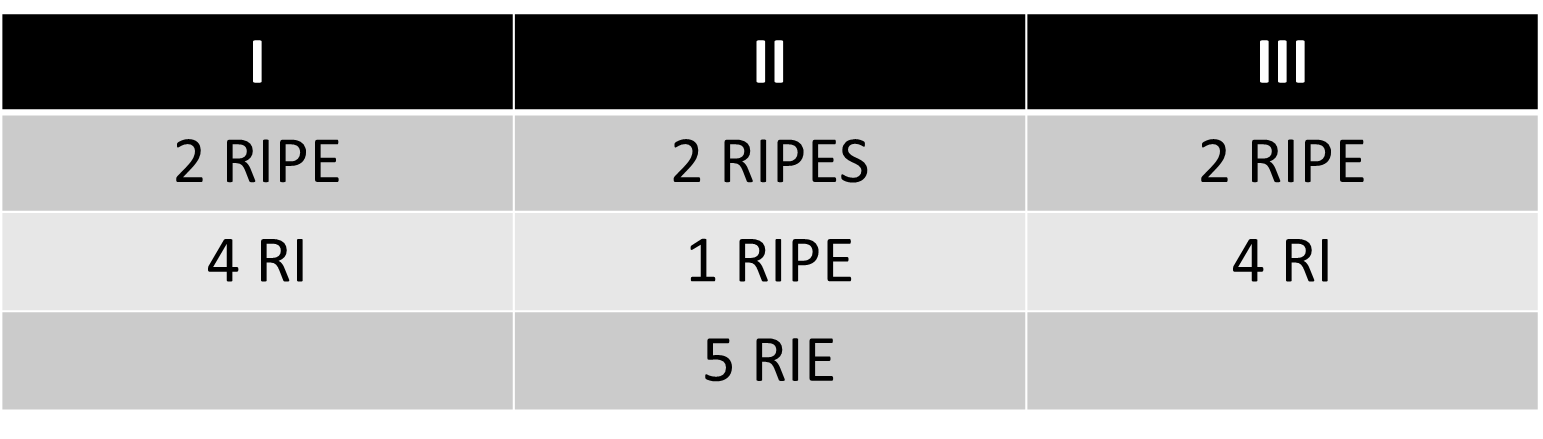
Management: DOTS
Category I
New patient
DSSM (+)
Serious
Category II
Default
Relapse
Failure
Category III
Children
DSSM (-)
Less serious
Category IV
Chronic
MDR
Drugs: RIPES
Rifampicin
Nephrotoxic
Discoloration of secretions
Isoniazid (INH)
Hepatotoxic (SGPT, SGOT, ALT)
Peripheral neuritis
Pyrazinamide (PZA)
Hyperuricemia
Gout
Ethambutol
Opthotoxic (-) 6y/o and below
Streptomycin
Ototoxic
vertigo, deafness
Prevention: BCG vaccination
Gastrointestinal Diseases
1. Schistosomiasis
Snail fever
Katayama disease
Bilhariasis
Agent:
Schistosoma japonicum
Schistosoma haematobium
Schistosoma mansoni
Reservoir: Oncomelania quadrasi
MOT: Direct inocculation
Signs and Symptoms
Fever
Hepatosplenomegaly
Eosinophilia
Cough
Dx: Katokatz test - diagnostic technique for the detection of helminth eggs in stool using a light microscope
DOC: Praziquantel
Prevention:
Boots
Molluscicides
2. Cholera
“El Tor”
MOT: Fecal-oral
Agent:
Vibrio Cholerae
Vibrio El Tor
Signs and Symptoms
Rice water stool
Washer woman’s hands
Vomiting
Diarrhea (10-20L)
Oliguria
Management
Tetracycline
Nalidixic Acid
3. Amoebiasis
Figure:
Amoebic Dysentery
Mucoid
Blood
Agent:
Protozoa: Entamoeba Hystolytica (cyst)-resistant to chlorine
Signs and Symptoms: Bloody mucoidal stool
DOC: Metronidazole (Flagyl)
4. Leptospirosis
Figure:
Weil’s disease
Canicola fever
Trench fever
Mild fever
Canefield fever
Swineherd’s fever
Nanukayami disease
Flood Fever
Spirochetal Jaudice Disease
Agent:
Spirochete
Leptospira interrogans
MOT:
Vector – Rodents
Direct contact to skin on open wounds
Signs and Symptoms
GI
Fever
Jaundice
Conjunctival suffusion
Renal interstitial tubular necrosis
Nausea and vomiting
Meningeal irritation
Headache
Myalgia
Dx:
MAT (Microscopy Agglutination Test)
LAT (Leptospira Antigen-Antibody Test)
DOC: Penicillin
Prophylaxis: Doxycycline
Prevention: Eradication of Rodents
5. Typhoid fever
Enteric Fever
Agent:
Salmonella Typhii
Typhoid bacillus
MOT: Fecal-oral
Signs and Symptoms
Rose spots/Red spots
Ladder-like fever
Splenomegaly
Dx:
Typhidot
Widal test
DOC: Chloramphenicol
6. Parasitism
Ascariasis
Ascaris lumbrecoides (giant round worm)
Ancylostomiasis
Ancyclostoma duodenale (hookworm)
Necator americanus
Trichuriasis
Trichuris trichuria (whipworm)
Enterobiasis
Enterobium vermicularis (pinworm)
Taeniasis and Cystiscercosis
Taenia solium (flat/tapeworm)
Taenia saginata
Trichinosis
Trichinosis spiralis
DOC: Mebendazole
Reproductive Tract Diseases
1. Gonorrhea
N. gonorrhea
Purulent discharge
Penicillin
2. Candidiasis
Candida albicans
Cheese-like/curd like secretions
Mycostatin (Nystatin)
3. Herpes Simplex
HSV
Blisters
Antiviral/not curable
4. Syphilis
Spirochete: Treponema palidum
VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Lab Test)
RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagin)
Penicillin G
5. Chlamydia
Chlamydia trachomatis
Azithromycin
6. Trichomoniasis/Vaginitis
Trichomonas vaginalis
Frothy/bubble-like discharge
Metronidazole
7. Condyloma accuminata lata
Genital warts
HPV
Cauliflower-like lesions
TIP:
-nazole is antifungal
-dazole is for da-gut
 Knowt
Knowt