****040 - Part 1 Recap, Taliban, Planes Operation
U.S. National Security - Dr. Jason Brownlee
Page 1: Introduction
Subject: U.S. National Security
Lecture Title: Bringing Peace to Afghanistan, 9 February 2020
Presented by Dr. Jason Brownlee, University of Texas at Austin, Department of Government.
Page 2: Course Overview
Annual Lecture: Lecture 040
Focus on national security policies and their implications.
Page 3: Key Figures and Groups in Afghanistan
Taliban Government (Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan): Key players before and after seizing power.
Ethnic Groups: Major ethnicities include Pashtuns (42%), Tajiks (27%), Uzbeks (9%), and Hazaras (9%).
Prominent Leaders:
Gulbuddin Hekmatyar
Ahmad Shah Massoud
Mullah Mohammed Omar
Abdul Rasul Sayyaf
Key Events & Concepts:
Relationship between U.S. policy shifts and the Taliban from 1996-2001.
Links to key figures in terrorism, including Ramzi Youssef and Mohammed Atta.
Page 4: Taliban Rule (1996-2001)
Overview of Taliban governance and its impact on Afghanistan's political landscape.
Page 5: Afghan Ethnic Composition
Population Stats:
Total Population: 28.6 million (2006).
Growth Rate: 2.4%.
Main Ethnic Groups:
Pashtun: Predominant group, Sunni Muslim.
Tajik: Persian origins, Sunni Muslim.
Uzbek: Turkish origins, Sunni Muslim.
Hazara: Mongolian origins, Shia Muslim.
Geographic Distribution: Where each group predominantly lives in Afghanistan.
Page 6: Map of Afghanistan
Visual representation of Afghanistan's ethnic distribution and borders.
Page 7: Historical Site
Mausoleum of Ahmad Shah Durrani: Significant historical landmark in Kandahar, reflecting Afghan heritage.
Page 8: U.S. Involvement in Afghanistan
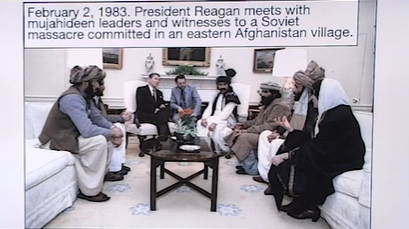
1983 Meeting: President Reagan with mujahideen leaders regarding Soviet actions in Afghanistan.
Page 9: Key Figures in Mujahideen Politics
Major Leaders:
Burhanuddin Rabbani (Tajik)
Ahmad Shah Massoud (Tajik)
Gulbuddin Hekmatyar (Pashtun)
Page 10: Civil War Aftermath
Description of the chaos following Najibullah’s rule.
Conditions:
Infighting among mujahideen groups.
Civilian casualties and suffering in Kabul from 1992 onwards.
Page 11: Consequences of Civil Conflict
Poor governance and militarized factions leading to further instability.
Page 12: Emergence of the Taliban
Mullah Omar: Personal motivation to form Taliban due to civil war atrocities.
Pages 13-15: Questions on Taliban's Ascendancy
Critical inquiries surrounding the Taliban's rise to power:
Reasons for overpowering the Mujahideen government.
Differences in ideology between Taliban and Mujahideen.
Connections with Osama bin Laden.
Treatment of non-Pashtun Afghans.
Relations with foreign powers, especially the U.S.
Page 16: Women's Dress Codes in Islam
Definitions and differences in various forms of women's clothing:
Hijab: General modest dress.
Niqab: Covers face except eyes.
Burka: Complete covering associated with Afghanistan.
Chador: Common in Iran, full-body cloak.
Page 17: Discussion on Gender Policies
Kathy Gannon's Remarks: Discourse on women's issues under Taliban rule vs. perceptions of the mujahideen government.
Page 18: Education and Gender Rights
Comparison of mujahideen and Taliban perspectives on women's education.
Page 19: Map Overview of Factions
Shifts in Control (1992-2001): Overview of major conflicts and territorial controls in Afghanistan.
Page 20-24: Review Questions
Recapitulation of central questions regarding Taliban governance, ideology, and relationships.
Page 25: The Planes Operation
Introduction to lecture focusing on September 11, 2001, attacks.
Page 26: Key Individuals in 9/11 Attacks
Khaled Sheikh Mohammed and Mohamed Atta: Central figures in the planning of 9/11.
Page 27: Timeline of Hijacked Flights
Details of the American airlines flights involved in the 9/11 attacks and their outcomes:
Flight 11: Crashed into North Tower at 8:46 AM.
Flight 175: Crashed into South Tower at 8:52 AM.
Flight 77: Crashed into Pentagon at 9:37 AM.
Flight 93: Crashed in Pennsylvania at 10:02 AM.
Page 28: Impact of the 9/11 Attacks
Overview of casualties, the nationality of hijackers, and implications for U.S. foreign policy.
Lecture 040 - Part I Recap, the Taliban, and the "Planes Operation"
/
recap

focus
southwest asia/ middle east, pakistan, iraq, iran, afghanistan, iraqa nieghbors or arabian peninusla
america did not make military intervention a main policy until 1979
iran hostage crisis
prior 1979
trumen 1947
nixon 1969
did not extent to deployment
january 1980
carter doctrain
u.s still sus into big intervention at this time
part 1 of this course
seizure of u.s embessay in tehran (nov 4 1979)- sept 11, 2001 terriorist attacks
5 presidents leading during these years
vietnam lost 58000 military personnel during the conflict, highlighting the significant human cost of war and the complex geopolitical landscape that shaped U.S. foreign policy in the following decades.
u.s conducted itself in southwest asia cautiously
last decade of the cold war, first decade of the new unipolar era
deciding when to intervene or leave govts not able to lead their countires
desert storm
showed u.s was willing to stop without conquering baghdad
operation cyclone
This demonstrated a shift in military strategy, focusing on targeted operations rather than full-scale invasions.
moving w afghan
1979-1979
iranian toppled sha
This event led to a significant shift in the geopolitical landscape, influencing the rise of various militant groups, including the Taliban, who gained power in the 1990s.
1980-1988
hopes to defeat islamic govt in iran
sadam used lethal gas on battlefield against iran
clinton
did not want to send troops to tehran
did not land trooops in afghan or other countires
did not wnat to risk desert 1 again
Ben lahden
did not pose threats like other countires who had weapons
Lecture 040 - Part I Recap, the Taliban, and the "Planes Operation"
2021 = 60 million Pashtuns in afghanistan
16 percent in pakistan
larget ethinic group in afghanistant but more in pakistan
language is more attributed to ethnicity but not always necessarily phenotype
the pashtuns live in kandhar and are known for their distinct cultural practices, including traditional dress and hospitality, which play a significant role in their identity.
the taliban stood a part bc of reginal and ethinic
difference btwn taliban and mujahedeen
the taliban did not exsisit as org in 1983
ppl in pic would eventually oppose taliban
omar
politically leader al Mullah Omar emerged as a significant figure, eventually becoming the spiritual leader of the Taliban and guiding its rise to power in the mid-1990s.

their (mujaahideen) politically authority was restircted by region and ethnicity
operated as warlords, min kingdom
taliban in 1994 represented unity
loyalty to higher cause that they could market
This unity was instrumental in consolidating power, as the Taliban sought to establish a cohesive governance structure that transcended regional and ethnic divisions.
the most secular least religous govt of the time was replaced by a regime that emphasized strict adherence to Islamic law, which significantly altered the social fabric of Afghanistan.
they supported conservative views that ppl felt and made them law
looked to saudia arabia as example

people didnt rll ysee this as a problem bc they got saftey
no real social outcry
most of their approach came from islamic unity and how the first leaders of islmaic leaders govt
certiain level of predictability
no say from the people
contorversial poppy farming the taliban allowed
ltr outlawed it but faced criticism for the economic impact on farmers who relied on this crop for their livelihood.
pro pashtun
only offically reconginzed by pakistan, saudiarabia, and united arab emirities
none of them supported the taliban policies
Despite this limited recognition, these countries maintained a cautious approach, emphasizing diplomatic channels while expressing concerns over human rights violations and the treatment of women under Taliban rule.
energy situation
The energy situation in the region became increasingly complex, as the Taliban sought to leverage their control over natural resources to gain further legitimacy and financial support from international allies.

unitl 1996, u.s couldnt achieve number 1
the seige- poor protrayal of relations and middle east
Lecture 040 - Part I Recap, the Taliban, and the "Planes Operation"
9/11
how it happend
The events leading up to 9/11 involved a complex interplay of geopolitical tensions, including the rise of extremist groups in the region and the subsequent military responses from Western powers.
threatend the ppl on hijakced plane
all hijackers were arab men

 Knowt
Knowt