The Political Economy of Sports Media
Commodification of Sport
Our premise: Sport is a Commodity
Commodity - a product that is bought and sold
Commodification - the process of turning something into a product that can be bought and sold
Throughout this class, we will analyze how commodification influences different aspect of sport and the consequences of the commodification of sport
Media is the main form through which sport has been commodified
In the “Golden Age of Sport” (post WW1/1920s), the modern American sports industry emerged with sport celebrities such as Babe Ruth, Jack Dempsey, Red Grange and Knute Rockne
Their popularity was intensified by the new forms of sports media, exuberant prose of sports journalists, and the efforts sports promoters
How did we get here?
Historically, sport was a source of popular content as media evolved
As advertisers would spend money to reach sports consumers, media companies paid right fees to broadcast events
Simultaneously, media interest and hype generated broader consumer interest in sport
Athletes are brands
Media Sport
We will analyze the individual elements and the relations between them
We will focus on media sport INSTITUTIONS (production), TEXTS (products), AND AUDIENCES (consumption)
Mediasport → a compound word that captures the unavoidable connections between concepts
What is Media?
Media → the platform/technology for disseminating/communicating information (ideas, thoughts, values, and/or feelings)
Traditional Mass Media:
Print
Cinema
Broadcast
“New” Mass Media:
Digital Platforms
The Reithian Principles of [public service] Broadcasting
Media should do three things
Inform
Educate
Entertain
Entertain → maximize audience ; broadcast and advertising revenues
Mediasport Responsibilities
Inform and Educate = ethical “public” duty
Entertain = commercial “corporate” duty
Media differs from other commodities
No content is not an option
The cynical yet widely-held perspective
Commercial media has very little commitment to quality, credibility, or even accuracy
Rather, its primary aim and function is to create, then monetize audiences
This is accomplished through the production of popular/entertaining/profitable content
The Mass Media’s Interest in Sport
Sage:
Merely a means for profit making
Media are advertisements which carry news, features and entertainments in order to capture audiences for advertisers
Media’s job is to sell audiences to advertisers
Sport + Audiences = Corporate Advertising
“TV is now merely a delivery system for football”
Football audiences to corporate advertisers
The broadcast networks subsequently pays the NFL for the rights to deliver NFL entertainment
CAPITALISM has influenced and changed sport in a number of different ways, and this week examines the process through which capital is generated through sport
Late Capitalism
Theoretical Framework: Political Economy
Political economy in interested in examining the relationships between political institutions, economic systems, and broader social structure
Political economy = The intersection of politics and economics
Politics → various practices surrounding the structures, processes, and systems by which people are governed (on a macro or micro scale)
Economics → resources are produced, used and/ore managed in reproducing and shaping lives
Allows for a greater understanding of power relationships under capitalism
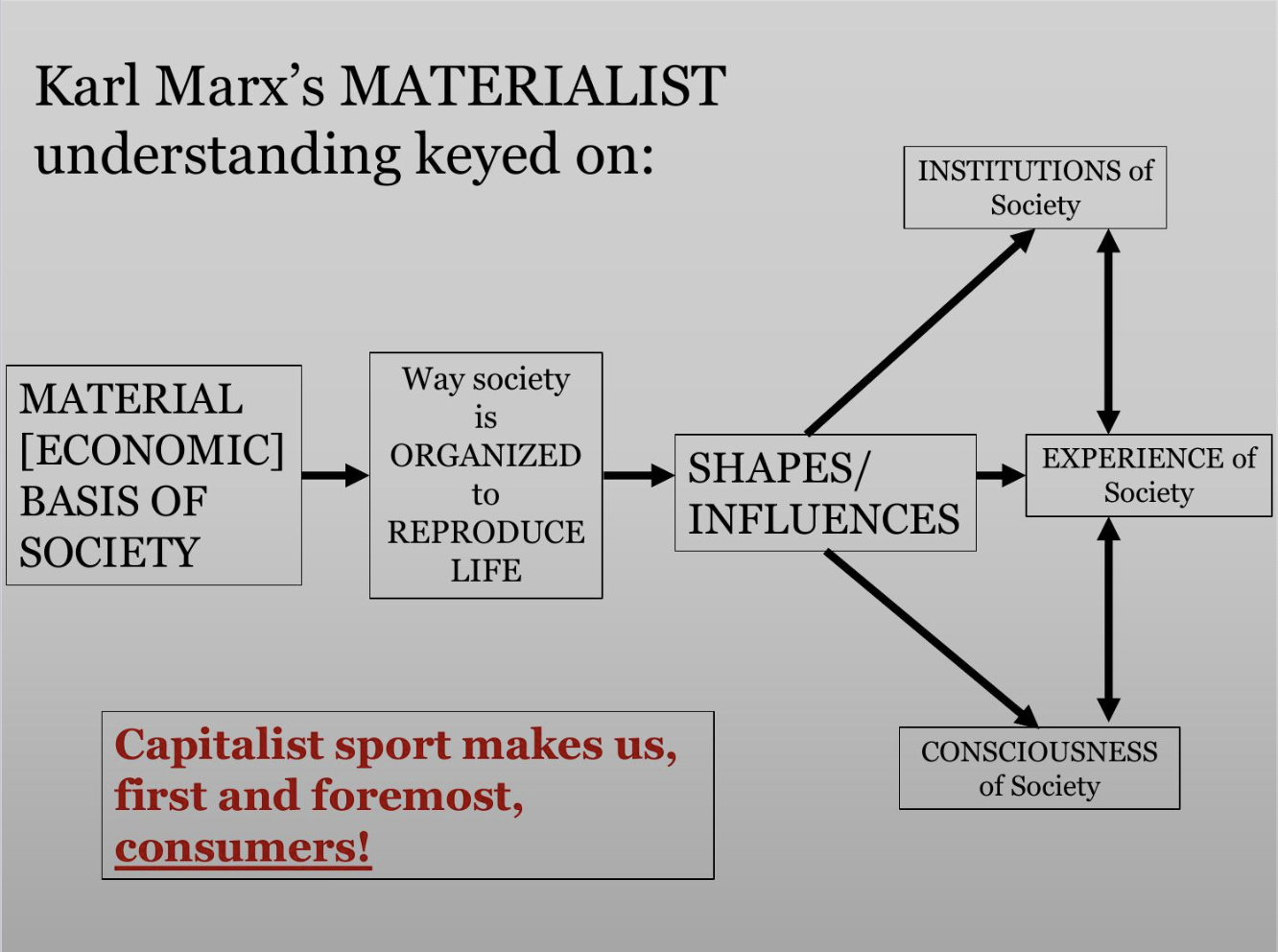
Karl Marx
Karl Marx’s theories form the basis of the sociological imagination, and for analyzing any form of power in society: “What they are, therefore, coincides with their production, both with what they produce and with how they produce. The nature of individuals thus depends on the material conditions determining their production”
Marx’s Key Argument: A society’s economy directly shapes its other elements (culture, politics, art, religion, sports, etc)
Put more simply → economic power shapes everything else
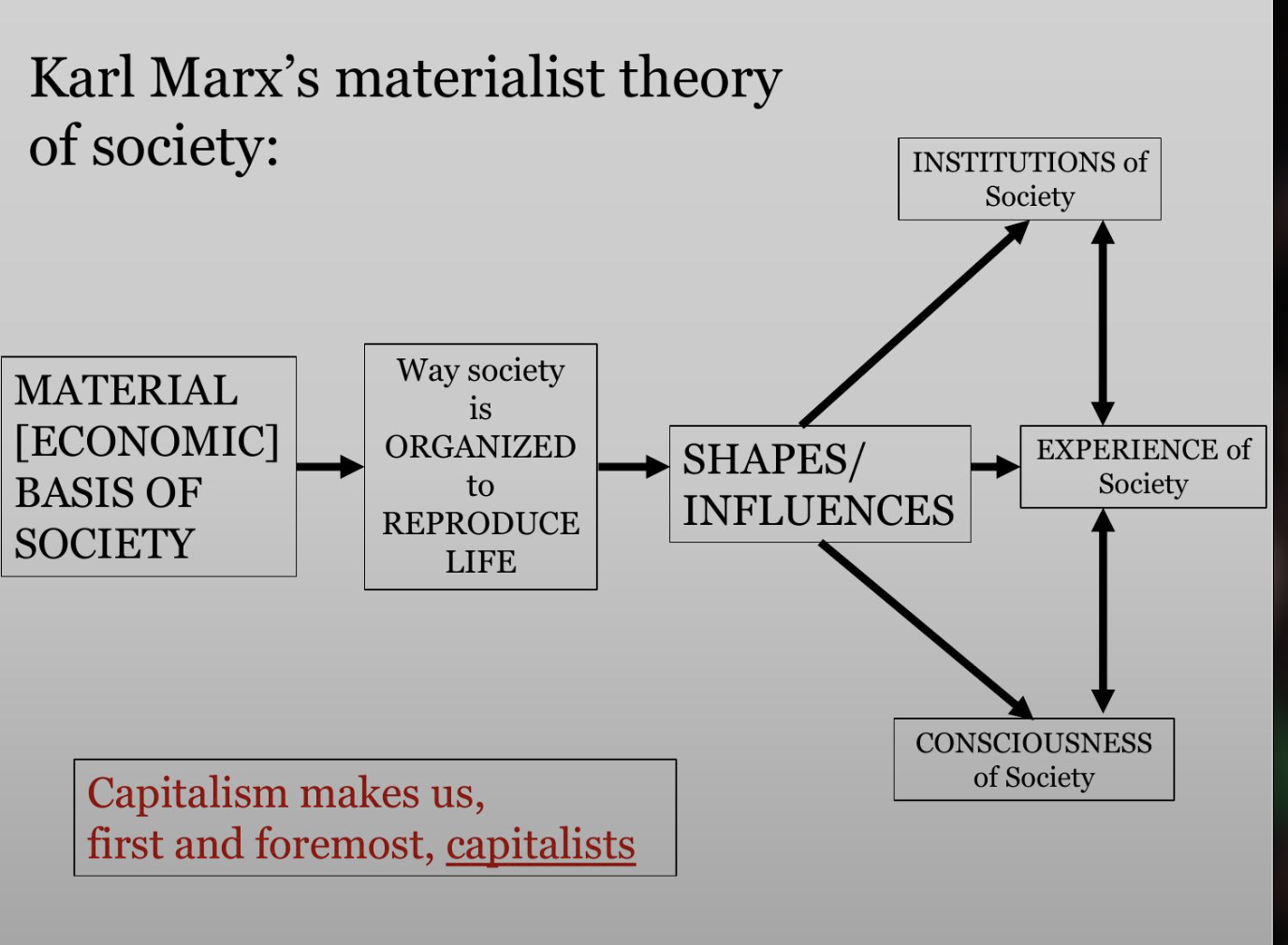
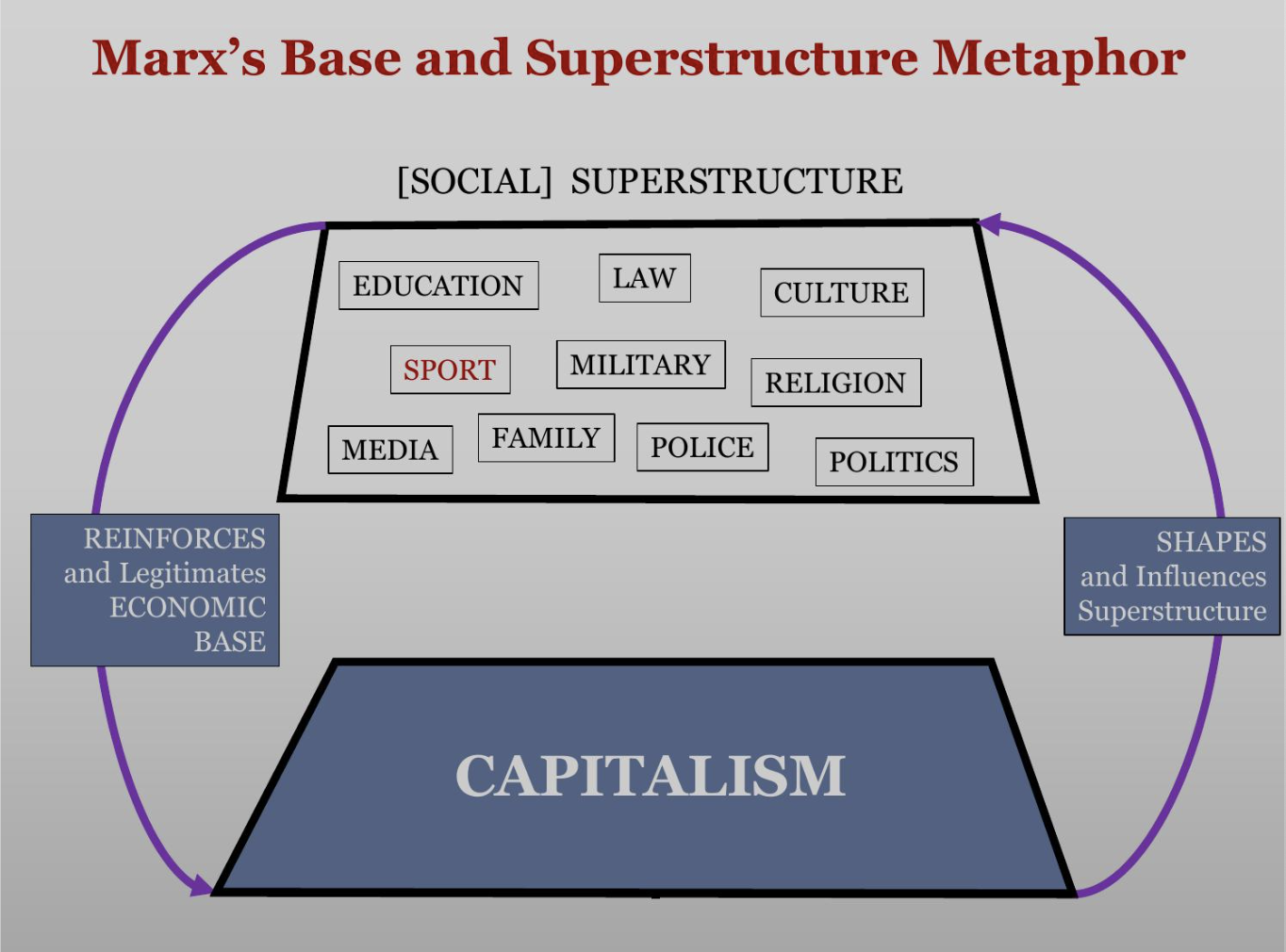
Capitalism: A system of social organization structured around the production, circulation, and accumulation of private capital
Contemporary American society is dominated and defined by the accumulation of capital
How is capital produced in capitalism?
Private ownership of the means of production
Profit motive
Labor exchanged for a wage
Free market competition
Supply and demand
What type of capitalist society is the US?
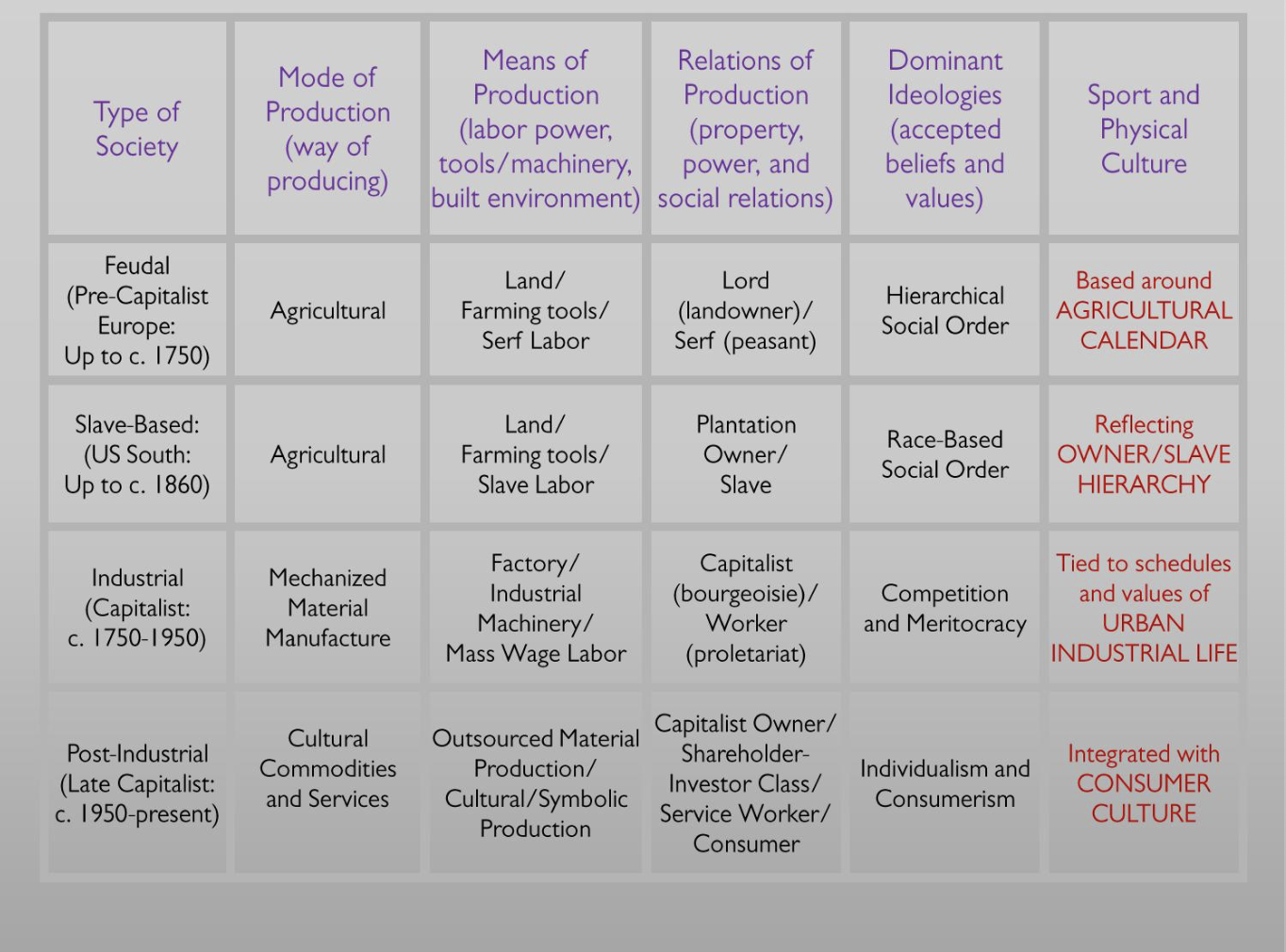
Competitive capitalism (c. 1700 to mid/late 19th century) → Monopoly Capitalism (c. 1870 to early 20th century) → Fordist Capitalism (early 20th century to c. 1950s) → Late Capitalism (c. 1960s to present)
Industrial Capitalism → Capital generated from mass production and consumption of relatively narrow range of material products
Late (cultural) Capitalism → Capital increasingly generated from production and consumption of cultural products and related cultural (symbolic) processes
Health, education, financial services, non-essential consumption, information/knowledge, entertainment/leisure, media
the commercialization of virtually all sectors of culture/society/life
Culturally, Jameson argues that late capitalist society is one in which money is made through buying and selling “culture”
every aspect of culture is increasingly structured for the purpose of generating profit in the consumer marketplace
Late Capitalist Mediasport
Forces, institutions, and processes shaping contemporary late capitalist society
SPORT → commercialization, digitalization, globalization, neoliberalism, financialization, consumerism, attention, spectacularization, corporatization
In late capitalism, elite sport is primarily a catalyst for revenue generation, including not not restricted to:
At Venue:
Ticket sales
Concessions
Sponsorship
Licensed Merchandise
Away From Venue:
Media rights
Media advertising/sponsorship
Media Subscription
Licensed Merchandise
Product Endorsement
Gambling
Sport + Late Capitalism → Highly rationalized to most efficiently generate profit
Theory 2: Weber’s Theory of Rationalization
According to German Sociologist, Max Weber, the process of rationalization is a central feature of modern society
Rationalization of society refers to the process whereby there is a shift
Rationalized Modern Capitalism: Rational structures (organizational bureaucracy) and logics (profit focus), of for-profit mass industrial corporations
Rationalization: The use of scientific precision and coordination to most efficiently pursue a goal
Rationalized Modern Sport: Rational Structures (organizational bureaucracy) and logics (profit focus), of For Profit sport industry
Sport Industry structured to generate capital (profit)
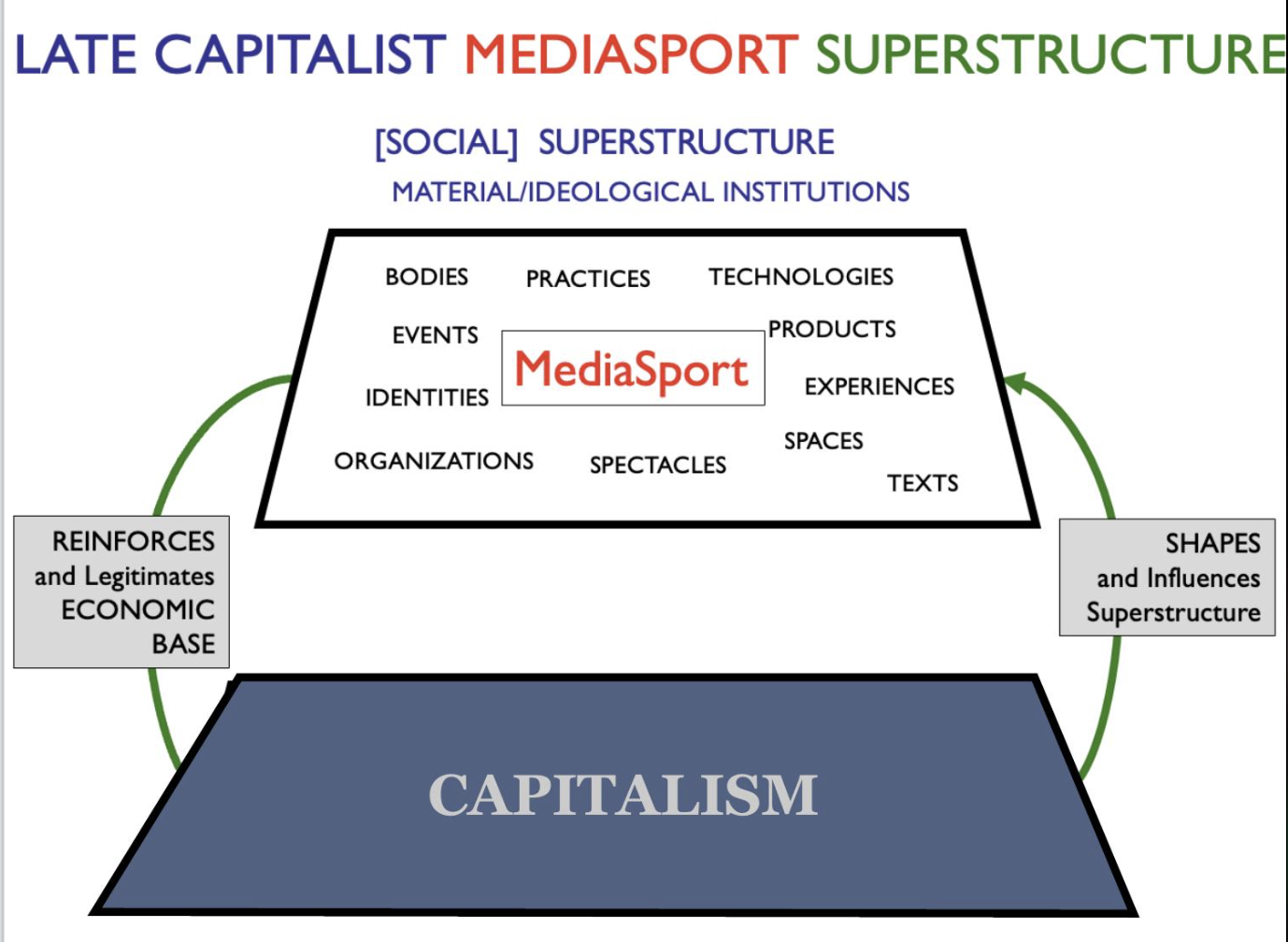
Mediasport Delivery Model
Remember, sport (in all its forms) is a: societal construct whose form and function is a product of (and simultaneously) produces the society in which it is situated
Mediasport Cycle → Corporatization, Commercialization, Spectacularization, Celebritization, Digitalization, Financialization
Corporatization
The reorganization of society around profit-driven structures and objectives; the world comes to resemble a corporation
Social Institutions (of all kinds) organized as CORPORATIONS through adopting:
institutional structure
managerial hierarchies
profit-driven focus
rational efficiencies
investment objectives
strategic location
Rationalizing the Media-Sport Corporation: Cartelized Structure
Cartel: a group of firms that organize together to restrict membership, control production, sales, and wages within and industry
Although seemingly competitors, Sport leagues and franchise collaborate to produce and protect their profits
Rationalizing the Media-Sport Corporation: Closed League
No promotion or relegation:
Involvement Guaranteed: Revenue guaranteed
“a machine for controlled capital accumulation”
Financialization
Sport increasing becoming a target/site for investment capital, and becomes ever more subject to financial motives, actors, markets, and institutions
Major sport entities have become lucrative cultural properties, which business investors look to nurture for:
Short term financial gain
Long term returns on financial investment
______________________________________
Cultural prominence and influence (soft power)
Commercialization
Structuring of an institution primarily for the purpose of generating profit in the consumer marketplace
Selling Loyalties → Player and brand sponsorship
Spectacularization
Production of sport events as either “live” or mass-mediated entertainment-focused spectacles
Late capitalist media-sport centers on the production “impossible-to-repeat live events” as branded entertainment spectacles designed to generate high volume
Spectators
Viewers
Rationalizing the Media-Sport Entertainment Product: Spectacular [commercial] spaces
Rationalizing the Media-Sport Entertainment Product: Salary Cap
The search for parity
Rationalizing the Media-Sport Entertainment Product: Resource/Talent Distribution
Standardizing the Media-Sport Entertainment Product: Rule Changes
Protect quarterback
Encourage more passing plays
Celebration
Mass-mediated individuals as the defining elements of sport spectacles/entities
Sport celebrities are the product of numerous authorized and unauthorized sources of media representation that shape the public image/understanding of private individuals
Sport celebrities are made to embody and reflect back to the public the values of a culture/society
Digitalization
The increased use of digital technologies as both a form of media-sport related communication, a platform for algorithm-based marketing and advertising, and even as an alternative sport practice
The eSport digital revolution → digital technology transforming sport practice
“Second screening" turns “passive” consumers into active producers (or prosumers) of the sport events/spectacles they consume, via user-generated content
Sports prosumers generate digital content which contributes to the advertising costs social media platforms are able to charge
As Sports Media Workers, Consider…
The pressures to generate revenue at all costs
The way this pursuit may modify the nature and meaning of sport
How to balance the responsibilities of educating and informing with entertaining
Is the current commodified spectacle the only way to experience and deliver sport?
Quotes
“as soon as we concentrate specifically on the subject of sports in capitalism, it becomes apparent that we can talk only about a sports/media complex” - Jhallu
“What starts as a sporting contest played between lines becomes transformed into spectacle that seems to have no bounds” - Wenner
“The economics of the commercial media are premised on the continued availability of ‘new’ material (however familiar in form and predictable in content) that will constantly stimulate popular attention… in this way