Lecture 7 - Factorial design & ANOVA
Page 1: Introduction
Factorial Design & ANOVA
PSYC 71, Week 7 Lecture
Date: February 19th, Winter 2025
Page 2: Reminders
Week 7:
Due: Stats HW #2 by Sunday at 11:59pm (available on Canvas)
Week 8:
Exam 2: First half of lecture (12:00 - 12:50pm)
Due: Stats HW #3 by Sunday at 11:59pm (released on Canvas one week prior)
Week 9:
Due: Poster (PDF version submitted through Canvas by Sunday at 11:59pm)
Page 3: Lecture Outline
Topics:
Factorial design & notation
Between, within, and mixed designs
Main effects & interactions
Eyeballing effects
Factorial ANOVA model
Decomposing cell means into main effects and interactions
Tests of effects in the two-factor model
ANOVA output table for the two-factor model
Page 4: Factorial Design
Focus on analyzing multiple independent variables.
Page 5: Experiment with 2 Independent Variables
Example Questions:
Which is more delicious: hot food or cold food?
Which is more delicious: hamburgers or ice cream?
Answer: It depends on various combinations of food types.
Page 6: Manipulating Multiple Factors
Investigates the interaction effect of one independent variable with another.
Factorial Design: Each level of one IV combined with each level of the others for all combinations.
Page 7: Factorial Design Definition
Investigates the effect of two or more independent variables (factors) on the dependent variable.
Factors: Price and style affecting wine rating.
Example of levels: Cheap/Expensive and Sweet/Dry can result in different ratings.
Page 8: Factorial Notation
Written like a multiplication expression: # x # x #
# of IVs = number of factors
# of levels = specific values of each factor
# of conditions = product of the factors
Examples include:
2x2 = 2 IVs, each with 2 levels = 4 conditions
2x2x2 = 3 IVs, each with 2 levels = 8 conditions
3x3 = 2 IVs, each with 3 levels = 9 conditions
Page 9: Peer Instruction #1
Scenario: Researchers study the impact of stereotype threat on intelligence tests with 4 conditions.
Notation for Design:
a) 2x2 factorial
b) 1x4 factorial
c) 3x3 factorial
d) None of the above
Page 10: Between, Within, & Mixed Factorials
Definitions and examples of these designs will follow.
Page 11: Between- vs. Within-Subjects Factorial Design
Between-Subjects Design: Each subject in just one condition.
Within-Subjects Design: Each subject in ALL conditions.
Mixed Design: Some factors between subjects, some within; subjects in more than one but not all conditions.
Page 12: Between-Subjects Example
Different conditions assessed by different subjects:
Sweet, Cheap / Sweet, Expensive / Dry, Cheap / Dry, Expensive
Page 13: Within-Subjects Example
Subjects participate in all conditions;
Order does not have to be counterbalanced, could be randomized.
Page 14: Mixed Design Example
Subjects experience more than one condition but not all; example shown with price and style combinations.
Page 15: Additional Mixed Design Example
More variety in how participants experience combinations of factors.
Page 16: Peer Instruction #2
Scenario: Robert's study on age and emotion's effect on memory with conditional manipulation:
Design type:
a) 2x2 between-subjects factorial
b) 2x2 within-subjects factorial
c) 2x2 mixed design factorial
d) None of the above
Page 17: Main Effects and Interactions
Main effect - on average, are the levels of one factor different from each other?
Simple effect - at a specific level of one factor, are the levels of the other factor different from each other?
interaction - is the pattern/effect at one level of a factor different from the pattern/effect at another level of that factor?
Page 18: Kinds of Statistical Effects
Main Effect: Average differences between levels of a factor.
Simple Effect: Differences at a specific level of one factor.
Interaction: Differences in patterns across levels of factors.
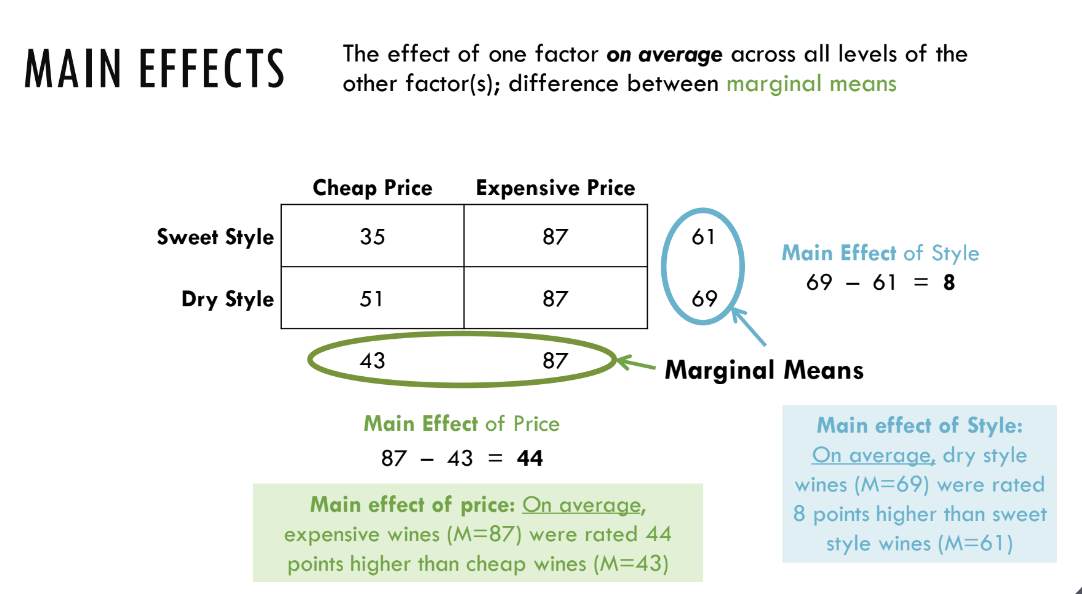
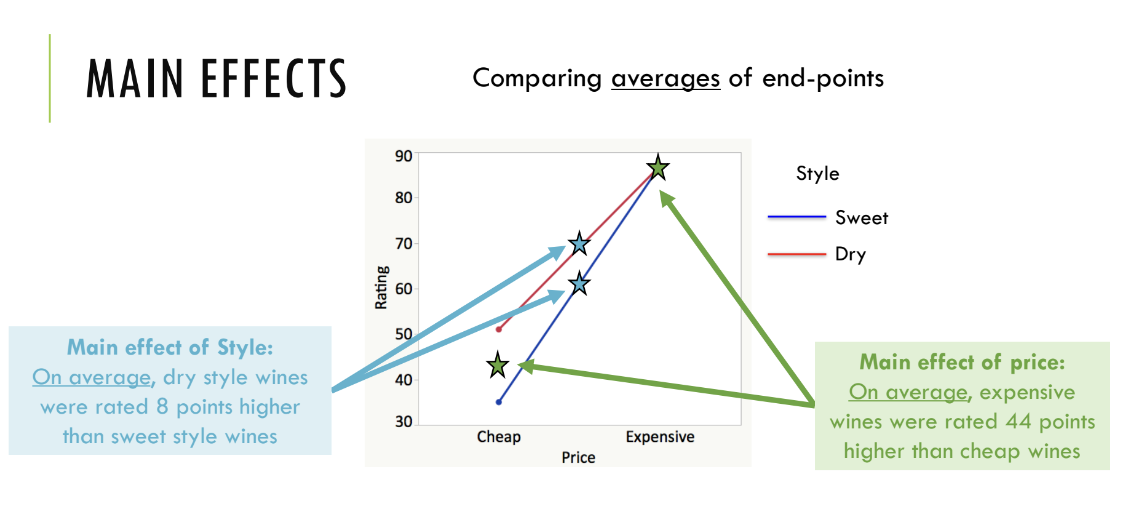
Page 19: Main Effects Calculation
Example calculations shown using price and style, with marginal means detailed.
Page 20: Main Effects Continued
Reiteration of the main effects of style across different types of wine ratings.
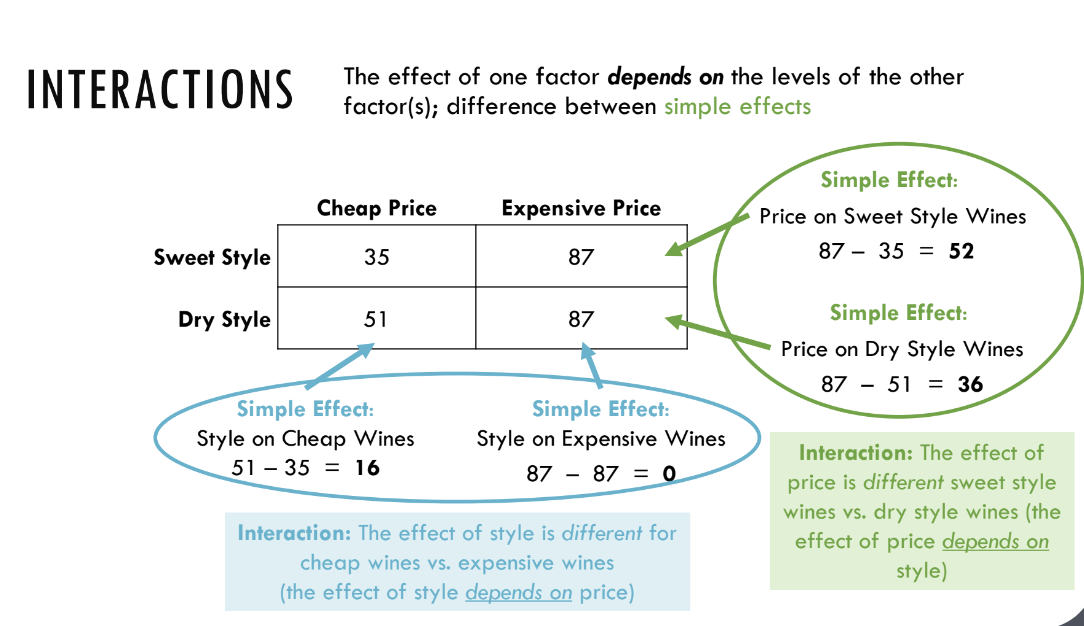
Page 21: Simple Effects Calculation
Sample simple effects calculated for each type of wine helping illustrate interactions.
Page 22: Interactions Explained
The dependence of effect of one factor on the level of another demonstrated through wine rating differences.
Page 23: Interactions & Effects
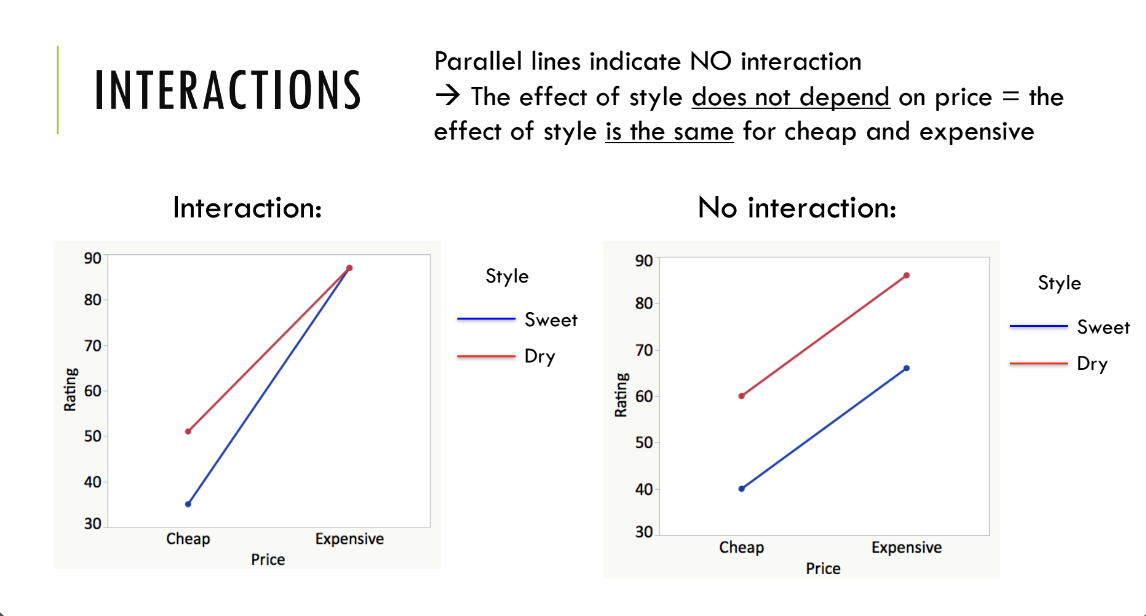
Page 24: No Interaction Visual
Explanation of parallel lines indicating no interaction between factors.
Page 25: Peer Instruction #3
Evaluation of potential statistical effects from provided data table.
Page 26: Peer Instruction #4
Evaluation of effects shown in a figure based on quality ratings.
Page 27: Peer Instruction #5
Reiteration of evaluating effects from another figure representation.
Page 28: More Practice
Eyeballing Effects: Worksheet available on Canvas to aid practice.
Page 29: Factorial ANOVA Model
Introduction to models related to factorial ANOVA.
Page 30: One Factor General Linear Model
Equations demonstrating the general model structure for one factor.
Page 31: Two Factor Linear Model
Description of how to formulate a two-factor linear model with examples.
Page 32: Decomposing Group Means
Steps to analyze variance of component scores relative to residual variance after group mean decomposition.
Page 33: Testing Main Effect Offsets
Concept of treatment offsets within routes and time when examining deviations.
Page 34: Estimating Interaction Offsets
Detailed calculations illustrating how offsets derived from observed cell means reflect interaction laws.
Page 35: Checking the Math on Cell Means
Confirming calculations around the grand mean of given data.
Page 36: Tests of Effects for Two Factors
Overview of tests regarding main effects and interactions in factorial ANOVA.
Page 37: ANOVA Table With Two Factors
Structure and specifics of how to populate an ANOVA table for two-factor designs.
Page 38: Peer Instruction #6
Task to complete Annotated ANOVA table for the Times to Campus data, prompting calculation and estimation.