Matter and Atoms
Classifying Matter:
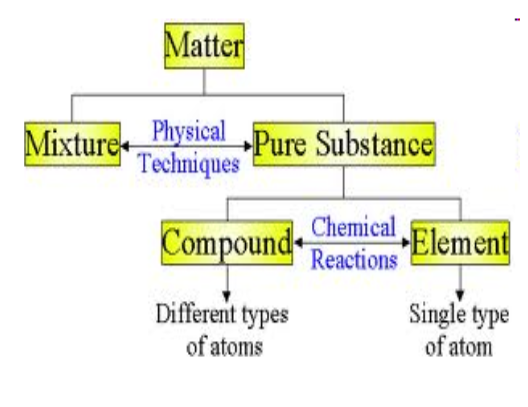
In chemistry, we sort them based on 3 categories:
- ==Element==
- Substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical changes
- Examples: Any element on the periodic table
- ==Compound==
- A substance that are made up of 2+ different elements, and can be decomposed by chemical means into simpler substances- always in the same ratio by mass
- Example: Water (H2O) is always 2 hydrogen molecules and 1 oxygen molecule
- ==Mixture==
- Combinations of 2+ substances where each substance is still could be separated
- Homogeneous Mixtures
- Mixtures that don’t contain visibly different parts
- Example: Air
- Heterogeneous Mixtures
- Mixtures that visibly show different parts
- Example: Chocolate Chip Cookies
[EXTRA note: Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element… meaning they’ll have different chemical and physical properties]
%%Quick Comparison:%%
| Compounds | Mixture |
|---|---|
| composed of 2+ different elements that are CHEMICALLY COMBINED | consists of 2+ different substances that are PHYSICALLY COMBINED |
| can be broken down into simpler substances (elements) | could be separated by physical means \n Example: water and sand (filtering) |
| composition is in a fixed ratio: meaning the ratio can’t be varied and the compound still being the same thing | the composition isn’t constant, meaning there could be 20% water and 80% sand but it still is sand water |
Methods of Separation:
- ==Filtration==
- Used to separate suspended particles from mixtures
- Example: water and sand
- ==Distillation==
- Used to separate solid-liquid mixtures or liquid-liquid mixtures by using their different boiling points
- Example: water and alcohol
- ==Chromatography==
- Used to separate dyes and other soluble materials
- Example: separation of plant pigments
Physical and Chemical Changes:
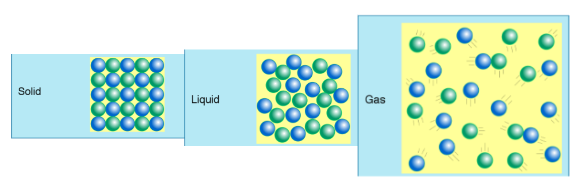
States/Phases of Matter
Solid
- Definite Shape and Volume
Liquid
- Indefinite Shape
- Definite Volume
Gas
- Indefinite Shape
- Indefinite Volume
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|
| Incompressible: \n - Solid particles are close together | Relatively incompressible: \n - Liquid particles are close together as well | Very Compressible: \n - Gas particles are far apart |
| Do not conform the shape or the volume of the container: \n - Already have fixed positions | Conform the shape of the container: \n - Particles could slide past one another | Conform the shape of the container: \n - Particles randomly move about and collide with each other on the wall |
Physical Properties:
Physical Properties:
- Quality of a substance that can be observed or measured WITHOUT changing the substance’s identity
- Examples: Boiling point, Taste, Odor, Dissolves in water, Luster, Density, Hardness, etc.
Chemical Properties:
- Any of a material’s properties that becomes evident during a chemical reaction
- Basically, it can’t be determined just by viewing for touching the substance
- Examples: Flammability, Ability to Rust
Physical Changes:
- Some properties of a substance change but the identity of the chemical does not
- PHASE CHANGES ARE PHYSICAL CHANGES !
- boil, freeze, condense, break, crack
Chemical Changes:
- A new chemical forms !
Structure of an Atom:
%%Atoms:%%
- the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical identity of that element
- basic unit of matter
%%History of atoms:%%
Democritus: a fifth century B.C. Greek philosopher proposed that all matter was composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms (which is Greek for uncuttable)
Billiard Ball Model: John Dalton viewed the atom as a small solid sphere. (1803)
Plumb Pudding Model: J.J. Thompson proposed that the atom was a sphere of positive electricity with negative particles imbedded throughout after discovering the electron (1897)
- It looks like a plum pudding :)
Electron Cloud Model: An atom consists of a dense nucleus composed of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons that exist in different clouds at the various energy levels.
%%Discovery of Nucleus:%%
Ernest Rutherford: Gold foil experiment involved during the firing of radioactive particles through thin gold foils and observed them. Because only about 1/20,000 rays were deflected, this led to his theory that most of the atom was empty space
Atomic Structures using Periodic Table:
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons:
^^Protons:^^
- They have a mass of approximately 1
- Protons are in the nucleus
- Positive charge
- They determine the identity of each element: Also represents the atomic number
^^Neutrons:^^
- These also have a mass of approximately 1
- Neutrons are also located in the nucleus
- Neutral Charge
^^Electrons:^^
- These have really small mass, often times they aren’t counted
- Electrons have negative charge
- They’re located around the nucleus, in rings
Atomic Structures:
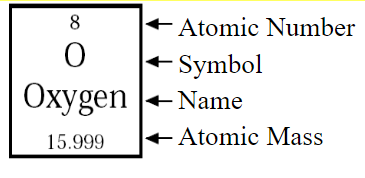
Atomic Number: Numbers of Protons
Atomic Mass: Numbers of Protons + Neutrons
Isotopes:
Different atoms of the same element can have different mass numbers depending on how many neutrons they have. Atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers are called isotopes.
Lewis Dot (Electron Dot) Structures:
@@Valence Electrons:@@ The amount of electrons an element has on their most outermost shell
- Elements with the same amount of valence electrons are typically part of the same group/family
- When drawing Electron Dot Structures, we use their valence electrons
@@Octet Rule:@@ States that the atoms would tend to lose/gain/share electrons in order to acquire a full set of valence electrons, which is 8 electrons
@@Ground State:@@ Electrons are in their lowest energy levels, or their normal energy levels
@@Excited State:@@ When heat, electricity, or light would move the electron up to different energy levels
- When the electron falls back down to the ground, it releases energy and gives off light energy or a spectrum
- Spectrums are unique to each element, and could be used to identify elements
- When the electron becomes excited, it takes in/absorbs energy