DCIT 21A
Introduction to Computer Concepts and History of Computers
Computer
electronic device that takes data, processes the data according to a series of instructions called a program and produces information.
an electronic device capable of performing mathematical and logical operations.
an electronic system designed to manipulate data.
IPO (input, process, output)
Program
series of instruction that a computer must follow in order to process data into information
Capabilities of Computer
It has the ability to perform mathematical and logical operations.
It has the ability to store or remember a great amount and variety of information and retrieve or recall the information needed almost instantly.
It has the ability to handle large volumes of repetitive tasks accurately over a long period of time.
It can communicate with its operators and other machines.
It has the ability to control errors and check itself.
Limitations of Computers
The computer functions only when input and the necessary instructions to process the information have been provided by a human being.
It can detect but generally cannot correct inaccurate entries by itself.
It is subject to occasional breakdown or computer malfunction because of power failures, computer failure, humidity, temperature and maintenance
Characteristics of Computers
MACHINE
ELECTRONIC
AUTOMATIC
MANIPULATE DATA
MEMORY
LOGIC FUNCTIONS
Computers can be used in:
Business
Home
Entertainment
Scientific Research
Military
Benefits of Computers
Storing or memorizing large amounts of information.
Quickly recalling a single piece of information.
Rapidly performing a series of sequential tasks.
Carrying out a specific action based on sensor reading or other quantifiable information.
Types of Computers
Mainframes
Personal Computers
Desktop Computers
Laptop Computers
Tablet PCs
Media Centre
Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs)
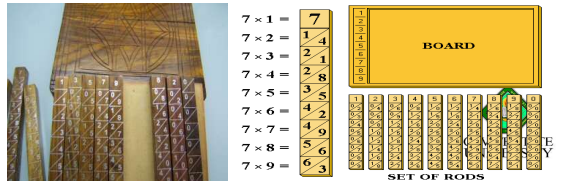
History: Earliest Computing Device
ABACUS
considered as the 1st manual data processing device
developed in China in the 12th century A.D.
performs arithmetic calculations

NAPIER’S BONES
developed by a Scottish mathematician John Napier
obtain products & quotients of large numbers
OUGHTRED’S SLIDE RULE
invented by William Oughtred in 17th century
arithmetic operations could be done by simply sliding the rulers

PASCAL’S CALCULATOR
developed by a French mathematician Blaise Pascal in 1645
could add & subtract numbers up to 8 digits

LEIBNIZ CALCULATOR
invented by Gottfried Leibniz in 1694
it utilized the same techniques for addition & subtraction as Pascal’s device but could also perform multiplication, division & square root

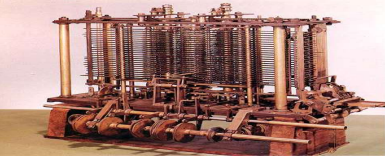
BABBAGE ANALYTICAL ENGINE
designed to use 2 types of cards: operation cards & variable cards
developed by Charles Babbage, the Father of Modern Computers. It is not because of the machine he build but rather his ideas became the basis for modern computation devices
Augusta Ada Byron, worked with Babbage & considered as the First female Programmer
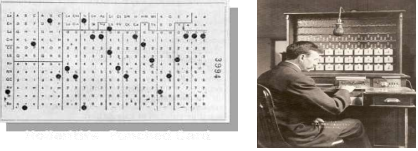
Hollerith’s Punched Card Machine
developed by a statistician named Herman Hollerith in 1880 considered as the 1st commercially successful data processing machine.
Hollerith made a census machine used by the US Bureau of Census in 1890
1800’s
George Boole
“Boolean Algebra”
1930’s
Alan Turing
“General Purpose Programmable Computer”

John Atanasoff
“first electronic digital purpose computer” or “Atanasoff Berry Computer”.
1940’s
Grace Hopper
Introduced the concept of debugging or finding errors
ENIAC
Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer
EDVAC
Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer
EDSAC
Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer

Stanislaw Ulam
“computer simulation”
1960’s
Ted Hoff
microprocessor chip
1970’s
Paul Allen and William Howard (Bill Gates)
The co-founders of the Microsoft Corporation
1980’s
Tim Berners-Lee
proposed/invented the World Wide Web (www)
Computer Classifications
According to age and component generations
According to size
According to Operation
According to Application
According to Design
According to Age and Component Generations
First Generation
VACUUM TUBES
slow
expensive
fragile
very large
Second Generation (Assembly Language and first OS)
TRANSISTORS (transfer resistance)
much simpler
much smaller
much cheaper
more reliable
no warm up
much faster
Third Generation
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
miniaturization added to all the existing benefits
enabled un-thought of possibilities
Fourth Generation (High-level Programming Language)
Medium Scale Integration (MSI)
Large Scale Integration (LSI)
Fifth Generation
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)
making computers behave like humans
Games Playing, Expert Systems, Natural Language, Neural Networks, Robotics
According to Size
Mainframe
used to describe large computers. It can process large amounts of data at very high speed, hold up to millions of characters in its storage and support many input, output, and storage devices.
Minicomputers
relatively smaller and slower computers compared to mainframe.
Microcomputers
typically fits a desktop. Inside of it is microprocessor, which has control capability for memory and I/O access, and which contains an arithmetic logic unit all on a single, chip less than one quarter of an inch square
According to Operation
Digital Computers
operates essentially on the basis of distinct (discrete) “on” and “off” states which can be represented by 1’s and 0’s referred to as binary digits.
Analog Computers
operate by measuring continuous physical or electrical magnitudes such as pressure, current, voltage, length or shaft rotations.
Hybrid Computers
combination of the desirable qualities of the analog and digital computers
According to Applications
Scientific Computers
computers that can manipulate numbers according to sophisticated formulas and keep track of the results to several decimal places.
Business Computers
computers that usually handle large volumes of data for input, perform simple calculations like addition and subtraction and print vast numbers of reports.
According to Design
General Purpose Computers
designed to perform a variety of operations by simply changing instructions.
Special Purpose Computers
built for specific operation and usually satisfies the needs for a particular type of problem.
Operating System
System Software vs. Application Software
System Software
The operating system and utility programs that control a computer system and allow you to use your computer
Enables the boot process, launches applications, transfers files, controls hardware configuration, manages files on the hard drive, and protects from unauthorized use
Application Software
Programs that allow a user to perform specific tasks on a computer
Word processing, playing games, browsing the Web, listening to music, etc.
The Operating System
Operating System
A collection of programs that manage and coordinate the activities taking place within a computer
Acts as an intermediary between the user and the computer and between the application programs and system hardware
“Control program”, controls the execution of computer programs to prevent errors and misuse of resources of computer systems
Functions of an Operating System
Interfacing with Users (typically via a GUI)
Booting the Computer
Kernel - basic unit of OS
Configuring Devices
Managing Network Connections
TCIP - Transmission Computer Internet Protocol
Ping - a command to test network connectivity
Managing and Monitoring Resources and Jobs
File Management
Path - shows the folders you must travel through to get to a particular file
Security
Processing Techniques for Increased Efficiency
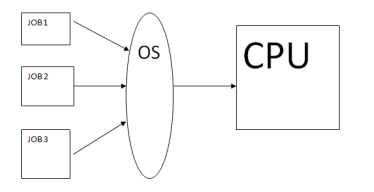
Multitasking
The ability of an operating system to have more than one program (task) open at one time
CPU rotates between tasks
Switching is done quickly
Appears as though all programs executing at the same time
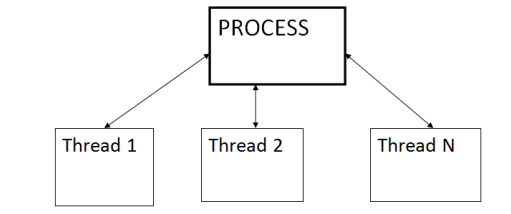
Multithreading
The ability to rotate between multiple threads so that processing is completed faster and more efficiently
Thread
Sequence of instructions within a program that is independent of other thread
There is prioritization in a single process with numerous tasks inside
Sequential Processing - tasks are performed one right after the other
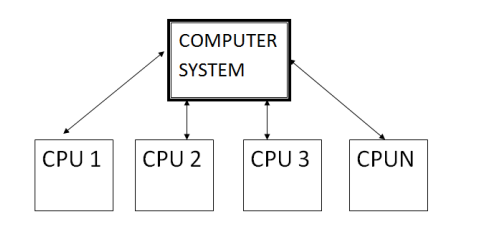
Multiprocessing and Parallel Processing
Multiple processors (or multiple cores) are used in one computer system to perform work more efficiently
Tasks are performed sequentially
In multiprocessing, tasks are divided to each core
In parallel processing, cores cooperate on one task at a time
Simultaneous processing - multiple tasks are performed at the exact same time
Memory Management
Optimizing the use of main memory (RAM)
Virtual memory
Memory-management technique that uses hard drive space as additional RAM
Buffering and Spooling
Buffer
Area in RAM or on the hard drive designated to hold data that is used by different hardware devices or programs
Buffering or Spooling
Placing items in a buffer so they can be retrieved by the appropriate device when needed
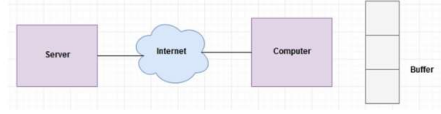 Buffering
Buffering
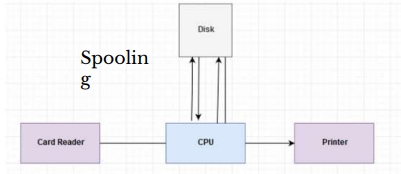 Spooling
Spooling
Differences Among Operating Systems
Command Line Interface
Require users to input commands using the keyboard
Graphical User Interface
Graphics based interface
Used by most operating systems
Categories of Operating Systems
Personal (Desktop) Operating Systems
Designed to be installed on a single computer
Server (Network) Operating Systems
Designed to be installed on a network server
Client computers still use a personal operating system
Server operating system controls access to network resources
Mobile and embedded operating systems are also common
The Types of Processors Supported
Desktop, mobile, server processors
32-bit or 64-bit CPUs
32-b programs can’t run in 64-b CPUs
Support for Virtualization and Other Technologies
New types of buses
Virtualization
Mobility
Security concerns
Power-consumption concerns
Touch and gesture input
The move to cloud
Operating Systems for Personal Computers and Servers
DOS (Disk Operating System)
DOS traditionally used a command-line interface
Dominant operating system in the 1980s and early 1990s
PC-DOS
Created originally for IBM microcomputers
MS-DOS
Created for use with IBM-compatible computers
Can enter DOS commands in Windows
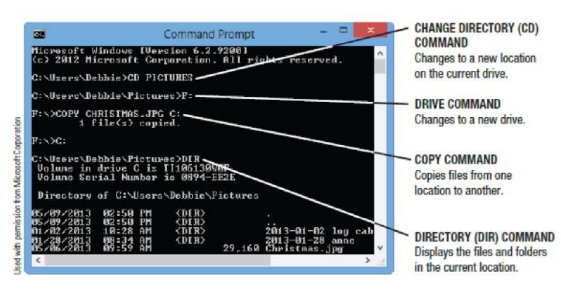
Windows
The predominant personal operating system developed by Microsoft Corporation
Windows 1.0 through Windows 11
Windows 1.0 released in 1985
Windows 1.0 through Windows 3.x were operating environments for DOS
Designed for personal computers
Windows NT (New Technology)
First 32-bit version of Windows designed for high-end workstations and servers
Replaced by Windows 2000
Windows XP
Replaced both Windows 2000 and Windows Me
Windows Vista
Replaced Windows XP
Introduced the Aero interface and Sidebar feature
Windows 7
Released in late 2009
Home Premium (primary version for home users)
Professional (primary version for businesses)
Libraries feature gives you virtual folders
Windows 8
Designed to be used with smartphones, desktop computers, with or without a keyboard or mouse
Supports multi-touch input
Includes Start screen, tiles, and charms bar
Windows 10
Replaced Windows 8 and 8.1
Includes new Start menu, Microsoft Edge, Cortana, Multiple desktops and Task view, Action Center and Tablet mode
Windows 11
Current version of Windows
On June 24, 2021, Windows 11 was announced as the successor to Windows 10 during a livestream. The new operating system was designed to be more user-friendly and understandable. It was released on October 5, 2021. Windows 11 will be a free upgrade to all Windows 10 users.
Windows Server
The version of Windows designed for server use
Windows Server 2022 is the latest version
Supports both virtualization and cloud computing
Windows Home Server
Preinstalled on home server devices
Designed to provide services for a home network
Can be set up to back up all devices in the home on a regular basis
Mac OS
Proprietary operating system for computers made by Apple Corporation
Based on the UNIX operating system
Originally set the standard for graphical user interfaces
Latest version: macOS 14 Sonoma
unix
Operating system developed in the late 1960s for midrange servers
Multi User, multitasking operating system
More expensive, requires high level of technical knowledge; harder to install, maintain, and upgrade
“UNIX” initially referred to the original UNIX operating system, now refers to a group of similar operating systems based on UNIX
Single UNIX Specification
A standardized UNIX environment
Linux
Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991—resembles UNIX but was developed independently
Is open-source software; has been collaboratively modified by volunteer programmers all over the world
Originally used a command line interface, most recent versions use a GUI
Strong support from mainstream companies, such as IBM, NVIDIA, HP, Dell, and Novell
Individuals and organizations are switching to Linux and other open source software because of cost
chrome OS
The first cloud operating system
Essentially is the Chrome Web browser redesigned to run a computer, in addition to accessing Web resources
Replaces traditional desktop operating systems
Is currently only available pre installed on Chrome devices
Operating Systems for Mobile Devices
Windows Phone 8, Windows RT, and Windows Embedded
Windows Phone
Latest version of Windows designed for smartphones
Windows Phone 8 is based on the Windows 8 operating system
Windows RT
Designed for tablet use
Windows Embedded
Designed primarily for consumer and industrial devices that are not personal computers
Operating Systems for Mobile Phones and Other Devices
Android
Linux-based operating system created with current mobile device capabilities in mind
Can create applications that take full advantage of all the features a mobile device has to offer
Open platform
Current version is Android 14 – Upside Down Cake
Devices support multitasking, multiple cores, NFC mobile payment transactions, Internet phone calls
iOS
Designed for Apple Mobile phones and mobile devices
Current version is iOS 17
Supports multitasking
Includes Safari Web browser, the Siri intelligent assistant, Facetime video calling, AirDrop to send items to others, and apps for email, messaging, music, and search
Blackberry OS and Blackberry PlayBook OS
Designed for Blackberry devices
Mobile Linux
Other mobile operating systems based on Linux besides Android and iOs
Ubuntu, webOS, Firefox OS, and Tizen
Utility Programs
Software that performs a specific task, usually related to managing or maintaining the computer system
Many utilities are built into operating systems (for finding files, viewing images, backing up files, etc.)
Utilities are also available as stand-alone products and as suites
Uninstall and Cleanup Utilities
Uninstall utilities remove programs from your hard drive without leaving bits and pieces behind
Important to properly uninstall programs, not just delete them
Cleanup utilities delete temporary files
Files still in Recycle Bin
Temporary Internet files
Temporary installation files
File Compression Programs
Reduce the size of files to optimize storage space and transmission time
Both zip and unzip files
WinZip (Windows users) and Stuffit (Mac users)
Backup and Recovery Utilities
Make the backup and restoration process easier
Creating a backup means making a duplicate copy of important files
Can use a recordable or rewritable CD or DVD disc, a USB flash drive, or an external hard drive
Good backup procedures are critical for everyone
Individuals should back up important documents, e-mail, photos, home video, etc.
Performing a backup can include backing up an entire computer (so it can be restored at a later date)
Can do the backup manually or use backup utility programs (stand alone or those built into operating systems)
Can also backup individual files are they are modified
Antivirus, Antispyware, Firewalls, and Other
Security Programs
Security Concerns
Viruses, spyware, identity theft, phishing schemes
Security programs protect computers and users
Antivirus programs
Anti Spyware programs
Firewalls
Many are included in Windows and other operating systems
File Management Programs
Enable the user to perform file management tasks
Looking at the contents of a storage medium
Copying, moving, and renaming files and folders
Deleting files and folders
File management program in Windows 8 is File Explorer
To copy or move files, use the Home tab to copy (or cut) and then paste
To delete files, use the Delete key on the keyboard or the Home tab
Search Tools
Designed to search for documents and other files on the user’s hard drive
Windows 8 has Search charm to search for files, apps, and Store items
Are often integrated into file management programs
Third-party search tools are also available
Diagnostic and Disk Management Programs
Diagnostic programs evaluate your system and make recommendations for fixing any errors found
Disk management programs diagnose and repair problems related to your hard drive
THE FUTURE OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Will continue to become more user-friendly
Will eventually be driven primarily by a voice interface, touch, and/or gesture interface
Likely to continue to become more stable and self healing
Will likely continue to include security and other technological improvements as they become available
Will almost certainly include improvements in the areas of synchronizing and coordinating data and activities among a person’s various computing and communicating devices
May be used primarily to access software available through the Internet or other networks
DATA
A collection or independent raw facts and figures (numbers, letters, symbols or combination of these)
INFORMATION
Data that is made meaningful to someone. Information
INFORMATION
DESIRABLE QUALITIES
Relevance – all of the information supplied must be important to the person receiving it.
Completeness – no vital information should be missed out.
Timeliness – information must be available when in time of need arises.
Accuracy – Correctness or validity of information is necessary because no sound decision is made of poor information.
Presentable – understandability of information is a function of presentation.
DATA PROCESSING
Composed of a series of activities responsible for transforming data into information.
DATA PROCESSING
CONCEPTS
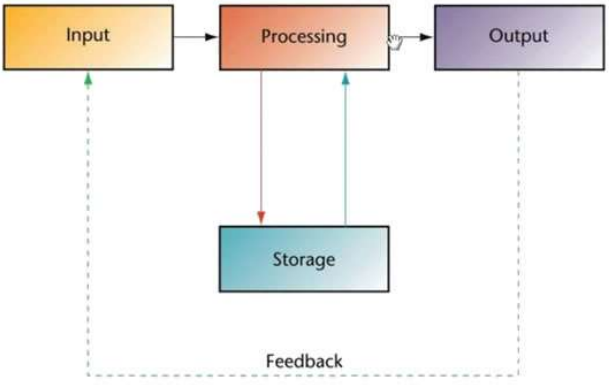
INPUT – PROCESS – OUTPUT (I-P-O) Model
A conceptual framework wherein input in the form of data or information is processed which result in the generation of an output basically in the form of information.
Data Processing Cycle
The flow of data from the moment it is recorded until the time it becomes a usable piece of information is traced taking into consideration what is actually done on the data in the process of transforming it into information.
INPUT-PROCESS-OUTPUT (I-P-O) MODEL
DATA PROCESSING METHODS
Manual Data Processing – implies the extend use of manual labor in the processing of data (slow, relatively inaccurate and could not support the rapidly expanding information requirements).
Mechanical Data Processing – involves the use of machines or devices that alter, transmit and direct applied forces (greater computational speed).
Electromechanical Data Processing – involves the use of mechanical devices with electric motors allowing them to carry out any operation.
Printers which give a permanent record
Electronic Data Processing – it has superior capacity to perform computations and other functions at incredible speeds.
DATA PROCESSING CYCLE
MAJOR PHASES
Origination Phase – involves basic capturing and recording of data (filling in the form in which its data is called source documents).
Sales order, cheque, materials requisition slip, birth certificate
Input Preparation Phase – it is concerned with the accuracy and completeness of data to ensure data integrity.
Minimize Data Error by:
Editing – process of selecting significant data and eliminating that, which does not need to be recorded for processing.
Coding – process that reduces the amount of data to be processed through the use of a code (a symbolic representation of a thing or a fact comprised of numeric or alphabetic characters).
Verifying – checking the accuracy of data gathered.
Processing Phase – conversion of data into useful and meaningful information.
Kinds of Processes:
Classifying – systematically grouping data into classes of common characteristics or attributes.
Sorting – process of physically separating classified data and rearranging these into a predetermined sequence (numerically or alphabetically, ascending or descending order).
Calculating – involves arithmetical processes.
Summarizing – process of decreasing the level of details of data. It involves listing or tabulating data and totaling each list.
Output Preparation Phase – result or information is generated.
Several Ways How Information is provided to the User:
Reproduction
Communication – could be transmitted in printed or oral form
SYSTEM
A system is a group of organized interdependent components that interact with and complement one another to achieve one or more predetermined goals.
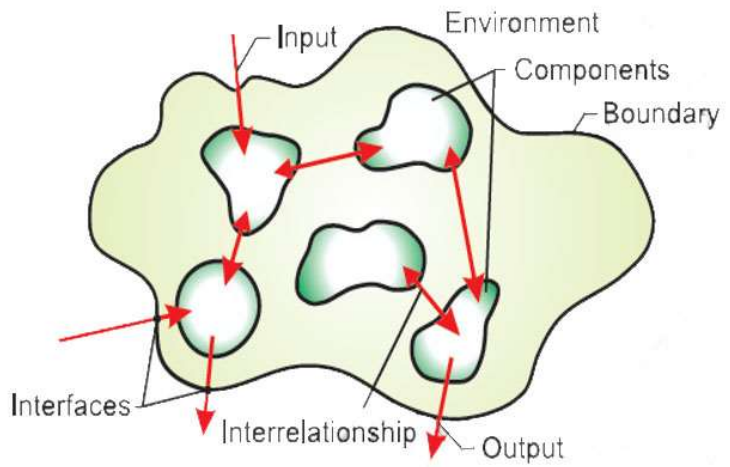
SYSTEM: CHARACTERISTICS
Unitary Whole – a system is the sum of its parts glued into one distinct entity.
Composed of Parts – a system is made up of functionally oriented parts.
Bounded – boundaries separate the system from its environment.
System Parts Interact With Each Other – the parts are related and have definite interactions and interdependencies.
Hierarchical – Each system is likely to be part of another larger system just as it is likely to be divided into subsystems.
Goal-Oriented – The components all work toward a particular purpose of function.
SYSTEM: BASIC COMPONENTS
Inputs – elements that enter the system and take the form of energy, materials or information.
Processes – actions on the inputs that converts it to outputs.
Outputs – the finished product, which resulted from processing the inputs.
Environment – the set of all outside elements or focuses that influence the system.
SYSTEM TYPES
Information System – a group of related activities (manual or computerized) designed to collect, process, generate and exchange information for the exclusive support of a major functional area to fulfill the problemsolving and decision-making information needs of business workers of the organization.
Personnel Management Information System, Financial Management Information System Types of System
Application System – a group of related activities designed to support a very specific function.
Payroll System, Accounting System
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
HARDWARE – supported by auxiliary or peripheral
computer equipment or physical components that are used in data preparation, data input, data storage, data computation and logic comparisons, control functions and outputting information
Central processing unit (CPU) and the storage, input, output and communication devices
SOFTWARE – non-physical components such as the machine coded instructions used by the different hardware facilities. It refers to all computer programs which direct and control the computer hardware in data processing
SYSTEMS SOFTWARE
A collection of programs that facilitates the programming and operation of the computer. An integral part of the computer system itself (supervises the operations of the CPU, controls the input/output functions of the computer system, translates programming languages, and provides other support services)
Disk Operating System (DOS), Database Management System (DBMS), interpreters and compilers, and data communication software
APPLICATIONS SOFTWARE
Not an integral part of the computer system. It may be written to solve a specific problem and may be written by programmers or may be purchased or leased from computer vendors, software companies or other computer users.
PEOPLEWARE – refers to the personnel who manage, designs the application, writes and encodes the program.