ch 9 rivers and ground water
earth’s water supply
96% earth’s water in oceans
3.5% drinking water (but can’t use all of it)
in order of most to least
water
glaciers
groundwater
non glacial ice and snow
lakes
rivers
the hydrologic cycle
precipitation
evaporation
infiltration
runoff
transpiration
running water - on the surface
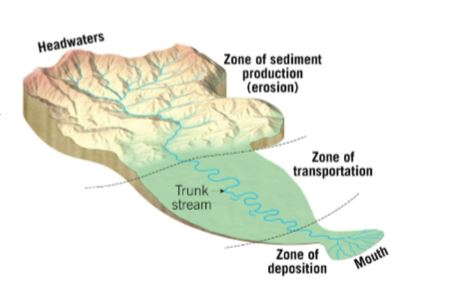
drainage basin: land area that contributes water to a river system
divide: seperates drainage basins (usually a mountain peak)
river systems have 3 zones
sediment production
sediment transport
sediment deposition
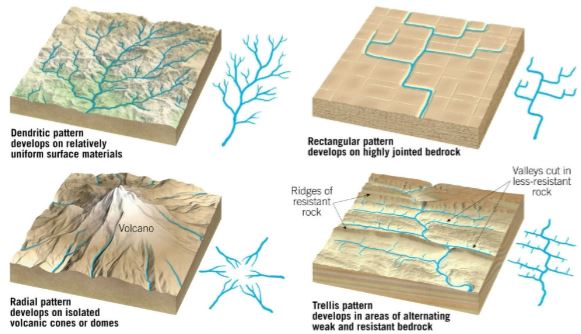
drainage patterns
networks of streams form distinctive patterns
vary by terrain
4 common
dendritic
rectangular
radial
trellis
streamflow
streams/rivers are concentrated flows of water in channels
factors that determine velocity
gradient or slope
channel characteristics: shape, size, roughness
discharge: volume of water flowing in the strea (expresses as cubic feet per second)
how sheet flow changes:
runoff coalesces into sheet wash (thin surface layer of water)
gets pulled down the steepest slope
erodes soft soil
creates rills - small channels
rills deepen and coalesce into tiny tributaries (channels)
tributaries enlarge and merge
eventually flow into a single strunk stream
all of this forms into a drainage network
work of running water
erosion: happens as moving water comes into contact with rock material
transportation: transported material is called the stream’s load
load: related to a stream’s competence (max particle size) and capacity (max load and is related to discharge)
types of loads:
dissolved load (invisible)
suspended load (silt, clay)
saltation (bouncing)
bed load (sand, gravel, boulders)
deposition: caused ny a decrease in velocity, competence is reduced,
sediment drops out stream sediments: known as alluvium and well-sorted deposits
transportation: features produced by deposition
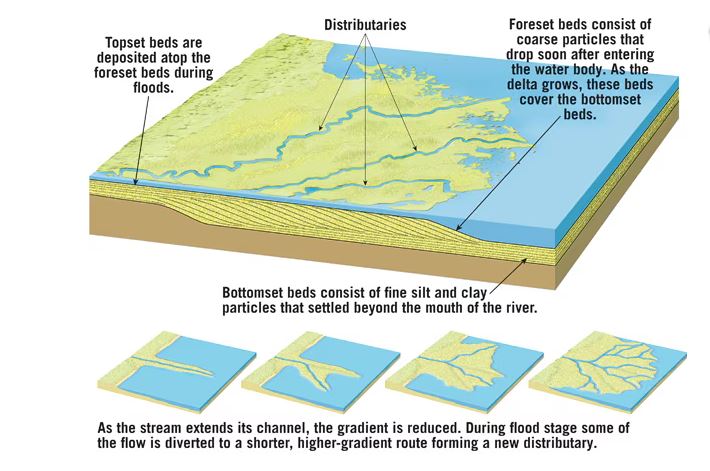
deltas - exist in oceans or lakes. an accumulation of sediment formed where a stream enters a lake or ocean
natural levees - form parallel to the stream channel
yazoo tributaries/back swamps - area behind levees

stream channels:
bedrock channels - cut into strata
alluvial channels - loosely consolidated sediment

meander: a bend in the course of a stream
crescent shaped accumulation of sand and gravel deposited on the inside of a meander
cut-off meander/oxbow lake: when the bend becomes so looplike that it becomes it’s own circle (oxbow lake)
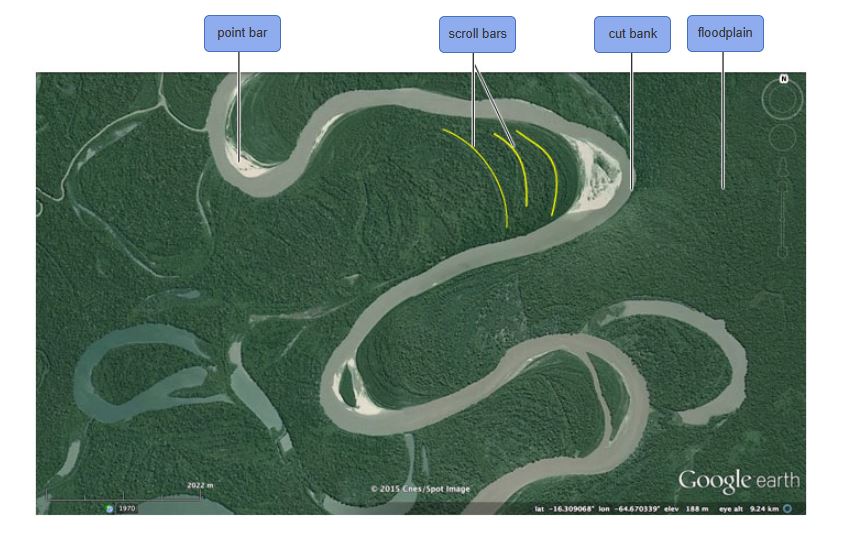
meandering stream: streams that transport their load in suspension in meanders. move in sweeping bends
cut bank: area of active erosion on the outside of a meander
braided stream: stream channel with numerous intertwining channels
gravel bar: island of sediment deposited in the middle of a braided stream

shaping stream valleys
base level
lowest point a stream can erode to
ultimate base - sea level
temporator or local base
changing causes readjustment of the stream - depo or erosion
valley sides are shaped by
weathering
overland flow
mass wasting
characteristics of narrow valleys
v shaped
downcutting toward base level
incised meanders
often include rapids and waterfalls
characteristics of wide valleys
stream is near base level
erosion is less dominant
stream energy is directed from side to side
floodplain
often include meanders, cutoffs, and oxbow lakes
floods - most common and destructive geologic hazard
causes
weather
human interference with stream system
flood control
engineers help control them with
artificial levees
flood-control damns
channelization
nonstructural approach through sound floodplain management
groundwater
water in the ground
largest freshwater reservoir for humans
geological roles
erosional agent. dissolving by groundwater produces sinkholes and caverns
equalizer of stream flow
distribution and movement of groundwater - belt of soil moisture
zone of aeration
unsaturated zone
pore spaces in material are mainly filled with air
zone of saturation
all pore spaces in material are filled with water
water within pores is groundwater
water table - upper limit of the zone of saturation
porosity
percentage of pore spaces
determines storage of groundwater
permeability
ability to transmit water through connected pore spaces
aquitard - impermeable layer of material
aquifer - permeable layer of material
features associated with groundwater
springs
hot springs - heated by xooling of igneous rock, and water is 6-9 degrees c warmer than air temperature of the locality
geysers - intermittent hot spirngs where water turns to steam and erupts
wells
man made structures to get water to surface
pumping can cause drawdow/lowering of water table
pumping can form a cone of depression in the water table
artesian wells
water in the well rises higher than the initial groundwater level
natural deologic feature
groundwater environmental problems
treating it as a nonrenewable resource
land subsidence caused by its withdrawal. ex: leaning tower of pisa
contaimination
geologic work of groundwater
mindly acidic
contains weak carbonic acid
dissolves calcite in limestone
caverns
formed by dissolving rock beneath earth’s surface
formed in saturation zone
features found within caverns
form in zone of aeration
composed of dripstone
calcite deposited as dripping water evaporates
stalactites - hanging from celing and form on the roof of a cave from the deposition of calcium carbonate by dripping water.
stalagmites - growing upward from floor
karst topography
formed by dissolving rock at or near earth’s surface
sinkholes - surface depressions that form by dissolving bedrock and cavern collapse
caves and caverns
area lacks good surface drainage
extra:
In a river, what happens to the channel size and discharge downstream? Channel size and discharge increase
If the velocity of a stream decreases, competence __________ and sediment is _____. decreases, deposited
Competence: A measure of the largest particle a stream can transport; a factor that is dependent on velocity.
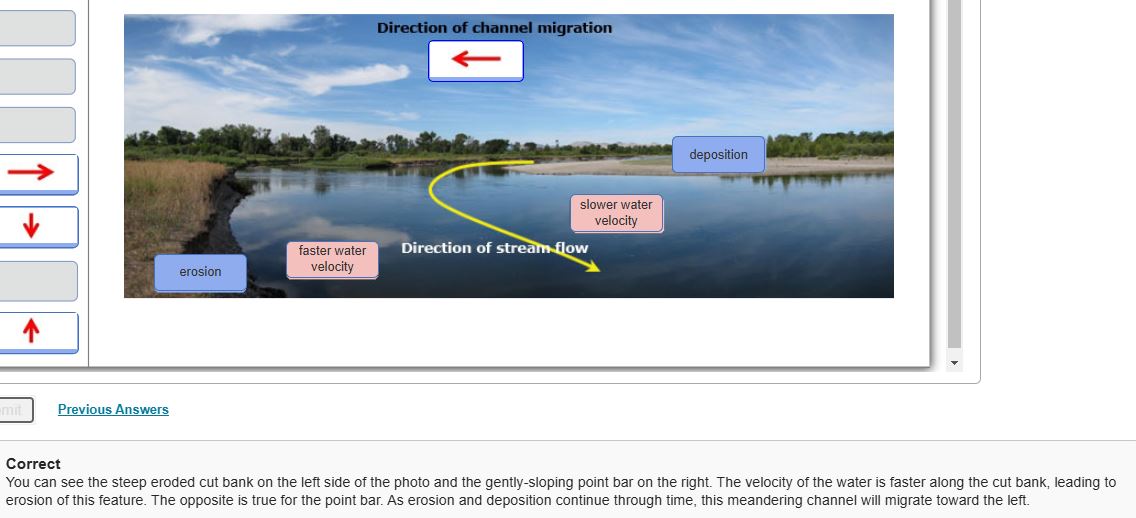
Velocity and turbulence are _____ at the __________. Greatest, cutbank/outside the meander