psych unit 3- personality
Unit 3: personality
- Personality: a pattern of thoughts, feelings, behaviors that make us unique
- Nature v nurture
- Stability
- Studying personality:
- Idiographic method: case studies
- Nomothetic method: surveys, assumes all people share the same basic traits
- Theories:
- Freudian theories:
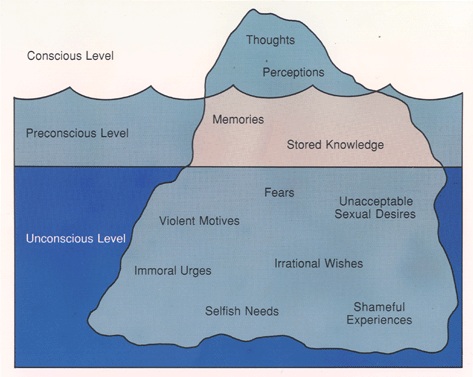
- Focuses on uncovering and understanding the influence of unconscious conflicts, especially those rooted in early childhood
- Psychodynamic
- Free association: when you say a word you say the 1st thing that comes to mind (follows unconscious mind)
- Freud’s iceberg metaphor
- Freud’s psychoanalytic theory:
- Eros: instinctual life drive directed by sexual energy (libido)
- Thanatos: death drive which accounts for our aggressive and self-destructive thoughts
- Id: primitive drives, based on pleasure principal
- Devil
- Ego: balance, based on reality
- Compromise
- Superego: based on morality
- Angel
- Id: take the cake, Ego: ask if you can have some cake, Superego: do not take or have any cake
- Id: look at the answers, Ego: look at the answers to prepare a study guide, Superego: do not look at the answers
Defense mechanisms: unconsciously used by the ego to protect itself from pain & anxiety
- \
- Denial: ego refuses to acknowledge anxiety
- \
- Displacement: ego shifts feeling towards an unacceptable object to a more acceptable object, angry at a person/object
- \
- Projection: ego attributes problems & faults to others, angry at yourself
- \
- Rationalization: ego replaces a less acceptable motive w/ an acceptable one
- \
- Reaction formation: ego transforms an unacceptable motive into its opposite
- \
- Regression: ego seeks security of an earlier developmental period in times of stress
- \
- Repression: ego pushes unacceptable impulses out of awareness
- \
- Sublimation: ego replaces unacceptable impulse w/ a socially acceptable one
- \
- Intellectualization: people reason about a problem to avoid uncomfortable feelings
Freud’s phsycosexual stages: people go through 5 psychosexual stages of development. In each stage the child’s libido is focused on a different area of the body. If conflicts are not resolved appropriately at each stage the child becomes FIXATED on certain stage
- Oral stage:
- birth -> 18 months
- pleasure is derived from mouth
- (ex: drinking, excessive eating)
- Anal stage:
- 18 months to 3 years
- if parents are too hard during this stage the child may be “anal retentive”
- (ex: uptight, controlling)
- overindulgent parents may have “anally impulsive” kids
- (ex: messiness, impulsive)
- Phallic stage:
- 3-> 6 years old
- Pleasure from genital stimulation
- Child identifies w/ thier same sex parent
- Development of superego
- Latency period:
- Middle childhood to adolescence
- Sexual energy is hidden, chanelled into socially acceptable activities
- Genital stage:
- Final stage of adult sexuality
Critics of Frued theory:
- Male centered
- Small number of case studies
- Lack of scientific validity
Neo freudians
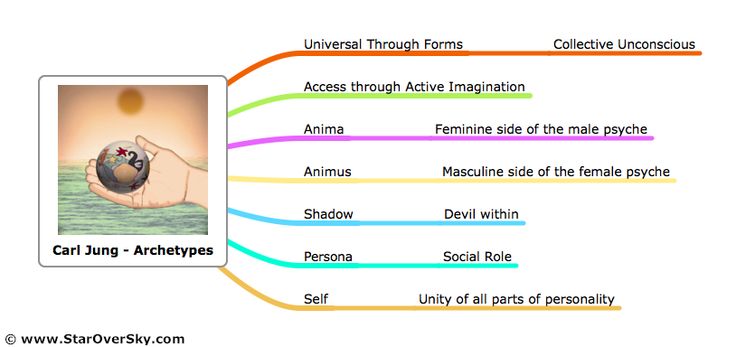
- Carl jung
- Collective unconscious:
- Set of common themes (archetypes) inherited from human experience & shared by all people
- Karen horney
- Womb envy:
- Males jealous of female ability to have children
- Basic anxiety:
- We all have a feeling of unease in dangerous world
- Alfred adler:
- Focused on role of social factors in personality development
- Inferiority complex:
- We strive for superiority to consequate for our inadequacies
Projective personality tests:
- Rorschach inkblot test:
- Seeks to identify people’s inner feelings by analyzing their interpreting of the ink blot
- Thematic apperception test:
- Person views an ambiguous image and make up a story about it
Behaviorist theory: who you are is a reflection of your childhood, you learn behaviors & traits
- Nurture focused
- John watson
- B.F. skinner
Humanistic theory:
- Carl rogers: person can reach goals in relationships characterized by unconditional positive regard (UPR). Unfortunately, many relationships are built upon “conditions of worth”. Emphasized role of self concept (how one thinks of oneself) in happiness. Believed most contented people had smallest gap between real self and ideal self.
- Through relationship where someone thinks well of you no matter what
- Abraham maslow: self actualization
- BEHAVIOR THEORY: ASSUMES BEHAVIOR IS STABLE, ONCE U HIT 30 NO CHANGE
- Cardinal trait: overriding trait
- Reymund
- Factor analysis statistical grouping
- Grouping traits tg into 16
- Paul costa and
- Big 5 trait theory-
- Know the definitions
- Stable over time after 30
- Type a: ambitious
- Type B: laid back
Personality inventories
Barnum effect: not accuare
Locus of control
- Internal: can control your own fate
- External: outside world controls fate
Reciprocal determinism: people choose to go to certain environments
- We choose certain environments
- These environments change us
Personal constructs: your understanding of how the world works
Explamnatory styles:
- We fall into one of 2 basic categories
- Optimistic: bad events as temporary, good events as permanent, good is the usual
- Pesimistic: something bad is bound to happen, bad is the usual
Spotlight effect: we overestimate how much people are looking at us
Self esteem
Self ethicacy: feeling of capability
Narcissism: excessive self love
Apply something from those theories
Psychodynamic apply to id, superego
25 mc 1 frq