
Unit 6: Urban Land Patterns and Processes
General terms:
Urban: densely populated city
Central Business District: commercial & business center of a city (downtown)
Metropolitan: a densely populated urban core and its surrounding connected areas
Urbanization: the shift from rural to urban areas
Influences on Urbanization:
Site: exact location or feature of a place
Harbor: Istanbul
Island: Paris
Port cities: coastal or river
Situation: surrounding features of a place
Along a trade route: Beijing, Istanbul (Silk Road)
Command land between bodies of water: Baghdad, Mesopotamia
Transportation: Public Transit/ Highways
Government policies: Incentives for businesses (rebates, tax credits)
Types of Urban Areas:
World Cities: cities that function at the top of the world’s urban hierarchy
NYC, London, Paris, Tokyo
Megacity: population over 10M
Metacity: population over 20M
Sprawl: unplanned rapid expansion of development
Suburbanization: a pop. shift from historic core cities into residential suburban areas
addresses housing needs
allows for commuters
Edge City: a city that grows outside the traditional CBD with jobs & services
Exurbs: a wealthy region beyond the suburbs with connections to an urban area
Boomburbs: a suburban area experiencing significant growth in population & prosperity
Urban Model Concepts:
Rank Size Rule: pop. of cities are more evenly spread out
usually 1, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, …
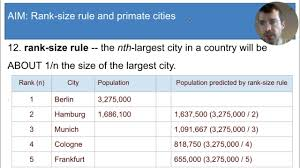
pro: industries spread out & variety of services
con: Rule not always consistent
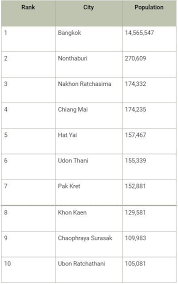
Primate City: lead city in a country due to size & influence
Pros: central capital with vast resources
Cons: disproportionate allocation of resources
Bangkok, Thailand
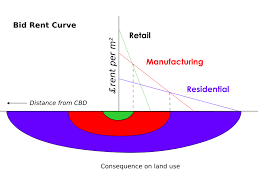
Bid-Rent Theory:
land closer to the CBD is more expensive
suburbs- larger homes away from CBD
Christaller’s Central Place Theory:
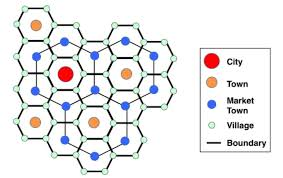
Hexagonal patters that explain distribution of goods & services across a region
Impacted by:
Population size
Distance: Assumes people will always purchase goods from the closest place offered
Urban Sustainability: reducing a city’s negative impacts on the environment, livability (QOL), strong infrastructure
Walkability: City layouts and infrastructure built to safely walk.
Smart Growth: Urban planning strategy that concentrates on compact design & walkable cities to avoid sprawl
New urbanism: A smart growth design which promotes environmentally friendly habits by creating walkable neighborhoods containing a wide range of housing & job types (mixed land use)
Slow Growth Cities: use smart growth strategies to decrease outward growth/sprawl
Zoning laws, Farmland Protection Policy, Greenbelts, infilling
Greenbelt: protected undeveloped land around urban areas
Parks, farmland, “green spaces”
London, Toronto
Gentrification: renewal of a lower-class neighborhood to a middle or upper class one.
Pros:
improved property value &tax revenue
Economic development
Infrastructure improvements
Decreases crime rates
Cons:
Higher rent displace residents
leads to homelessness
placelessness
Urban Issues:
Gentrification
Redlining: banks refusal to grant loans to ethnic races
Blockbusting: realtors get individuals to sell their house for cheaper in fear of black people moving in
“White Flight”: white people moving out of cities due to black people moving in
More white people in suburbs and black people in the cities today
Crime Rates: Poor urban areas have more crime
Environmental injustice: high pop. cities have high amounts of pollution
Disamenity zones: locations not connected to city services
Zones of abandonment: places abandoned due to lack of jobs, housing, value
Brownfields: abandoned areas that were used for industrial activities
typically have unsafe chemicals in the area
De facto segregation: while it is not encouraged by the law, segregation still occurs in the real world due to people
Range and Threshold:
Range: maximum distance people will travel for a good or service
High: sports games, fine dining, specialty hospital
Low: coffee shop, groceries, gas station
Threshold: size of pop. needed to support business & make a profit
High: concert, specialized stores
Low: Big Box Stores (Walmart), Gas station
Unit 6: Urban Land Patterns and Processes
General terms:
Urban: densely populated city
Central Business District: commercial & business center of a city (downtown)
Metropolitan: a densely populated urban core and its surrounding connected areas
Urbanization: the shift from rural to urban areas
Influences on Urbanization:
Site: exact location or feature of a place
Harbor: Istanbul
Island: Paris
Port cities: coastal or river
Situation: surrounding features of a place
Along a trade route: Beijing, Istanbul (Silk Road)
Command land between bodies of water: Baghdad, Mesopotamia
Transportation: Public Transit/ Highways
Government policies: Incentives for businesses (rebates, tax credits)
Types of Urban Areas:
World Cities: cities that function at the top of the world’s urban hierarchy
NYC, London, Paris, Tokyo
Megacity: population over 10M
Metacity: population over 20M
Sprawl: unplanned rapid expansion of development
Suburbanization: a pop. shift from historic core cities into residential suburban areas
addresses housing needs
allows for commuters
Edge City: a city that grows outside the traditional CBD with jobs & services
Exurbs: a wealthy region beyond the suburbs with connections to an urban area
Boomburbs: a suburban area experiencing significant growth in population & prosperity
Urban Model Concepts:
Rank Size Rule: pop. of cities are more evenly spread out
usually 1, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, …

pro: industries spread out & variety of services
con: Rule not always consistent
Primate City: lead city in a country due to size & influence
Pros: central capital with vast resources
Cons: disproportionate allocation of resources
Bangkok, Thailand

Bid-Rent Theory:
land closer to the CBD is more expensive
suburbs- larger homes away from CBD

Christaller’s Central Place Theory:

Hexagonal patters that explain distribution of goods & services across a region
Impacted by:
Population size
Distance: Assumes people will always purchase goods from the closest place offered
Urban Sustainability: reducing a city’s negative impacts on the environment, livability (QOL), strong infrastructure
Walkability: City layouts and infrastructure built to safely walk.
Smart Growth: Urban planning strategy that concentrates on compact design & walkable cities to avoid sprawl
New urbanism: A smart growth design which promotes environmentally friendly habits by creating walkable neighborhoods containing a wide range of housing & job types (mixed land use)
Slow Growth Cities: use smart growth strategies to decrease outward growth/sprawl
Zoning laws, Farmland Protection Policy, Greenbelts, infilling
Greenbelt: protected undeveloped land around urban areas
Parks, farmland, “green spaces”
London, Toronto
Gentrification: renewal of a lower-class neighborhood to a middle or upper class one.
Pros:
improved property value &tax revenue
Economic development
Infrastructure improvements
Decreases crime rates
Cons:
Higher rent displace residents
leads to homelessness
placelessness
Urban Issues:
Gentrification
Redlining: banks refusal to grant loans to ethnic races
Blockbusting: realtors get individuals to sell their house for cheaper in fear of black people moving in
“White Flight”: white people moving out of cities due to black people moving in
More white people in suburbs and black people in the cities today
Crime Rates: Poor urban areas have more crime
Environmental injustice: high pop. cities have high amounts of pollution
Disamenity zones: locations not connected to city services
Zones of abandonment: places abandoned due to lack of jobs, housing, value
Brownfields: abandoned areas that were used for industrial activities
typically have unsafe chemicals in the area
De facto segregation: while it is not encouraged by the law, segregation still occurs in the real world due to people
Range and Threshold:
Range: maximum distance people will travel for a good or service
High: sports games, fine dining, specialty hospital
Low: coffee shop, groceries, gas station
Threshold: size of pop. needed to support business & make a profit
High: concert, specialized stores
Low: Big Box Stores (Walmart), Gas station
 Knowt
Knowt