OSCE
Station 1: Drug inquiry (requestor telephones)
Step 1: Identifying self and checking with the caller who they are
(question → identify category)
| |||||||
Step 2: Checking background information and active listening
| |||||||
Step 3: Categorise question Availability/ Identification/ Administration/ Compatibility/stability/Cost/Dosage/Drug Safety/Adverse reaction Drug interactions/Choice of therapy/Pharmaceutical/Pharmacology/indications/Supply of literature/ Poisoning/overdose | |||||||
Step 4: Search Strategy Micromedex, LexiComp/UpToDate, MIMS, BNF, PIL/HSA infosearch, PubMed | |||||||
Saying bye bye and thank you **Readback Okay, that's all I have to clarify, I will check back with you in about 10 minutes. How may I contact you? Thank you, byebye | |||||||
Step 5,6,7: Evaluate/Analyse/Synthesise, Response, F/U & document NIL |
DI category 1 Resources |
Pregnancy + Lactation PREGNANCY
PBMO ** want to use the lowest effective dose for as short a period as possible LACTATION
LHBM Others: PIL (cautious side), BNF (too generic), MIMS (too little info) |
Availability + identification
Martindale? |
Dosing + choice of therapy DOSING
CHOICE OF THERAPY
|
Parenteral ADMINISTRATION
|
Parenteral COMPATIBILITY
|
ADR, DDI 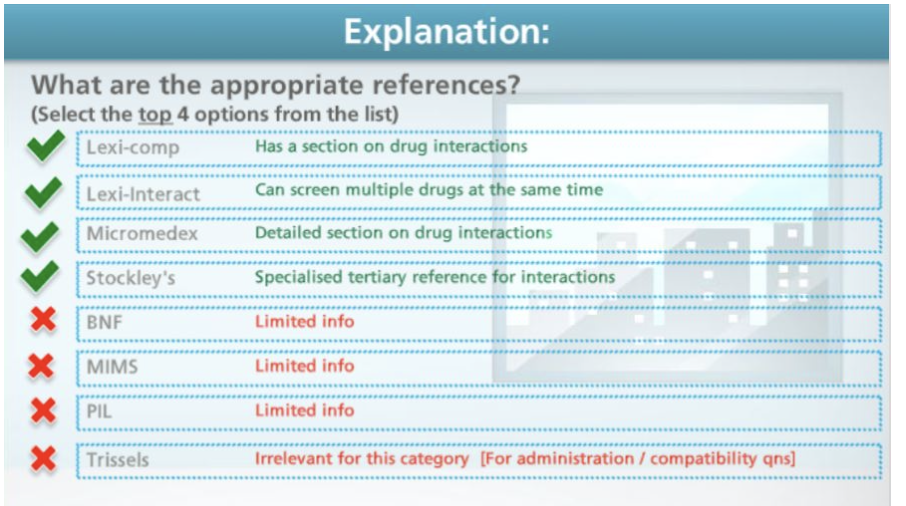  ADR ^^ |
Station 2: Communications (Patient education and counselling)
Rubrics
1. Initiating the session
| ||||||
2. Building RS with patient Involving patient *Actively encourages patient to share concerns and to seek clarifications Uses appropriate non-verbal behaviour *Dresses appropriately for professional encounter *Demonstrates eye contact and appropriate facial expression Demonstrates appropriate posture, position, movement Uses appropriate verbal cues eg volume, tone, pace of speech Demonstrates appropriate confidence Developing rapport Uses non-judgmental tone of communication *Acknowledges patient’s concerns Engages in empathic, compassionate and respectful conversation with patient about her condition and concern(s) | ||||||
3. Communicate information about new medicine
| ||||||
4. Steps in effective patient counselling *Avoids jargons and/or uses plain language to explain medical terms if use is unavoidable *Use of demo sets to demonstrate techniques (where relevant) Organises information into chunks to aid retention and recall of information *Performs teach-back to validate patient’s understanding at appropriate times or important sections of information (eg dosing, monitoring parameters) (_____, do you mind if i ask you some questions to check if you remembered the important points that we discussed today please?) Actively solicits patient’s questions and concerns before moving on | ||||||
5.Communication Skills to Encourage Behaviour Change (Technique) Uses open-ended questions to assess current behaviours and motivation to change (where relevant) Praises and provides affirmation on efforts made to change (where relevant) Demonstrates reflective listening (where relevant) Provides summary of the discussion (where relevant) Rolls with resistance to SP’s wish for information/change (where relevant) Address patient’s concerns | ||||||
6. Closing the session *Actively solicit patient’s questions and concerns (last opportunity before closing) *Summarises the session (Okay so in this session, we have gone through….) *Contracts with patient regarding next steps (eg calling pharmacy for drug enquiries) *Thank patient for time and attention |
Unsafe medications for pregnancy:
ACEi/ARB in 2nd and 3rd trimesters INSTEAD → methyldopa, nifedipine and/or Labetalol
Decongestants → use chlorpheniramine/ or dextromethorphan or guaifenesin (if cough)
Isotretinoin
NSAIDs
2516 EYE
Condition Explanation/Cause Medication given Administration/Dosing/Device use/Counselling ** teach back Non-pharmacological Monitoring |
Acute bacterial conjunctivitis 1. Caused by certain bacterias 2. Inflammation of eyelid base - could be from previous infected individuals with directed hand-eye contact, oculogenital spread.. - Patient’s own sinus/mucus Signs and symptoms: - Hyperaemia (Red eye)
1. Fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin), polymyxin (typically gentamicin), fusidic acid (Fucithalmic)
|
Viral conjunctivitis 1. Inflammation of eyelid base 2. Caused by certain viruses - sick contacts, recent history of URI Signs and symptoms:
1. Antihistamine for itching
1. Supportive with artificial tears and cool compress 2. Exposure precautions as extremely contagious |
Allergic conjunctivitis
ACUTE: Exposure to known allergen eg cat dander SEASONAL (or ALLERGIC RHINO-CONJUNCTIVITIS (ARC)): Outdoor airborne pollens e.g. pollens ; develops over days and weeks PERENNIAL: Environmental exposure e.g. indoor allergens like dust mites, animal dander and mould
RED FLAGS:
First-gen antihistamines: Competitively and reversibly block histamine receptors in the conjunctiva. Lipophilic, crosses blood-brain barrier and causes sedation Alosyn: Antazoline - immediate but temporary relief. Tetrahydrozoline - vasoconstrictors for redness Newer-gen antihistamines: Levocabastine Olopotadine Preventative - avoid allergen Non-pharmaceutical - Avoid rubbing eyes, cool compress, artificial tears, saline rinses, |
Dry eye disease It is a multifactorial disease of the ocular surface, loss of homeostasis of tear film “Eyes can’t produce enough tears Signs and symptoms: dry eyes, red Cause/ Etiology: - Sjogren syndrome (Autoimmune) o Primary and secondary - Non-Sjogren syndrome o Systemic drugs (antihistamine drug e.g. Chlorphenamine) o Lacrimal deficiency o Obstruction of the lacrimal gland duct o Reflex B. Evaporative (lipid layer) Etiological causes: Intrinsic o Meibomian oil deficiency o Drug action e.g. Accutane to treat acne vulgaris o Low blink rate (naturally) Extrinsic o Contact lens wearer o Ocular surface disease e.g. allergy o Topical preservatives e.g. BAK o Vitamin A Deficiency C. Environment - Air con workplace - Computer use -> low blink rate Risk Factors: - Aging - Female - Asian - Contact lens Goal of treatment: restore homeostasis of ocular surface/on the cornea 1. Ocular lubricants (replenish tear vol, stabilise tear film) E.g. Tears Naturale, Hypotears
1. Education on: local environment, lid hygiene, lid massage, warm compresses, using the computer less/more short breaks, take a break from wearing contact lenses 2. |
Blepharoconjunctivitis 1. Antibiotic containing ointment (Gentamicin, also known as Gentamicin POS) 2. Topical antibiotic eyedrops (levofloxacin hydrate, also known as Cravit Ophthalmic Solution) 3. Corticosteroids (dexamethasone sodium phosphate and gentamicin sulfate, also known as Dexa-Gentamicin |
Blepharitis 1. Inflammation of the eyelids due to eye glands being clogged 2. Posterior (tear film instability) or anterior (infection of the base) 3. Caused by some conditions like rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, infections, certain irritants (contact blepharitis), certain Medications 4. Associated with dry eye disease, red and swollen eyelid, itchy eye, irritation, scales on eyelids 1. Heat - Bring turbid lipid material to melting point - Use of warm compress 2. Clean - Remove scruf, collarettes, crusting - Use of warm washcloth |
Hordeolum (stye) ≠ cyst 1. Bacterial infection 2. Causes acute inflammation of the oil gland on the eyelid 3. Small yellow-pus filled lesion may be visible - can be internal or external, developed over a few days - self-limiting → signs and symptoms: Red eyelid, swollen eyelid, pain and sensitive to the touch NIL NIL Apply a warm compress to relieve the pain and discomfort of the stye (around 5-10 minutes several times a day and gently massage the eyelid) - Ensure you have good and proper hand hygiene |
Chalazion 1. Blocked zeis or meibomian glands causing accumulation of material ont he eyelid 2. May be from a previous stye after 10 days to 2 weeks 3, NOT PAIN, bump, slightly red eyelid, no head Consider incision + curettage or glucocorticoid injection NIL Self limiting but can Apply warm compress – soften the cyst and facilitate drainage to the eyelid for 10 to 15 minutes, 4 to 6 times a day for several days. |
Primary open-angle Glaucoma normal appearing anterior chamber angle + raised IOP - Due to clogging of drainage canals - Gradual loss of peripheral visual field Goal of treatment: Prevent further deterioration of vision from disease progression → so lower IOP Targeted for IOP >25 to 30% below initial IOP (for normal pressure and high pressure) Prostaglandins (e.g Latanoprost, Bimatoprost) > beta-blockers (timolol) > alpha-adrenergic agonists (Brimonidine) > carbonic anhydrase > cholinergic 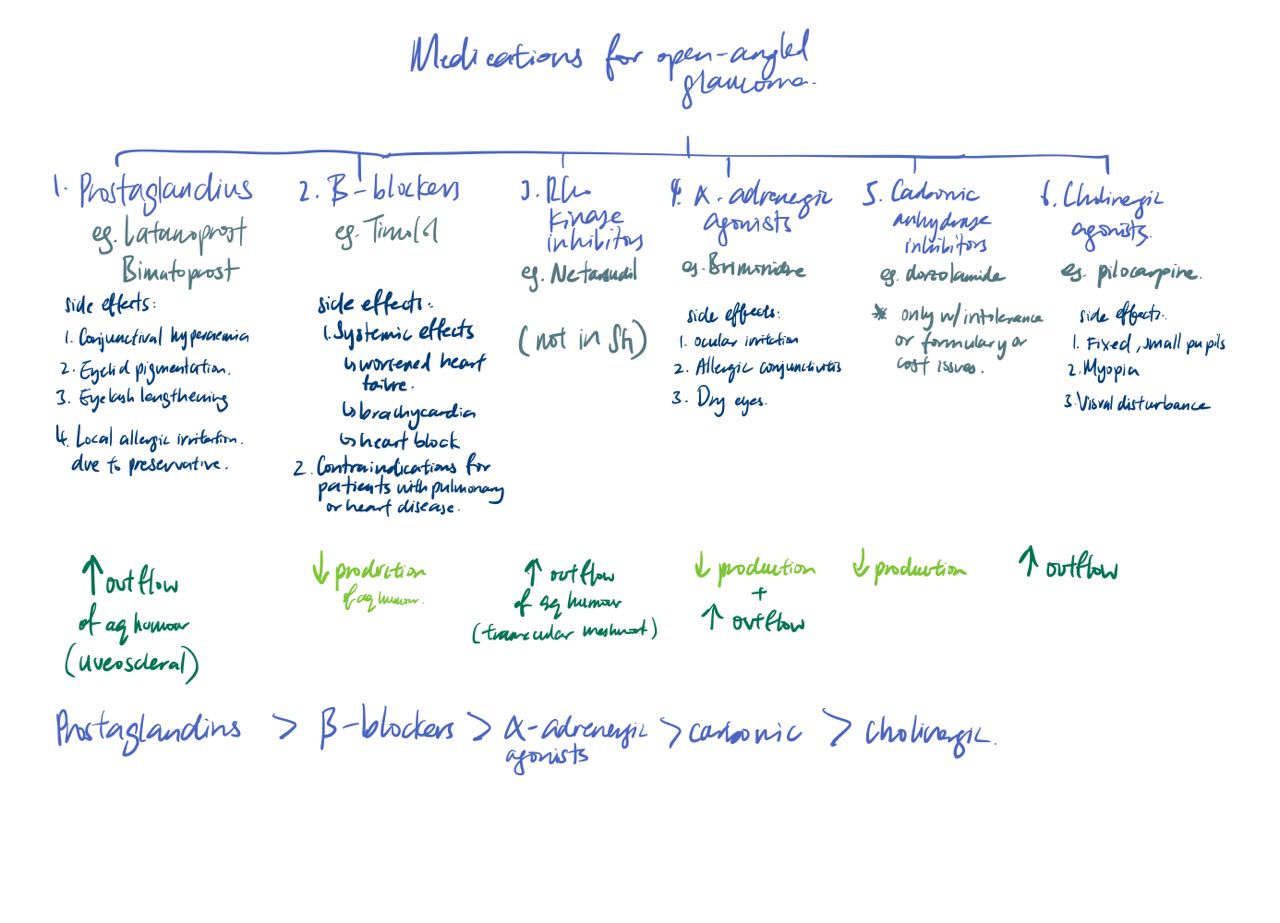 |
Others: Primary acute angle-closure glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, dry (atrophic) ARMD, wet (exudative) ARMD,
Device use:
A. Eye drops
1. Wash hands before applying any medication in the eye
2. Tilt your head slightly backward and look upward
3. Gently form a sac by pulling down lower lid using non-dominant hand. Press against the nose at the side of the eye using non-dominant
hand.
4. Squeeze the bottle of eye drop in the sac. Never touch tip of applicator to the eyelid or eyelashes to prevent contamination, applying more
than the recommended dosing of medication will not increase the efficacy of the medicine but may increase side effects.
5. Close the eye for about 1-2 minutes to allow absorption. Do not blink
6. Gently wipe away any excess liquid from skin around the eye with clean tissue
7. Wait for about 5 minutes between eye medications before applying the next eye drop
8. Wait for about 10 minutes between eye medications before applying the next eye ointment
9. Wait for about 15 minutes before wearing back contact lens
If patient uses eye drop dispenser,
1. Gently pull down your lower eyelid.
2. Tilt your head back and rest the eyepiece gently against the upper eye socket
3. Gently squeeze the dispenser to deliver drops into your eye.
B. Ointment (use at night)
1. Wash your hands with soap and water before you apply the eye ointments
2. Read the instructions on the label.
3. Sit with your head tilted backward and look up.
4. Using a finger, gently pull down the lower eyelid to form a pocket
5. Squeeze the ointment along the inside margin of the lower eyelid. Do not touch your eye with the tip of the ointment tube.
6. Gently close your eyes and keep them closed for 1-2 minutes. With a piece of tissue, wipe off any excess ointment from your eyelids and
eyelashes.
7. If you have to apply both eye drop and eye ointment, apply the eye drop at least 10 minutes before the ointment. Do NOT apply the
ointment first, this affects the absorption of the eye drop.
8. Your vision may be temporarily blurred after using eye ointment. Avoid activities that require good visual ability (e.g. driving) until your
vision clears.
● Store in a cool, dry place
● Keep the medicine out of the reach of children
● Do not keep expired medicines or medicines that are no longer needed. Discard your eye ointments 30 days after opening
2156 SKIN
Condition Explanation/Cause/Signs and symptoms Medication given Administration/Dosing/Device use/Counselling/SE ** teach back Non-pharmacological Monitoring |
Acne |
Atopic dermatitis Disruption of the outer layer of the skin/skin barrier caused by irritants or allergens → from a gene mutation? - dry, itchy skin w/ redness, swelling, crusting, oozing - common on hands and feet in adults → personal/family hist of atopic dermatitis → is there any atopic triad? 1. Topical corticosteroids → Hydrocortisone 1% (cream, ointment or lotion) = 1. 1 tube 15g (30 FTU) → Use 1 FTU (0.5g) → treats an area of skin the size of 2 hands 2. Avoid application on thinner region of the skin like face, eyelids and genital areas 3. Use for shortest possible duration + apply a thin layer → otherwise increase the risk of getting side effects 4.Do not bandage or cover the area unless instructed otherwise → may lead to more being absorbed and increase side effects 5. Common side effects: Redness, Steroid telangiectasia →dilation of capillaries (into clusters), Tinea faciei 6. If dose if missed, apply as soon as you remember. If it is near the time for the next application, only apply the usual amount. DO NOT apply extra ointment or cream to make up for missed application ● Aim to reduce the discomfort and restore the skin barrier ● Avoid any known allergens (food, cosmetics, dust mite etc) ● Avoid potential pollutants ● Loose-fitting clothes ● Advise against scratching that may increase risk of infections ● Use of emollients (Cetaphil) → Baseline: Basic therapy - morning before the flare, 2x a day at the peak, morning after the flare ○ Avoid the use of aqueous cream as it contains irritants ○ Using non drying, soap free products in the shower or moisturiser after showering ○ 2-3 times a day ○ Should use even when AD is dormant ○ Avoid irritants such as sodium lauryl sulfate (found in aqueous cream) ● Use of Suu Balm Menthol Cream to maintain skin barrier and reduce itch |
Cold sores Caused by herpes simplex virus - prodromal symptoms of itching, burning, pain or tingling symptoms 6-48 hours - trigger factors: stress, ill health, sunlight, viral infection and menstruation Goal of treatment: aim to resolve the condition 1. Topical acyclovir (Antiviral) cream
|
Psoriasis |
Relevant device use:
2152 GI
Condition Explanation/Cause Medication given Administration/Dosing/Device use/Counselling ** teach back Non-pharmacological Monitoring |
Oral ulcers 1. Single or small crops of ulcers that are typically found in the cheek, mouth or lips Oracort E paste, apply liberally 2-3 times a day |
Xerosstemia 1. Dry mouth from reduced or absent saliva flow 2. Could be caused side effects from drugs, disease 3. Signs and symptoms: difficulty swallowing, eating and wearing dentures, taste disorder, painful tongue.. Hydroxyethyl cellulose solution This medication will help to replace the moisture and lubricate the mouth |
PUD 1. PUD is where your stomach lining has an ulcer caused by an ulcer called H.pylori (an infection by bacteria that weakens the protective mechanisms of the stomach, allowing acid to get to the sensitive lining) /NSAIDs (when you take too much, it can cause damage to the lining and unable to be repaired) Common cause: NSAIDs and H.pylori Signs and symptoms: pain wakes patient up at night Goal of treatment: Eradicate the bacteria, relieving the ulcer disease, healing ulcer, preventing recurrence, reducing complications 2 weeks: PPI triple therapy (PPI OD/BD, amoxicillin 1g BD/metronidazole 500mg BD, Clarithromycin 500mg PO BD Or Bismuth quadruple therapy (PPI or H2RA OD/BD, metronidazole 250-500mg QDS, Bismuth Salicylate, Tetracycline 500mg QDS) Or Non-Bismuth Quadruple (PPI BD/OD 10-14 days, Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin, Metronidazole days 1-10) Goal of treatment for NSAID prone: Heal ulcers 1. STOP the NSAIDs 2. Omeprazole 20mg daily Bismuth, tetracycline Omeprazole: take 30 min before food (just on an empty stomach), sawllow whole Amoxicillin and clarithromycin: take tgt after food Avoid drinking milk tetracycline N/V, diarrhea Amoxicillin, tetracycline Metallic taste in mouth Clarithromycin, metronidazole Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation Levofloxacin Urine or stool discoloration, constipation Bismuth Abdominal pain, passing of gas, diarrhea, constipation PPIs N/V: take with, or after food except for tetracycline Diarrhea: drink more water Metallic taste: reversible upon discontinuing medication Constipation: take more fibre/fruits and drink more water Urine/stool discoloration: reversible upon discontinuing medication 1. Emphasise on the importance of taking the medications in its full course to kill the bacteria otherwise the infection might return or the bacterial resistance could occur such that the antibiotics won't work anymore. Ulcers also take time to heal hence you should not stop taking the medications even when the pain goes away. 2. Stress reduction Smoking cessation Dietary: avoid spicy foods, caffeine and alcohol Urea breath Follow up in 2 weeks |
GERD
Signs and symptoms: Heartburn, acidic sour taste in the mouth, regurgitation Complications; esophagitis, barette’s oesophagus, strictures, chronic cough.. Goal of treatment: alleviate or eliminate symptoms, decrease frequency of recurrence, promote healing of injured mucosa, prevent complications If frequent heartburn >2 days per week: 1. PPI (omeprazole 20mg OD) If episodic heartburn, 2. Antacids (Gavison liquid 2 5mL spoonfuls 4x a day, PRN) 3. H2RAs (Famotidine 20mg BD)
Try elevating the head of the bed, avoid certain foods that can cause lower esophageal relaxation, avoid foods that may have a direct irritant effect, stop smoking, eat smaller meals avoid sleeping immediately after meals Up to 2 weeks, follow up after 4 weeks for PPIs |
Dyspepsia (indigestion) 1. Symptoms in the gastroduodenal area (upper area or around the chest) 2. Usually followed by a sense of heaviness in the stomach after eating, epigastric pain or burning (location above the umbilicus) 3. Can be caused by many things e.g. H.pylori (have they been tested)?, spicy foods Trigger points: anorexia, loss of weight, persistent pain.. Goal of treatment: relieve the symptoms 1. Alginates 2.Antacids (Magtasil magnesium trisilicate → slightly slower. Constipation..?, Gaviscon tabs, liquid, double action + liquid) 3. H2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) (Ranitadine - 150mg) 4. Proton Pump inhibitors (PPIs) *liquids will have faster onset of action *take note if CVS patient cause sodium content to be known (like the double action one)
More than 2 weeks |
Nausea + vomiting
1. Dimenhydrinate tablets 50-100mg every 4-6h PRN **ASSOCIATED WITH SEDATION 2. Domperidone 10mg TDS 3. Scopolamine patch but POM ONLY 1. May experiences drowsiness, constipation, dry mouth ○ Changes in diet Restricting oral intake Rating small meals Avoiding spicy foods Eating bland foods Behavioural interventions Acupuncture Ginger and pyridoxine (especially for pregnancy) Biofeedback, chewing gum?, hypnosis, relaxation, yoga |
Constipation 1. Uncomfortable, infrequent bowel movement (<3x per week), feeling of incomplete defecation, straining.. 2. Likely caused by lifestyle choices i.e. poor diet, low fibre intake, lack of exercise, medications (Calcium carbonate, aluminium hydroxide, NSAIDs, antihistamines) (functional, slow-transit, pelvic floor dysfunction) Goal of treatment: relieve symptoms, reestablish normal bowel habits, improve QOL 1. Bulk forming agents (Methylcellulose) 2. Lactulose 3. Glycerin (suppository) 1. For bulk forming agents, it aids in increasing the water content of the stool. Some side effects would include diarrhoea. Lifestyle modifications: Dietary management (foods like whole grain, eat plenty of fresh fruits… prunes..replacing white rice with brown rice) , adequate hydration, fibre supplements, laxatives, exercise, timed bowel management |
Diarrhoea 1. Increase in frequency of stools for more than 3 times a day. Stools often appear pasty and liquidy 2. Can be acute, prolonged, persistent, chronic. Chronic can be caused by IBD, malabsorption syndrome.. Drugs like laxatives, NSAIDs, PPI 3. Or could also be caused by food poisoning which will have vomiting, a temperature.. Goal of treatment: Manage the diet, prevent excessive water/electrolyte/ acid-based disturbances, provide symptomatic relief, treat curable causes, manage secondary disorders 1. Loperamide (4mg, max 16mg/day + 1mg/5ml for liquid) 2. Diphenoxylate (2.5 - 5mg 3-4x daily) 3. Adsorbants (charcoal?) 1. Loperamide works by slowing down the contraction of the gut and allowing more water to be absorbed. Side effects would include dizziness and constipation 2. Diphenoxylate also slows down the contraction of the gut and helps to increase residence time that allows more water to be absorbed. Side effects include dizziness, constipation.. (do not take with alcohol) Fluid/electrolyte replacement (Repalyte) Drink more water Eat soft and more plain food BRAT diet - bland so doesn't aggravate the digestive system Avoid eating spicy/fatty food |
Ulcerative Colitis - Autoimmune-mediated intestinal inflammation where the inflammation is distributed continuously, involves the rectum and limits itself to colon Risk Factors: - Family history - Infection - NSAIDs - Stress - antibiotics S&S: - fever - Uveitis (Iritis/conjunctivitis) - Mouth ulcer - Abdominal pain - Large joint arthritis (asymmetrical) - Skin Rash (Erythema nodosum and/or Pyoderma gangrenosum) - Blood in stools + Anaemia Complication: - Pseudopolyps → regeneration of cells, but in a weird way - Toxic Megacolon - Perforation - Massive haemorrhage - Strictures - Carcinoma of the colon Goals of treatment: -Resolve acute inflammation -Relive extraintestinal symptoms -Resolve and prevent complication -Maintain in remission Algorithm: IF distal mild: oral sulfasalazine ↓dose(3-4wks) IF extensive mild/moderate: oral mesalamine/budesonide↓ IF moderate: budesonide MMX/prednisone ↓dose(8wks) IF no response: infliximab + azathioprine (good for remission) IF severe: methylprednisolone/hydro prednisone(8wk) + AZA IF no response: infliximab/cyclosporine IV PO +AZA/6MP IF INF cannot: vedolizumab -Low in FODMAPs food -Avoid wheat, diary products, artificial sweeteners |
Chron’s disease |
2153 CVS
Condition Explanation/Cause Medication given (the doctor has prescribed you with… this is to help you (goal of treatment)) Administration/Dosing/Device use (Have you used the device before? Do you mind if I teach you how to use it?) /Counselling ** teach back Non-pharmacological Monitoring |
HTN 1. HTN is when there is an increase in your blood pressure in your blood vessels 2. Is mostly asymptomatic but severe cases can have some symptoms of headache, visual changes, blurred vision.. 3. There are some risk factors like sedentary lifestyles, diabetes, stress 4. If poorly controlled, can lead to bad consequences such as stroke, visual loss, heart attack.. Goal of treatment: BP goal of <130/80 mmHg or <140/80 mmHg (if >65) 1a. ACEi e.g. Lisinopril 10mg OD 1b. ARB e.g. Valsartan 80mg OD 2. CCB e.g. Amlodipine 2.5mg OD or Nifedipine 3. Diuretics (DHPs) e.g. Hydrochlorothiazide ACEi counselling: 1. Dry cough as a side effect may be observed - please see a doctor if so 2. Side effects include CCB counselling: 1. Edema/Swelling may be observed which should go away after 2 weeks. Can elevate legs with a pillow or so. Diuretics counselling: 1. May have to go to the toilet more often because of its effects, it works by helping you pee out more water so that it reduces blood pressure 1. Restrict sodium intake which is cutting down foods like processed foods, fast foods and increase potassium intake like eating bananas and mango 2. Decrease alcohol intake to under 1/2 drinks a day 3. Would be beneficial to have moderate exercise of 150 mins a week 4. Measure BP 2x daily (see below) 5. Note if your BP exceeds >180/110 mmHg please go AnE 6. Some of these drugs may lead to hypotension so do note to stand up slowly to prevent fainting ACEi: 1-2w, renal panel (SCr,K), follow Q4 monthly
CCB: 2-4 weeks, PR control Diuretic: Monitor SCr and K, weight |
HF 1. Heart failure is a condition whereby your heart is unable to function optimally, and unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the demands of your body or is only able to do so when the blood pressure increases 2. However, this leads your heart to work too hard, and overtime it will make your heart muscles become stiffer and harder, therefore it is less efficient in pumping out your blood. 3. Risk factors: Hypertension, AF.. 4. Some signs and symptoms: increased swelling of legs.., sudden weight gain in a short period of time, dry hacking cough Goal of treatment: Improve QOL, relieve symptoms, reduce or prevent hospitalisations, slow progression of disease, increase survival TARGET HR: 50-70 1. ARNi > ACEi > ARBs 2. BB (+ivabradine if PR not at goal // +digoxin if concomitant AF) e.g. Bisoprolol, Carvedilol, Metoprolol, Nebivolol 3. MRA e.g. Spironolactone 4. SGLT2i e.g. Dapagliflozin or Empagliflozin (10mg OD - take note if diabetes then 25mg) 5. (if needed) Diuretics e.g. Frusemide (20mg BD), Bumetanide ACEi counselling: 1. Dry cough as a side effect may be observed - please see a doctor if so 2. Side effects include the dry cough ARNi counselling: 1. Monitor BP, may experiences dizziness, cough, lightheadedness BB counselling: BB work by reducing your heart rate and slows down the heart contraction. You may experience side effects of tiredness, fatigue and shortness of breath. You may also not see the effects until 3-6 months but it will get better! CCB counselling: 1. Edema/Swelling may be observed which should go away after 2 weeks. Can elevate legs with a pillow or so. Diuretics counselling: 1. May have to go to the toilet more often because of its effects, it works by helping you pee out more water so that it helps to treat fluid retention and reduces blood pressure. 2. May experience dehydration - avoid by consuming the amount of fluid specified by your doctor. 3. May also experience dizziness or lightheadedness - get up slowly from sitting or lying down to prevent this MRA counselling: 1. Side effects include gynaecomastia SGLT2i counselling: side effects of 1. Daily weight check (before breakfast) 2. Fluid restriction (1.2L bottle) 3. Sodium intake and salt substitution 4. As some of your medications cause an increase in potassium levels, eat less high K foods, can boil your veggies. 5. Take note of any sudden weight gain of 2-3kg in a day (pls inform doctor) 6. Use all drugs at the same time!! These are to ensure that you achieve the goals of treatment 7. Monitor BP 8. If you experience sudden weight gain, new worsening of dizziness, sudden increased swelling please go to the doctor (but dont worry these are rare SEs) At your next checkup in about 2-4 weeks, he will have to draw blood to ensure that the medications are working safely and effectively for you. (if given ARNI after ACE, wait 36h for wash out period) ACEi: 1-2w, renal panel (SCr,K), follow Q4 monthly
CCB: 2-4 weeks, PR control Diuretic: Monitor SCr and K, weight BB: BP, PR, clinical status. TCU in 2-4 months SGLT2i: SCr, BP. Follow up 2-4w (take note if any euglycemia ketoacidosis if diabetic) MRA: SCr, K, urea. Check 1w then 4w Monitoring is to ensure that the medications are working safely for you |
Hyperlipidemia (statins) 1. Hyperlipidemia is when you have high levels of cholesterol in your blood 2. This may be caused by family history (pri dyslipidemia) or others like obesity, diabetes, hypothyroidism, alcoholism (sec dyslipidemia) 3. Risk factors (overweight, obesity, DM, metabolic syndrome) 4. Poorly controlled hyperlipidemia can put you at risk of heart attack or stroke so it’s very important to take your medications even if you dont feel any symptoms Goal of treatment: Control blood cholesterol levels Medications: 1. Statins (Rosuvastatin 10mg ON or OM > atorvastatin ON or OM > Simvastatin > Lovastatin) !. Rosuvastatin or atorvastatin can be taken any time of the day 1. Statins: May experience some SEs like mild muscle aches, tenderness or weakness. , … please take note of more serious SEs (but are rare) if the muscle aches become more pain. 2. DDIs: Amiodarone, colchicine.. Please don’t eat any grapefruit, gemfibrozil, red yeast rice? 3. If you observe any severe muscle aches, and your urine is brown or tea coloured, light coloured stools, loss of appetite then please seek medical help immediately. Rare side effects 4. You can also lower your cholesterol levels 4 weeks TCU (will take 6-8w for effect) Baseline CK, lipid panel, LFTs |
Atrial Fibrillation 1. This is an when your heart has abnormal heart rhythms which means that the Goal of therapy: Rate control: Class II (BB e.g. atenolol, bisoprolol) OR Class IV (non-DHP CCB e.g. diltiazem, verapamil), Digoxin, Ivabradine Rhythm control: Class I and class III (amiodarone) Amiodarone: TFT, LFT, chest x ray, ECG and physical exam required @ baseline + !6 monthly |
Angina pectoris 1. Occurs when there are fat deposits in your blood vessels → forms what is called a ‘fatty plaque’. This narrows the blood vessel and reduces the supply of blood to the heart muscles. 2. Some risk factors: family hist, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, hypertension 3. May have experienced some signs and symptoms like squeezing chest pain, pain radiating to jaw, neck, shoulder, pain is relieved after rests of nitrates Goal of therapy: Reduce angina symptoms, reduce exercise-induced ischaemia, prevent CV events/stroke/death TARGET HR = 55-60 1. Sublingual GTN 2. (first line) BB (atenalol, bisoprolol 2.5-20mg or carvedilol) + DHP CCB (nifedipine 30mg-180mg OD) OR non DHP **not in HFrEF (verapamil 30mg-120mg TDS/QDS) 3. Nitrates e.g. Isosorbide mononitrate 60mg OD 4. Ivabradine (add on therapy if target HR not achieved) 5mg or max 7.5mg BD 5. Antiplatelet therapy (Aspirin 75-100mg/day or clopidogrel 75mg/day) 1.. BB/NDHP help to reduce your heart rate and muscle contraction to slow down overworked heart. They will also increase your oxygen supply through dilation of your blood vessels. (if verapamil - might have constipation, bradycardia, headache..) (DHP CCB will have vasodilated related) 2. Nitrates help by helping to increase the blood and oxygen supply. It helps to prevent or relief your angina symptoms. Some common side effects are headache, dizziness and hypotension. You may treat the headache with paracetamol if necessary. 3. Sublingual GTN: Use this medicine when there is a sign of angina attack. Preferably eat it while you are sitting. Place under your tongue and allow it to dissolve completely - this allows the drug to absorb faster and have a faster onset of action (5 mins) than your other medicines. Do not swallow or eat. If you still feel chest pain after 5 mins, please call 995 and use it otw. As for storage, keep it in a cool dry place and carry it with you where you go in a bag or purse to avoid keeping it near your body. Please only keep the bottle within 8 weeks of opening and then after that obtain a fresh supply. You can date the bottle if needed. - Diet: reduce intake of salt, reduce saturated fat intake, increase fruits and vegetables, less high in sugar food, less alcohol - exercise - weight reduction - smoking cessation (other management: influenza vax, body weight, diet, smoking cessation, hypertension, hyperlidpidemia) |
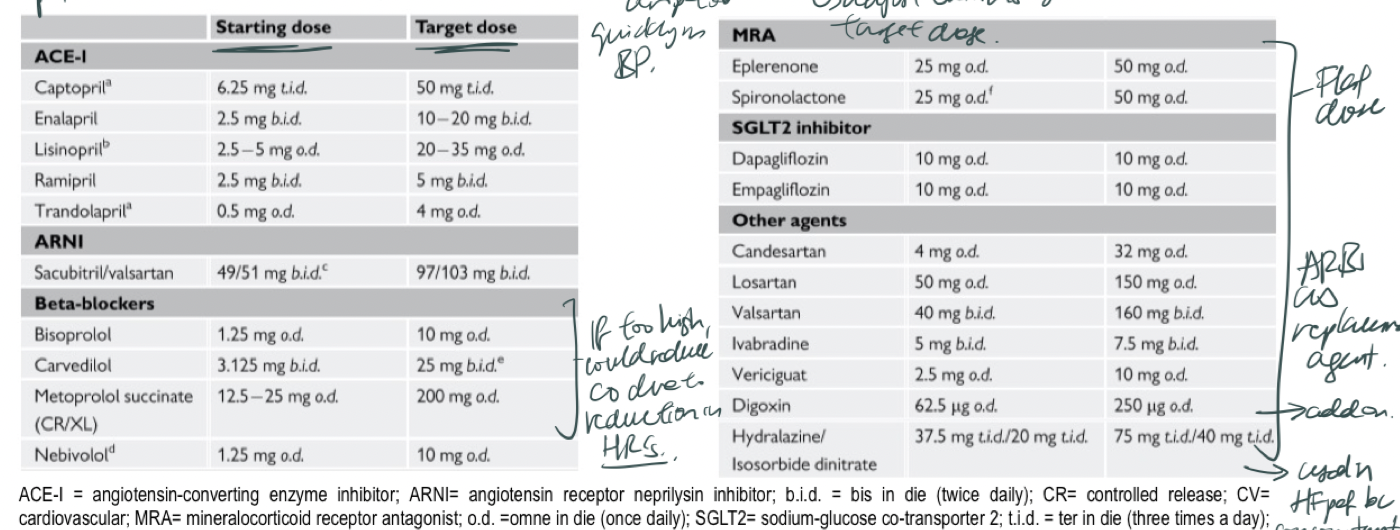
Heart failure^^
Angina ^^
BLOOD PRESSURE MACHINE
First i will be teaching how to set up your BP meter for your reading. You gotta put in batteries and attach the cuff to the BP meter monitor.
When taking a blood pressure reading,
Place both feet flat on the floor (do not cross your legs!!) and make sure youre wearing loose clothing
you can place the automatic machine on the table
you will have to place the bottom of the cuff, about 1-2cm above the bend of your elbow with the arrow pointing towards your inner elbow downwards.
Ensure that the cuff is at heart level and is also placed on bare skin and not over clothing.
Remember to wrap the cuff appropriately, so not too tight or too loose as it can give rise to inaccurate readings.
Then, press the “start button” to take the reading and wait for the machine to automatically calculate your blood pressure reading.
While taking your reading:
Remain still and relax, avoid talking as it can lead to inaccurate blood pressure readings
Have your back straight and supported against the chair
Legs and ankles uncrossed
Feet flat on the floor
Rest arms on the table
Take a second reading after 1-2minutes
Record the blood pressure readings immediately + date and time in your log sheet
It would be good to take 2 readings in the morning and 2 readings at night @ the SAME TIME EVERYDAY. BEFORE TAKING MEDICATIONS AND AFTER PEEING
Some things that may affect your readings: Avoid food, caffeine, alcohol, smoking and exercise 30 minutes before measuring (may artificially raise blood pressure), Avoid placing the cuff too tight or too loosely on your arm, avoid placing the cuff over clothing, which can artificially lower BP
Avoid rolling long sleeves up as it may falsely increase blood pressure
2154 RESPI
Condition Explanation/Cause (Layman terms) Medication given Administration/Dosing/Device use/Counselling ** teach back Non-pharmacological Monitoring |
Asthma 1. Having asthma means that your airways are inflamed so are more sensitive than the regular. 2. Signs and symptoms: Shortness of breath, cough, wheezing Risk factors: family members have asthma, eczema or allergic rhinitis - respiratory infections - Environmental factors Goals of treatment: (long term) → symptom control, risk reduction (minimise future risk of asthma-related mortality) 1. Maintenance “Controller” medications a. Low dose ICS-formoterol (Symbicort Turbuhalor - Budesonide + formoterol → 1-2 puffs BD with additional reliever doses up to max 12 puffs/day) OR Beclomethasone-formoterol (100mcg/6mcg) → 1 puff BD for maintenance and 6 puffs additional for reliever. Max 8 puffs per day 2. Reliever medications a. Rapid-acting inhaled B2-agonists (Ventolin MDI - containing salbutamol, 2 puffs PRN) B. ICS - formoterol C. ICS-SABA 1. This medication is called the controller medication which will help provide symptomatic relief and reduce the risk of exacerbations. You may experience symptoms of change in voice, different taste in your mouth, dry mouth or throat. It is important to take the required maintenance even if you miss the dose. 2. This second medication is supposed to provide your relief when you feel a flare up occurring. Do remember to take this with you wherever you go. You may experience some symptoms such as tachycardia, palpitations, headache and restlessness. The headache and dizziness should subside over time. Do check with your doctor if these symptoms do not go away. Avoidance of tobacco, physical activity (general health benefits , if aware that you have exercise-induced bronchospasm then you can use your ICS-formoterol 5-20mins before exercising), occupational asthma (work history), avoid medications that may worsen asthma (NSAIDs + beta blockers can exacerbate), vaccinations, remediation of dampness or mould |
Cerumen impaction 1. An accumulation of earwax in the ear 2. Risk factors (genetics, elderly, skin conditions like eczema, dermatitis, wearing hearing aids, inadequate bod hygiene) 3. Signs and symptoms: feeling of pressure/fullness, ear discomfort, NO PAIN!! 1. Docusate sodium 0.5% w/v apply 5-10 drops into the ear 1 time a day 2. Hydrogen peroxide 3% 1. It works by breaking down the ear wax and disperse it. May experience some hypersensitivity or allergy 2. Releases oxygen when exposed to oxygen and loosens the ear wax 1. Can use an isotonic seawater sp ray/wash?? Should resolve in 4 days |
Water-clogged ears 1. Accumulation and retention of water in your ear canals that leads to gradual hearing loss and sensation of fullness 2. Trapped moisture could weaken your immune system and increase risk of infection More likely if you have a lot of contact with water 1. Ear drops containing Isopropyl alcohol (95%) and glycerin Reduce water exposure -Wear shower/swimming cap -Wear ear plugs while showering -Tilt affected ear downwards and gently shake water from ears Should resolve in 4 days |
Common cold 1. Presented with cough, sore throat, nasal congestion… Explain + Cause: -Viral infection of upper airways by various viruses e.g. rhinovirus Transmission: - Hand contact - Breathing in large particle droplets from close contact with an infected person - Small particle droplets from airborne particles that stays in the air for 5hrs Patho: - Virus attaches to receptors found along your airway, they could cause damage to your hair-like structures on your cells. This releases signals to cause inflammation in your airways. Risk Factors: -Crowded spaces -weakened immunity(stress, sleep deprived, underlying medical condition) - smoking S&S: - Sore throat, runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion, cough -Last for 7-14 days -(rare) fever, muscle aches and pain Complications: -Acute rhinosinusitis -Acute otitis media -LRTI -Asthma, COPD exacerbation For symptomatic relief of runny nose: 1. H1 antihistamines e..g chlorpheniramine 4mg tabs, 1 tab 4-6 times a day if needed. 2. 2nd gen H1 antihistamines e.g. Fexofenadine 120mg 1 tab a day or Loratadine 10mg OD For symptomatic relief of congestion: 1. Topical decongestants nasal spray e.g. Oxymetazoline 0.05% nasal spray 1-2 sprays into each nostril 2-3 times daily 2. Nasal saline For oral combination: 1. Zyrtec-D cetirizine HCl 5mg Pseudoephedrine HCl 120mg 1 tab BDS (OM, ON) 1. Some side effects you may experience with this are drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, anticholinergic (dry mouth..) … take note if elderly, glaucoma patient. Avoid drinking alcohol. 2. Avoid drinking fruit juice with fenofexadine 3. This medication help you to relieve your congestion by constricting your blood vessels and reduce blood flow so that it reduces the mucus secretion. You may experience some side effects of skin irritation, burning, stinging or some dryness. Just dont use it too often. ALSO do not use for more than 5 days as it can cause rebound congestion whereby your congestion will actually get worse bc it may lead to inflammation of your nasal tissues. ALSO do not share this with others, point away from nasal septum. To reduce bothersome symptoms and boost immunity: - Drink more water - Adequate rest - Nutritious diet Prevent transmission of virus: - Practise good respiratory hygiene e.g. cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze - Practise Good Hand Hygiene e.g. wash your hands with soap, use hand sanitizers that contain 60-80% alcohol |
Acute cough Non productive cough: Dextromethorphan or codeine Productive cough Fluimucil 600mg |
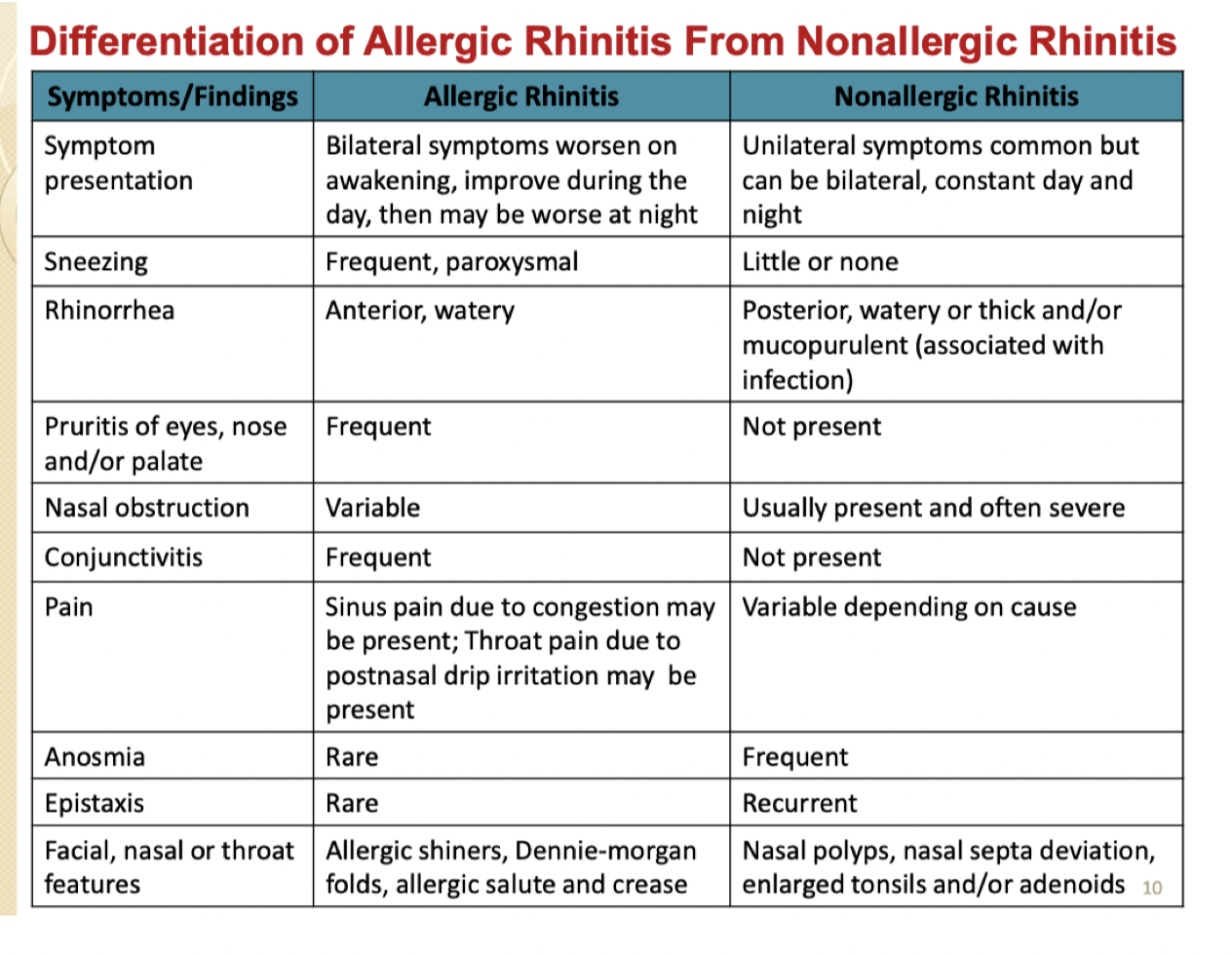
Allergic rhinitis |
COPD |
Not included: otitis externa, tinnitus
  |
Asthma
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
Where relevant | ||||||||||||||
|
Relevant device use:
Administration of Topical Decongestant Nasal Sprays / intranasal Steroid Sprays
1. Wash your hands well with soap and water.
2. Remove the packaging from the nasal spray pump.
3. Some nasal sprays need to be primed before use. As well, some nasal sprays need to be shaken. If your spray needs to be primed before using, squeeze it a few times into the air as directed until a fine mist appears.
4. Gently blow your nose to clear your nostrils
5. Tilt your head forward, depress one nostril, insert the tip into other nostril. Aim the nozzle away from the middle of your nose, and gently squeeze the nozzle. Inhale gently and breathe out through the mouth after each spray.
6. If more than 1 spray is required per nostril, alternate the spray between nostrils one by one to prevent medication wastage.
7. Put the cap back onto the nasal spray container.
8. Try not to blow your nose for several minutes after using the spray to ensure that your medications are well absorbed
9. Do not use for more than 5 consecutive days to prevent rebound congestion (FOR DECONGESTANT NASAL SPRAYS)/ If taste of medication is present, rinse mouth after use (FOR STEROIDS)
ADMINISTRATION OF EAR DROPS
1. Wash hands well with soap.
2. Carefully wash and dry the outside of the ear with a damp washcloth, taking care not to get water in the ear canal
3. Warm the eardrop bottle to body temperature by holding it in the palm for a few minutes. This will make the eardrops more comfortable to instill.
4a. Tilt head to the side opposite the affected ear. Gently pull the top of the ear upward and backward to open the ear canal.
4b. For children under three, gently pull the bottom of the ear backward and downward to straighten the ear canal.
5.Open the ear drop container carefully. Position the dropper top near, but not inside, the ear canal opening. Do not allow the dropper to touch the ear to prevent contamination.
6.Place the recommended number of drops into the ear canal. Replace the cap on the container.
7. Keep the head in the same tilted position for a few minutes after instillation
8. Regain normal position, gently wipe excess medication off the outside of the ear using a clean tissue. Do not clean the inside of the ear canal!!
9.Wash your hands to remove any medication
If you are instilling drops into both ears, wait 5-10 minutes between ears to allow the ear drops to run into the ear canal.
INHALERS
If first time use:
The inhalers each contain a set dose of medication and aim is to get the drug into the lungs
Introduce key landmarks of an inhaler eg dose counter + priming: for first time and after 5-7 days of no use
Show them the metered dose / remind them to keep track if non-metered. When it drops to 20 and below, make sure there is a new inhaler on standby.
Metered-dose Inhaler (MDI) - Ventolin (SABA), Atrovent (LAMA), Symbicort Rapihaler (ICS-LABA), Symbicort Evohaler (ICS-LABA), Seretide Evohaler (ICS-LABA))
Without Spacer With Spacer |
Preparing the device
*Prime the inhaler before first use, or if not used for several days by spraying 2 puffs into the air (cont’d from w/o spacer)
|
Administering a puff
*If need 2nd puff, wait ≈1min b4 repeating steps to administer a puff
*NO NEED to take the spacer out of your mouth to exhale *If need 2nd puff, release another puff after 1min. Only one puff into the spacer each time |
What to do after administering the dos
*After using corticosteroid containing inhalers, rinse your mouth with water, gargle and spit (do not swallow the water)
|
Cleaning
*Wash 1x/ week
*Wash 1x/ month ✗ scrub/ place breathing valve directly under running water ✗ wipe dry with cloth (∵↑static in plastic container, may affect amt of medication received) ✗ rinse spacer as detergent ↓static charges |
Avoid:
✗ Hold inhaler upside down
✗ Press inhaler >once at a time
(↓solved with spacer)
✗ Press inhaler too early/ late
✗ Open mouth when jet of inhaled medication hits the back of your throat
✗ Not inhaling deeply/ holding your breath long enough
Dry Powder Inhaler (DPI) - (Accuhaler, Elipta, Turbuhaler)
Preparing the device
*Prime the inhaler before first use, or if not used for several days (Twist base as far as possible in 1 direction, twist it back in the opp direction until u hear a click. Repeat again. Inhaler is now ready for use) 🡪
✗ DO NOT shake inhaler ✗ DO NOT invert inhaler aft loading a dose |
Administering a puff
*If need 2nd puff, wait ≈ 1min b4 repeating steps to administer a puff |
What to do after administering the dose
*After using corticosteroid containing inhalers, rinse your mouth with water, gargle and spit (do not swallow the water) to avoid oral thrush ✗ wash with water; keep inhaler dry |
Smoking Cessation:
(Patch)
- Wash hands
- Clean area that you will be placing patch on
- Do not apply oil, lotion on skin before putting on the patch as it may prevent it from sticking properly
- Remove patch from the sachet and peel one part of the silvery aluminium backing away. Avoid touching the sticky part with your fingers
- Carefully apply the sticky part of the patch to the chosen area of skin, somewhere with less hair like chest, thigh, hip, and peel off the remaining half of the silvery backing foil
- Do not place it on skin that is red, cut or irritated
- If take BP daily, do not put on upper arm
- Press the patch firmly onto the skin with your palms or fingertips
- Run your fingers around the edge of the patch to ensure that it sticks firmly
- Apply patch when you wake up and remove it the next morning (24h patch) OR 16h later at bedtime (16h patch)
- 16h patch: If you forget to remove the patch the night before, continue treatment the next morning by removing the old patch and apply the new one
- If sleep disturbed, remove patch before sleeping. Use 16h patch
- Can shower/swim even while using patch. If it drops, replace with new one but unlikely to happen as it is very adhesive
- When disposing it, fold it into half with the sticky side inwards and throw it away such that it is away from the reach of children and animals
- Place new patch at different site to reduce skin irritation
(Gum)
- Chew a piece of chewing gum when feeling the need to smoke
- First, place a gum in the mouth and start chewing. Chew until a strong taste or mild burning sensation is experienced (~1min, 10 chews)
- Then stop chewing and rest the gum between the cheek and gums until the taste and/or sensation have disappeared (~1min)
- This is because the chewing action releases nicotine, and chewing is paused to allow the nicotine to be taken through the mouth. Swallowing the nicotine is not beneficial and it can irritate your throat or stomach if ingested, causing side effects like nausea, hiccups
- Once it is gone, then chew again slowly and repeat
- The gum should be chewed for a total of 30min, including pauses
- Do not eat or drink 15min before or during use
(Lozenge) suck to release peppery taste. Park between cheek and gum. Resume sucking when taste fades. Do not chew or swallow. Repeat ~30min then discard. No food or drinks 15min before or during use
- Use 1 lozenge when urge to smoke occurs. Do not use more than 1 lozenge at a time. Do not use more than 1 lozenge per hour as it can cause more side effects
- Suck the lozenge to release peppery taste
- Once the taste is strong, place it between the cheek and the gum
- Resume sucking when taste fades
- Repeat for ~30min then discard
- Do not chew or swallow them like other lozenges
- Do not eat or drink 15min before using lozenge as it can decrease nicotine absorption thus making it be ineffective
- Duration of treatment:
- Instruction for missed dose (where relevant):
- Storage instructions: cool dry place
2155 RENAL HEPATIC
Condition Explanation/Cause Medication given Administration/Dosing/Device use/Counselling ** teach back Non-pharmacological Monitoring |
CKD-associated anemia Goal of treatment: 1. Epoetin Beta (Recormon) → 40 units/kg, 3x per week 1. Expectations: will take about 7-10 days for medicine |
CKD-MBD Hyperphosphatemia |
CKD-MBD
|
CKD-anemia
[NOT IN RUBRICS] Diagnosis Your doctor has diagnosed you with anemia, meaning that you have a low red blood cell count in your body. The kidney plays a role in making new red blood cells and when the kidney is damaged, it can no longer make red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen and when you have low amounts of it, you might feel a little more tired than normal. Not to worry, there are treatments for this such as what you have been prescribed. |
*Name/dosage form/strength Your new medication is an injection known as epoetin beta, also known as Recormon. It helps your body produce more red blood cells and you won’t feel as tired as before. The strength is 4000 IU and it is given via SC/IV injection. |
*Purpose/benefit/onset |
*Dosing/administration instruction Dosing for HD patients:
Dosing for PD or pre-dialysis patients
To inject it, use your thumb and index finger and pinch about 5cm of skin in your stomach/thigh and inject (number of syringe) into the skin. |
*Duration and quantity dispensed Recormon has been prescribed for 1/2/3 months and there will be (number) syringes in total. |
*Assess and address possible non-adherence (as relevant) It is important to take this medication even if you do not feel anything as production of red blood cells is an ongoing process and this medication helps it |
*Advice on missed dose (as relevant) If you miss your dose or forget to inject your medication, inject it as soon as you can. However, if it is almost time for your next injection, wait until then and skip the missed injection. Do not double your injection to make up for a missed injection. |
*Appropriate storage (as relevant) This should be stored in your refrigerator at 2-8°C but do not freeze and protect from light |
Are your following me so far? |
*Common SE and ways to manage (as relevant) Some side effects include increased in BP, stomach upset, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, shortness of breath and headaches
|
*Rare but serious SEs requiring immediate medical advice and ways to manage (as relevant) Painful, swelling redness of legs, slurred speech, vision changes, chest pain: if any of these occurs, seek medication immediately. These may sound scary, but I would like to assure you that these side effects are very rare |
*Interactions (DDI/supplement/food) (as relevant) Poorly controlled hypertension |
*Monitoring parameters (as relevant) Measure Hgb every 1-2 weeks following initiation/dose change After target stable Hgb and EPO dose, monitor Hgb at least monthly (HD), every 3 months (other CKD patients) -> this also means that when you come back to see the doctor, you will be doing blood tests |
[NOT IN RUBRICS] Non-pharmacological management No specific ones for anemia, but for CKD:
|
Station 3: Medication management and calculation
Main dispensing label Title: Brand name, pack size, total quantity dispensed, active ingredients and strength Body: Dosing instruction (dose, frequency, route, duration), Pertinent administration instructions (e.g. before or after food) Others: Patient name (ref. no.) Date dispensed (expiry date) |
Precautionary Label(s)
External Internal |
For external use only (dermatology) This medicine may cause drowsiness & may increase the effects of alcohol. If affected do not drive a motor vehicle or operate machinery. |
Shake the bottle (suspensions) Shake the bottle |
Store in a cool place (< 30˚C) Store in a cool place |
Not to be taken (non-oral) Sip & swallow slowly (linctus) |
Not to be taken in large quantities (mouth gargle) |
For nasal/ rectal/ vaginal use only |
To note:
Days: 4 weeks = 28 days and 1 month = 30 days
Eye drops: Discard after 28 days, indicate expiry labelled on formulary BUT must write ‘discard unused eye drops 4 weeks after opening’, AND 1 drop = 0.05ml, so 20 drops = 1 ml AND not to be taken orally
Dermatological products: “For external use only”
Label Examples
Eye drops Non-oral, gels, creams, suppositories etc. |
4 Xalatan 0.005% Eye Drops (2.5mL/ bottle) Latanoprost 0.005% (1.5mg/ drop) Instil 1 drop into the RIGHT eye ONCE every night. Discard unused eye drops 4 weeks after opening. Name: Kent See Date: 10/02/2022 Ref no.: 103 Expiry date: 08/12/2024 Precaution labels:
2 Dermasone 0.1% Cream (15g/ tube) Betamethasone Valerate 0.1% w/w Apply a thin layer to the affected skin TWO times a day for 2 weeks, then when necessary (when eczema flares). Name: Yang Yang Date: 10/02/2022 Ref no.: 103 Expiry date: 10/11/2024 Precaution labels:
|
1 Voltaren (Diclofenac) Emugel 1% gel 50g/tube Apply and massage on the left knee three times a day, when required to relieve pain. Name: John Payne Date: 20/01/2022 Ref No.: TOP-NSAID-1 Exp Date: 30/01/2024 Precaution labels:
|
112 KefenTech Plasters (Ketoprofen 30mg/patch) Apply 1 patch to each knee two times a day when necessary to relieve pain, for 4 weeks. Name: Yang Yang Date: 10/02/2022 Ref no.: 103 Expiry date: 10/11/2024 Precaution labels:
|
Inhalers Tablets |
1 Ventolin 100mcg Evohaler (200 actuations/ inhaler) Salbutamol 100mcg/ actuation Inhale 1-2 puffs by mouth THREE times a day/ every 4-6 hours, when necessary, to relieve shortness of breath Name: Chin Chia Chuan Date: 15/03/2023 Ref no.: 103 Expiry date: 31/08/2025 60 Singulair 4mg Chewable Tablets Montelukast (4mg/ tab) Take 1 tablet by mouth, ONCE every night. Chew the tablet before swallowing. Name: Brandon Lee Date: 15/03/2023 Ref no.: 103 Expiry date: 31/09/2026 |
2 Anoro 62.5/25mcg Ellipta (30 puffs/ellipta) (Umeclidnium 62.5mcg, Vilanterol 25mcg/Puff) Inhale 1 puff by mouth once in the morning for 2 months. Do NOT shake the ellipta. Name: Beh Chuan Kui Date: 29/03/2025 Ref no.: 90/01 Expiry date: 31/07/2025 Liquids |
1 Pulmicort Turbuhaler 100mcg Evohaler (200 actuations/ inhaler) Budesonide 100mcg/ actuation Inhale 1 puff by mouth TWO times a day for 2 months. Rinse mouth with water after each use Name: Tan Xiao Ming Date: 15/03/2023 Ref no.: 103 Expiry date: 31/10/2025 2 Nurofen suspension Ibuprofen (60mL/bot) Ibuprofen 100mg/5mL Take 7.5 mL every 6 hours as required for fever Name: Xiao Hai Zhi Date: 20/01/2022 Ref No.: DISP1-Case-4 Exp Date: 30/01/2024 Precaution labels:
|
TO NOTE:
Dosing Frequency
Abbreviation Meaning |
O/ QD Once a day |
BD Twice a day |
T/ QDS Three/ four times a day |
OM/ N Every morning/ night |
EOD Every other day |
h. s. At bedtime |
a./ p.c Before/ after meals |
(numeric) H hourly |
prn. When required |
o.d./ s. Right/ left eye |
Duration of use
Abbreviation Meaning |
3/7 3 days |
2/52 2 weeks |
7/12 7 months |
Administration instruction
Action Dosage form |
Take Tablet/ capsule |
Swallow whole, do not chew Timed/ sustained release |
Chew before swallowing Chewable oral |
Put under tongue Sublingual tablet |
Suck Lozenge |
Dissolve … in water before taking Effervescent tablet |
Administer puff/ spray Oral inhaler/ nasal spray |
Instil drops Eye/ nose/ ear drops |
Insert Suppository/ pessary |
Inject SC insulin |
Station 4: MTM and pharmaceutical care plan (PCP)
Patient’s Information:
Name
Age
Gender
Race
Subjective:
Chief complaint (CC): (what brings the Pt to the clinic, symptoms that pt reports with)
History of Presenting Illness (HPI): (location, when did it start, aggravating or remitting factors, anything that has been done)
Past Medical History:
(ONLY if diagnosed)
Patient Medication List:
Includes includes POM, P, GSL, vitamins, supplements, herbal products + compliance, adverse effects
Allergies:
Social History:
Family History:
Objective:
Include only those pertinent to the assessment & plan of the patient encounter
Examples include:
Observations – appearance of lesion, location of pain, pallor etc.
Weight, height, vital signs
Other relevant physical exam findings
Diagnostic tests
Lab results
Serum drug concentrations
Include:
ROS
E.g. HFrEF might have abnormal lung sounds?
Lab findings
(write as a trend like LDL…. (date 1) then LDL…. (date 2)
Relevant baseline parameters
Notes:
Check if the medications are causing the abnormalities?
↑K: CKD, MRA, ACEi, ARB, ARNi
↓K: Diuretics, Digoxin
↑SCr(kidney): ARNi, fenofibrates
↑CK(muscle): Statin, alcohol, seizures, rigour Activ., massage, glucocorticoids, colchicine, some antiretrovirals(HIV)
↑transaminase: Amiodarone, Statins, fenofibrates
CKD indicators: hyperK/P/Mg, increased protein & albuminuria, ↑SCr, BP, and DECREASED GFR CrCl, Hgb, iron stores.. (might have some complications like CVD, malnutrition, anemia..congestion)
Goals for CKD management: slow down progression of disease, maintain fluid and electrolyte homeostasis, provide adequate nutritional and metabolic support, prevent and treat extra-renal complications, reduce morbidity and mortality
Goals for CVD in CKD: Lower BP, reduce risk of CVD, slow progression of CKD → smoking cessation, (HTN, DM and dyslipidemia management), lifestyle + diet modifications. TARGET: SBP < 120 mmHg, start RASi if A2/3
Metabolic acidosis when CO2 < 20-22 mmol/L, start sodium bicarbonate 500mg PO
Starting ESA when Hgb < 10g/dL consistently
PUD indicators objective tests?: Urea breath test, antibody detection, culture results. Histology, physical exam
Assessment:
Assess and prioritise patient’s current issues – whether there are existing drug-related problems (DRPs) to resolve, whether the patient’s medical condition is at agreed goals of therapy, and/or whether there are potential DRPs to anticipate and prevent.
Can include what worked, or what didn’t work eg if patient has started on lifestyle modifications but now start on drug therapy, can say lifestyle modifications didn’t work
Goals of Therapy: (look at Patient counselling notes)
As agreed with the patient. Goals set should be SMART (specific for each indication, measurable and/or observable, achievable, realistic and within a time frame)
Plan:
WRITE BY CONDITION:
Treatment recommendations – Both pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic (according to priority of patient’s issues)
Monitoring parameters
Monitoring safety and efficacy
Be specific in monitoring what
Patient counselling if needed
Follow-up:
To check effectiveness and safety of therapy
Include time to return for review and any relevant tests required (refer to monitoring parameters
Examples:
Patient information Jessica Chan 28y/o Female Chinese |
Subjective Chief complaint (CC): worsening acne vulgaris for the past 2 weeks History of Presenting Illness (HPI): long standing acne vulgaris on her face since teenagers years with moderate scarring, maintained on EPIDUO. Reported new papules and pustules spreading to her shoulders and back in the last 2 weeks, accompanied by more papules and pustules pn her face. She has been applying EPIDUO to newly affected areas on shoulders and back with minimal improvement. Patient believes to be related to increased stress from starting new job |
Past medical history Acne vulgaris GERD |
Patient medication list EPIDUO topical gel apply to affected areas once daily TUMS Regular strength 2 tablets PO PRN |
Allergies NKDA |
Social history Does not smoke or drink alcohol |
Family history NA |
Objective Physical exam is normal except for numerous papules and pustules on face, shoulder and back which appear red and inflammatory |
Assessment 1. Acne vulgaris - Applied EPIDUO to newly affected areas on shoulders and back with minimal improvement (Worsening symptoms on epiduo) - Starting Doxycycline 200mg PO BD but dose higher than recommended 2. GERD - Well controlled on TUMS prn |
Goals of therapy Reduce the papules and pustules on the face, shoulders and back Reduce or minimize scarring on the face |
Plan
Recommend to start on Doxycycline 100mg PO BD instead of 200mg Administration: take with water after food Managing side effects: use sunscreen Non-pharm: relieve stress by doing breathing exercises, eat less high in sugar food, do not touch or squeeze the papules and pustules, cleanse face 2 times a day Monitor: improvement in papules and pustules on face, shoulder and back, side effects e.g. photosensitivity of skin
Continue on TUMS Regular strength 2 tablets PO PRN Non-pharm: eat less spicy/fatty/acidic food, avoid eating food 3 hours going to bed,eat smaller meals and elevate the head end of the bed Monitor: maintenance of low or no symptoms |
Follow-up Return to clinic in 3 months after starting doxycycline |
Patient information Mr Don Wan Yoke 52 Male Chinese |
Subjective Chief complaint (CC): Hypertensive emergency – severe headaches and dizziness, raised SCr, presenting BP 180- 200/100mmHg History of Presenting Illness (HPI): Feeling down due to losing his job. Developed persistent dry cough, looked up the internet and figured it was his ramipril. While at it, looked up on nifedipine LA and saw that it could cause “lower limb swelling”. As he was busy job hunting, he did not want “anything to get in the way of finding another job”. Furthermore, his company doctor prescribed him proprietary Adalat LA and Tritace which he felt was expensive. He stopped both his medicines because he “felt fine” a week back. Developed headaches and dizziness about 2 days ago and decided to come to A&E because it was affecting his ability to concentrate on driving his two young children around. |
Past medical history Hypertension |
Patient medication list Nifedipine LA tablet 30mg PO OM Ramipril tablet 5mg PO OM |
Allergies NKDA |
Social history Married, 2 children aged 10 and 12yo, lives in a 5-room HDB flat. Wife works as a personal assistant to a director in an NMC. 52yo technician who has been in events and sound-mixing since graduating from polytechnic. Smoker, and started taking approximately 6 cans of beer a week. |
Family history Nil |
Objective Creatinine was slightly raised No brain bleed on CT brain scan BP since admission 180–200/100mmHg RP SCr 156 micromol/L (elevated) , K 4.0mmoL/L, Ca (total) = 1.80 mmoL/L |
Assessment
|
Goals of therapy
|
Plan Pharmacological Management:
Non-pharmacological management:
Monitoring parameters: BP, SCr, K Patient counselling: ensure patient understands what HTN is and complications that can arise from it take note of SDM |
Follow-up Check BP, aim to lower to 140/90mmHg within 1 month Ensure no significant side effects such as angio-edema |
Patient information Tammy Lim 52 y/o Female Chinese |
Subjective Chief complaint (CC): No chief complaint History of Presenting Illness (HPI): diagnosed with hyperlipidemia for newly diagnosed hyperlipidemia in nov 2021 then adopted dietary lifestyle modifications, comes today for repeat lipid panel and consultation |
Past medical history Hyperlipidemia Type 2 Diabetes mellitus |
Patient medication list Metformin tablet 500mg PO TDS |
Allergies NKDA |
Social history do not smoke or drink alcohol |
Family history NA |
Objective LDL is 3.6 mmol/L which is higher than target of 2.6mmol/L AST and ALT are normal CK is normal Physical exam is normal |
Assessment |
Goals of therapy Reduce LDL to target of <2.6mmol/L |
Plan
|
Follow-up |
Patient information |
Subjective |
Past medical history |
Patient medication list |
Allergies |
Social history |
Family history |
Objective |
Assessment |
Goals of therapy |
Plan
|
Follow-up |
Patient information |
Subjective |
Past medical history |
Patient medication list |
Allergies |
Social history |
Family history |
Objective |
Assessment |
Goals of therapy |
Plan
|
Follow-up |