BIOCHEMISTRY LAB- SEMIFINALS NOTES (By: karylol)
EXPERIMENT 7: Separation of Amino Acids by Thin Layer
CHROMATOGRAPHY
SEPARATION TECHNIQUE
2 PHASES
STATIONARY
MOBILE (MOVING)
PRINCIPLES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
DIFFERENT COMPOUNDS, DIFFERENT SOLUBILITIES/ADSORPTION TO 2 PHASES BETWEEN WHICH THEY ARE TO BE PARTITIONED.
USES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
SEPARATION OF MIXTURES
IDENTIFICATION OF CPDS
DETERMINATION OF THE NUMBER OF COMPONENTS IN A MIXTURE
DETERMINATION OF PURITY OF SAMPLE
STATIONARY PHASE
FILTER PAPER
DEVELOPER(Mobile Phase)
CLOSED VESSEL WITH SHALLOW POOL OF LIQUID
CAPILLARY ACTION OF ADSORBENT
FUNCTION:
SELECTIVELY DESORB CPDS
TRANSPORT SOME CPDS FURTHER
MAJOR CONSIDERATION: POLARITY
TOO POLAR: WILL CARRY ALL OF THE COMPONENTS BY THE SAME DISTANCE
POOR SEPARATION
TOO NON-POLAR: NONE OF THE SPOTTED MATERIALS WILL BE MOVED
POOR SEPARATION
HIGHER POLARITY, HIGHER DESORBING AND TRANSPORTING CAPABILITY
HIGH POLARITY | LOW POLARITY |
Acetic Acid Methanol Ethanol anh Acetone Ethyl Acetate anh. Ether Chloroform Ch2Cl2 | Toluene CCl4 Pentane Hexane Pet. ether |
DEVELOPMENT
STRENGTH OF BINDING OF COMPOUND TO FILTER PAPER:
ACID & BASES>AMIDES>CARBOXYLIC ACIDS>ALCOHOLS>KETONES~ALDEHYDES>HALIDES>ESTERS>ETHERS>UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS>SATURATED HYDROCARBONS
STRONGER BINDING: SHORT DISTANCE TRAVELED
FACTOR AFFECTING RATE IN MOVING UP THE FILTER PAPER
POLARITY OF:
a. SP
b. MP
c. cpd
INTERACTIONS AMONG SP,MP AND SPOTTED COMPOUNDS
CPD BOUND TO ADSORBENT
MP ATTRACTS AND DESORBS IT
CPD CONTINUALLY ADSORB AND DESORB (Equilibrium) AS SOLVENT MOVES UP THE PLATE
IF CPD IS:
MORE SOLUBLE IN MP: EASILY DESORB
TIGHTLY BOUND TO CELLULOSE: SPEND MORE TIME IN SP
GOOD SOLVENT IN CHROM: GIVES GOOD RESOLUTION(SEPARATION)
HAS DIFFERENT INTERACTIONS WITH DIFFERENT SAMPLE COMPONENTS DESPITE SIMILARITY OF COMPONENTS
USUALLY MIXTURE OF LIQUIDS
DEVELOPING THE CHROMATOGRAM
KEEP COVERED TO KEEP CHAMBER SATURATED WITH SOLVENT VAPOR
MAINTAIN IN EQUILIBRIUM AS SOLVENT MOVES UPWARD
ADSORBENT WETTED WITH SOLVENT WILL LOOK LIKE WET SNOW
WHEN ABOUT 5mm FROM THE OPPOSITE UNSOAKED EDGE, REMOVE PLATE
FORGETTING TO REMOVE THE PLATE WHEN SOLVENT REACH THE TOP OF THE EDGE WILL ENABLE THE SPOT TO CONTINUALLY ASCEND
Rf VALUES WILL THEN BE HIGHER
MARK SOLVENT FRONT WHEN STILL VISIBLE
ALLOW SOLVENT TO EVAPORATE
IF SPOT ALREADY VISIBLE, OUTLINE THE SPOTS
NINHYDRIN
VISUALIZING AGENT
TEST FOR: FREE AA(ALPHA-AMINO GROUP)& FREE AMINO GROUPS
(+) RESULT: PURPLE COLOR
RETENTION FACTOR
MEASURED DISTANCE TRAVELED FROM ORIGIN BY:
EACH MIGRATED SPOT
AND SOLVENT FRONT
FOR TAILING(SPOT ELONGATED): MEASURE TO CENTER OF SPOT
Rf= dSOLUTE/dSOLVENT
Rf IS VERY DEPENDENT ON:
MOISTURE CONTENT(HUMIDITY)
THICKNESS OF ADSORBENT
PURITY OF SOLVENT
OTHER FACTORS
SAME Rf VALUES POSSIBLY SAME COMPOUNDS
IDENTITIES OF COMPOUNDS ESTABLISHED BY SPOTTING KNOWN COMPOUNDS TOGETHER WITH UNKNOWN COMPOUNDS

PRESENT AMINO ACIDS
GLYCINE (non polar)
TRYPTOPHAN (non polar)
TYROSINE (polar)
EXPERIMENT 8: NUCLEIC ACIDS
NUCLEIC ACIDS
MACRO-BIOPOLYMERS OF HIGH MW
REPEATING UNIT MONONUCLEOTIDE
2 STRUCTURAL KINDS OF NUCLEIC ACIDS
DNA
RNA
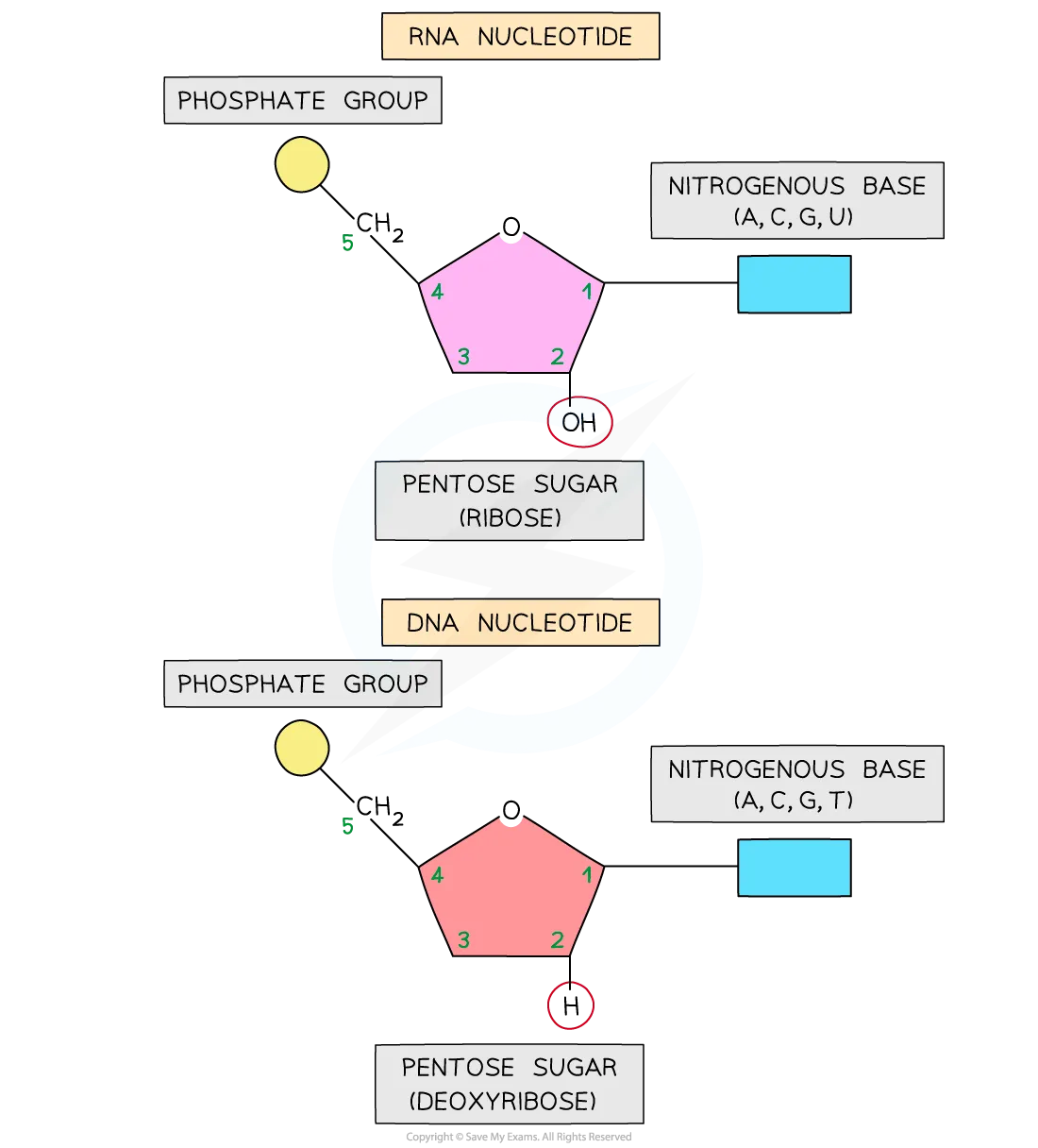
NITROGENOUS BASES
PYRAMIDINE
CYTOSINE (C)- DNA AND SOME RNA
THYMINE (T)- DNA ONLY
URACIL (U)- IN RNA ONLY
PURINE
ADENINE(A)- DNA AND RNA
GUANINE (G)- DNA AND RNA
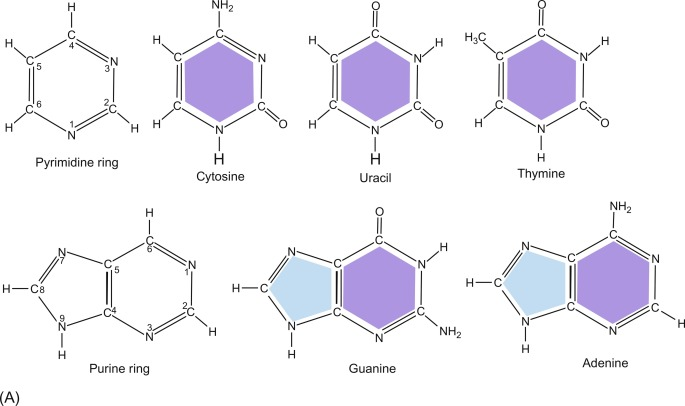
DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID
CARRIES GENETIC INFORMATION RESPONSIBLE FOR DEVT AND FXN OF AN ORGANISM
LOCATION: NUCLEUS

DNA IN FRUITS
0.1-1% DNA BY WEIGHT
STRAWBERRY- OCTOPLOID (8 CHROMOSOME SET)
KIWI- HEXAPLOID
BANANA- TRIPLOID
DNA EXTRACTION
LYSIS
BREAK OPEN:
CELL TO RELEASE NUCLEUS
NUCLEUS TO RELEASE DNA

EXTRACTION BUFFER
H2O
DETERGENT
CONTAINS SURFACTANTS
DISSOLVED CELL MEMBRANE (LIPID BILAYER)
SALT
REMOVES PROTEINS BOUND TO DNA
KEEPS PROTEINS DISSOLVED IN AQUEOUS LAYER
Na+IONS NEUTRALIZE(-) CHARGES IN DNA MOLECULES
MAKE DNA LESS WATER-SOLUBLE AND MORE STABLE
PRECIPITATION
SEPARATES DNA FROM INTERFERRING MATTER
COLD ETHANOL
PRECIPITATE DNA OUT
DNA: LOW SOLUBILITY IN EtOH
LEAST WHEN COLD
LOW Ts PROTECT DNA
SLOW DOWN ACTIVITY OF ENZYMES (NUCLEASES) THAT COULD BREAK IT APART AND DEGRADE IT
PURIFICATION
REMOVES ALL REMAINING CELLULAR DEBRIS AND UNWANTED MATERIAL
RINSING WITH ALCOHOL
HYDROLYSIS OF NUCLEIC ACIDS
2 METHODS:
CHEMICAL
ENZYMATIC
HYDROLYSIS PRODUCTS
PURINE BASES
A&G
PYRIMIDINE BASES
C,T,&U
OLIGONUCLEOTIDES
<20 RESIDUES
NUCLEOTIDES
BASE + SUGAR
DEOXYRIBOSE
PHOSPHATES
INTERACTION RESPONSIBLE FOR RIGID MOLECULAR CONFIGURATIONS OF NUCLEIC ACIDS
PHOSPHODIESTER BONDS
LINK THE NUCLEOTIES TOGETHER IN EACH CHAIN
HYDROGEN BONDS
BETWEEN COMPLIMENTARY BASES (eg. A-T)
VAN DER WAALS FORCES
BETWEEN STACKED BASES

QUALITATIVE TEST FOR NUCLEIC ACIDS
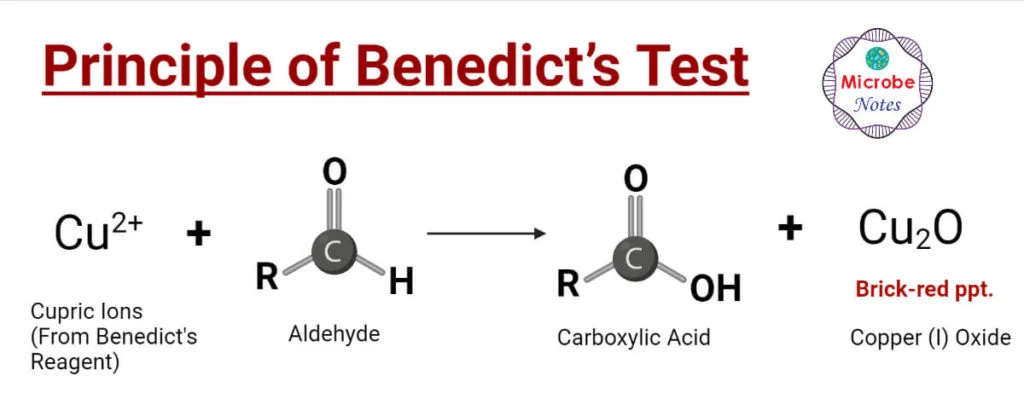
BENEDICTS TEST
FOR REDUCING SUGARS
(+) RESULT: BRICK RED PRECIPITATE
REACTION EQ.
RCHO-[O]-RCOO-
CU2+-[R]-CU++CuO
ORCINOL TEST
FOR PENTOSES
(+) RESULT: BLUE-GREEN
PRINCIPLE
PENTOSES+HCL+6-COMPOSITION+BLUE GREEN
FURFURAL+ORCINOL-CONDENSATION+BLUE GREEN PPT
ORCINOL=3,5-DIHYDROTOLUENE
TEST FOR PURINE BASES
HYDROLYSATE+NH4+ +AgNO3= WHITISH PPT
UNHYDROLYZED+ NH4+ + AgNO3= GRAYISH-WHITE PPT
TEST FOR INORGANIC PHOSPHATE

TEST FOR NUTRIENTS IN FOODS
NUTRIENTS
SUBSTANCE/CPDS THAT SUPPLY BODY WITH ENERGY
BUILDING BLOCKS OF MACRO-MOLECULES
IMPORTANT TO BODY
CARBOHYDRATES
Eg. SUGARS AND STARCHES
SUPPLY BODY WITH ENERGY
SOME STARCHES: PROVIDE INDIGESTIBLE FIBER (OR ROUGHAGE) WHICH AIDS DIGESTION
PROTEINS
FOR GROWTH AND REPAIR
FACTORS AFFECTING AMOUNT NEEDED IN DIET
WEIGHT
GENDER
AGE
HEALTH
NUTRITIONAL VALUE: MEASURED BY QUANTITY OF ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS
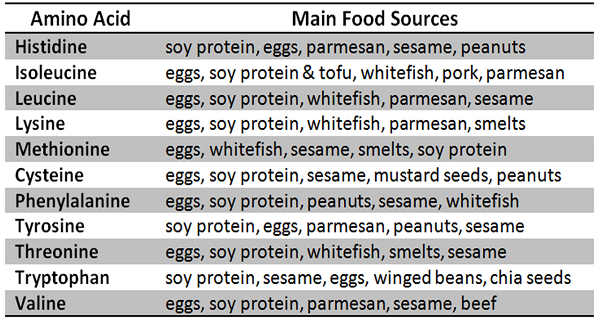
COMPLETE PROTEINS (HAS ALL 9 TYPES OF AA)
FISH
POULTRY (CHICKEN,DUCK, OR TURKEY)
EGGS
DAIRY PRODUCTS (MILK, YOGURT, OR CHEESE)
BEEF OR PORK
SOY PRODUCTS (TOFU AND EDAMAME)
LIPIDS
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
SUPPLY 4X AMOUNT OF ENERGY FROM CARBOHYDRATES AND PROTEINS
CARBS: 4kcal/g
LIPIDS: 9kcal/g
WHEN ENERGIES AROUND C ATOM IN FA ARE TRANSFERRED TO 0: MORE ENERGY FREED THAN WITH CARBS
QUALITATIVE TEST FOR NUTRIENTS IN FOODS
CARBOHYDRATES
PRESENT IN ALL FOOD SAMPLES
MOLISCH TEST
FORMATION OF PURPLE/VIOLET RING
1-Napthanol REACTS WITH THE CYCLIC ALDEHYDES TO FORM PURPLE COLORED CONDENSATION PRODUCTS (furfuryl-diphenyl-methane-dyes)
OSAZONE TEST
GLUCOSAZONE & FRUCTOSAZONE

TEST FOR FATS
TRANSLUCENT PAPER REGION
PRESENT IN ALL FOOD SAMPLES
OCCURRENCE:
TRACE (0.1-0.5%) IN FRUIT JUICE
TRACE (0.03%) IN EGG WHITE
TRACE (0.8%) IN COOKED RICE
TEST FOR VITAMIN A - CARR-PRICE REACTION
PRESENT IN MARGARINE & EGG YOLK
MINERALS
Ca
Cu
I
Fe
Mg
Mn
P
K
Se
Na
Zn
MINERAL MATTER
PRESENT IN ALL SAMPLES
INDICATED BY THE FORMATION OF WHITE POWDERY RESIDUE
ONLY 1-2% IN COOKED RICE
PRACTICE QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
SET 1:
1. In chromatography, what is used as the stationary phase?
- a) Solvent
- b) Developer
- c) Filter Paper
- d) Chromatogram
- Answer: c) Filter Paper
2. Which phase in chromatography is mobile?
- a) Stationary Phase
- b) Developer
- c) Adsorbent
- d) Amino acid
- Answer: b) Developer
3. What indicates a positive result for the presence of free amino groups with ninhydrin?
- a) Red color
- b) Green color
- c) Purple color
- d) Yellow color
- Answer: c) Purple color
4. The Retention Factor (Rf) in chromatography is calculated by dividing the distance traveled by:
- a) Solvent only
- b) Solute by solvent
- c) Solvent by solute
- d) Sample size
- Answer: b) Solute by solvent
5. Which of these solvents is the least polar, providing the lowest desorbing capability?
- a) Ethanol
- b) Chloroform
- c) Water
- d) Hexane
- Answer: d) Hexane
6. Which factor does NOT influence the Rf value in chromatography?
- a) Humidity
- b) Thickness of adsorbent
- c) Color of the spots
- d) Solvent purity
- Answer: c) Color of the spots
7. What type of bond links the nucleotides in a DNA chain?
- a) Hydrogen bond
- b) Van der Waals forces
- c) Phosphodiester bond
- d) Ionic bond
- Answer: c) Phosphodiester bond
8. Which nitrogenous base is present only in RNA?
- a) Thymine
- b) Uracil
- c) Adenine
- d) Guanine
- Answer: b) Uracil
9. What is the purpose of using cold ethanol in DNA extraction?
- a) To dissolve the DNA
- b) To neutralize charges on DNA
- c) To precipitate DNA
- d) To keep the DNA warm
- Answer: c) To precipitate DNA
10. The Carr-Price reaction is used to test for:
- a) Reducing sugars
- b) Vitamin A
- c) Fats
- d) Minerals
- Answer: b) Vitamin A
11. Complete proteins contain which of the following?
- a) Only essential amino acids
- b) All nine essential amino acids
- c) Only non-essential amino acids
- d) Primarily carbohydrates
- Answer: b) All nine essential amino acids
12. Which carbohydrate test produces a purple/violet ring as a positive result?
- a) Orcinol Test
- b) Benedict’s Test
- c) Molisch Test
- d) Ninhydrin Test
- Answer: c) Molisch Test
13. A positive Benedict’s test for reducing sugars is indicated by the formation of:
- a) Purple precipitate
- b) Green color
- c) Brick-red precipitate
- d) Blue color
- Answer: c) Brick-red precipitate
14. What is the major factor affecting the rate of movement of compounds in thin-layer chromatography?
- a) Molecular weight
- b) Solubility
- c) Polarity
- d) Viscosity
- Answer: c) Polarity
15. An amino acid with a non-polar side chain from those used in the provided chromatography example is:
- a) Glycine
- b) Tyrosine
- c) Glutamine
- d) Serine
- Answer: a) Glycine
16. A blue-green color in the orcinol test is a positive result for the presence of:
- a) Hexoses
- b) Pentoses
- c) Amino acids
- d) Lipids
- Answer: b) Pentoses
17. What type of chromatography phase is involved when the mobile phase moves by capillary action?
- a) Gas Chromatography
- b) Liquid Chromatography
- c) Thin-Layer Chromatography
- d) Paper Chromatography
- Answer: d) Paper Chromatography
18. In DNA, guanine pairs with:
- a) Thymine
- b) Cytosine
- c) Adenine
- d) Uracil
- Answer: b) Cytosine
19. An amino acid's retention factor (Rf) is low if:
- a) The stationary phase is too polar
- b) The mobile phase is non-polar
- c) It binds tightly to the stationary phase
- d) All of the above
- Answer: d) All of the above
20. In DNA extraction, what is the purpose of detergent?
- a) Neutralizing DNA charges
- b) Precipitating DNA
- c) Dissolving cell membrane
- d) Visualizing amino acids
- Answer: c) Dissolving cell membrane
21. The Benedict’s test detects:
- a) Non-reducing sugars
- b) Reducing sugars
- c) Proteins
- d) Fats
- Answer: b) Reducing sugars
22. What type of force exists between stacked bases in a DNA molecule?
- a) Ionic bonds
- b) Covalent bonds
- c) Van der Waals forces
- d) Hydrogen bonds
- Answer: c) Van der Waals forces
23. Amino acids like tyrosine, that contain a polar side chain, travel
- a) Farther in a non-polar mobile phase
- b) Not as far as non-polar amino acids in a polar stationary phase
- c) The same distance regardless of the mobile phase
- d) Only in non-polar stationary phases
- Answer: b) Not as far as non-polar amino acids in a polar stationary phase
24. When a spot appears elongated on a chromatogram, measurement should be taken from:
- a) The top of the spot
- b) The bottom of the spot
- c) The center of the spot
- d) The origin point
- Answer: c) The center of the spot
25. What does the positive test for purine bases with AgNO3 look like?
- a) Grayish-white precipitate
- b) Brick-red color
- c) Blue-green color
- d) White powdery residue
- Answer: a) Grayish-white precipitate
26. In chromatography, which substance serves as the mobile phase?
- a) Stationary phase
- b) Developer solvent
- c) Filter paper
- d) Adsorbent
- Answer: b) Developer solvent
27. In paper chromatography, high polarity solvents:
- a) Lead to poor separation
- b) Transport all components at the same distance
- c) Prevent separation by holding compounds together
- d) Both a and b
- Answer: d) Both a and b
28. A substance with a lower Rf value generally:
- a) Is highly polar
- b) Is non-polar
- c) Moves quickly
- d) Dissolves entirely in the solvent
- Answer: a) Is highly polar
29. Which amino acid does not interact well with polar mobile phases?
- a) Tyrosine
- b) Tryptophan
- c) Glycine
- d) Serine
- Answer: b) Tryptophan
30. Why is polarity important in chromatography?
- a) It affects how compounds dissolve in the solvent
- b) It determines the movement rate of compounds
- c) It only impacts the stationary phase
- d) It has no effect on separation
- Answer: b) It determines the movement rate of compounds
31. In the context of DNA extraction, what is the primary role of a lysis buffer?
- a) To precipitate DNA
- b) To dissolve nucleotides
- c) To break open cells and release DNA
- d) To increase the temperature for DNA extraction
- Answer: c) To break open cells and release DNA
32. What principle explains the movement of substances between the stationary and mobile phases in chromatography?
- a) Molecular diffusion
- b) Adsorption and desorption equilibrium
- c) Ionic bonding
- d) Solute crystallization
- Answer: b) Adsorption and desorption equilibrium
33. What type of visualization might be necessary to observe amino acids on a chromatogram if they are not naturally visible?
- a) Heat application
- b) Use of a color-developing agent like ninhydrin
- c) Applying a polar solvent
- d) Measuring solubility
- Answer: b) Use of a color-developing agent like ninhydrin
34. When performing a separation of amino acids using thin-layer chromatography, why might the plate need to be removed before the solvent reaches the top?
- a) To maintain equilibrium
- b) To prevent over-elongation of spots
- c) To avoid incorrect Rf values
- d) All of the above
- Answer: d) All of the above
35. Amino acids differ in their Rf values primarily because of differences in their:
- a) Solubility in non-polar solvents
- b) Adsorption to the stationary phase due to polarity
- c) Chemical composition
- d) Interaction with other amino acids
- Answer: b) Adsorption to the stationary phase due to polarity
36. What is a major purpose of using chromatography in biochemical analysis?
- a) To destroy mixtures
- b) To combine all components of a sample
- c) To separate and identify components in mixtures
- d) To change the color of the substances
- Answer: c) To separate and identify components in mixtures
37. In the orcinol test, a blue-green color is an indication of:
- a) Pentose sugars
- b) Hexose sugars
- c) Amino acids
- d) Fatty acids
- Answer: a) Pentose sugars
38. Which of the following best describes the function of a mobile phase in chromatography?
- a) It remains fixed and binds to solutes
- b) It helps in moving the compounds along the stationary phase
- c) It only supports non-polar molecules
- d) It absorbs light to reveal spots
- Answer: b) It helps in moving the compounds along the stationary phase
39. During DNA extraction, cold ethanol helps in DNA precipitation because DNA is:
- a) Very soluble in ethanol
- b) Less soluble in cold ethanol
- c) More soluble in the lysis buffer
- d) Warmed by the ethanol
- Answer: b) Less soluble in cold ethanol
40. What does the term "retention factor" (Rf) represent in chromatography?
- a) The solubility of compounds in a liquid
- b) The fraction of solvent absorbed
- c) The ratio of distance traveled by the solute to distance traveled by the solvent
- d) The color intensity of the sample
- Answer: c) The ratio of distance traveled by the solute to distance traveled by the solvent
41. In an experiment, a spot representing an amino acid travels 3 cm from the origin, while the solvent front travels 6 cm. What is the Rf value for this amino acid?
- a) 0.2
- b) 0.5
- c) 1.0
- d) 1.5
- Answer: b) 0.5
- Solution: Rf = distance traveled by solute / distance traveled by solvent = 3 cm / 6 cm = 0.5
42. A chromatography experiment shows a dye spot moving 4.5 cm from the starting point, and the solvent front reaches 9 cm. Calculate the Rf value of the dye.
- a) 0.25
- b) 0.5
- c) 0.75
- d) 1.0
- Answer: b) 0.5
- Solution: Rf = 4.5 cm / 9 cm = 0.5
43. In an experiment, the distance from the origin to a compound's spot is measured as 2 cm, and the solvent front traveled 8 cm. What is the Rf value of the compound?
- a) 0.25
- b) 0.5
- c) 0.75
- d) 1.0
- Answer: a) 0.25
- Solution: Rf = 2 cm / 8 cm = 0.25
44. A scientist observes that a compound travels 5 cm on a chromatography plate, while the solvent moves 10 cm. What is the Rf value of the compound?
- a) 0.25
- b) 0.5
- c) 0.75
- d) 1.25
- Answer: b) 0.5
- Solution: Rf = 5 cm / 10 cm = 0.5
45. If a pigment travels 6.5 cm on the chromatography plate and the solvent front is 13 cm from the origin, what is the Rf value of the pigment?
- a) 0.25
- b) 0.5
- c) 0.75
- d) 1.0
- Answer: b) 0.5
- Solution: Rf = 6.5 cm / 13 cm = 0.5
SET 2
Separation of Amino Acids by Thin-Layer Chromatography (Questions 1-20)
1. In thin-layer chromatography, which material typically serves as the stationary phase?
- a) Ethanol
- b) Filter Paper
- c) Water
- d) Amino acids
- Answer: b) Filter Paper
2. What is the purpose of the mobile phase in thin-layer chromatography?
- a) To keep compounds in place
- b) To move compounds along the stationary phase
- c) To dissolve the stationary phase
- d) To stop the reaction
- Answer: b) To move compounds along the stationary phase
3. Which factor primarily affects the movement of amino acids on a chromatography plate?
- a) pH
- b) Temperature
- c) Polarity
- d) Volume of amino acid
- Answer: c) Polarity
4. What is the Retention Factor (Rf) in chromatography?
- a) The total distance the solvent moves
- b) The distance traveled by solute relative to solvent
- c) The distance from the top of the plate
- d) The time taken for separation
- Answer: b) The distance traveled by solute relative to solvent
5. An Rf value close to 1 indicates that the compound:
- a) Barely moved
- b) Traveled very far along with the solvent
- c) Remained at the origin
- d) Has high molecular weight
- Answer: b) Traveled very far along with the solvent
6. Which amino acid would likely have the highest Rf value?
- a) Tyrosine (polar)
- b) Glycine (nonpolar)
- c) Lysine (charged)
- d) Glutamate (charged)
- Answer: b) Glycine (nonpolar)
7. If a solvent is highly polar, it may result in:
- a) Poor separation due to equal movement
- b) Strong binding of compounds at the origin
- c) Faster movement of nonpolar compounds
- d) Separation of only charged compounds
- Answer: a) Poor separation due to equal movement
8. Why is it important to cover the chromatography chamber during development?
- a) To maintain solvent vapor saturation
- b) To prevent spills
- c) To increase temperature
- d) To decrease the Rf values
- Answer: a) To maintain solvent vapor saturation
9. In TLC, ninhydrin is used to visualize:
- a) Carbohydrates
- b) Lipids
- c) Amino acids
- d) Nucleic acids
- Answer: c) Amino acids
10. A spot that appears elongated on the chromatogram should be measured:
- a) From the bottom
- b) From the top
- c) From the center
- d) From the origin
- Answer: c) From the center
11. What result would you expect for an amino acid tightly bound to the stationary phase?
- a) High Rf value
- b) Low Rf value
- c) Moves as far as the solvent
- d) No movement
- Answer: b) Low Rf value
12. In chromatography, a substance that barely moves from the origin is likely:
- a) Very polar
- b) Nonpolar
- c) Neutral
- d) Highly volatile
- Answer: a) Very polar
13. Thin-layer chromatography can be used to:
- a) Separate amino acids
- b) Destroy amino acids
- c) Measure protein content
- d) Decrease amino acid reactivity
- Answer: a) Separate amino acids
14. The Rf value for an amino acid is influenced by:
- a) Humidity
- b) Temperature
- c) Solvent purity
- d) All of the above
- Answer: d) All of the above
15. In TLC, which result indicates that two compounds are likely identical?
- a) Different Rf values
- b) Same Rf values
- c) Same color but different distances
- d) No movement
- Answer: b) Same Rf values
16. If an amino acid spot is very faint, you should:
- a) Apply more amino acid
- b) Change the solvent
- c) Use a stronger developing agent
- d) Adjust the stationary phase
- Answer: c) Use a stronger developing agent
17. In TLC, a mobile phase that is too nonpolar will likely result in:
- a) No movement of solutes
- b) High Rf values
- c) Movement of polar compounds
- d) Uneven separation
- Answer: a) No movement of solutes
18. Which of the following is critical in chromatography experiments?
- a) Room ventilation
- b) Solvent evaporation rate
- c) Solvent polarity
- d) Plate temperature
- Answer: c) Solvent polarity
19. The stationary phase in paper chromatography works by:
- a) Adsorbing the compounds
- b) Evaporating compounds
- c) Providing a smooth surface
- d) Reacting chemically with solutes
- Answer: a) Adsorbing the compounds
20. If a compound has an Rf of 0.5, and the solvent moved 10 cm, the compound traveled:
- a) 5 cm
- b) 10 cm
- c) 15 cm
- d) 2.5 cm
- Answer: a) 5 cm
Experiment for Nucleic Acids (Questions 21-40)
21. What are the two main types of nucleic acids?
- a) DNA and RNA
- b) DNA and ATP
- c) RNA and ATP
- d) DNA and proteins
- Answer: a) DNA and RNA
22. In DNA extraction, cold ethanol is used to:
- a) Increase enzyme activity
- b) Precipitate DNA
- c) Dissolve proteins
- d) Break cell walls
- Answer: b) Precipitate DNA
23. DNA contains which unique nitrogenous base?
- a) Uracil
- b) Thymine
- c) Adenine
- d) Cytosine
- Answer: b) Thymine
24. Which nitrogenous base is found only in RNA?
- a) Thymine
- b) Uracil
- c) Adenine
- d) Guanine
- Answer: b) Uracil
25. The bonds that hold together complementary bases in DNA are called:
- a) Ionic bonds
- b) Covalent bonds
- c) Hydrogen bonds
- d) Peptide bonds
- Answer: c) Hydrogen bonds
26. Which enzyme might be deactivated during DNA extraction to protect DNA?
- a) Polymerase
- b) Nuclease
- c) Helicase
- d) Ligase
- Answer: b) Nuclease
27. In a DNA extraction buffer, salt is used to:
- a) Increase DNA solubility
- b) Neutralize DNA charges
- c) Dissolve cell walls
- d) Precipitate DNA immediately
- Answer: b) Neutralize DNA charges
28. Which base pairing is correct in DNA?
- a) A-T
- b) G-U
- c) C-A
- d) T-G
- Answer: a) A-T
29. What method of nucleic acid hydrolysis yields free bases and oligonucleotides?
- a) Chromatography
- b) Chemical hydrolysis
- c) Enzymatic hydrolysis
- d) Sublimation
- Answer: c) Enzymatic hydrolysis
30. In a cell, DNA is primarily located in the:
- a) Cytoplasm
- b) Nucleus
- c) Mitochondria
- d) Ribosomes
- Answer: b) Nucleus
31. What test produces a blue-green color for pentoses in nucleic acids?
- a) Benedict’s test
- b) Orcinol test
- c) Ninhydrin test
- d) Iodine test
- Answer: b) Orcinol test
32. **Which DNA extraction step involves breaking
open the cell to release the nucleus?**
- a) Precipitation
- b) Lysis
- c) Purification
- d) Hydrolysis
- Answer: b) Lysis
33. The phosphodiester bond in DNA links:
- a) Two sugar molecules
- b) A base to a sugar
- c) Nucleotides in each DNA strand
- d) DNA and RNA
- Answer: c) Nucleotides in each DNA strand
34. Van der Waals forces are crucial in DNA for:
- a) Forming base pairs
- b) Linking nucleotides
- c) Stabilizing base stacking
- d) Hydrogen bonding
- Answer: c) Stabilizing base stacking
35. Which nitrogenous bases are purines?
- a) Adenine and Cytosine
- b) Thymine and Guanine
- c) Adenine and Guanine
- d) Cytosine and Uracil
- Answer: c) Adenine and Guanine
36. The Benedict’s test in nucleic acids indicates:
- a) Proteins
- b) Reducing sugars
- c) Phosphates
- d) Carbohydrates
- Answer: b) Reducing sugars
37. The role of detergent in DNA extraction is to:
- a) Dissolve proteins
- b) Dissolve lipids and cell membranes
- c) Enhance DNA precipitation
- d) Denature DNA
- Answer: b) Dissolve lipids and cell membranes
38. A nucleotide is composed of:
- a) Sugar, base, and phosphate
- b) Sugar and lipid
- c) Amino acid and phosphate
- d) Only a base
- Answer: a) Sugar, base, and phosphate
39. To protect DNA during extraction, cold conditions are used to:
- a) Denature enzymes
- b) Slow down nuclease activity
- c) Increase DNA solubility
- d) Dissolve cell walls
- Answer: b) Slow down nuclease activity
40. A strawberry is often used in DNA extraction due to its:
- a) High acidity
- b) Large number of chromosomes
- c) Low water content
- d) Small genome
- Answer: b) Large number of chromosomes
Test for Nutrients in Food Samples (Questions 41-60)
41. Which nutrient supplies the most energy per gram?
- a) Carbohydrates
- b) Lipids
- c) Proteins
- d) Vitamins
- Answer: b) Lipids
42. Which test produces a purple ring for carbohydrates?
- a) Benedict’s test
- b) Sazone test
- c) Molisch test
- d) Iodine test
- Answer: c) Molisch test
43. A brick-red precipitate in the Benedict’s test indicates the presence of:
- a) Proteins
- b) Reducing sugars
- c) Starch
- d) Lipids
- Answer: b) Reducing sugars
44. The test used to detect pentose sugars in food is:
- a) Benedict’s test
- b) Orcinol test
- c) Ninhydrin test
- d) Sazone test
- Answer: b) Orcinol test
45. A translucent spot on paper indicates the presence of:
- a) Carbohydrates
- b) Fats
- c) Proteins
- d) Minerals
- Answer: b) Fats
46. Complete proteins are foods that:
- a) Contain all nine essential amino acids
- b) Are entirely composed of lipids
- c) Contain only carbohydrates
- d) Lack essential amino acids
- Answer: a) Contain all nine essential amino acids
47. Which type of carbohydrate is tested with the Iodine test?
- a) Glucose
- b) Sucrose
- c) Starch
- d) Fructose
- Answer: c) Starch
48. What result is expected if a food sample contains Vitamin A?
- a) Positive Benedict’s test
- b) Positive Carr-Price reaction
- c) Positive Ninhydrin test
- d) Positive Iodine test
- Answer: b) Positive Carr-Price reaction
49. Carbohydrates are essential because they:
- a) Provide amino acids
- b) Provide the body with energy
- c) Store genetic information
- d) Synthesize enzymes
- Answer: b) Provide the body with energy
50. The Molisch test detects:
- a) Lipids
- b) Proteins
- c) Carbohydrates
- d) Vitamins
- Answer: c) Carbohydrates
51. For growth and repair, the body needs:
- a) Vitamins
- b) Lipids
- c) Proteins
- d) Carbohydrates
- Answer: c) Proteins
52. What is indicated by a positive Osazone test?
- a) Lipids
- b) Carbohydrates
- c) Fats
- d) Proteins
- Answer: b) Carbohydrates
53. In biochemistry, lipids are important because they:
- a) Provide 4 kcal/g
- b) Provide 9 kcal/g
- c) Do not provide energy
- d) Are made of amino acids
- Answer: b) Provide 9 kcal/g
54. Which compound would test positive in the translucent paper test?
- a) Lipids
- b) Proteins
- c) Starch
- d) Minerals
- Answer: a) Lipids
55. For detection of amino acids, which test would you use?
- a) Benedict’s test
- b) Orcinol test
- c) Ninhydrin test
- d) Iodine test
- Answer: c) Ninhydrin test
56. Amino acids required in the diet are classified as:
- a) Non-essential amino acids
- b) Essential amino acids
- c) Carbohydrates
- d) Fatty acids
- Answer: b) Essential amino acids
57. Which mineral is commonly detected as a white powdery residue in food tests?
- a) Iron
- b) Potassium
- c) Calcium
- d) Iodine
- Answer: c) Calcium
58. What type of test would reveal the presence of starch in food samples?
- a) Ninhydrin test
- b) Iodine test
- c) Molisch test
- d) Carr-Price test
- Answer: b) Iodine test
59. Which macronutrient is primarily responsible for building and repairing tissues?
- a) Carbohydrates
- b) Vitamins
- c) Proteins
- d) Minerals
- Answer: c) Proteins
60. Nutrients that do not provide energy but are necessary for cellular functions are called:
- a) Carbohydrates
- b) Minerals
- c) Lipids
- d) Amino acids
- Answer: b) Minerals
Identification (10 Items)
1. Test that identifies the presence of reducing sugars, with a positive result indicated by a brick-red precipitate.
- Answer: Benedict’s Test
2. Test used to detect pentose sugars, showing a blue-green color as a positive result.
- Answer: Orcinol Test
3. Test that detects carbohydrates, where a purple/violet ring formation indicates a positive result.
- Answer: Molisch Test
4. A test for the presence of amino acids (specifically free amino groups), with a positive result shown by a purple color.
- Answer: Ninhydrin Test
5. This test identifies Vitamin A in a sample, with a blue-green color indicating a positive result.
- Answer: Carr-Price Reaction
6. A test for carbohydrates in food samples, specifically identifying starch with a positive result shown by a blue-black color.
- Answer: Iodine Test
7. Test that reveals fats in samples, where a positive result is indicated by a translucent spot on paper.
- Answer: Translucent Spot Test
8. Test for the presence of fats or lipids, which results in a translucent oily mark as a positive indication.
- Answer: Grease Spot Test / Test for Fats
9. A qualitative test for protein presence, resulting in a purple or violet color as a positive outcome.
- Answer: Biuret Test
10. A test used to detect glucose and fructose by forming glucosazone or fructosazone crystals.
- Answer: Osazone Test