MICB 212 Chapter 1 Notes
Introduction to the Immune System
-environment is filled with microorganisms that humans encounter everyday
bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites
-some microorganisms can cause disease but most people are healthy most of the time
-humans and other vertebrates protect themselves with a complex array of defensive mechanisms
3 Levels of Defense Against Infection
anatomical and physical barriers
intact skin provides a physical barrier
mucosal surfaces of gut, respiratory urogenital and conjunctivae surfaces
stomach acid, lysozyme and other antimicrobial body secretions
innate immune response (initial internal defense)
quick and non-specific
involves phagocytosis and activation of complement proteins
limits spread of infection
often resolves infection
adaptive immune response (last line of defense)
slow to respond but specific to particular pathogen
involve antibody-mediated responses and cell-mediated responses
Cells of Immune System
2 Major Cell Populations in Blood
erythrocytes/red blood cells (RBCs)
carries oxygen to the tissues
leukocytes/white blood cells (WBCs)
cells of immune system
-all blood cells arise from hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
-hematopoietic cells are self-renewing
found in bone marrow, umbilical cord, in blood (small amounts)
Leukocytes
-separated into
myeloid cells
lymphoid cells
Myeloid Cells
participate in innate immune response
includes
monocytes (mature into macrophages)
mast cells
granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils)
Lymphoid Cells (Lymphocytes)
participate in adaptive immune response
includes
cytotoxic T cells (CTLs)
T helper (Th) cells
T regulatory (Treg) cells
B cells
Dendritic Cells
-link between innate and adaptive response
-important cells for
activating T cells
initiating adaptive immune response
-dendritic cells derived from lymphoid cells or myeloid cells
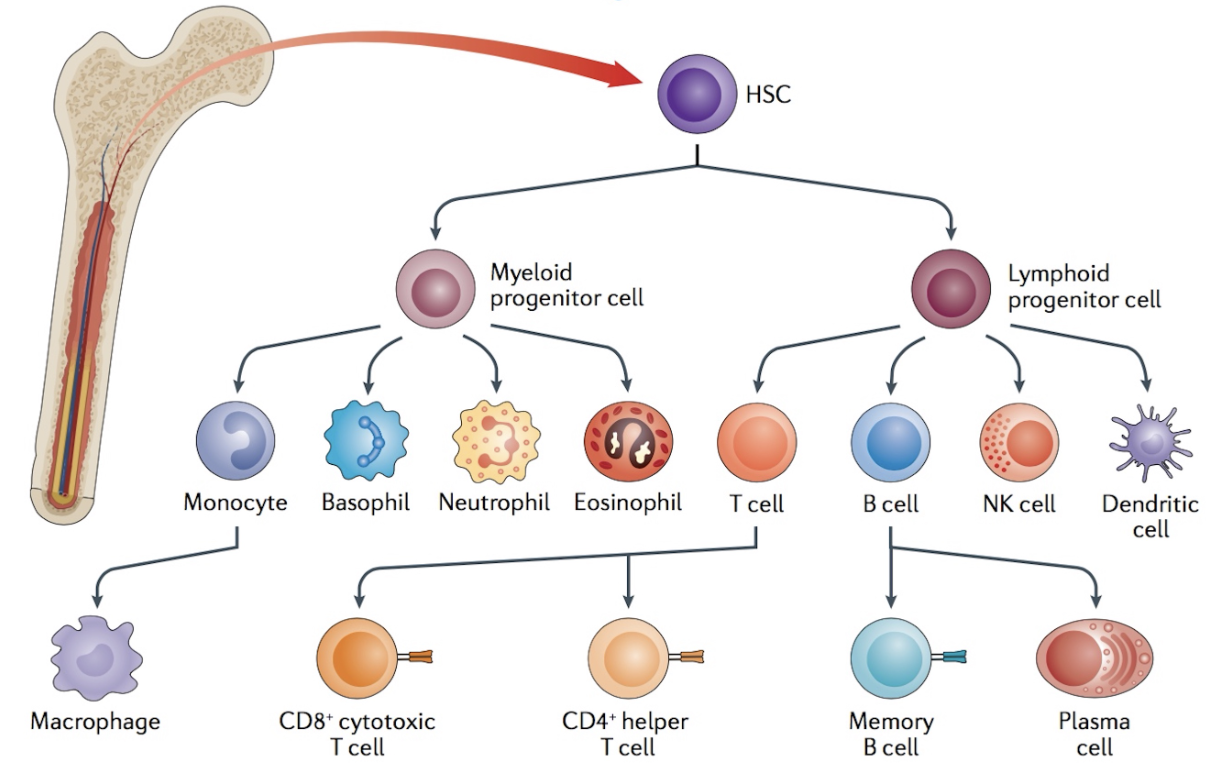
all cells of blood and immune system derived from common hematopoietic stem cell
Location of Immune System
-distributed throughout the body
-cells of immune system found in
blood circulatory system
lymphatic circulatory system
enables lymphocytes and proteins to move around body
lymph fluid similar to blood but lacks RBCs and platelets
connects different lymph nodes together
lymphoid organs
primary lymphoid organs
secondary lymphoid organs
-lymphatic circulatory system and blood circulatory system are connected
fluids in tissues drain into lymphatic capillaries then into lymph nodes
lymphatic fluid returns to blood circulatory system via thoracic duct located near heart
Primary Lymphoid Organs
-sites where lymphocytes develop and mature
includes
bone marrow
thymus
-all hematopoietic cells (blood & immune cells) complete process (developmentation & maturation) in bone marrow
except T cells → begins in bone marrow → completes in thymus
Secondary Lymphoid Organs
-sites where mature lymphocytes encounters pathogens/foreign molecules and begins adaptive immune responses
includes
spleen
lymph nodes
 Knowt
Knowt