WK5D: Normal Diagnostic Laboratory Findings and Deviation
Purpose:
Predict the outcomes of the pregnancy
Manage the remaining weeks of pregnancy
Plan for possible complications at birth
Decide whether to continue the pregnancy
Find conditions that may affect future pregnancy
Medical Diagnosis
A medical diagnosis of pregnancy serves to date when the birth will occur and also helps predict the existence of high-risk status.
Pregnancy tests - are commercially available and can be performed by the trained personnel that are highly accurate and precise, if done with the correct technique
Pregnancy testing – relies on the detection of an antibody to the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or a subunit in the urine or serum
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin – the first placental hormone produced and can be found shortly after implantation
Specimens:
1. Urine – test to yield accurate results and it should be done 10 to 14 days after the missed menstrual period. This period guarantee level of hCG and prevents false negative results.
a. Gravindex and Pregnosticon - are immunologic pregnancy test and approximately 95% accurate in diagnosing pregnancy and 98% accurate in determining the absence of pregnancy
b. Radioimmunoassay – tests for the beta subunit of hCG and considered to be so accurate as to be diagnostic for pregnancy
Urine Tests: (hCG)
Collect first voided urine using clean, dry bottle free of detergent or contamination.
Do not drink fluids from 8pm the night before to concentrate the urine
Refrain from taking any drug 24 hrs. before the test
Label the specimen with the woman’s name, date, and time of voiding.
Bring the specimen to the laboratory immediately
Refrigerate urine specimen-if more than one hour is pass before the specimen gets to the laboratory because room temperature is high enough to destroy hCG
2. Blood – with sensitive assays hCG can be detected in maternal blood at 7 days after conception and are accurate close to 100% of the time.
Progesterone Withdrawal test – a contraceptive pill is taken OD or TID (3xdays)
If menstruation occurs within 10-15 days, the woman is not pregnant.
If corpus luteum produces enough hormones to neutralize the effect of withdrawn synthetic progesterone and no bleeding occurs, the woman is pregnant
Ultrasound imaging – (Ultrasound scanning or Scanning)
involves exposing a part of the body to high frequency sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the body
It is a popular and safe diagnostic tool in the care of the pregnant woman and her fetus.
It provides the physician, and other members of the health team the ability to approach the developing fetus aa a separate patient with an identifiable set of reflexes reactions to outside stimuli and activity patterns.
7-11 wks. if the date of LMP is unknown, between 16-20 wks. gestation to verify fetal structures and gender
The sound waves reflect best if the uterus can be held stable and it is helpful if the woman has a full bladder at the time of procedure
Purpose:
1. Diagnose pregnancy as early as 6 wks. Gestation.
2. Confirm the size, location of the placenta and amniotic fluid.
3. Discover complications of pregnancy.
4 . Establish if fetus is growing and no congenital anomalies.
5. Predict maturity by measurement of biparietal diameter of the head
Types of Pelvic Ultrasound
a. Abdominal or Transabdominal – with the woman in supine position, the sonographer/radiologist applies the transducer on the lower abdomen
b. Vaginal or transvaginal – with the woman in lithotomy position, the sonographer/radiologist inserts into the vagina 2-3 inches of the vaginal transducer’s end with the protective cover and lubricating gel
Ultrasonography
Biparietal diameter – used to predict fetal maturity.
a. Measurement of fetal head (8.5 cm. or greater)
b. Weight. 2500 g (5.5 lb.)
Doppler Umbilical Velocimetry – measures the velocity at which RBC in the uterine and fetal vessels to assess blood flow
Determine the vascular resistance present in woman with Gestational diabetes or Hypertension and placental insufficiency
Decreased Velocity – predictor of Uterine Growth Restriction
Placental grading for maturity – graded based on the amount of calcium deposits present in the base of the placenta
Grades 0: between 12 and 24 wks.
No calcification, no indentations
Grade 1: 30 – 32 wks.
small diffuse calcifications
randomly distributed in placenta
Grade 2: 36 wks.
dot dash calcifications along the basal plate
larger indentations
Grade 3: 38 wks. – suggest fetus is mature
complete indentations of the chorionic plate
hyper mature placenta associated with placental insufficiency
A calcified placenta occurs when small, round calcium deposits build up on the placenta, causing it to deteriorate gradually. The process occurs naturally as closer to the end of pregnancy. • if placental calcification occurs before your 36th week, it could cause complications to the mother and her baby.
Complications:
Fetal growth restriction
Fetal distress in cases of preterm placental calcification.
Decreased blood flow in the placenta and compromise fetal circulation and growth
Preterm birth
Low birth weight
Low Apgar score
Postpartum hemorrhage
Placental abruption
Fetal distress
Stillbirth
Amniotic fluid volume (ULTRASOUND) – The amount of amniotic fluid can estimate fetal health because a portion of the fluid is formed by fetal kidney output
If a fetus is becoming so stressed in utero that circulatory and kidney function is failing urine output and the volume of amniotic fluid will decrease
THE AMOUNT OF AMNIOTIC FLUID PRESENT ESTIMATE FETAL HEALTH
20-24 cm. – indicates Hydramnios
12 -15 cm. average between 28 and 40 wks.
<5-6 cm – Oligohydramnios
decrease in amniotic fluid volume puts the fetus at risk for compression of the umbilical cord
Nuchal translucency – described the appearance of a collection of fluid under the skin behind fetal neck
a number of genetic disorders can be detected on sonogram during the 11 wks.-13 wks. of pregnancy
children with a number of chromosomes anomalies have unusual pockets of fat or fluid deposits at the back of the fetal neck
Magnetic resonance Imaging (MRI) – can identify structural anomalies or soft tissue disorder
most helpful in diagnosing complications
a. Ectopic pregnancy
b. Trophoblastic disease
Lateral Pelvimetry
in suspected cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD) with a danger sign of absence of lightening in a primigravida in active labor
Indications for lateral Pelvimetry
Suspected CPD
Previous difficult delivery
History of severe vitamin D and calcium deficiency in childhood
History of pelvic or spine injury
Cases of severe scoliosis
LABORATORY ASSESSMENT
Urinalysis – tested for proteinuria, glycosuria, nitrates, pyuria
Complete blood count
Genetic screen (G6PD glucose6phosphate dehydrogenase)
VDRL serologic test for syphilis
Blood typing (Rh factor)
Maternal serum a-fetoprotein – done between 16-18 wks. of pregnancy
Combs test – determination of whether Rh antibodies are present in an Rh (-) woman
HIV screening
Serum antibody titers for rubella, hepatitis, varicella
Blood Serum Studies
Tuberculosis Screening (Mantoux Test)
ASSESSING FETAL WELLBEING
Fetal Biophysical Profile
Is a noninvasive method of assessing the general well being of the fetus and the fetal assessment.
BPP may be used as early as 26-28 weeks for the surveillance of high risk pregnancy.
The test requires the use of an ultrasound and the electronic fetal monitor and the observation time takes about 30 minutes
Indications:
Mother with gestational hypertension
Fetus appears to be small or not growing properly
Fetus is less active than normal (movement)
Too much or too little amniotic fluid
combines five parameters into one assessment
the fetal heart and breathing record measures short-term central nervous system function
amniotic fluid volumes helps measures long-term adequacy of placental function
Five Parameters:
Fetal reactivity
Fetal breathing movements
Fetal body movements
Fetal tone
Amniotic fluid volume
Biophysical Profile Scoring
Fetal breathing - at least one episode of 30secs. of sustained breathing movement w/in 30mins
sonogram
Fetal movement - at least 3 episodes of fetal limb or trunk movement w/in 30mins.
sonogram
Fetal tone - Observation must extend and then flex extremities or spine at least once in 30 mins.
sonogram
Fetal heart reactivity - 2 or more heart accelerations at least 15 beats/min
Nonstress test
Amniotic fluid volume - A range of amniotic fluid between 5 and 25 cm must be present
sonogram
Results:
8 - 10 fetus is considered to be doing well
6 - is considered suspicious
4 - denotes a fetus probably in jeopardy
Fetal Growth (Fundal Measurement)
over the symphysis pubis – 12 wks.
at the umbilicus – 20 wks.
at the xyphoid process – 36 wks.
Mc Donald’s rule = Formula:
AOG in months – FH in cm. x 2/7
AOG in weeks – FH in cm. X 8/7
Fetal heart sounds
10 – 11 wks. – ultrasound
10 wks. – Doppler
Daily fetal Movement Count (Kicks Count)
18 – 20 wks. – quickening felt by the mother
28 – 38 wks. – 10 x / hr. peaks in intensity
Rhythm Strip testing – use for assessment of the fetal heart rate
Average FHR – 130 beats/ min.
Average fetal moves – twice every 10 mins. - causes heart rate to increase
Vibroacoustic Stimulation – for acoustic (sound) stimulation
Acoustic stimulator applied to the mother’s abdomen to produce sharp sound (80 db.), startling and waking the fetus
If spontaneous acceleration has not occurred within 5 mins, a 1-2 secs sound stimulation to the lower abdomen and can be repeated at the end of 10 mins
MATERNAL SERUM ALPHA- FETOPROTEIN SCREENING: AFP/Triple Screen
This test involves measurement of Alpha fetoprotein (AFP), estriol and HCG in maternal serum at 15-20 weeks of gestation to screen for fetal structural & chromosomal abnormalities.
Alpha-feto protein is a substance produced by the liver that is present in amniotic fluid and maternal serum.
Estriol is initially tested. If the result is abnormal, the woman is next referred for ultrasound to confirm gestational age and to evaluate for neural tube defects (NTD) and other structural abnormalities.
A low estriol, elevated HCG, and low AFP finding is often associated with Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).
High in the maternal serum (MSAFP) if the fetus has an open spinal or abdominal defect.
AFP is a substance produced by the fetal liver that can be found in both amniotic fluid and maternal serum between 15th and 20 wks. of pregnancy
Level low – Chromosomal defect Trisomy 21 (Down’s syndrome)
Level High – begins to rise at 11 wks. and steadily increase until term gestation
Fetus has an Open spinal (Neural tube defect) or abdominal defect, allow more AFP to enter the mother’s circulation
FETAL GENDER
Ultrasound – determined at about 4 months
Maternal serum analysis – as early as 7 wks. and could be helpful to a woman who has a X-carrying genetic disorder
Male fetus – inherited the disease
Female fetus – disease free
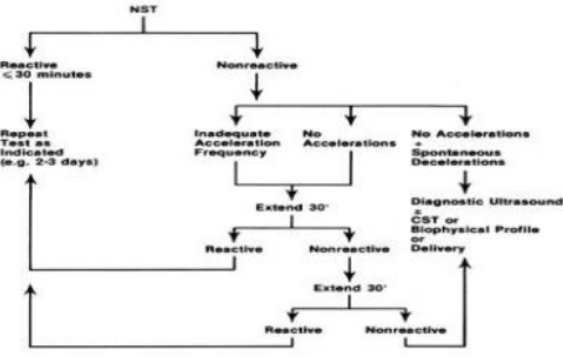
Non- Stress Test (NST)
An assessment of fetal well-being that analyses the response of the fetal heart to fetal movement
When the fetus has adequate oxygenation and intact CNS, the are accelerations of FHR with fetal movement.
The baby’s heart rate should accelerate, by 15 beats for at least 15 seconds, twice in a twenty minute period. This is called a reactive NST and is a good sign that the fetus is healthy.
A reactive NST indicates intrauterine survival for one week. The doctor may order a CST if the NST is nonreactive. The usual preparation is to feed the mother with food or fluids before the test to stimulate fetal movements
MEASURES THE RESPONSE OF THE FETAL HEART RATE TO FETAL MOVEMENT
Fetal moves – HR increase 15 beats/ min. and remain elevated for 15 seconds
If no increase in beats/minute on fetal movement – indicates poor oxygen perfusion of the fetus
usually done for 20 minutes
Test is Reactive (Healthy) if 2 acceleration of FHR (by 15 beats or more) lasting for 15 secs
Nonreactive (fetal health may be affected) if no acceleration with the fetal movement
If a 20 minute passes without any fetal movement, means the fetus is sleeping
When the fetus has adequate oxygenation and intact CNS, there are acceleration of FHR with fetal movement
Contraction Stress Test
Assess the ability of the fetus to withstand the stress of uterine contraction done during labor
CST is a means of evaluating the respiratory function of the placenta.
Induced or spontaneous contraction decrease transport of O2 to the fetus. A healthy fetus maintains a steady heart rate.
If placental reserve is insufficient, fetal hypoxia and decrease in FHR occur.
Testing is initiated when 3 contractions in every 10 minutes are attained. The test takes about 60-90 minutes to perform.
Periodic Changes: Evaluating the respiratory function of the placenta
a. Accelerations - temporary normal increases in FHR caused by fetal movement or compression of the umbilical vein during contraction
b. Early Decelerations - periodic decreases in FHR resulting from pressure of the fetal head during contractions.
Beginning when the contractions begins and ending when the contractions end (mirror image)
Normal – late in labor
c. Late Decelerations - delayed decelerations until 30 to 40 seconds after the onset of a contraction and continue beyond the end of the contraction
Ominous pattern in labor (uteroplacental insufficiency) or ↓ blood flow through the intervillous spaces of the uterus during contraction
Management for Late Decelerations:
Administer IVF
O2 as prescribed - If late decelerations persist prepare for possible prompt birth of the infant
The lowest point of the deceleration (nadir) occurs near the end of the contraction instead of at its peak
Occur with hypertonia or with abnormal uterine tone caused by administration of oxytocin
Management for Nadir:
Stop or slow the administration of oxytocin
Change the position from supine to lateral to relieve pressure from the Vena Cava
d. Variable Decelerations - Decelerations that occur at unpredictable times in relations to contractions - Indicate compression of cord
Cord prolapsed
Fetus is lying on the cord
Occurs more frequently: - after rupture of membranes
Oligohydramnios
U, V or W – shaped waves
Position: lateral or T-position
MANAGEMENT FOR OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS
Administer fluids and O2 as prescribed
If not relieved, amnioinfusion may be prescribed
Amnioinfusion – is the instillation of fluid into the amniotic cavity to treat severe deceleration.
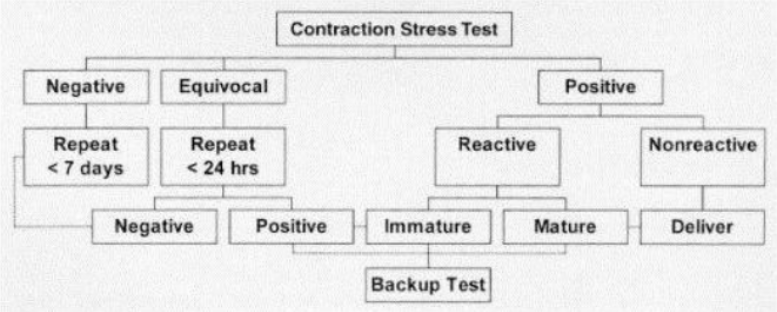
Interpretation Results of CST
Positive : there is persistent late decelerations w/ more than half the contractions; maybe associated w/ minimal or absent variability. A positive CST means that the fetus is no longer receiving adequate oxygen and needs to be delivered.
Negative : There is no late deceleration in a 10-minute period and this means that it is safe for the fetus to remain in utero for the next 7 days
Prenatal testing maybe offered to women during pregnancy - to determine if the fetus has a possibility to be born with a genetic condition or birth defect.
INVASIVE FETAL TESTING
Chorionic Villi Sampling
Is a transcervical or transabdominal insertion of a needle into the fetal portion of the placenta, at the area of the chorion frondosum
CVS is performed at 8-12 weeks gestation under ultrasound guidance to ensure that the fetus is unharmed.
Chorionic villi cells are examined to detect chromosome abnormalities such as Down syndrome and genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis
Is a biopsy & analysis of chorionic villi for chromosomal analysis done at 8 to 10 weeks of pregnancy chorion cells are located by ultrasound
A thin catheter is inserted vaginally or needle biopsy is inserted intravaginally or inserted abdominally, and a number of chorionic cells are removed chromosone analysis (genetic defect)
Nursing Responsibilities: Instruct client to report bleeding, infection or leakage of fluid after procedure
Some instances of limb reduction syndrome
Less than 1% risk leading to excessive bleeding, or pregnancy loss
Reportable s/sx:
Chills or fever (infection)
Uterine contraction or vaginal bleeding (threatened miscarriage)
Amniocentesis
Amnion for sac and kentesis for puncture. Scheduled between the 14th and 16th week
Amniocentesis is the removal of fluid from the amniotic cavity by needle puncture. An ultrasound is performed first to determine the safe site where the needle can be inserted.
Scheduled between 14th and 16th wk.
During the procedure, the fetus is continuously monitored by ultrasound to ensure its wellbeing.
Complications includes hemorrhage from the penetration of the placenta, infection of the amniotic fluid and puncture of the fetus
Purposes of Amniotic Fluid Analysis
Detection of fetal abnormalities early in pregnancy
To determine fetal lung maturity
Lecithin/Sphingomyelin ratio
Lung Profile
Amniotic Fluid Bilirubin
Rh incompatibility
For detection of certain infections
Detection of fetal abnormalities early in pregnancy
AMNIOTIC FLUID CAN BE ANALYZED FOR:
AFP (Acetylcholinesterase) - a compound that rises to high levels if a neural tube anomaly is present
Color
Normal amniotic fluid - color of water, late in pregnancy, it may have a slightly yellow tinge
Strong yellow – suggest a blood incompatibility (presence of bilirubin released from the breakdown of RBC)
Green – suggest meconium staining a phenomenon associated with fetal distress
Fibronectin – is a glycoprotein plays a part in helping the placenta attach to the uterine decidua
can be assess in woman cervical mucus in early pregnancy
damage to fetal membranes from cervical dilatation releases fibronectin and preterm labor may be begin
Inborn error of metabolism – inherited diseases that can be detected by amniocentesis
The body cannot breakdown and metabolized food due to defects of protein enzymes
Detect the following diseases:
Sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, Tay-Sachs disease, amino acid disorder
Lecithin and sphingomyelin – are protein components of the lung enzyme surfactant that the alveoli begin to form at the 22nd -24 wks. of pregnancy
can be determined by a shake test (if bubbles appear in amniotic fluid after shaking, the ration is mature
L/S ratio of 2:1 is accepted as lung maturity
Nursing Care during Amniocentesis
Assist client to empty her bladder before the procedure
Place in supine position and drape properly
Put rolled towel under right hip to tip body to the left and remove pressure of uterus on vena cava
Instruct not to take a deep breath and hold it while the needle is being inserted as it will shift the uterus and needle may hit placenta or fetus
Inform the patient that it is not painful because anesthesia will be applied at the insertion site. She may experience pressure sensation during the insertion of the needle.
Monitor (fetal heart tones) FHT before, during and in 30 minutes after the test.
Instruct patient to observe for:
Infection
Uterine cramping
Vaginal bleeding
PERCUTANEOUS UMBILICAL BLOOD SAMPLING
also called Cordocentesis or Funicentesis – is the aspiration of blood from umbilical vein for analysis
a thin needle is inserted by amniocentesis technique into the uterus and is guided by ultrasound
PUBS test reveals that the fetus is anemic, blood may be transfused into the cord
the blood obtained sample of blood is then removed for blood studies (CBC, direct Combs test, bloods gases and Karyotyping)
Kleihauer-Betke test - is utilized to determine if there is fetal blood in maternal circulation,