Forces
What is a force?
something that can change the shape of an object
something that can change the size of an object
something that can change the motion of an object —> move/stop/ turn/ direction
something that can cause a turning effect
something that can increase/ decrease pressure
a push or pull acting on an object
it is measured by a spring balance or dynamometer.
Unit of force
Newton/ N
Mass vs weight
Mass
the amount of substance in the body/ object
never changes/ is constant
unit —> kg
beam balance and electronic balance are used to measure mass.
Weight
The force on a body/object due to gravity/ the total amount of gravitational force acting on any object of mass
changes according to the force of gravity—> the greater the mass of an object, the greater the amount of gravitational force acting on it.
unit—> newton/ N
weight of an object can be calculated using—> W=m x g
Pressure vs Force
pressure is the amount of force applied to an area of contact.
Si unit of pressure= Pa(pascal)/ N/m2
formula—> p= force/ Area (f/a)—> only if answer is N/m2 then we can pascal
the amount of pressure applied depends on the area of the object that is in contact with the surface. The larger the area, the lesser the pressure. The smaller area, the greater the pressure.
Pressure due to liquid.
Formula—> p=density x gravity x height of water(dgh)
The deeper you are in the water, the greater the pressure applied on you.
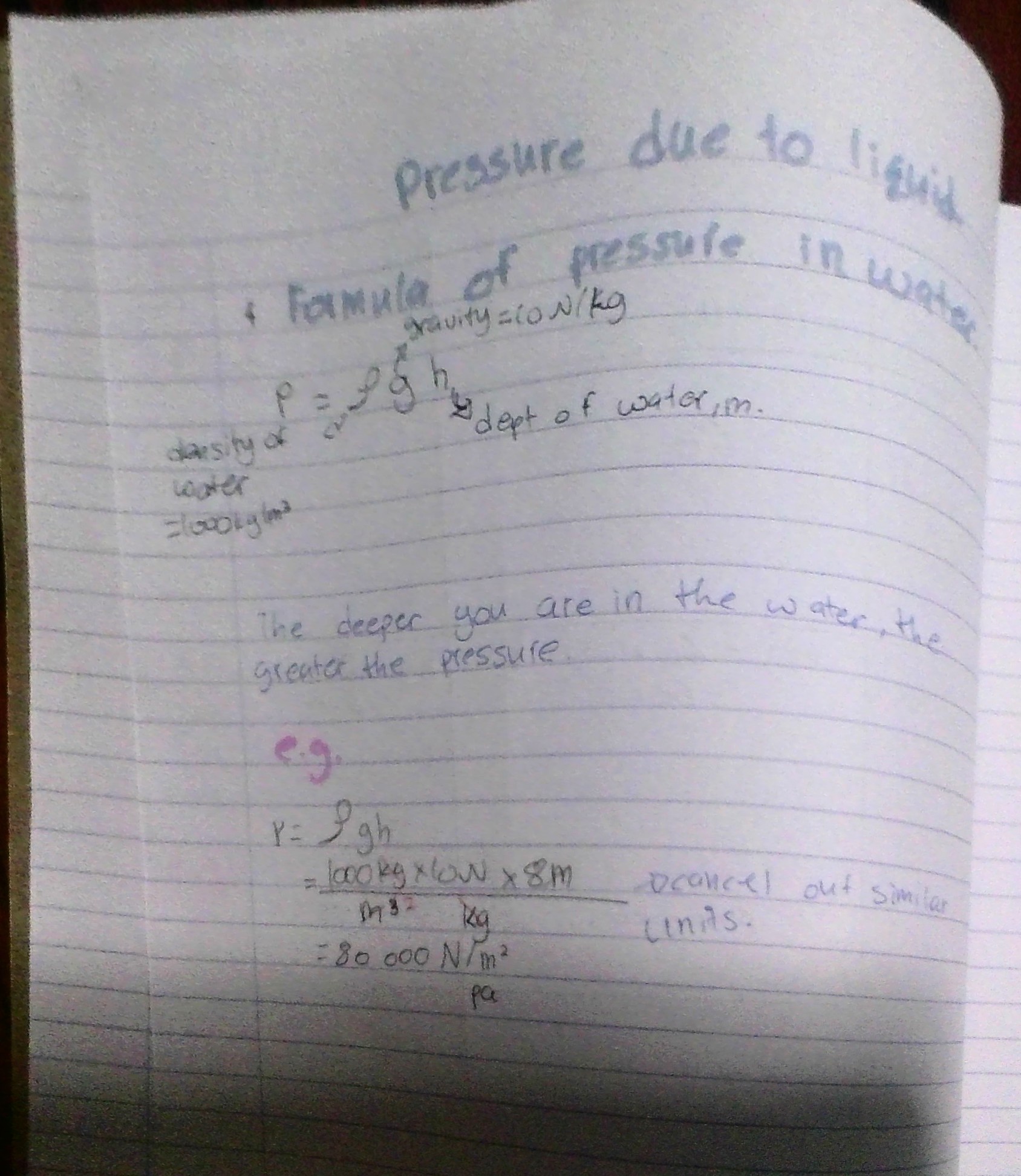
this is why a base of a dam is much thicker than the top as it must withstand the higher pressure as the dept of the water gets deeper
Atmospheric pressure
the higher up you are, a lesser amount of pressure is applied on you as the density of air gets lower the higher we go. Hence, there are fewer air particles to push down on us, resulting in lesser atmospheric pressure.
for example, a drinking straw uses atmospheric pressure→ when you suck on the straw, some air is removed from it. which reduces the pressure inside straw, allowing the higher atmospheric pressure outside to push the liquid up into the straw and into our mouths.
Transfer of energy due to application of forces
forces applied may cause an object to move in the same direction as the force—> results i transfer of energy—> called as work is done through the application of the force
the SI unit for energy and the amount of work done through the application of a force—> Joule (J)
conditions for work to be done on an object—> a force has to be applied to an object and the object must move when the force is applied. The object must move in the same direction as the force.
formula for work—> Work(J)= Force(N) x Distance (m)
How is energy conserved
when the total energy remains constant, we say that energy is conserved—> energy is not created or lost but is instead transferred form one object to another/ converted from one form to another.
total energy is made up of useful energy and energy transferred to the surroundings.
What are the sources of energy that we use
most energy on earth comes directly or indirectly from the sun.
we use fossil fuels, solar energy, hydroelectric energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, biofuels and nuclear energy
Fossil fuels
formed by the remains of dead plants and animals buried in earth millions of years ago—> limited and will run out.
they are burnt in chemical stations and then undergo a chemical process, releasing their heat energy. the heat energy is converted into kinetic energy which can be used to produce electrical energy.
electricity in power fuels are produced through this —> chemical potential energy(fossil fuels)—> heat energy(burning fossil fuels)—> kinetic energy(turbine)—>electrical energy(generator)
Impact of using fossil fuels
burning them releases air pollutants and greenhouse gases.
greenhouses gases contribute to global warming and increase the rate of climate change—> causes natural disasters to be more intense
reduce the harmful impacts by using alternatives—> solar energy, hydroelectric energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, biofuels and nuclear energy.
Solar energy
use solar panels to harness solar energy from the sun as they are made of materials that capture sunlight and convert light energy into electrical energy.
the energy conversion of light= light energy(from sun) —> electrical energy(solar cell)
Impact of using solar energy on the environment
it generates energy without releasing air pollutants and greenhouse gases (advantage)
productions of solar panels requires energy (disadvantage)
the process of harnessing energy has minimal impact on the environment ( advantage)
sufficient care is need to reduce the amount of toxic waste generated during the production and disposal of solar panels.
Hydroelectric energy
electrical energy generated by turbines when moving water powers them.
hydroelectric power stations store water in a reservoir behind a dam, when the water is released, the moving water powers the turbines to generate electrical energy.
the energy conversion= gravitational potential energy (water stored in the dam)—>kinetic energy(moving water)—> kinetic energy(turbines)—> electrical energy(generator)
Impacts of using hydroelectric energy on the environment
it produces very little greenhouse gases. (advantages)
the reservoir floods the area behind the dam, causing plants to die and forces animals to move to a different place. People who make a living by fishing may also have to relocate further inland and thus may not be able to catch fish anymore. (disadvantage)
Wind energy
wind turbines converts the energy from the wind to electrical energy—> when the wind blows at a turbine, the kinetic energy of the wind is transferred to the blades of the turbine which causes the blades to rotate. the generator that is connected to the turbine will spin and generate electrical energy.
the energy conversion= kinetic energy (wind)—> kinetic energy(wind turbine)—> electrical energy(generator)
Impact of using wind energy on the environment (disadvantage)
large plots of land need to be cleared to build wind farms—> potential loss of wildlife as natural habitats are destroyed.
bird may be killed if they fly into the turning blades of the wind turbines.
the noise produced by the rotating blades can also be a source of noise pollution to nearby communities.
Geothermal energy
heat generated within earth which can be harnessed to generate electrical energy
a geothermal power plant pumps cooled water into the hot rocks inside earth’s core. The cooled water is boiled to its boiling point by geothermal energy and turns into steam which is then pumped up to earth’s surface. The steam is used to power the turbine and generator to produce electrical energy.
the energy conversion= heat energy(earth’s core)—> kinetic energy(steam)—> kinetic energy(turbine)—> electrical energy(generator)
Impact of geothermal energy on the environment (disadvantages)
geothermal sites require the clearing of large areas of land—> destroys the habitats of wildlife which affects the diversity of species.
traces of toxic elements buried underground are also drawn out and can cause harm to the environment if not properly handled.
Biofuels
made from animal waste or from plant materials that cannot be eaten by humans they can also be produced from recycling food waste like used cooking oil and plant pulp
Biofules can be used to power motor vehicles. The carbon dioxide produced from the vehicles is reabsorbed by plants when they photosynthesise.
the energy conversion= chemical potential energy (biofuels) —> heat energy(vehicle engine)—> electrical energy(vehicle)
Impacts of using biofuels on the environment
burning of biofuels releases air pollutants like carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.(disadvantage)
the plants used to make biofuels can be grown in a short time (advantage)
Biofuels are also made from used cooking oil and food waste which helps to reuse and reduce waste. (advantage)
When the plants that are used for biofuel carry out photosynthesis, they take in carbon dioxide which balances the amount of carbon dioxide in the environment when biofuels are burnt. (advantage)
Nuclear Energy
The energy harnessed from the nucleus of an atom which can be obtained through nuclear reactions and then converted into electrical energy.
Electricity is generated by using nuclear fission where a heavy atom splits into smaller atoms. This released a large amount of heat which is used to boil water. The steam produced powers turbines to generate electrical energy.
the energy conversion= nuclear energy(atoms)—> heat energy(nuclear reaction)—> kinetic energy(turbine)—> electrical energy (generator)
Impact of the use of nuclear energy on the environment
it is a source of clean energy and requires less land space to generate the same amount of energy compared to other alternative sources of energy (advantage)
It may pose potential risks to the health and safety of communities living near nuclear power plants. (disadvantage)
There may be leakages when disposing and storing nuclear waste. (disadvantage)
there may be accidents. (disadvantage)
Forces in nature
Phenomenon | How it occurs | How it affects us |
Tropical cyclone | Warm oceans near the equator provides energy for formations of long and powerful storms which bring heavy rains and strong winds | - heavy rains cause flooding. The forces exerted by the rapidly moving floodwaters loosens the soil and causes landslides - strong winds moving at greater speed exert greater forces on objects, destroying them. The objects carried away by the wind also causes more damage to the environment |
Earthquakes | constantly slow moving tectonic plates slide over or against each other, the forces exerted between them during this process can lead to massive amounts of energy which triggers earthquakes on land | - strong forces produced by the earthquake can lead to intense ground shaking, potentially causing widespread harm to buildings, infrastructure, and roadways. |
Volcanic eruption | - magma formed by melting of rocks are forcefully pushed out towards the earth’s surface. This causes a volcanic eruption. | - the eruption released massive energy stored within the earth, in the form of kinetic energy of the magma, heat and light that can cause great damage to the surroundings. |
Tsunami | - Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions beneath the ocean floor can cause the ocean floor to move vigorously and displace ocean water, resulting in tsunamis | - Huge waves with great hight possess high potential energy that converts into greater kinetic energy, allowing these waves to travel at high speed towards the shore and strike coastal objects wit great force. Resulting to extensive damage to the environment. |
Landform | - a natural feature or shape found on the earth’s surface that was created by a variety of forces in nature. | ———— |
Types of forces
two types of forces, contact and non-contact
*Type* *What is it?* *Example*
Contact forces - force acting between two objects that are in physical contact friction and elastic force | ||
Non-contact forces | -force acting between two object that are not in physical contact | gravitational force and magnetic force |
Friction
A contact force that opposes the motion between two surfaces in contact
occurs when two objects are in direct physical contact and one attempts to slide or move across the surface of the other
friction slows things down
friction helps us grip things without dropping them
friction is greater when an object moves on a rough surface than it moving on a smooth surface
increases as gravity increases
Advantages How friction helps us | |
Improved grip | Increases friction on our hands, enhancing our ability to grip objects securely |
slowing or stopping objects | friction between brakes and wheels enables vehicles to slow down or stop as needed |
Prevents slipping and sliding | Friction between shoe soles and road surfaces ensures secure walking, standing, or running without slipping |
Disadvantages How its a nuisance to us | |
Wear and tear | Shoes, tyres, moving parts in machines, or other objects that are used for moving will wear out due to friction over time |
Energy wastage | friction produces, which results in a waste of energy and more energy is needed to move an object as friction opposes motion |
Ways to overcome friction How it works | |
lubricating oils or grease | makes a smoother surface, hence the object will move across it with less friction and wont wear out easily |
using ball bearings, rollers or wheels | can be used to move things with ease and aviod waste of energy and wear and tear |
a cushion of air | Reduces the direct contact between two surfaces which reduces friction |
Elastic force
a contact force that acts when an object is stretched or compressed from its original shape.
elastic force exerted by an object act in opposites directions to the force applied whether through compression or stretching.
The opposing force opposes the motion to restore the object to its original shape or state.
Advantages of elastic force
climbers use ropes to climb as when they fall, the rope undergoes stretching, increasing elastic force in the opposite direction of the fall, which helps to slow down the climber’s fall and reduces the impact of their fall.
Gravitational force
any object that posses mass exerts an attractive force on each other
force of attraction between objects of mass
a non-contact force
whether objects have the same or different mass, they can exert gravitational force on each other from a distance
gravitational force between two objects become significant when at least one of them has a substantial mass (a large amount of mass)
Gravitational field strength
the gravitational field strength refers to the amount of gravitational force is exerts per 1kg
its expressed in newtons per kilograms (N/kg) and denoted as g where g refers to gravity/ gravitational force.
the greater the mass of the object the stronger its gravitational field strength.
it is also affected by the distance an object is from the centre, as the distance from the centre increases, its gravitational force decreases.
Magnetic Force
force exerted between magnets or between a magnet and magnetic substances
non-contact force
two different types of magnetic forces—> force of attraction on a magnet or a magnetic material and force of repulsion on another magnet
magnets interact with each other through their north and south poles.
Like poles repel
unlike poles attract
Uses of magnetic force
Maglev trains use powerful magnets to create forces of repulsion to lift the train above the track, decreasing friction and enabling smoother travel.
A compass uses a magnetic needle to indicate the direction which helps us navigate our way through forests and oceans.