Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are the monomers of carbohydrates.
Isomers - molecules with the same molecular formul but with their atoms in arranged in a different way. Examples of isomers are alpha and beta glucose.
Hexose sugar - a monosaccharide with six carbon atoms in each molecule, such as glucose.
Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides bond together.
Glycosidic bond - the bond that is formed when monosaccharides are joined together by condensation reactions. This bond is broken in hydrolysis reactions.
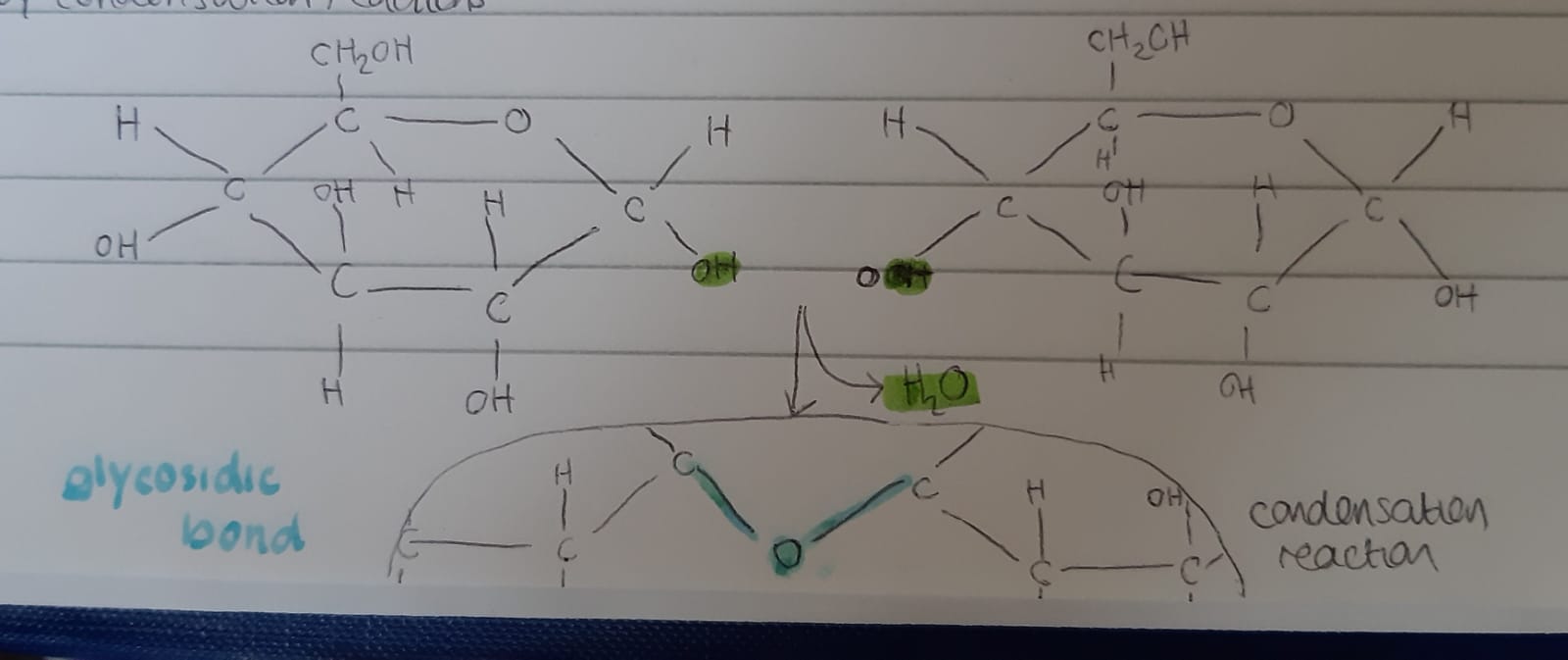
Above: A glycosidic bond being formed when two molecules of alpha glucose bind together. The disaccharide formed is called maltose.
| Glucose + … | Disaccharide formed |
|---|---|
| Glucose = | Maltose |
| Fructose = | Sucrose |
| Galactose = | Lactose |
The test for sugars is called the Benedict’s reagent.