Chapter 5: Nucleic Acid Extraction
5.1: Basic Principles of DNA Extraction
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): A linear polynucleotide consisting of four types of monomeric nucleotides.
- Each nucleotide contains three components:
- a deoxyribose,
- a nitrogenous base, and
- a phosphate group.
- The four bases for DNA are:
- adenine (A),
- cytosine (C),
- guanine (G), and
- thymine (T)
- The deoxyribose is attached to the nitrogen of a base.
- The phosphate group is attached to the deoxyribose.
- In a polynucleotide, individual nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds.
- Friedrich Mescher: a Swiss physician to first attempt and accomplish isolate DNA from humans, which involved the use of human leucocytes.
- This study led to the discovery of the DNA molecule, which he referred to as “nuclein.”
Cell and Tissue Disruption
- In most DNA extraction protocols, enzymatic digestions are used for cell and tissue disruption.
- The disruption process can also be carried out by boiling and by using alkali treatment and mechanical methods.
- A decalcification process removes calcium ions from the matrix, thus making the specimen suitable for DNA extraction.
Lysis of Cellular and Organelle Membranes
- During or after tissue disruption, membranes are lysed in order to release DNAs.
- The lysis can be carried out using salts and chaotropic agents and detergents.
- These substances can destroy membranes, denature proteins, and dissociate proteins such as histones from DNA. The lysis procedure is usually carried out in a buffer in order to maintain a pH where endogenous deoxyribonucleases (DNases) remain inactive.
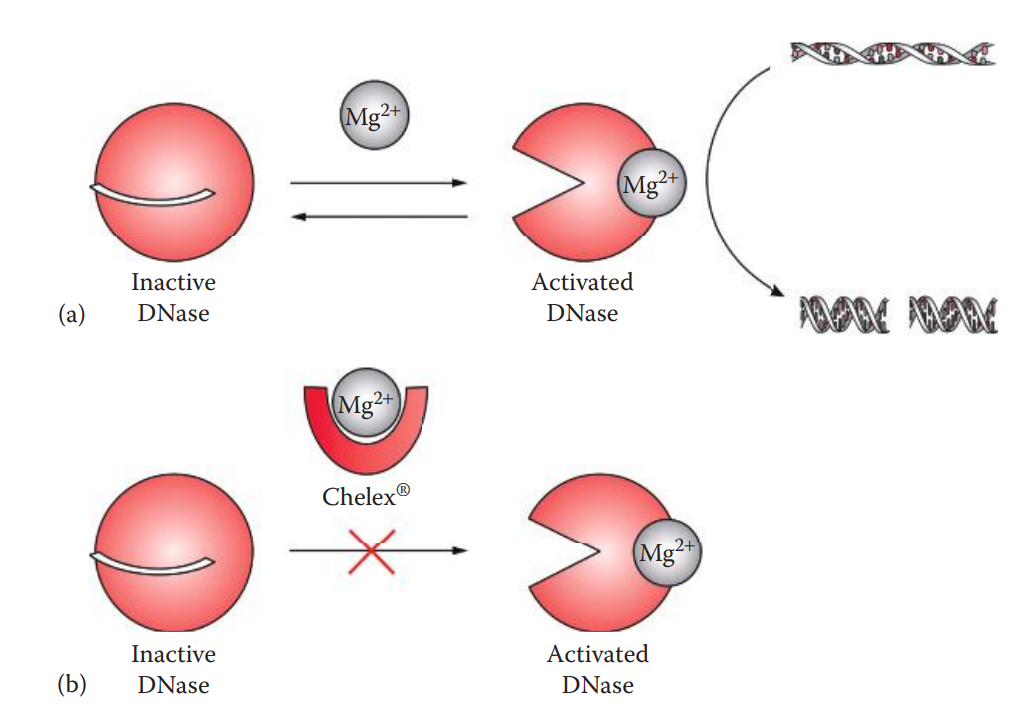
- DNases: A type of nuclease that catalyzes the cleavage of phosphodiester bonds of DNA.
- Endogenous DNases are located in cytoplasmic lysosomes and play a role in degrading the DNA of invading viruses. When cells are lysed, the DNases that are also released can degrade the extracted DNA.
- Chelating agents such as EDTA or Chelex® can therefore be used to chelate the divalent cations that are the cofactors of DNases, in order to inhibit DNase activities.
Removal of Proteins and Cytoplasmic Constituents
- After lysis, cytoplasmic constituents are removed.
- Proteins and lipids are usually removed by one or more rounds of extraction with organic solvents.
- Another strategy to remove cytoplasmic constituents is to utilize the reversible binding of DNA to a solid material such as silica, which selectively binds DNA in chaotropic salt solutions.
- The proteins and cytoplasmic constituents can then be removed through washing steps.
Storage of DNA Solutions
- Purified high-molecular-weight DNA is usually stored in TE buffer.
- EDTA is usually included in storage solutions to chelate divalent cations and thereby inhibit DNases.
- Frequent freezing or thawing cycles should be avoided because temperature fluctuations may cause breaks of single- and double-stranded DNA.
- The presence of heavy metals can cause the breakage of phosphodiester bonds in the molecules.
- Unsuccessful removal of exogenous or intracellular free radicals can cause DNA damage such as strand breaks.
Contamination
- Contamination is usually caused by the introduction of exogenous DNA to an evidence sample.
- It can occur between samples, between an individual and a sample, between other organisms and a sample, or between amplified DNA and a sample.
- Evidence and reference samples should be processed separately in different rooms to avoid sample-to-sample contamination.
- In situations where space is limited, the evidence sample should be processed before the reference sample.
- Evidence samples should be processed and extracted for isolating DNA in separate areas (or at different times) from DNA amplification areas.
- The levels of contamination should be monitored by using extraction reagent blanks (having reagents but no samples), which monitor contamination from the extraction.
5.2: Methods of DNA Extraction
Extraction with Phenol–Chloroform
Cell Lysis and Protein Digestion: These steps can be achieved by digestion with proteolytic enzymes such as proteinase K before extraction with organic solvents.
Extraction with Organic Solvents
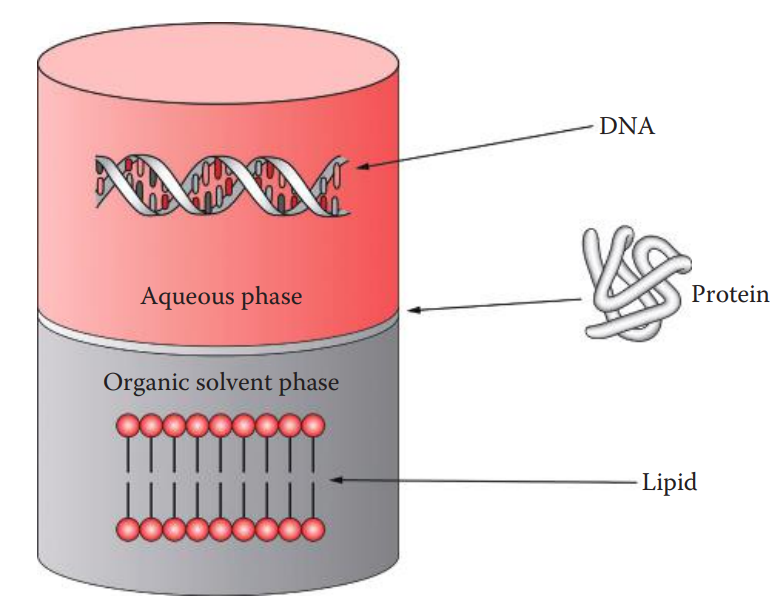
- The removal of proteins is carried out by extracting aqueous solutions containing DNA with a mixture of phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol.
- Phenol is used to extract the proteins from the aqueous solution.
- Chloroform is utilized as it has a higher density than phenol
- Isoamyl alcohol is often added to the phenol–chloroform mixture to reduce foaming.
Concentrating DNA
- Ethanol Precipitation: The DNA is precipitated from the aqueous solution with ethanol and salts.
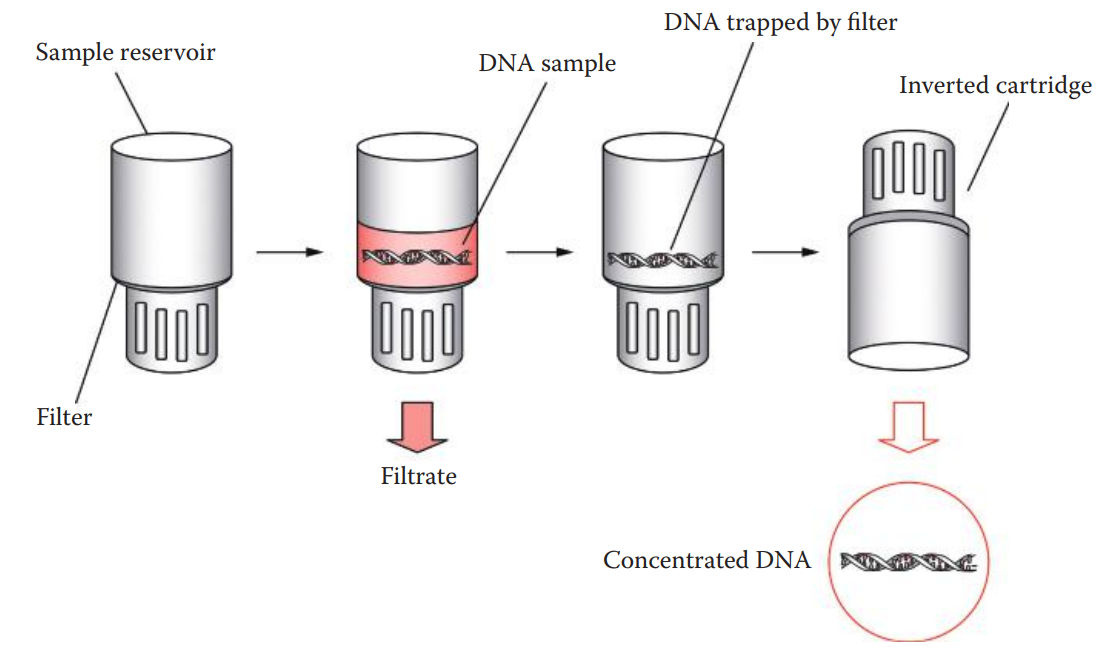
- Ultrafiltration:
- An alternative to ethanol precipitation for concentrating DNA solutions.
- The Microcon® and Amicon® are centrifugal ultrafiltration devices that can concentrate DNA samples.
Extraction by Boiling Lysis and Chelation
Washing: This step removes contaminants and inhibitors that may interfere with DNA amplification.
Boiling
- Cells are suspended in a solution and incubated at 56°C, where DNases are not active, for 20 min.
- This pre boiling step softens cell membranes and separates clumps of cells from each other.
- The cells are then lysed by heating to boiling temperature in order to break open the membranes and to release the DNA.
Centrifugation
- Brief centrifugation is performed to pull the Chelex® 100 resin and cellular debris to the bottom of the tube. The supernatant is used for DNA analysis.
- This method is simple and rapid and uses only a single tube for extraction, thus reducing the risks of contamination and sample mix-ups.
Silica-Based Extraction
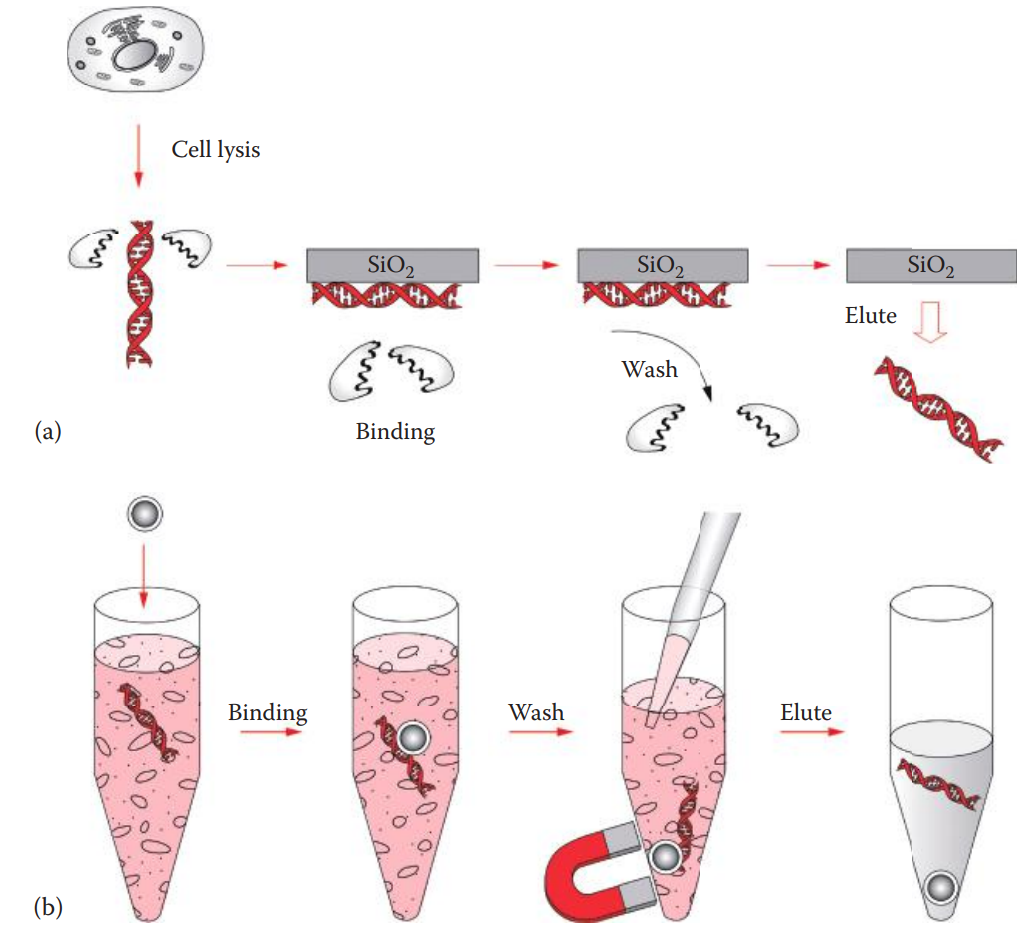
The method is based on the phenomenon that DNA is reversibly adsorbed to silica— silicon dioxide (SiO2)—in the presence of high concentrations of chaotropic salts.
Chaotropic salts can disrupt hydrogen bonding, affecting the three-dimensional structures of macromolecules. These salts are used to denature proteins.
Common chaotropic salts utilized for DNA extraction include guanidinium salts.
Cell Lysis and Protein Digestion
- This is carried out by proteinase K digestion.
- The cell membranes are broken open, and DNA is released.
DNA Adsorption onto Silica
- This step utilizes silica as the stationary phase in a membrane configuration to which the DNA in the cell lysate binds. Adsorption of the DNA to the silica occurs in the presence of high concentrations of chaotropic agents.
Washing
- This step removes chaotropic agents and other contaminants.
- An ethanol-based wash solution is used.
Elution of DNA
- The adsorbed DNA can be eluted by rehydration with aqueous low-salt solutions.
- Silica-coated paramagnetic particles that adsorb DNA in the solution. They are magnets that is used for particle capture instead of centrifugation or vacuum filtration.
- The magnetic particles can be resuspended during the wash steps, and the solution containing contaminants and cellular materials is then discarded.
- DNA is eluted after washing.
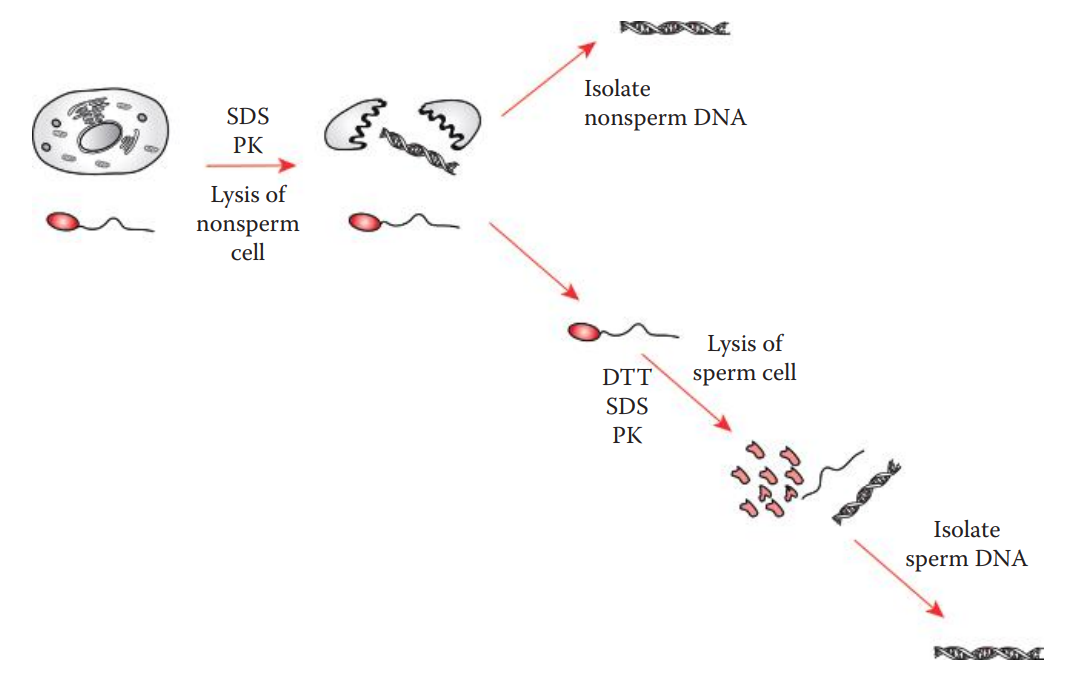
Differential Extraction
This method is very useful for the extraction of DNA from biological evidence derived from sexual assault cases, such as vaginal swabs and bodily fluid stains.
These types of evidence often contain mixtures of spermatozoa from a male contributor and non-sperm cells such as epithelial cells from a female victim.
This method selectively lyses the non-sperm and spermatozoa in separate steps based on the differences in cell-membrane properties of spermatozoa and other types of cells.
The differential extraction procedure involves preferentially lysing the non-sperm cells with proteolytic degradation using proteinase.
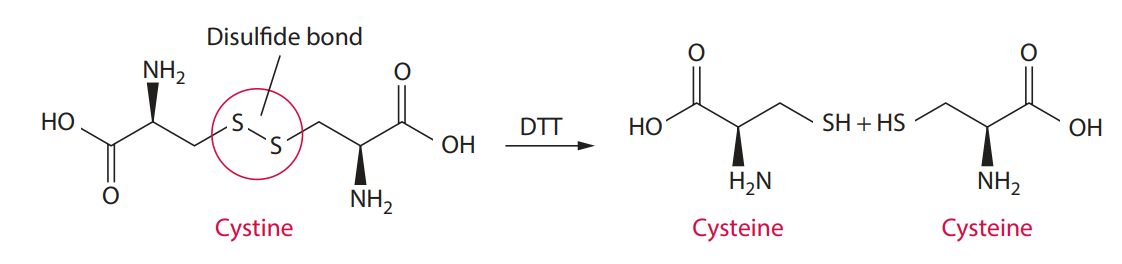
Sperm plasma membrane contains proteins cross-linked by disulfide bonds.
This process isolates sperm and non-sperm cell DNA separately for obtaining DNA profiles from male and female contributors.
5.3: Essential Features of RNA
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): A linear molecule containing four types of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds.
- The sugar residue of RNA is a ribose, which has a hydroxyl (OH) group at the 2′ carbon position.
- RNA has a lower pKa, which means that it is more acidic than DNA.
- RNA contains uracil (U) in place of thymine in DNA.
- It is typically found in cells as a single-stranded molecule, while DNA is double-stranded.
- The RNA that carries codes from a DNA template is called messenger RNA (mRNA) and usually contains a cap and polyadenine tail at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the molecule.
- Endogenous Ribonucleases: Represent the major factor causing RNA degradation.
- RNases are very stable and usually do not require cofactors to carry out enzymatic reactions. Small amounts of RNases are sufficient to degrade RNA.
5.4: Methods of RNA Extraction
RNA–DNA Coextraction
The total RNA isolated usually contains a sufficient amount of mRNA for subsequent reverse transcriptase PCR.
If the quantity of a target mRNA is very low, the procedures specifically for isolating mRNA should be used.
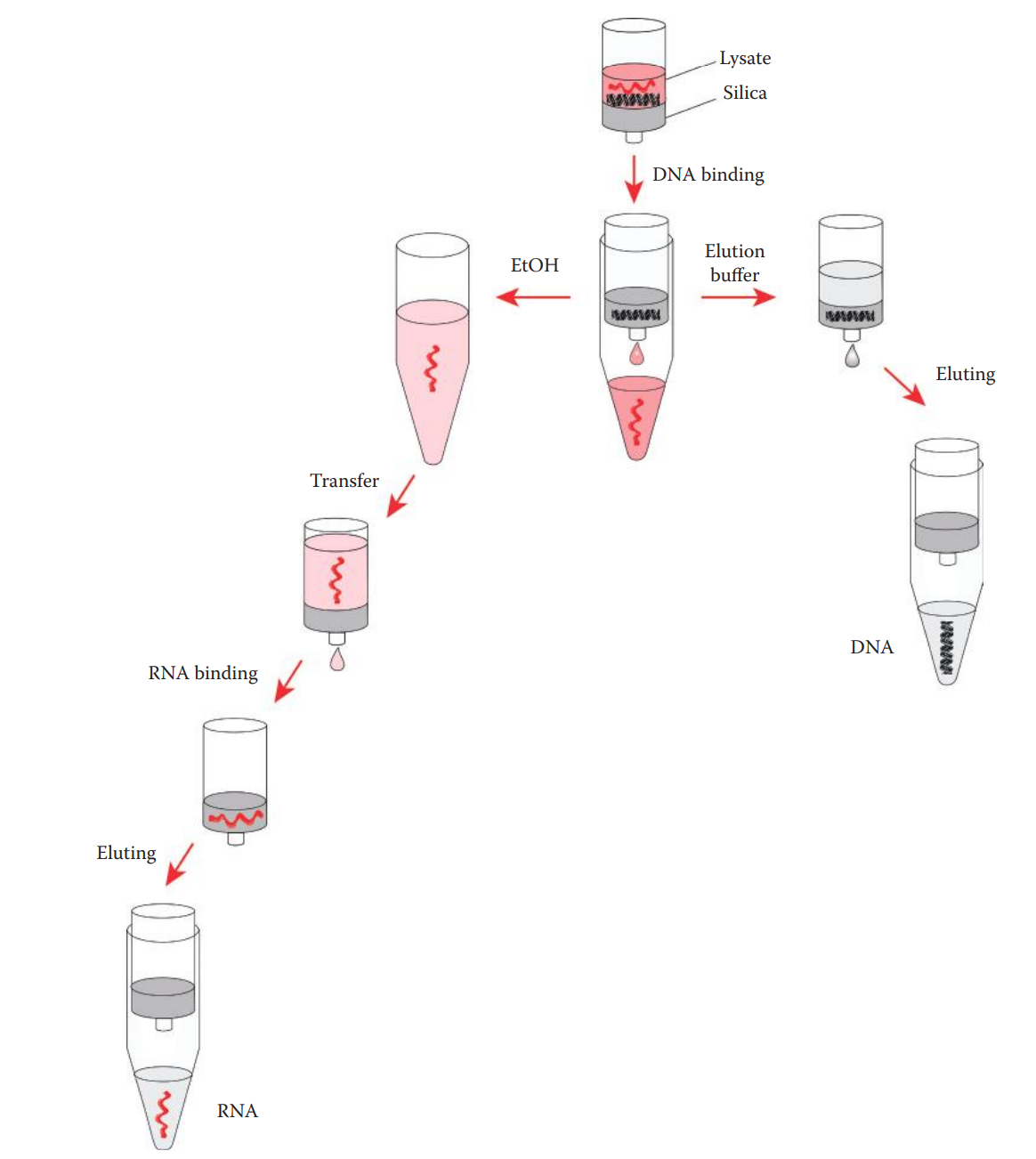
RNA–DNA coextraction methods allow for the simultaneous extraction of high-quality DNA and RNA for forensic DNA analysis and bodily-fluid identification.
Biological samples are first lysed in a lysis buffer.
The lysis buffer usually contains chaotropic salts that can facilitate the lysis of cells and denature proteins, thus inactivating endogenous RNases to protect RNA.
- A high-salt environment in the lysate allows the selective binding of silica to genomic DNA over RNA.
The extraction of RNA is achieved by utilizing a high concentration of chaotropic salts that are already present in the lysate, along with ethanol, in order to decrease the hydrophilic property of RNA and increase its affinity for silica.
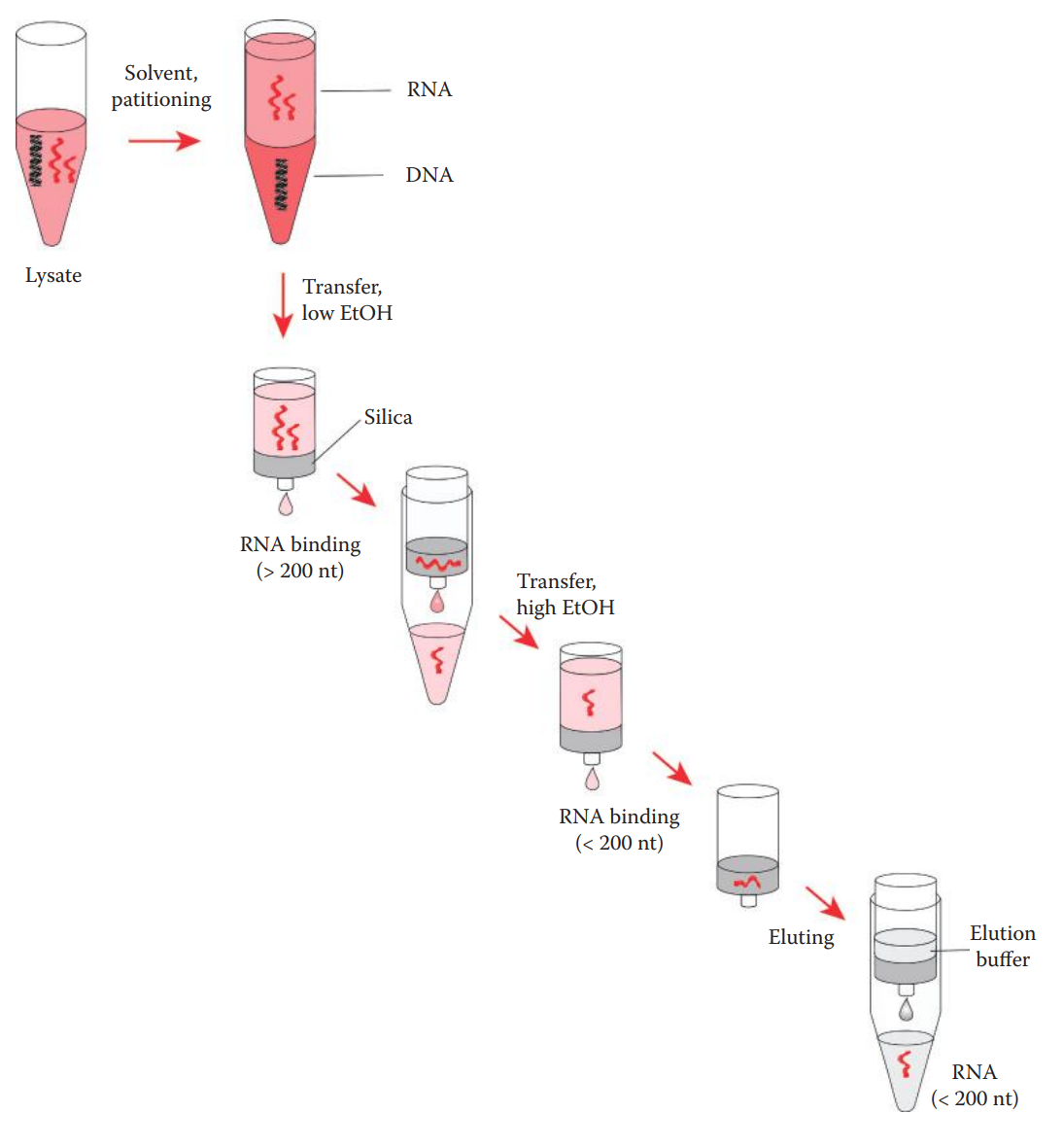
miRNA Extraction
miRNAs are low-molecular-weight RNAs ranging between 15 and 30 nucleotides in length.
Conventional methods routinely used for extracting total RNA do not effectively recover small RNAs; thus, they are not suitable for isolating miRNA.
One approach to extracting small RNA molecules including miRNA involves two steps:
- organic-solvent extraction to isolate total RNA; and
- solid-phase extraction to enrich small RNA.
Purified RNA can be stored at −80°C in RNase-free water or Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 7).
Single-use aliquots are preferred when possible to avoid multiple freeze–thaw cycles.
RNA Integrity Number (RIN): A software algorithm that takes the electrophoretic RNA measurements into account in order to assign integrity values to RNA samples.
- Its method facilitates the assessment of the integrity of RNA samples.
- As reflected by RIN, RNA degradation has a negative influence on the reproducibility of the results of RNA-based forensic analysis.
 \n \n \n \n
\n \n \n \n