CHAPTER 8 Female Reproductive System
Introduction
Sexual reproduction is the union of the ovum (female sex cell) and the sperm (male sex cell). Each sex cell, known as a gamete, has half the number of chromosomes needed to create a new organism. In fertilization, nuclei of the two gametes unite to form a single nucleus with half of the chromosomes and genetic code from each parent.
Sinh sản hữu tính là sự kết hợp giữa trứng (tế bào sinh dục nữ) và tinh trùng (tế bào sinh dục nam). Mỗi tế bào sinh dục, được gọi là giao tử, chứa một nửa số nhiễm sắc thể cần thiết để tạo ra một sinh vật mới. Trong quá trình thụ tinh, nhân của hai giao tử hợp nhất để tạo thành một nhân đơn với một nửa số nhiễm sắc thể và mã di truyền từ mỗi phụ huynh.
Special organs called gonads in males and females produce the egg and sperm cells. The female gonads are the ovaries, and the male gonads are the testes. After an ovum leaves the ovary during ovulation, it travels down one of two fallopian tubes leading to the uterus (womb). If coitus (copulation, sexual intercourse) has occurred, millions of sperm cells travel into the fallopian tubes, but only one sperm cell can penetrate the ovum. This is fertilization. The fertilized ovum is then known as a zygote. After many cell divisions, a ball of cells forms, and the zygote is called an embryo (2 to 8 weeks) and finally a fetus (8 to 38 or 40 weeks). The period of development within the uterus is gestation, or pregnancy.
Các cơ quan đặc biệt gọi là tuyến sinh dục ở nam và nữ sản xuất ra trứng và tinh trùng. Tuyến sinh dục nữ là buồng trứng, còn tuyến sinh dục nam là tinh hoàn. Sau khi một trứng rời khỏi buồng trứng trong quá trình rụng trứng, nó di chuyển xuống một trong hai ống dẫn trứng dẫn đến tử cung (dạ con). Nếu giao hợp (quan hệ tình dục) đã xảy ra, hàng triệu tế bào tinh trùng di chuyển vào ống dẫn trứng, nhưng chỉ có một tế bào tinh trùng có thể xâm nhập vào trứng. Đây là quá trình thụ tinh. Trứng đã thụ tinh sau đó được gọi là hợp tử. Sau nhiều lần phân chia tế bào, một khối tế bào được hình thành, và hợp tử được gọi là phôi (từ 2 đến 8 tuần) và cuối cùng là thai nhi (từ 8 đến 38 hoặc 40 tuần). Thời kỳ phát triển trong tử cung được gọi là thai kỳ.
The female reproductive system consists of organs that produce ova (singular; ovum) and provide a place for the growth of the embryo. In addition, the female reproductive organs supply important hormones that contribute to the development of female secondary sex characteristics (body hair, breast development, structural changes in bones and fat).
Hệ sinh sản nữ bao gồm các cơ quan sản xuất trứng (đơn: trứng) và cung cấp nơi cho sự phát triển của phôi. Ngoài ra, các cơ quan sinh sản nữ cung cấp các hormone quan trọng đóng góp vào sự phát triển của các đặc điểm giới tính thứ cấp của nữ (lông cơ thể, sự phát triển của ngực, thay đổi cấu trúc xương và mỡ).
The eggs, or ova, are present from birth in the female ovary but begin to mature and are released from the ovary in a 21- to 28-day cycle when secondary sex characteristics develop. The occurrence of the first cycle is called menarche. Menstrual cycles continue until menopause, when all eggs have been released, hormone production diminishes, and menstruation ends. If fertilization occurs during the years between menarche and menopause, the fertilized egg may grow and develop within the uterus. A new, blood vessel–rich organ called a placenta (connected to the embryo by the umbilical cord) develops to nourish the embryo, which implants in the uterine lining. Various hormones are secreted from the ovary and from the placenta to stimulate the expansion of the placenta. If fertilization does not occur, hormonal changes result in the shedding of the uterine lining, and bleeding, or menstruation, occurs.
Trứng, hay còn gọi là trứng, có mặt từ khi sinh ra trong buồng trứng nữ nhưng bắt đầu trưởng thành và được phóng thích từ buồng trứng trong chu kỳ 21 đến 28 ngày khi các đặc điểm giới tính thứ cấp phát triển. Sự xuất hiện của chu kỳ đầu tiên được gọi là kinh nguyệt đầu tiên (menarche). Chu kỳ kinh nguyệt tiếp tục cho đến khi mãn kinh, khi tất cả các trứng đã được phóng thích, việc sản xuất hormone giảm và kinh nguyệt kết thúc. Nếu thụ tinh xảy ra trong những năm giữa kinh nguyệt đầu tiên và mãn kinh, trứng đã thụ tinh có thể phát triển và lớn lên trong tử cung. Một cơ quan mới, giàu mạch máu gọi là nhau thai (kết nối với phôi qua dây rốn) phát triển để nuôi dưỡng phôi, và phôi cấy vào lớp niêm mạc tử cung. Các hormone khác nhau được tiết ra từ buồng trứng và từ nhau thai để kích thích sự mở rộng của nhau thai. Nếu thụ tinh không xảy ra, thay đổi hormone dẫn đến việc rụng lớp niêm mạc tử cung và chảy máu, hay còn gọi là kinh nguyệt, xảy ra.
The hormones of the ovaries, estrogen and progesterone, play important roles in the processes of menstruation and pregnancy, and in the development of secondary sex characteristics. The pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, secretes other hormones that govern the reproductive functions of the ovaries, breasts, and uterus.
Các hormone của buồng trứng, estrogen và progesterone, đóng vai trò quan trọng trong quá trình kinh nguyệt và thai kỳ, cũng như trong sự phát triển của các đặc điểm giới tính thứ cấp. Tuyến yên, nằm ở đáy não, tiết ra các hormone khác điều chỉnh chức năng sinh sản của buồng trứng, vú, và tử cung.
Gynecology is the study of the female reproductive system (organs, hormones, and diseases); obstetrics (Latin obstetrics means midwife) is a specialty concerned with pregnancy and the delivery of the fetus; and neonatology is the study of the care and treatment of the newborn.
Phụ khoa là nghiên cứu về hệ sinh sản nữ (cơ quan, hormone và các bệnh); sản khoa (từ tiếng Latin "obstetrics" nghĩa là "bà đỡ") là chuyên khoa liên quan đến thai kỳ và việc sinh con; và sơ sinh học là nghiên cứu về chăm sóc và điều trị trẻ sơ sinh.
Organs of the Female Reproductive System
Uterus, Ovaries, and Associated Organs
Label Figures 8-1 and 8-3 as you read the following description of the female reproductive system.
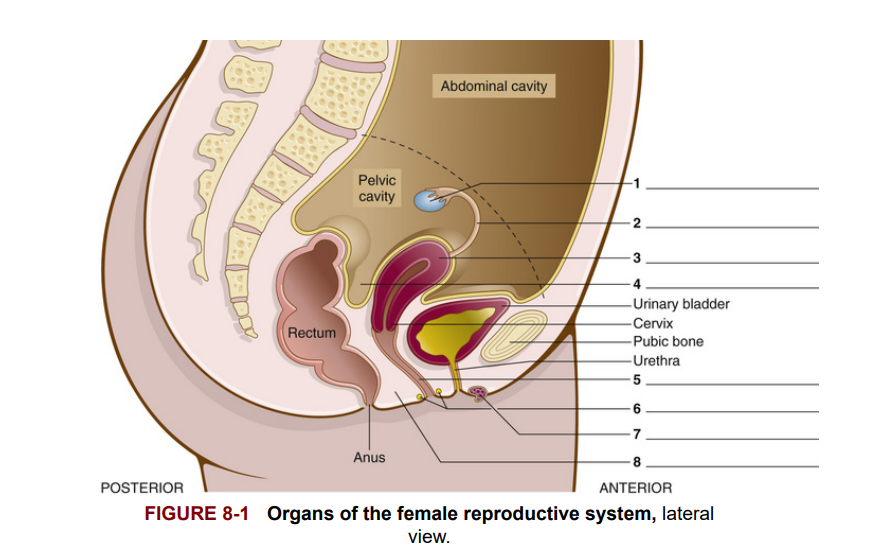 Figure 8-1 shows a side view of the female reproductive organs and their relationship to other organs in the pelvic cavity. The ovaries [1] (only one ovary is shown in this lateral view) are a pair of small almond-shaped organs located in the pelvis. The fallopian tubes [2] (only one is shown in this view) lead from each ovary to the uterus [3], which is a fibromuscular organ situated between the urinary bladder and the rectum. The uterus normally is the size and shape of a pear and is about 3 to 4 inches long in a nonpregnant woman. Midway between the uterus and the rectum is a region in the abdominal cavity known as the cul-de-sac [4]. The vagina [5], a tubular structure, extends from the uterus to the exterior of the body. Bartholin glands [6] are two small, rounded glands on either side of the vaginal orifice. These glands produce a mucous secretion that lubricates the vagina. The clitoris [7] is an organ of sensitive, erectile tissue located anterior to the vaginal orifice (opening) and in front of the urethral orifice. The region between the vaginal orifice and the anus is the perineum [8].
Figure 8-1 shows a side view of the female reproductive organs and their relationship to other organs in the pelvic cavity. The ovaries [1] (only one ovary is shown in this lateral view) are a pair of small almond-shaped organs located in the pelvis. The fallopian tubes [2] (only one is shown in this view) lead from each ovary to the uterus [3], which is a fibromuscular organ situated between the urinary bladder and the rectum. The uterus normally is the size and shape of a pear and is about 3 to 4 inches long in a nonpregnant woman. Midway between the uterus and the rectum is a region in the abdominal cavity known as the cul-de-sac [4]. The vagina [5], a tubular structure, extends from the uterus to the exterior of the body. Bartholin glands [6] are two small, rounded glands on either side of the vaginal orifice. These glands produce a mucous secretion that lubricates the vagina. The clitoris [7] is an organ of sensitive, erectile tissue located anterior to the vaginal orifice (opening) and in front of the urethral orifice. The region between the vaginal orifice and the anus is the perineum [8].
Hình 8-1 cho thấy một cái nhìn từ bên của các cơ quan sinh sản nữ và mối quan hệ của chúng với các cơ quan khác trong khoang chậu. Buồng trứng [1] (chỉ có một buồng trứng được hiển thị trong cái nhìn bên này) là một cặp cơ quan nhỏ hình quả hạnh nhân nằm trong khung chậu. Ống dẫn trứng [2] (chỉ có một được hiển thị trong cái nhìn này) dẫn từ mỗi buồng trứng đến tử cung [3], một cơ quan cơ sợi nằm giữa bàng quang và trực tràng. Tử cung thông thường có kích thước và hình dạng giống quả lê và dài khoảng 3 đến 4 inch ở người phụ nữ không mang thai. Giữa tử cung và trực tràng là một vùng trong khoang bụng được gọi là túi cùng [4]. Âm đạo [5], một cấu trúc dạng ống, kéo dài từ tử cung ra bên ngoài cơ thể. Các tuyến Bartholin [6] là hai tuyến nhỏ, tròn ở hai bên của lỗ âm đạo. Các tuyến này tiết ra một chất nhầy bôi trơn âm đạo. Âm vật [7] là một cơ quan có mô cương nhạy cảm nằm phía trước lỗ âm đạo và phía trước lỗ niệu đạo. Vùng giữa lỗ âm đạo và hậu môn là đáy chậu [8].
The external genitalia of the female are collectively called the vulva. Figure 8-2 shows the various structures that are part of the vulva. The labia majora, the outer lips of the vagina, surround the smaller, inner lips, the labia minora. The hymen, a thin membrane partially covering the entrance to the vagina, is broken apart during the first episode of intercourse. The clitoris and Bartholin glands also are parts of the vulva.
Các cơ quan sinh dục ngoài của nữ giới được gọi chung là âm hộ. Hình 8-2 cho thấy các cấu trúc khác nhau là một phần của âm hộ. Môi lớn, môi ngoài của âm đạo, bao quanh các môi nhỏ hơn, môi bé. Màng trinh, một màng mỏng bao phủ một phần lối vào âm đạo, bị phá vỡ trong lần giao hợp đầu tiên. Âm vật và các tuyến Bartholin cũng là một phần của âm hộ.
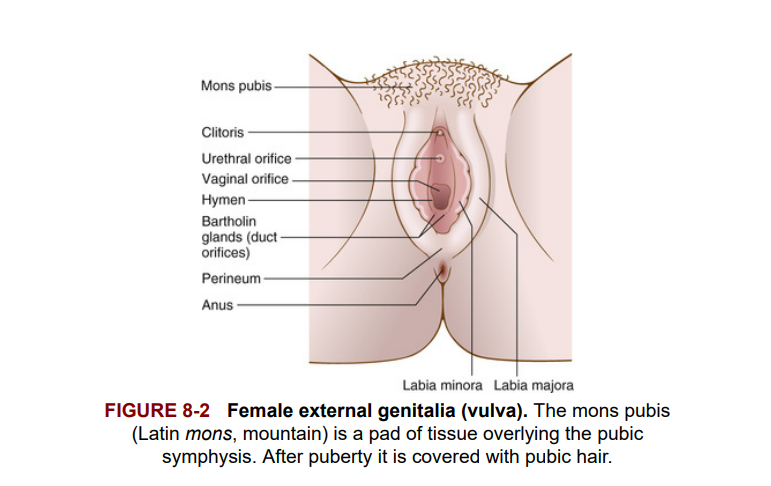 Figure 8-3 shows an anterior view of the female reproductive system. Each ovary [1] is held in place on either side of the uterus by a utero-ovarian ligament [2].
Figure 8-3 shows an anterior view of the female reproductive system. Each ovary [1] is held in place on either side of the uterus by a utero-ovarian ligament [2].
Hình 8-3 cho thấy một cái nhìn từ phía trước của hệ thống sinh sản nữ. Mỗi buồng trứng [1] được giữ cố định ở hai bên của tử cung bằng dây chằng tử cung-buồng trứng [2].
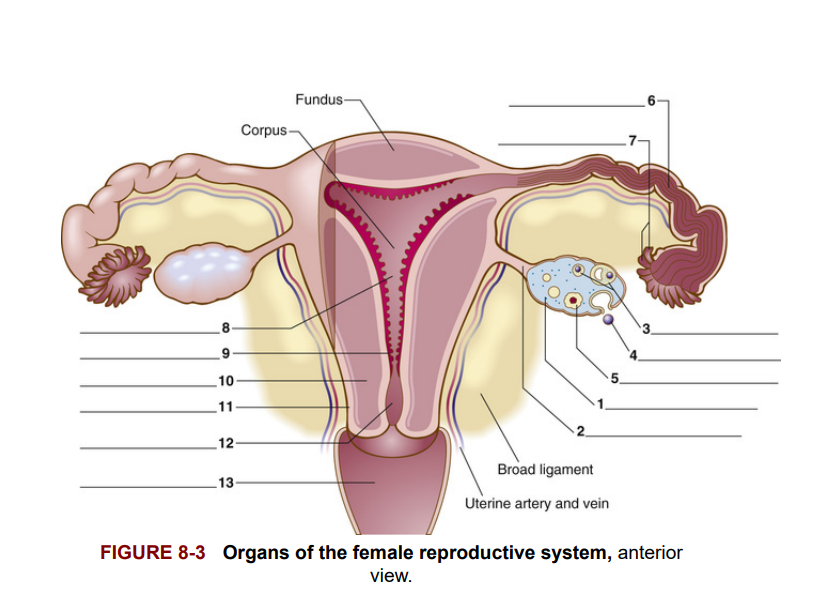 Within each ovary are thousands of small sacs—the ovarian follicles [3]. Each follicle contains an ovum [4]. During ovulation, an ovum matures; its follicle ruptures through the surface and releases the ovum from the ovary. A ruptured follicle fills with a yellow, fat-like material. It is then called the corpus luteum [5], meaning yellow body. The corpus luteum secretes hormones (both estrogen and progesterone) that maintain the very first stages of pregnancy.
Within each ovary are thousands of small sacs—the ovarian follicles [3]. Each follicle contains an ovum [4]. During ovulation, an ovum matures; its follicle ruptures through the surface and releases the ovum from the ovary. A ruptured follicle fills with a yellow, fat-like material. It is then called the corpus luteum [5], meaning yellow body. The corpus luteum secretes hormones (both estrogen and progesterone) that maintain the very first stages of pregnancy.
Bên trong mỗi buồng trứng có hàng ngàn túi nhỏ - nang buồng trứng [3]. Mỗi nang chứa một trứng [4]. Trong quá trình rụng trứng, một trứng trưởng thành; nang của nó vỡ ra qua bề mặt và giải phóng trứng từ buồng trứng. Nang bị vỡ được lấp đầy bởi một chất béo màu vàng. Sau đó nó được gọi là hoàng thể [5], nghĩa là thể vàng. Hoàng thể tiết ra các hormone (cả estrogen và progesterone) duy trì các giai đoạn đầu tiên của thai kỳ.
A fallopian tube [6] is about 5.1/2 inches long and lies near each ovary. Collectively, the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and supporting ligaments are the adnexa (accessory structures) of the uterus. The finger-like ends of the fallopian tube are the fimbriae [7]. They catch the egg after its release from the ovary. Cilia (small hairs) line the fallopian tube and, through their motion, sweep the ovum toward the uterus. It usually takes the ovum about 2 to 3 days to pass through the fallopian tube.
Ống dẫn trứng [6] dài khoảng 5,5 inch và nằm gần mỗi buồng trứng. Tập hợp các ống dẫn trứng, buồng trứng, và dây chằng hỗ trợ là các phần phụ (cấu trúc phụ) của tử cung. Các đầu dạng ngón tay của ống dẫn trứng là tua vòi trứng [7]. Chúng bắt lấy trứng sau khi nó được giải phóng từ buồng trứng. Cilia (các sợi lông nhỏ) lót bên trong ống dẫn trứng và, thông qua chuyển động của chúng, quét trứng về phía tử cung. Thông thường, trứng mất khoảng 2 đến 3 ngày để đi qua ống dẫn trứng.
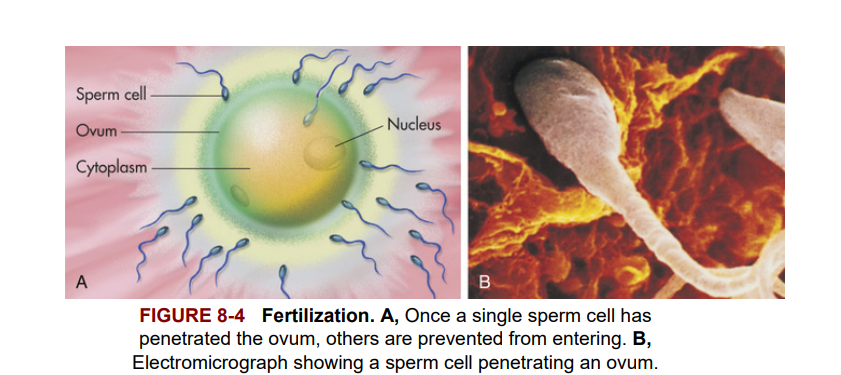
If sperm cells are present in the fallopian tube, fertilization may occur (Figure 8-4). If sperm cells are not present, the ovum remains unfertilized and eventually disintegrates.
Nếu có các tế bào tinh trùng trong ống dẫn trứng, quá trình thụ tinh có thể xảy ra (Hình 8-4). Nếu không có các tế bào tinh trùng, trứng vẫn không được thụ tinh và cuối cùng phân rã.
 The fallopian tubes, one on each side, lead into the uterus [8], a pear-shaped organ with muscular walls and a mucous membrane lining filled with a rich supply of blood vessels. The rounded upper portion of the uterus is the fundus, and the larger, central section is the corpus (body of the organ). The inner layer, a specialized epithelial mucosa of the uterus is the endometrium [9]; the middle, muscular layer of the uterine wall is the myometrium [10]; and the outer, membranous tissue layer is the perimetrium (uterine serosa) [11], a lining that produces a watery, serumlike secretion. The outermost layer of an organ in the abdomen or thorax is also known as a serosa. The narrow, lowermost portion of the uterus is the cervix [12] (Latin cervix means neck). The cervical opening leads into a 3-inch-long muscular, mucosa-lined canal called the vagina [13], which opens to the outside of the body.
The fallopian tubes, one on each side, lead into the uterus [8], a pear-shaped organ with muscular walls and a mucous membrane lining filled with a rich supply of blood vessels. The rounded upper portion of the uterus is the fundus, and the larger, central section is the corpus (body of the organ). The inner layer, a specialized epithelial mucosa of the uterus is the endometrium [9]; the middle, muscular layer of the uterine wall is the myometrium [10]; and the outer, membranous tissue layer is the perimetrium (uterine serosa) [11], a lining that produces a watery, serumlike secretion. The outermost layer of an organ in the abdomen or thorax is also known as a serosa. The narrow, lowermost portion of the uterus is the cervix [12] (Latin cervix means neck). The cervical opening leads into a 3-inch-long muscular, mucosa-lined canal called the vagina [13], which opens to the outside of the body.
Hệ thống ống dẫn trứng, mỗi bên một ống, dẫn vào tử cung [8], một cơ quan hình quả lê với thành cơ và lớp màng niêm mạc chứa nhiều mạch máu. Phần trên tròn của tử cung là đáy tử cung, và phần trung tâm lớn hơn là thân tử cung (thân tử cung). Lớp bên trong, một lớp biểu mô chuyên biệt của tử cung là nội mạc tử cung [9]; lớp giữa, lớp cơ của thành tử cung là cơ tử cung [10]; và lớp ngoài, lớp mô màng là lớp thanh mạc (màng thanh dịch tử cung) [11], một lớp lót tiết ra dịch tiết loãng giống huyết thanh. Lớp ngoài cùng của một cơ quan trong ổ bụng hoặc ngực cũng được gọi là lớp thanh mạc. Phần dưới cùng, hẹp nhất của tử cung là cổ tử cung [12] (từ tiếng Latinh cervix có nghĩa là cổ). Lỗ cổ tử cung dẫn vào một ống cơ dài 3 inch lót niêm mạc gọi là âm đạo [13], nơi mở ra ngoài cơ thể.
The Breast (Accessory Organ of Reproduction)
Label Figure 8-5 as you read the following description of breast structures.
Hãy ghi nhãn Hình 8-5 khi bạn đọc mô tả sau về các cấu trúc của ngực.
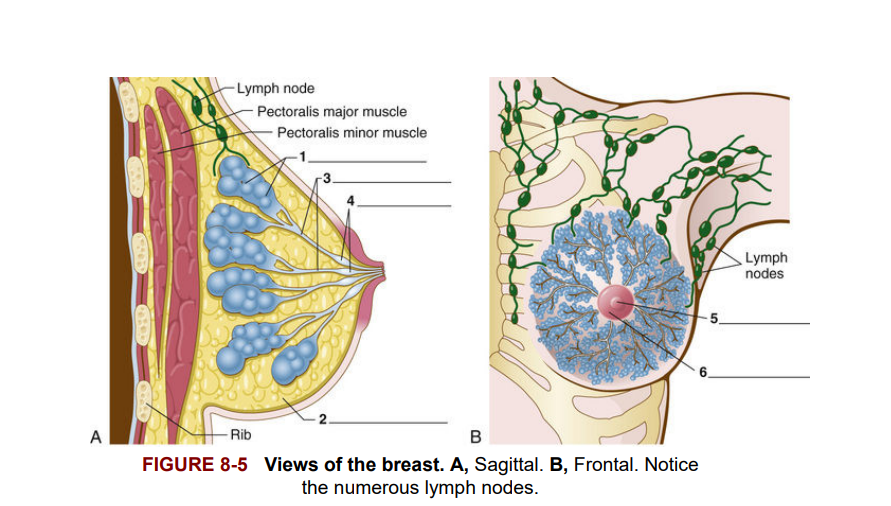 The breasts, located on the upper anterior region of the chest, are composed mostly of mammary glands. The glandular tissue [1] contains milk glands that develop in response to hormones from the ovaries during puberty. The breasts also contain fibrous and fay tissue [2], special lactiferous (milk-carrying) ducts [3], and sinuses (cavities) [4] that carry milk to the nipple, which has small openings for the ducts to release their milk. The breast nipple is the mammary papilla [5], and the dark-pigmented area around the mammary papilla is the areola [6].
The breasts, located on the upper anterior region of the chest, are composed mostly of mammary glands. The glandular tissue [1] contains milk glands that develop in response to hormones from the ovaries during puberty. The breasts also contain fibrous and fay tissue [2], special lactiferous (milk-carrying) ducts [3], and sinuses (cavities) [4] that carry milk to the nipple, which has small openings for the ducts to release their milk. The breast nipple is the mammary papilla [5], and the dark-pigmented area around the mammary papilla is the areola [6].
Ngực, nằm ở vùng phía trước trên của ngực, chủ yếu được cấu tạo từ các tuyến vú. Mô tuyến [1] chứa các tuyến sữa phát triển để phản ứng với hormone từ buồng trứng trong thời kỳ dậy thì. Ngực cũng chứa mô sợi và mỡ [2], các ống dẫn sữa đặc biệt [3], và các xoang (khoang) [4] mang sữa đến núm vú, có các lỗ nhỏ để các ống dẫn sữa tiết ra sữa. Núm vú được gọi là nhũ hoa [5], và vùng da tối màu xung quanh nhũ hoa được gọi là quầng vú [6].
During pregnancy the hormones from the ovaries and the placenta stimulate glandular and other tissues in the breasts to their full development. After parturition (giving birth), hormones from the pituitary gland stimulate the normal secretion of milk (lactation).
Trong thời kỳ mang thai, các hormone từ buồng trứng và nhau thai kích thích mô tuyến và các mô khác trong ngực phát triển đầy đủ. Sau khi sinh (sinh con), các hormone từ tuyến yên kích thích tiết sữa bình thường (cho con bú).
Menstruation and Pregnancy
Menstrual Cycle (Figure 8-6)
Menarche, or onset of menstruation with the first menstrual cycle, occurs at the time of puberty. An average menstrual cycle lasts for 28 days but may be shorter or longer, and cycles may be irregular in length. These days can be divided into four time periods, useful in describing the events of the cycle. The approximate time periods are as follows:
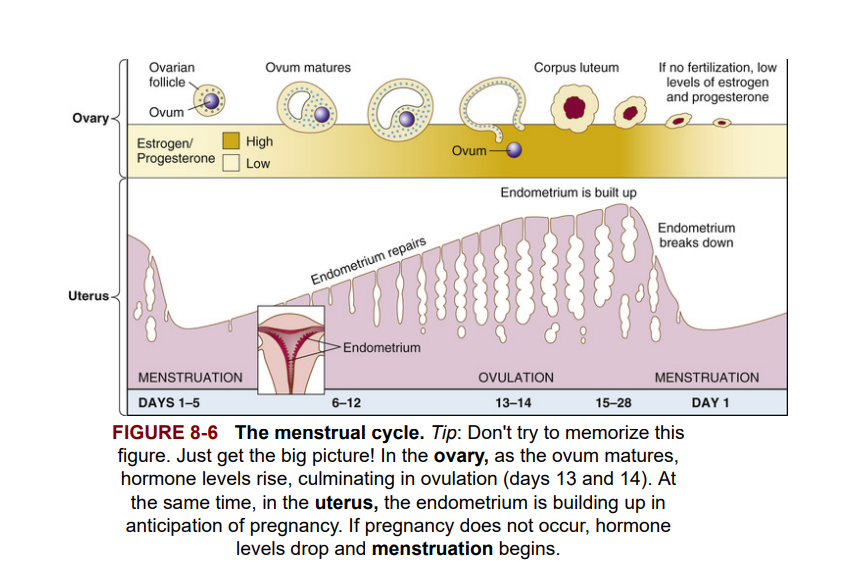 Days 1 to 5 (menstrual period) (Ngày 1 đến 5 (kỳ kinh nguyệt))
Days 1 to 5 (menstrual period) (Ngày 1 đến 5 (kỳ kinh nguyệt))
Discharge of bloody fluid containing disintegrated endometrial cells, glandular secretions, and blood cells.
Tiết ra dịch máu chứa các tế bào nội mạc tử cung bị phân hủy, các tiết dịch tuyến và các tế bào máu.
Days 6 to 12 (Ngày 6 đến 12)
After bleeding ceases, the endometrium begins to repair itself. The maturing follicle in the ovary releases estrogen, which aids in the repair. The ovum grows in the follicle during this period.
Sau khi ngừng chảy máu, nội mạc tử cung bắt đầu tự sửa chữa. Nang trứng đang trưởng thành trong buồng trứng giải phóng estrogen, giúp trong quá trình sửa chữa này. Trứng phát triển trong nang trứng trong giai đoạn này.
Days 13 and 14 (ovulatory period) (Ngày 13 và 14 (giai đoạn rụng trứng))
On about the 14th day of the cycle, the follicle ruptures and the egg leaves the ovary (ovulation), passing through the fallopian tube.
Vào khoảng ngày thứ 14 của chu kỳ, nang trứng vỡ ra và trứng rời khỏi buồng trứng (rụng trứng), đi qua ống dẫn trứng.
Days 15 to 28 (Ngày 15 đến 28)
The empty follicle that has just released the egg becomes a corpus luteum (Latin for yellow body because of its color). The corpus luteum functions as an endocrine organ, continuing to make estrogen and now secreting the hormone progesterone into the bloodstream. Progesterone stimulates the endometrial buildup in anticipation of fertilization of the egg and pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum in the ovary stops producing progesterone and regresses. At this time, lowered levels of progesterone and estrogen probably are responsible for some women's symptoms of depression, breast tenderness, and irritability before menstruation. The combination of these symptoms is known as premenstrual syndrome (PMS). After 2 days of decrease in hormones, the uterine endometrium breaks down, and the menstrual period begins (days 1 to 5).
Nang trứng trống vừa giải phóng trứng trở thành thể vàng (tiếng Latin là "yellow body" vì màu sắc của nó). Thể vàng hoạt động như một cơ quan nội tiết, tiếp tục sản xuất estrogen và bây giờ tiết ra hormone progesterone vào máu. Progesterone kích thích nội mạc tử cung phát triển để chuẩn bị cho quá trình thụ tinh của trứng và mang thai. Nếu không có sự thụ tinh, thể vàng trong buồng trứng ngừng sản xuất progesterone và thoái hóa. Tại thời điểm này, mức progesterone và estrogen giảm có thể là nguyên nhân gây ra các triệu chứng như trầm cảm, đau ngực và dễ cáu gắt ở một số phụ nữ trước kỳ kinh nguyệt. Sự kết hợp của các triệu chứng này được gọi là hội chứng tiền kinh nguyệt (PMS). Sau 2 ngày giảm hormone, nội mạc tử cung bắt đầu phân hủy và chu kỳ kinh nguyệt bắt đầu (ngày 1 đến 5).
Note: Cycles vary in length, ranging from 21 to 42 days or longer. Ovulation typically occurs 14 days before the end of the cycle. A woman with a 42-day cycle ovulates on day 28, whereas a woman with a 21-day cycle ovulates on day 7.
Lưu ý: Chu kỳ kinh nguyệt có thể thay đổi về độ dài, dao động từ 21 đến 42 ngày hoặc lâu hơn. Rụng trứng thường xảy ra 14 ngày trước khi kết thúc chu kỳ. Một người phụ nữ có chu kỳ 42 ngày rụng trứng vào ngày 28, trong khi người phụ nữ có chu kỳ 21 ngày rụng trứng vào ngày 7.
Pregnancy (Mang Thai)
If fertilization does occur in the fallopian tube, the fertilized egg travels to the uterus and implants in the uterine endometrium. The corpus luteum in the ovary continues to produce progesterone and estrogen. These hormones support the vascular and glandular development of the uterine lining.
Nếu quá trình thụ tinh xảy ra trong ống dẫn trứng, trứng đã thụ tinh sẽ di chuyển đến tử cung và bám vào nội mạc tử cung. Thể vàng trong buồng trứng tiếp tục sản xuất progesterone và estrogen. Các hormone này hỗ trợ sự phát triển của các mạch máu và tuyến trong lớp nội mạc tử cung.
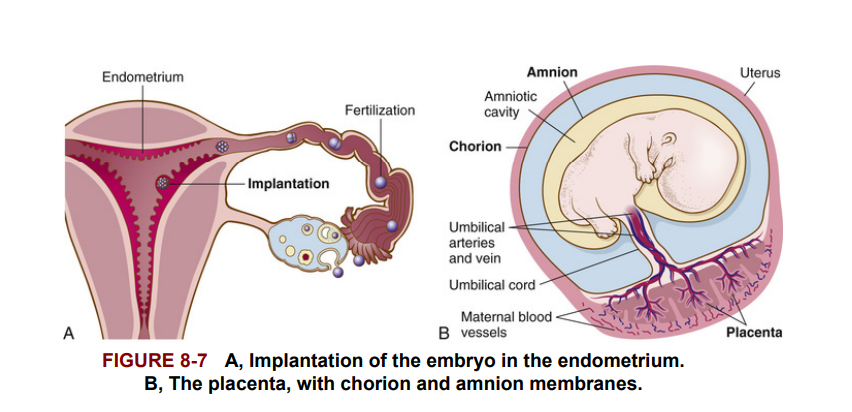
The placenta, a vascular organ, now forms, attached to the uterine wall. The placenta is derived from maternal endometrium and from the chorion, the outermost membrane that surrounds the developing embryo. The amnion, the innermost of the embryonic membranes, holds the fetus suspended in an amniotic cavity surrounded by a fluid called the amniotic fluid. The amnion with its fluid also is known as the “bag of waters” or amniotic sac, which ruptures (breaks) during labor.
Nhau thai, một cơ quan có mạch máu, bắt đầu hình thành và bám vào thành tử cung. Nhau thai được tạo ra từ nội mạc tử cung của mẹ và từ màng đệm, màng ngoài cùng bao quanh phôi phát triển. Màng ối, màng trong cùng của các màng phôi, giữ thai nhi trong một khoang ối, được bao quanh bởi chất lỏng gọi là nước ối. Màng ối và chất lỏng này còn được gọi là "túi nước" hay túi ối, và chúng sẽ vỡ ra (bị rách) trong quá trình chuyển dạ.
The maternal blood and the fetal blood never mix during pregnancy, but important nutrients, oxygen, and wastes are exchanged as the blood vessels of the fetus (coming from the umbilical cord) lie side by side with the mother's blood vessels in the placenta. Figure 8-7A and B shows implantation in the uterus and the embryo's relationship to the placenta and enveloping membranes (chorion and amnion).
Máu của mẹ và máu của thai nhi không bao giờ trộn lẫn trong thời kỳ mang thai, nhưng các chất dinh dưỡng quan trọng, oxy, và các chất thải được trao đổi khi các mạch máu của thai nhi (đến từ dây rốn) nằm cạnh các mạch máu của mẹ trong nhau thai. Hình 8-7A và B cho thấy sự bám vào tử cung và mối quan hệ của phôi với nhau thai và các màng bao quanh (màng đệm và màng ối).
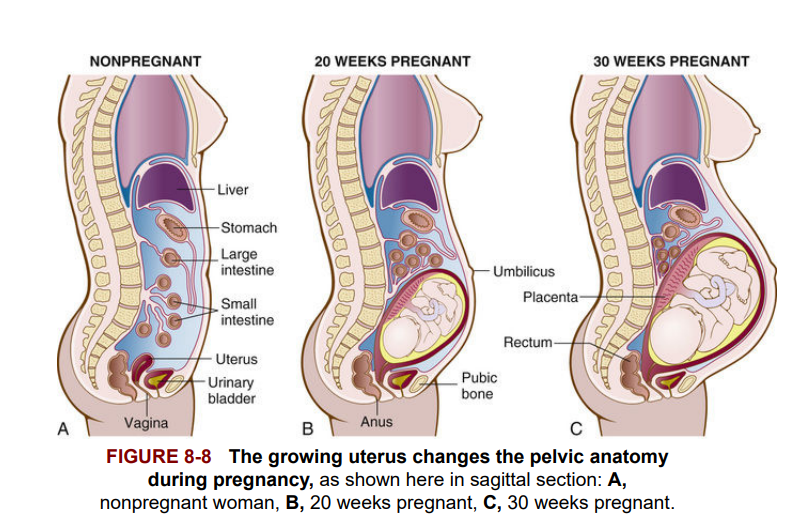
 As the placenta develops, it produces its own hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). When women test their urine with a pregnancy test kit, presence or absence of hCG confirms or rules out that they are pregnant. This hormone stimulates the corpus luteum to continue producing hormones until about the third month of pregnancy, when the placenta takes over the endocrine function and releases estrogen and progesterone. Progesterone maintains the development of the placenta. Low levels of progesterone can lead to spontaneous abortion in pregnant women and menstrual irregularities in nonpregnant women. The uterus normally lies within the pelvis. During pregnancy the uterus expands as the fetus grows, and the superior part rises out of the pelvic cavity to become an abdominal organ. By about 28 to 30 weeks, it occupies a large part of the abdominopelvic cavity and reaches the epigastric region (Figure 8-8).
As the placenta develops, it produces its own hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). When women test their urine with a pregnancy test kit, presence or absence of hCG confirms or rules out that they are pregnant. This hormone stimulates the corpus luteum to continue producing hormones until about the third month of pregnancy, when the placenta takes over the endocrine function and releases estrogen and progesterone. Progesterone maintains the development of the placenta. Low levels of progesterone can lead to spontaneous abortion in pregnant women and menstrual irregularities in nonpregnant women. The uterus normally lies within the pelvis. During pregnancy the uterus expands as the fetus grows, and the superior part rises out of the pelvic cavity to become an abdominal organ. By about 28 to 30 weeks, it occupies a large part of the abdominopelvic cavity and reaches the epigastric region (Figure 8-8).
Khi nhau thai phát triển, nó sản xuất hormone riêng của mình, đó là hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Khi phụ nữ thử nước tiểu bằng bộ dụng cụ thử thai, sự hiện diện hay không của hCG xác nhận hoặc loại trừ khả năng mang thai. Hormone này kích thích thể vàng tiếp tục sản xuất hormone cho đến khoảng tháng thứ ba của thai kỳ, khi nhau thai tiếp quản chức năng nội tiết và tiết ra estrogen và progesterone. Progesterone duy trì sự phát triển của nhau thai. Mức progesterone thấp có thể dẫn đến sảy thai tự nhiên ở phụ nữ mang thai và sự không đều trong chu kỳ kinh nguyệt ở phụ nữ không mang thai. Tử cung thường nằm trong vùng chậu. Trong thời kỳ mang thai, tử cung mở rộng khi thai nhi lớn lên, và phần trên của tử cung nâng cao ra khỏi khoang chậu để trở thành một cơ quan trong vùng bụng. Khoảng tuần thứ 28 đến 30, tử cung chiếm một phần lớn của khoang bụng-chậu và đạt tới vùng thượng vị (Hình 8-8).
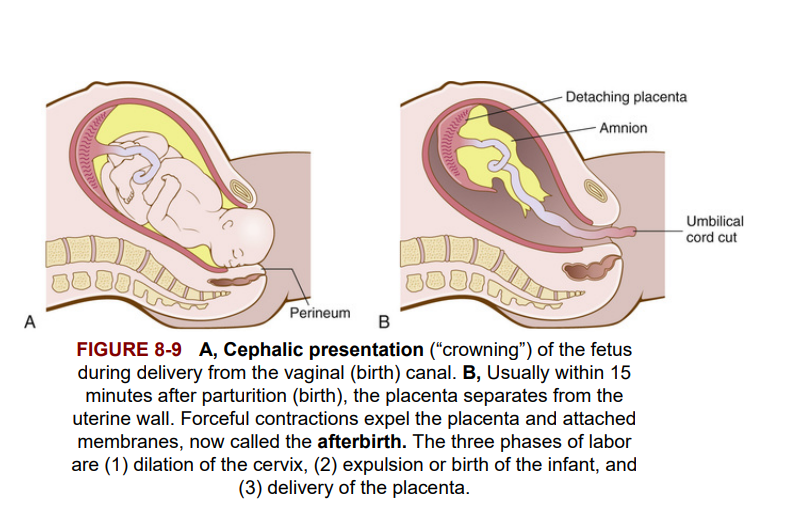
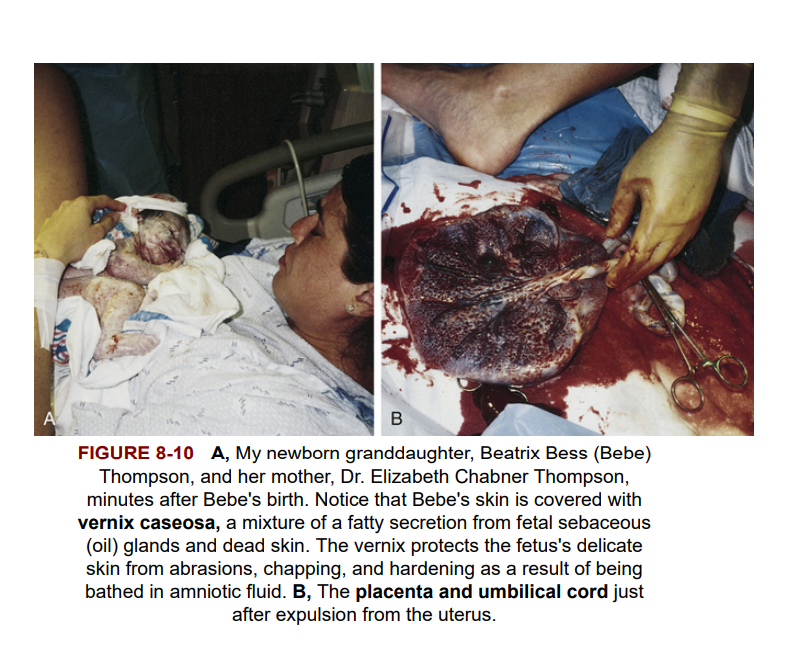
 The onset of true labor is marked by rhythmic contractions, dilation and thinning (effacement) of the cervix, and a discharge of bloody mucus from the cervix and vagina (the “show”). In a normal delivery position, the baby's head appears first (cephalic presentation). After vaginal delivery of the baby, the umbilical cord is cut and the placenta follows (Figure 8-9). Figure 8-10A and B shows photographs of a newborn and the placenta with aached cord, minutes after birth. The expelled placenta is the afterbirth.
The onset of true labor is marked by rhythmic contractions, dilation and thinning (effacement) of the cervix, and a discharge of bloody mucus from the cervix and vagina (the “show”). In a normal delivery position, the baby's head appears first (cephalic presentation). After vaginal delivery of the baby, the umbilical cord is cut and the placenta follows (Figure 8-9). Figure 8-10A and B shows photographs of a newborn and the placenta with aached cord, minutes after birth. The expelled placenta is the afterbirth.
Sự bắt đầu chuyển dạ thực sự được đánh dấu bằng các cơn co thắt nhịp nhàng, sự giãn nở và mỏng đi (xóa bỏ) cổ tử cung, đồng thời tiết ra chất nhầy có máu từ cổ tử cung và âm đạo (“biểu hiện”). Ở tư thế sinh thường, đầu của em bé xuất hiện đầu tiên (trình bày ở phần đầu). Sau khi sinh con qua đường âm đạo, dây rốn được cắt và nhau thai theo sau (Hình 8-9). Hình 8-10A và B thể hiện các bức ảnh của trẻ sơ sinh và nhau thai bị đau dây rốn vài phút sau khi sinh. Nhau thai bị trục xuất là hậu sản. Tương tác nội tiết tố
 Hormonal Interactions
Hormonal Interactions
The events of menstruation and pregnancy depend on hormones not only from the ovaries (estrogen and progesterone) but also from the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland secretes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) after the onset of menstruation. As their levels rise in the bloodstream, FSH and LH stimulate maturation of the ovum and ovulation. The spike in LH levels is called the LH surge. This triggers ovulation and the development of the corpus luteum. The surge can last for a few hours or a few days, and ovulation usually occurs 24 hours after its onset. Home ovulation kits track LH levels in urine. After ovulation, LH influences the maintenance of the corpus luteum and its production of estrogen and progesterone.
Các quá trình kinh nguyệt và mang thai phụ thuộc vào hormone không chỉ từ buồng trứng (estrogen và progesterone) mà còn từ tuyến yên. Tuyến yên tiết ra hormone kích thích nang trứng (FSH) và hormone luteinizing (LH) sau khi kinh nguyệt bắt đầu. Khi mức độ của chúng tăng lên trong máu, FSH và LH kích thích sự trưởng thành của noãn và rụng trứng. Sự tăng đột biến của LH, được gọi là đỉnh LH, kích hoạt rụng trứng và sự phát triển của thể vàng. Đỉnh LH có thể kéo dài vài giờ hoặc vài ngày, và rụng trứng thường xảy ra sau 24 giờ kể từ khi bắt đầu. Bộ dụng cụ theo dõi rụng trứng tại nhà theo dõi mức LH trong nước tiểu. Sau khi rụng trứng, LH ảnh hưởng đến việc duy trì thể vàng và sản xuất estrogen và progesterone của nó.
During pregnancy, the high levels of estrogen and progesterone from the ovary and placenta cause the pituitary gland to stop producing FSH and LH. Therefore, while a woman is pregnant, additional eggs do not mature and ovulation cannot occur. Oral contraceptives (birth control pills) work in the same way.
Trong quá trình mang thai, mức độ cao của estrogen và progesterone từ buồng trứng và nhau thai khiến tuyến yên ngừng sản xuất FSH và LH. Do đó, trong khi phụ nữ mang thai, không có trứng nào khác trưởng thành và rụng trứng không thể xảy ra. Thuốc tránh thai (thuốc uống ngừa thai) hoạt động theo cách tương tự.
Another female birth control method is an IUD (intrauterine device). A health care professional inserts the IUD, a small device designed to remain inside the uterus. It works by preventing implantation of the embryo. Birth control pills and an IUD do not protect a woman against sexually transmitted infections such as that caused by HIV. See page 274 for a table of contraceptive choices and their features.
Một phương pháp tránh thai nữ khác là vòng tránh thai (IUD). Một chuyên gia y tế sẽ đặt IUD, một thiết bị nhỏ được thiết kế để ở lại bên trong tử cung. Nó hoạt động bằng cách ngăn cản sự làm tổ của phôi. Thuốc tránh thai và IUD không bảo vệ phụ nữ khỏi các bệnh nhiễm trùng lây truyền qua đường tình dục như HIV. Xem trang 274 để biết bảng các lựa chọn ngừa thai và các đặc điểm của chúng.
How Do Birth Control Pills Work?
Birth control pills contain a combination of estrogen and progesterone or progesterone only. When taken as directed, they increase the levels of these hormones in the woman's bloodstream. High levels of estrogen and progesterone send a signal to the pituitary gland to shut down its secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). When these hormones are blocked, the ovaries will not release eggs, and pregnancy cannot occur. During pregnancy, levels of estrogen and progesterone also are high—and the ovaries will not release eggs then either! So birth control pills effectively fool the body into “thinking” that the woman is pregnant, and her ovaries stop producing eggs.
Thuốc Tránh Thai Hoạt Động Như Thế Nào?
Thuốc tránh thai chứa kết hợp của estrogen và progesterone hoặc chỉ progesterone. Khi được uống đúng cách, chúng làm tăng mức độ của các hormone này trong máu của phụ nữ. Mức độ cao của estrogen và progesterone gửi tín hiệu đến tuyến yên để ngừng tiết hormone kích thích nang trứng (FSH) và hormone luteinizing (LH). Khi các hormone này bị chặn, buồng trứng sẽ không phóng thích trứng, và không thể xảy ra mang thai. Trong suốt quá trình mang thai, mức độ estrogen và progesterone cũng cao—và buồng trứng sẽ không phóng thích trứng vào thời điểm đó! Vì vậy, thuốc tránh thai hiệu quả làm "lừa" cơ thể nghĩ rằng người phụ nữ đang mang thai, và buồng trứng của cô ấy ngừng sản xuất trứng.
When all of the ova are released and secretion of estrogen from the ovaries lessens, menopause begins. Menopause signals the gradual ending of menstrual cycles. Premature menopause occurs before age 40, whereas delayed menopause occurs after age 55. Artificial menopause occurs if the ovaries are removed by surgery or made nonfunctional as a result of radiation therapy or some forms of chemotherapy.
Khi tất cả các noãn được phóng thích và sự tiết estrogen từ buồng trứng giảm, mãn kinh bắt đầu. Mãn kinh đánh dấu sự kết thúc dần dần của các chu kỳ kinh nguyệt. Mãn kinh sớm xảy ra trước tuổi 40, trong khi mãn kinh muộn xảy ra sau tuổi 55. Mãn kinh nhân tạo xảy ra nếu buồng trứng được cắt bỏ bằng phẫu thuật hoặc trở nên không chức năng do liệu pháp bức xạ hoặc một số hình thức hóa trị liệu.
During menopause, when estrogen levels fall, the most common signs and symptoms are hot flashes (temperature regulation in the brain is disturbed), insomnia, and vaginal atrophy (lining of the vagina dries and thins, predisposing the affected woman to irritation and discomfort during sexual intercourse). Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), given orally or as a transdermal patch or vaginal ring, relieves these symptoms of menopause and delays the development of weak bones (osteoporosis). HRT use may be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, endometrial cancer, stroke, or heart attack. This therapy should be used only after careful consideration of potential risks and benefits.
Trong quá trình mãn kinh, khi mức estrogen giảm, các dấu hiệu và triệu chứng phổ biến nhất là bốc hỏa (việc điều chỉnh nhiệt độ trong não bị xáo trộn), mất ngủ và teo âm đạo (niêm mạc âm đạo khô và mỏng, khiến phụ nữ dễ bị kích ứng và khó chịu khi quan hệ tình dục). Liệu pháp hormone thay thế (HRT), được sử dụng qua đường uống, miếng dán da hoặc vòng âm đạo, giúp giảm bớt các triệu chứng này của mãn kinh và làm chậm quá trình phát triển của loãng xương (osteoporosis). Sử dụng HRT có thể liên quan đến nguy cơ gia tăng ung thư vú, ung thư nội mạc tử cung, đột quỵ hoặc đau tim. Liệu pháp này nên được sử dụng chỉ sau khi xem xét cẩn thận các nguy cơ và lợi ích tiềm năng.
Table 8-1 reviews the various female hormones, including the sites where they are produced, their target organs, and their effect on the body.
Bảng 8-1 xem xét các hormone nữ khác nhau, bao gồm các nơi chúng được sản xuất, cơ quan mục tiêu của chúng và tác dụng của chúng đối với cơ thể.
TABLE 8-1 FEMALE HORMONES
HORMONE | PRODUCTION SITE(S) | TARGET ORGAN | EFFECT |
|---|---|---|---|
FSH | Pituitary gland | Ovary | Stimulates maturation of the ovum |
LH | Pituitary gland | Ovary | Stimulates ovulation |
Estrogen | Ovary Placenta (during pregnancy) | Uterus | Builds up the endometrial lining |
Progesterone | Ovary (corpus luteum) Placenta (during pregnancy) | Uterus | Sustains uterine lining and placenta during pregnancy |
hCG | Placenta | Ovary (corpus luteum) | Sustains pregnancy |
FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone;
hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin;
LH, luteinizing hormone.
there is often puzzlement surrounding the reproductive system. Understanding its parts and how it works can help you maintain its health.
thường gây bối rối khi nói về hệ sinh dục. Hiểu về các bộ phận và cách hoạt động của hệ thống này có thể giúp duy trì sức khỏe sinh sản.
The reproductive system is the only system in which males and females have very different parts. This includes not only the external genitalia - the male penis and female vagina - but inside as well. The gonads are the organs which produce sex cells. In males the testes produce sperm, while in females the ovaries produce egg cells. Should a sperm cell reach an egg cell during intercourse, fertilization occurs.
Hệ thống sinh sản là hệ thống duy nhất trong đó nam và nữ có các bộ phận rất khác nhau. Điều này bao gồm không chỉ các bộ phận sinh dục bên ngoài như dương vật nam và âm đạo nữ, mà cả bên trong. Tuyến sinh dục là các cơ quan sản xuất tế bào sinh dục. Ở nam giới, tinh hoàn sản xuất tinh trùng, trong khi ở nữ giới, buồng trứng sản xuất trứng. Nếu tinh trùng tiếp cận được trứng trong lúc giao hợp, thụ tinh sẽ xảy ra.
At Southwest Reproductive Health Clinic we offer a variety of services to help you maintain reproductive health. We counsel sexually active patients about using birth control and preventing the spread of STDs such as HIV. We can advise on a variety of contraceptive methods, including condoms and the pill. If you or your partner suffers from infertility, we can present you with treatment options.
Tại Southwest Reproductive Health Clinic, chúng tôi cung cấp nhiều dịch vụ để giúp bạn duy trì sức khỏe sinh sản. Chúng tôi tư vấn cho các bệnh nhân có hoạt động tình dục về việc sử dụng các biện pháp tránh thai và ngăn ngừa lây nhiễm HIV và các bệnh lây truyền qua đường tình dục khác. Chúng tôi có thể tư vấn về nhiều phương pháp tránh thai khác nhau, bao gồm bao cao su và thuốc tránh thai. Nếu bạn hoặc đối tác của bạn gặp vấn đề về vô sinh, chúng tôi có thể cung cấp các phương pháp điều trị phù hợp.
Vocabulary
adnexa uteri
Fallopian tubes, ovaries, and supporting ligaments. (Ống dẫn trứng, buồng trứng và các dây chằng hỗ trợ.)
amnion
Innermost membrane surrounding the embryo and fetus. (Lớp màng trong nhất bao quanh phôi và thai nhi.)
areola
Dark-pigmented area surrounding the breast nipple. (Vùng da sậm màu bao quanh đầu vú.)
Bartholin glands
Small mucus-secreting exocrine glands at the vaginal orifice (opening to outside of the body). Caspar Bartholin was a Danish anatomist who described the glands in 1637. (Tuyến bài trừ tiết dịch nhầy nhỏ ở hậu môn âm đạo (lỗ mở ra bên ngoài cơ thể). Caspar Bartholin là nhà giải phẫu học Đan Mạch mô tả các tuyến năm 1637.)
cervix
Lower, neck-like portion of the uterus. (Phần cổ tử cung, phần giống cổ họng nằm ở dưới tử cung.)
chorion
Outermost membrane surrounding the embryo and fetus; it forms the fetal part of the placenta. (Lớp màng ngoài cùng bao quanh phôi và thai nhi; thành phần phần thai của dây rốn.)
clitoris
Organ of sensitive erectile tissue anterior to the opening of the female urethra. (Cơ quan mô mềm nhạy cảm nằm phía trước lỗ đường tiết nữ.)
coitus
Sexual intercourse; copulation. Pronunciation is KO-ihtus. (Giao hợp; quan hệ tình dục.)
corpus luteum
Empty ovarian follicle that secretes progesterone after release of the egg cell; literally means yellow (luteum) body (corpus). (Nang trứng trống sản xuất progesterone sau khi trứng được thải ra; chữ "luteum" có nghĩa là cơ thể màu vàng.)
cul-de-sac
Region in the lower abdomen, midway between the rectum and the uterus. (Vùng trong hạ bụng, nằm ở giữa ruột thừa và tử cung.)
embryo
Stage in prenatal development from 2 to 8 weeks. (Giai đoạn phát triển trước sinh từ 2 đến 8 tuần.)
endometrium
Inner, mucous membrane lining of the uterus. (Lớp niêm mạc nội bào tử cung.)
fallopian tube
One of a pair of ducts through which the ovum travels to the uterus; also called an oviduct. The tubes were named for Gabriello Fallopia, an Italian anatomist. (Một trong hai ống dẫn qua đó trứng đi đến tử cung; cũng được gọi là ống cơ tử. Các ống được đặt tên theo Gabriello Fallopia, một nhà giải phẫu học người Italy.)
fertilization
Union of the sperm and ovum from which the embryo develops. (Sự phối hợp giữa tinh trùng và trứng nơi mà phôi phát triển.)
fetus
Stage in prenatal development from 8 weeks to birth. (Giai đoạn phát triển từ 8 tuần đến khi sinh.)
fimbriae (singular: fimbria)
Finger- or fringe-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes. (Những chiếc ngón tay hoặc sợi mao mạch ở đầu ống dẫn trứng.)
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Secreted by the pituitary gland to stimulate maturation of the egg cell (ovum) (Hormone do tuyến yên tiết ra để kích thích sự chín trứng (nang trứng).)
gamete
Male or female sexual reproductive cell; sperm cell or ovum. (Tế bào sinh dục nam hoặc nữ; tế bào tinh trùng hoặc trứng nơi phụ nữ.)
genitalia
Reproductive organs; also called genitals. (Các cơ quan sinh dục; cũng gọi là cơ quan sinh dục.)
gestation
Time period from fertilization of the ovum to birth; pregnancy. (Thời gian từ thời điểm thụ thai đến khi sinh; thai kỳ.)
gonad
Female or male reproductive organ that produces sex cells and hormones; ovary or testis. (Cơ quan sinh dục nữ hoặc nam sản xuất tế bào sinh dục và hormone; buồng trứng hoặc tinh hoàn.)
gynecology
Study of the female reproductive organs, including the breasts. (Nghiên cứu về các cơ quan sinh dục nữ, bao gồm cả vú.)
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Hormone produced by the placenta to sustain pregnancy by stimulating (-tropin) the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone. (Hormone được sản xuất bởi nhau thai để duy trì thai kỳ bằng cách kích thích những buồng trứng tiết ra estrogen và progesterone.)
hymen
Mucous membrane partially or completely covering the opening to the vagina. (Màng nhầy một phần hoặc hoàn toàn che phủ lỗ vào âm đạo.)
labia
Lips of the vagina; labia majora are the larger, outermost lips, and labia minora are the smaller, innermost lips. (Môi của âm đạo; môi ngoài to (labia majora) và môi trong nhỏ (labia minora).)
lactiferous ducts
Tubes that carry milk from the mammary glands to the nipple. (Ống dẫn sữa từ tuyến sữa đến đầu vú.)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
Secreted by the pituitary gland to promote ovulation. (Hormone do tuyến yên tiết ra để khuyến khích sự rụng trứng.)
mammary papilla
Nipple of the breast. A papilla is any small nipple-shaped projection. (Đầu vú của vú. Một cái đầu vú là bất kỳ chiếc nhấn nhỏ nào dựng như hình núi nhỏ.)
menarche
Beginning of the first menstrual period and ability to reproduce. (Sự bắt đầu kỳ kinh nguyệt đầu tiên và khả năng sinh sản.)
menopause
Gradual ending of menstruation. (Sự dần dần kết thúc kinh nguyệt.)
menstruation
Monthly shedding of the uterine lining. The flow of blood and tissue normally discharged during menstruation is called the menses (Latin mensis means month). (Việc rụng lớp niêm mạc của tử cung hàng tháng. Dòng máu và mô bình thường được thải ra trong khi kinh nguyệt được gọi là kinh.)
myometrium
Muscle layer of the uterus. (Lớp cơ của tử cung.)
neonatology
Study of the medical care of the newborn (neonate). (Nghiên cứu chăm sóc y tế cho trẻ sơ sinh (trẻ sơ sinh).)
obstetrics
Branch of medicine and surgery concerned with pregnancy and childbirth. (Lĩnh vực y học và phẫu thuật liên quan đến thai kỳ và sinh nở.)
orifice
An opening. (Một lỗ.)
ovarian follicle
Developing sac enclosing each ovum within the ovary. Only about 400 of these sacs mature in a woman's lifetime. (Nang nảy mầm bao quanh từng trứng trong buồng trứng. Chỉ có khoảng 400 cái túi nàng này chín trong suốt cuộc đời của phụ nữ.)
ovary
One of a pair of female organs (gonads) on each side of the pelvis. Ovaries are almond-shaped, about the size of large walnuts, and produce egg cells (ova) and hormones. (Một trong hai cơ quan nữ (tinh hoàn) ở mỗi bên của chậu. Buồng trứng có hình hạnh nhân, khoảng cỡ của quả óc chó, và sản xuất tế bào trứng (trứng nơi).)
ovulation
Release of the ovum from the ovary. (Sự phóng trứng từ buồng trứng.)
ovum (plural: ova)
Mature egg cell (female gamete). Ova develop from immature egg cells called oocytes. (Tế bào trứng trưởng thành (gamete nữ). Ova phát triển từ tế bào trứng chưa trưởng thành gọi là nang.)
parturition
Act of giving birth. (Hành động sinh.)
perimetrium
Outermost layer of the uterus; uterine serosa. (Lớp ngoài cùng của tử cung; màng nhớ sự nhau thai.)
perineum
In females, the area between the anus and the vagina. (Ở nữ giới, khu vực giữa hậu môn và âm đạo.)
pituitary gland
Endocrine gland at the base of the brain. It produces hormones that stimulate the ovaries. The pituitary gland also regulates other endocrine organs. (Tuyến nội tiết ở cơ sở não. Nó sản xuất hormone kích thích buồng trứng. Tuyến yên cũng điều chỉnh các tuyến nội tiết khác.)
placenta
Vascular organ attached to the uterine wall during pregnancy. It permits the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products between mother and fetus. (Cơ quan mạch máu gắn vào thành tử cung trong khi mang thai. Nó cho phép trao đổi oxy, dưỡng chất, và chất thải của thai nhi giữa mẹ và thai nhi.)
pregnancy
Gestation. (Thai kỳ.)
progesterone
Hormone produced by the corpus luteum in the ovary and the placenta of pregnant women. (Hormone do nang trứng trống và nhau thai của phụ nữ sản xuất.)
puberty
Period of adolescent development at which secondary sex characteristics appear and gametes are produced. (Giai đoạn phát triển vị thành niên nơi những đặc điểm giới tính phụ và tế bào sinh dục được tạo ra.)
uterus
Hollow, pear-shaped muscular female organ in which the embryo and fetus develop, and from which menstruation occurs. The upper portion is the fundus; the middle portion is the corpus; and the lowermost, neck-like portion is the cervix (see Figure 8-3, page 244). (Bộ phận cơ thể phụ nữ hình trái lê phẳng trong đó phôi và thai nhi phát triển, và từ đó kinh nguyệt xảy ra. Phần trên là quỹ; phần giữa là người; và phần dưới cổ giống cổ họng (xem hình 8-3, trang 244).)
vagina
Muscular, mucosa-lined canal extending from the uterus to the exterior of the body. (Ống cơ bắp, niêm mạc dính nối từ tử cung ra ngoài cơ thể.)
vulva
External female genitalia; includes the labia, hymen, clitoris, and vaginal orifice. (Bộ phận sinh dục ngoài của nữ giới; bao gồm các môi, màng trinh, dương vật, và lỗ âm đạo.)
zygote
Stage in prenatal development from fertilization and implantation up to 2 weeks. (Giai đoạn trong phát triển tiền nhiệm từ thụ thai và cấy ghép cho đến 2 tuần đầu.)