Notes for psychology
Ch. 14
Delevant Behavior - (going naked) behavior considered in one culture “normal” is not normal in others.
Deviant Behavior - things that go against social norms or expectations, minor violations like “dressing in all black” clothing. Serious violations - “committing murder”
Dysfunctional - a disruption of a person’s ability to liv ehtier life productively or in a way that impairs their relationships, ability to think clearly, communicate with others, hold a job, or deal with stressful events.
Distressful Behavior - a state of emotional suffering characterized by symptoms of depression (e.g. loss of interest; unhappiness; desperateness) and anxiety (e.g. restlessness; feeling tense)
Psychopathology - psychological disorders are mental illnesses that need to be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which may include treatment in a psychiatric hospital.
Psychological Disorders - deviant behavior (slightly dysfunctional) + distressful behavior.
Medical Perspective: psychological disorders are sicknesses and can be diagnosed, treated and cured.
Biopsychosocial Perspective: assumes biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors combine to interact causing psychological disorders.
Early Theories
- Abnormal behavior was evil spirits trying to get out.
- Trephining - was often used (drilling a hole in skull). Also beatings, burnings, castration, teeth pulling transfusions of animal blood.
Philippe Pinel Medical Model - 1800s
- Discovery that syphilis infects brain and distorts mind. Provided incentive for further reform of treatments. Medical world began searching for physical causes for mental disorders.
DSM (Diagnostic and Statistic Manual of Mental Disorders) - keeps in track all mental disorders
Neurotic Disorders - Distressing but one can still function in a society and act rationally.
Psychotic Disorders - Person loses contact with reality, experiences distorted perceptions
DSM-IV - first to organize each psychiatric diagnosis into 5 dimensions (axes) relating to different aspects of disorder or disability
- (Relative to numbers:
- Axis 1 - is Clinical Syndrome present?
- Unit 5 - Sleep Disorders
- Unit 8A - Eating Disorder
- Axis 2 - is a Personality Disorder or Mental Retardation present?
- yadyayayada)
- Axis 1 - is Clinical Syndrome present?
DSM 5 (2013) *Latest edition:
- The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR) was published in 2022. Involving more than 200 experts, the majority who were involved in the development of DSM-5.
DSM 5 is an attempt to describe mental disorders in a dimensional manner rather than by strict categories…enables clinicians to better describe the symptoms experienced by individual patients.
Each DSM release has more info than the one prior.
Criticisms of the DSM
Dilemmas of diagnosis - if clinicians and researcher frequently disagree about a diagnosis with a patient, then research into the causes and effective treatments of those disorders cannot adance.
Medicalization - the process by which human conditions and problems come to be defined and treated as medical conditions, thus becoming the subject of medical study, diagnosis, prevention, or treatment.
Disease Mongering - the pejorative term for the practice of widening the diagnostic the diagnostic boundaries of illnesses (rising their prevalence) and aggressively promoting their public awareness in order to expand the markets for treatment.
Pharmaceutical Industry - an industry in medicine that discovers, develops, produces, and markets pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure and prevent diseases or alleviate symptoms.
Involuntary Commitment - a legal process through which an individual who is deemed by a qualified agent to have symptoms of severe mental disorder is detained in a psychiatric hospital which they can be treated involuntarily.
Involuntary Treatment - medical treatment undertaken without the consent of the person being treated.
Danger of Diagnostic Labels - Danger of Biases
Rosenhan’s study - his associates were faking symptoms of hearing voices. They were ALL admitted for schizophrenia. None were exposed as impostors. They all left diagnosed with schizophrenia in remission.
Anxiety Disorders - a group of conditions where the primary symptoms are anxiety or defenses against anxiety. The patient fears something awful will happen to them. They are in state of intense apprehension, uneasiness, uncertainty, or fear.
Other def: Distressing, persistent anxiety or dysfunctional anxiety-reducing behaviors.
Anxiety Disorders:
PTSD (Post-traumatic Stress Disorder) - Thoughts & Experiences of Horrible Event
SP (Social Phobia) - Embarrassment & Humiliation in Social Situations
GAD (Generalized Anxiety Disorder) - Constant worry and physical symptoms
OCD (Obssessive-compulsive Disolrder) - Excessive Repetitive Thoughts and Behaviors
PD (Panic Disorder) - Frequent Spontaneous Attacks + Avoidance
Panic Attack - Palpitations, Sweating, Trembling, Shortness of Breath, Choking, Chest Pain, Nausea, Dizziness, Unreality, Fear of Loss of Control, Fear of Dying, Paresthesias, Hot or Cold Flashes
Generalized Anxiety Disorder - in which a person is unexplainably continually tense and uneasy ~ restlessness, feeling on edge, irritability, sleep disturbance
~ ⅔ patients are women
Panic disorder - in which a person experiences sudden episodes of intense dread
~ experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, and other frightening sensations
→ leads to secondary disorders - agoraphobia (fear of open spaces-perceiving the environment in which you are in to be unsafe or uneasy)
Phobias - in which a person feels irrationally and intensely afraid of a specific object, activity, or situation
- Specific phobias ~ arachnophobia - fear of spiders
- Social Phobia (Agoraphobia) - fear of public places

Obsessive-compuslive disorder - in which a person is troubled by repetitive thoughts or actions
- Persistent unwanted thoughts (obsessions)
- Concern with dirt, germs, or toxins
- Something terrible happening (fire, death, illess)
- Symmetry, order, or exactness
- Cause someone to feel the need to engage in a particular repetitive action (compulsion)
- Excessive hand washing, bathing, tooth brushing, or grooming
- Repeating rituals/prayers
- Checking doors, locks, appliances, car brakes, homework
Post-traumatic stress disorder - in which a person has lingering memories, nightmares, and other symptoms for weeks after a severely threatening uncontrollable event
- Memories of the event cause anxiety
- Post-traumatic growt
- Survivor resiliency
Biological Causes of Anxiety Disorders
- Hereditary or predisposition (twin studies)
- Brain function - (fMRI scans of OCD patients show higher anterior cingulate cortex activity)
- Evolution - likely to fear situations that posed threat to early humans
Learning Factors and Anxiety Disorders
- Conditioning - Little Albert? Stimulus generalization!! → what condition provokes anxiety-inducing response
- Observational learning - seeing someone else respond with fear (i.e. a sibling) → siblings/peers may respond scared to something, which through learning the person can do so as well
- Reinforcement - learning to associate emotions with actions and the results that follow those actions. - some action could provoke anxiety, learning to associate it and prevent it
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
- Intellectual Disabilities - Problem solving, abstract thinking, and reasoning-perform low on IQ tests
- Communication disorders (language delays, written and spoken)
- Autism Spectrum Disorders - Emotion, Communication, Understanding
- Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) - inability to pay attention, impulsivity, hyperactivity, easily distracted, forgetful, impatient, problems with mood regulation
- Specific Learning Disorders - characterized by poor writing, reading, comprehension, intellectual and sensory deficits
- Motor Disorders - excessive clumsiness, awkwardness, motor skills that affect learning
- Tic Disorders - chronic, quick, impromptu, nonfluid behaviors (motor and/or vocal tics)
Rewiring the anxious brain - Neuroplasticity video notes
- Anxiety serves to motivate us to avoid real danger
- Disordered anxiety - anxiety that takes over our life
- The harder you try to take it away, the more severe it gets
- The Anxiety Cycle:
- Step 1: Interpret situation as dangerous
- Step 2: Escape, Avoid
- Step 3: Relief
- Step 4: Brain increases Anxiety
- Avoidance Grows Anxiety → as you can see from the anxiety cycle
- Coping skills like going on phone while situations or parties grows anxiety.
Rewiring the Anxious Brain Part 2: 10 Skills to Beat Anxiety: Anxiety Skills #22 video notes
- “He who has a why can endure any how” Opening yourself to facing anxiety provoking situations / talk about why you want to not experience anxiety
- Practice willingness - say it’s alright to be anxious
- Build emotional muscles - when you face your fears more and more, the smoother and thicker your neural pathways get, that wiring I can do hard things, just like muscles 20 lb weight might feel heavy at first, less and less after working out more.
- Let go of comparison as your source of self worth - let go of looking perfect all the time, or never messing up, FOCUS ON GROWTH from mistakes.
- Let go of belief that I can’t handle it-this is uncomfortable and I don’t like this but I can do hard things.
Somatoform Disorders - we all have experienced inexplicable physical symptoms under stress
- Nausea from stress…can’t tell how or why
Somatic Symptom Disorders - disorders in which symptoms take a bodily form without apparent physical cause - excessive thoughts, feelings, or behaviors associated health concerns from disproportionate and persistent thoguhts about seriousness of one’s symptoms, high levels of anxiety of health symptoms, excessive time and energy devoted to these symptoms or health concerns
Hypochrondiasis - relatively common, person interprets normal physical sensations/discomfort as symptoms of a disease.
Conversion Disorders - a rare somatoform disorder in which anxiety is presumably converted into a physical symptom.
Dissociative Disorders - Person represses the existence of past memories/trauma - bad past experiences. Escaping reality in ways that are not wanted and healthy…act as a different person, and let go of past traumatic experiences.
Dissociative Amnesia - A partial or total forgetting of past experiences, without organic cause, disconnected from the world around you, forgetting about certain time periods, events, and personal information.
Organic Amnesia - Results from other medical trauma (e.g. blow to the head, stroke, alcoholism) - disconnects from reality, forgetting past (NORMAL)
Dissociative Fugue - a symptom where a person with memory loss travels or wanders. This leaves the person in an unfamiliar setting with no memory or how they got there.
Dissociative Identity Disorder (D.I.D.) - Multiple Personality Disorder - often confused with schizophrenia, people with D.I.D. commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma, unlike schizophrenics, they have 2 or more distinct identities, are not psychotic, and have severe memory lapses (forgetting basic things).
Mood Disorders - psychological disorders characterized by emotional extremes (i.e. depression, mania, or both)
Major Depressive Disorder - occurs when at least 5 signs of depression (lethargy, feelings of worthlessness, or loss of interest in family, friends, and activities) lasts two or more weeks and aren’t caused by drugs or mental conditions)
- Women twice as vulnerable
- Men commit suicide more often
- 10-20 times much larger than 50 years ago
Martin Seligman: identifies 3 causes of learned helplessness
Out-of-control individualism/self centeredness: focuses on individual successes and failures rather than group accomplishments
The self-esteem movement - teaching a generation of children they should feel good about themselves irrespective of their efforts and achievements.
A culture of victimology - reflexively pointing the finger of blame at someone or something else when things or situations don't go right. - can cut the risk of depression in half!
Bipolar Disorder (formerly called manic depression) - involved periods of sleep and manic episodes - many episodes may involve long periods of little sleep, racing thoughts, and set impossible goals. High bursts of creative energy released during manic states. Followed by an ultimate crash or depressed state - low activity and energy.
Genetic Influences - mood disorders run in the families. HERITABILITY
The depressed brain:
- Less left frontal lobe activity, hippocampus vulnerability to stress-related damage.
Biochemical Influences - lowered norepinephrine and serotonin levels
- “feel good” neurotransmitter lowered and “lowered blood pressure in ‘fight’ or ‘flight’” neurotransmitter lowered.
The social-cognitive perspective suggests that self-defeating beliefs, which arise in part from learned helplessness, and a negative explanatory style (people tend to blame themselves for a disastrous outcome) feed depression.
Depression Vicious Cycle - a person sees a disorder as a vicious cycle in which negative stressful events are interpreted through, a ruminating pessimistic explanatory style (“it was inevitable to happen”) creating a hopeless, depressed state that hampers the way a person thinks and acts. This, in turn, fuels negative stressful experiences.
Biomedical therapy-uses physiological treatments such as medications to treat psychological disorders.
Schizophrenia - a psychological disorder involving distortions in thoughts, perceptions, and/or emotions - split mind - refers to a split from reality, not multiple personalities
Disorganized Thinking - the type of schizophrenia that is characterized by a) extremely disorganized behavior, b) disorganized speech and flat affect, c) delusions & hallucinations sometimes present but not organized, and d) silliness, laughing, and giggling may occur without apparent reason.
Disturbed perceptions
- Hallucinations
- hearing voices
- Not IRL things!!
Catatonic is the type of schizophrenia that is characterized by highly disturbed movements or actions and waxy flexibility.
Catatonic Stupor: patients remain motionless, statue like poses
Catatonic Excitement: Patients become agitated, hyperactive, rock in chairs
Paranoid is the type of schizophrenia that is characterized by a) delusions, hallucinations, or both
Undifferentiated - Persons displaying a combination of symptoms that do not clearly fit in one of the other categories of schizophrenia
Residual Type - Individuals who had a past episode of schizophrenia but free of symptoms
Positive Schizophrenia - Presence of inappropriate symptoms (hallucinations, disorganized or delusional talking)
Negative Schizophrenia - Absence of appropriate one (expressionless face, rigid body)
1.1% of US population schizophrenic
Chronic (process) schizophrenia
- Slow to develop!
- Doubt of recovery
- Typically display negative symptoms
Acute (reactive)
- Recovery is better
- Positive symptoms
Avoidant Personality Disorder – sensitive about being rejected so relationships become difficult.
Dependent Personality Disorder - clingy and submissive
OCD - Overly concerned with certain thoughts and performing certain behaviors. Self induced!
Paranoid Personality Disorder - show deep distrust of other people
Schizoid Personality Disorder - detached from social relationships
Schizoptypical Personality Disorder - Characterized by a need for social isolation, odd behavior and thinking, and often unconventional beliefs.
Histrionic Personality Disorder - Characterized by a pattern of excessive emotionality and attention seeking.
Narcissistic Personality Disorder - having a snese of self-importance, thinking you’re the center of the universe, react to criticism with rage or shame.
Borderline Personality Disorder - People with this disorder are prone to constant mood swings and bouts of anger…take anger out on themselves, self-harm and suicide.
Antisocial Personality Disorder - Antisocial personality disorder is characterized by a lack of conscience or shame. -- lower levels of stress hormones, start from early age.
26% of americans suffer from diagnosable mental health disorder.
Ch. 15
Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) in France and Dorthea Dix (1802-1887) in America founded humane movements to care for the mentally.
Went from harsh statements to helping mentally ill.
⅕ Humans live with a mental illness (51.5 million in 2019)
Most common: Anxiety and Depression
Women more willing than men to seek treatment
Stigma surrounding mental health
Psychotherapy - involves an emotionally charged, confiding interaction between a trained therapist and a mental patient.
Biomedical therapy - uses drugs or procedures that act on the patient’s nervous system, treating his or her psychological disorders.
Eclectic Approach - uses various forms of healing techniques depending upon the client’s unique problem.
FREUD = ***
ROGERS = ‘’’
***Psychoanalysis - the 1st formal psychotherapy to emerge was psychoanalysis, developed by Sigmund Freud…look at your past to see why you have problems currently.
- Since psychological problems originate from childhood repressed impulses and conflicts, the aim of psychoanalysis is to bring repressed feelings into conscious awareness where the patient can deal with them.
- When energy devoted to id-ego-superego conflicts is released, the patient’s anxiety lessens.
***Free association
- Patient lies on a couch and speaks whatever comes to his or her mind → aim to unravel the unconscious mind.
*** Because patients disclose personal info about themselves, they may find themselves experiencing strong positive/negative feelings towards the analyst (therapist) = transference
Psychoanalysis Criticisms
- Takes too much time
- Cannot be proven or disproven!
- Freud’s theories overemphasized the deterministic roles of biology and unconscious mind, leaving little room for the influence of the conscious mind
- Freud’s theories overemphasized the unconscious mind, sex, aggression, and childhood experiences.
Psychodynamic therapy vs. Interpersonal therapy
- Influenced by Freud
- Similarities with psychoanalysis
- Focus on common themes in relationships across life
- Differences with psychoanalysis
- Face to face
- Much shorter in duration - interpersonal psychotherapy
Humanistic Therapies
- Insight therapies focus more on:
- The present rather than the past.
- Conscious rather than the unconscious
- Taking immediate responsibility
- Promoting growth instead of curing.
- Client-centered therapy’’’
- Non-directive therapy
- Genuineness, acceptance, and empathy
- Active Listening
- Paraphrase - Summarize in your own words
- Invite clarification - “What might this be an example of?”
- Reflect feelings - “What you’re sensing from the speaker's body language
- Unconditional positive regard
Psychoanalytic vs Humanistic
- Humanistic therapists assume people are generally good and healthy, but negatively affected by pressure from oneself and society, contrasting psychoanalysis, which focuses towards fixing the problem.
Behavior Therapy - refers to a range of treatments and techniques which are used to change an individual’s maladaptive responses to specific situations - to change negative behaviors to uncontrollable situations to more positive ones ~ overall eliminate unwanted behaviors through applying learning principles.
“The behaviors are the problem, so we must change the behaviors!”
Counterconditioning is a procedure that conditions new responses to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors → conditions new responses to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors…If someone fears public speaking, counterconditioning may involve associating public speaking with positive experiences or rewards of ice cream or boba to alleviate the fear response.
Exposure Therapy -
Expose patients to things they fear and avoid. Through repeated exposures, anxiety lessens, because they habitate to the things feared.
Systematic Desensitization - a type of exposure therapy that assoicates a pleasant, relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli commonly used to treat phobias.
Asking them to feel relaxed or in meditation mode, and then inquire about how they feel when mentioning their fear or talking about their fear.
Extreme form: flooding - ask them to pet a dog, even if they’re scared of it.
Aversive Conditioning - A type of counter-conditioning that associates an unpleasant state with an unwanted behavior. - has been used to cure alcoholism
For example, a dog owner may spread a bitter liquid on objects, the dog should not chew.
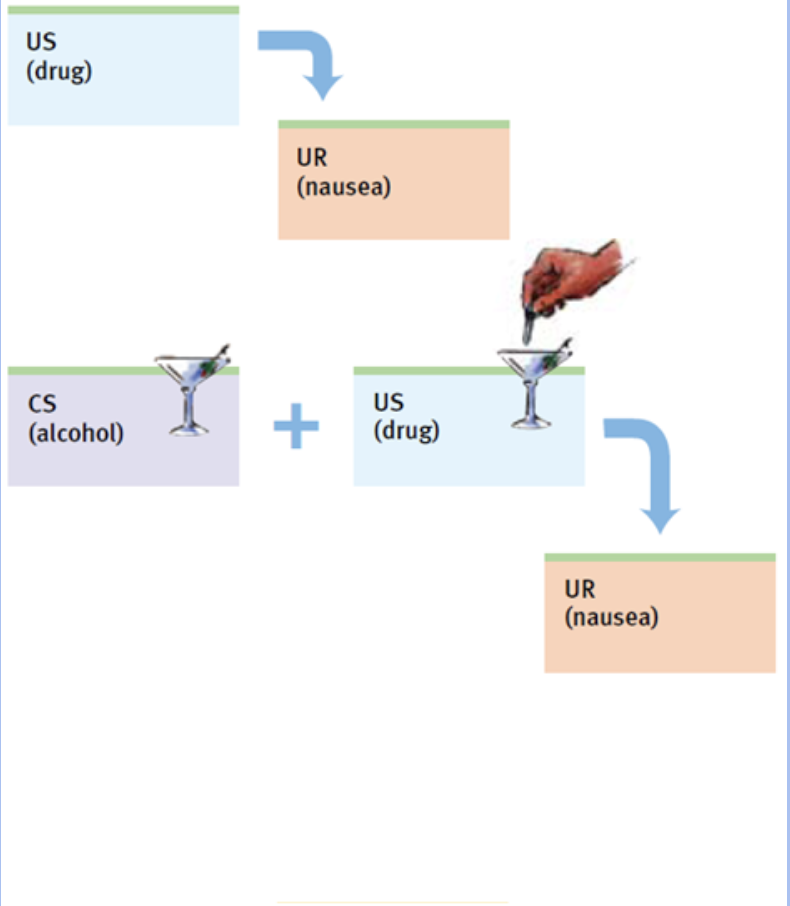
Operant conditioning - procedures that enable therapists to use behavior modification, in which desired behaviors are rewarded and undesired behaviors are either unrewarded or punished.
Token Economy - therapists create a toke economy in which patients exchange a token of some sort, earned for exhibiting the desired behavior, for various privileges or treats.
Criticisms of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Doesn’t fully fix all problems - fails to address underlying causes
- Doesn’t work for all psychiatric conditions
- Time consuming than alternative treatments
- Relies on patients to be effective. Do extrinsic rewards promote long term durable solution
- Not always easily available
- Depends on therapist ~ Is it right for one person to control another’s behaviors?
Cognitive Therapy
- Teaches people adaptive ways of thinking and acting based on the assumption that thoughts intervene between events and our emotional reactions.
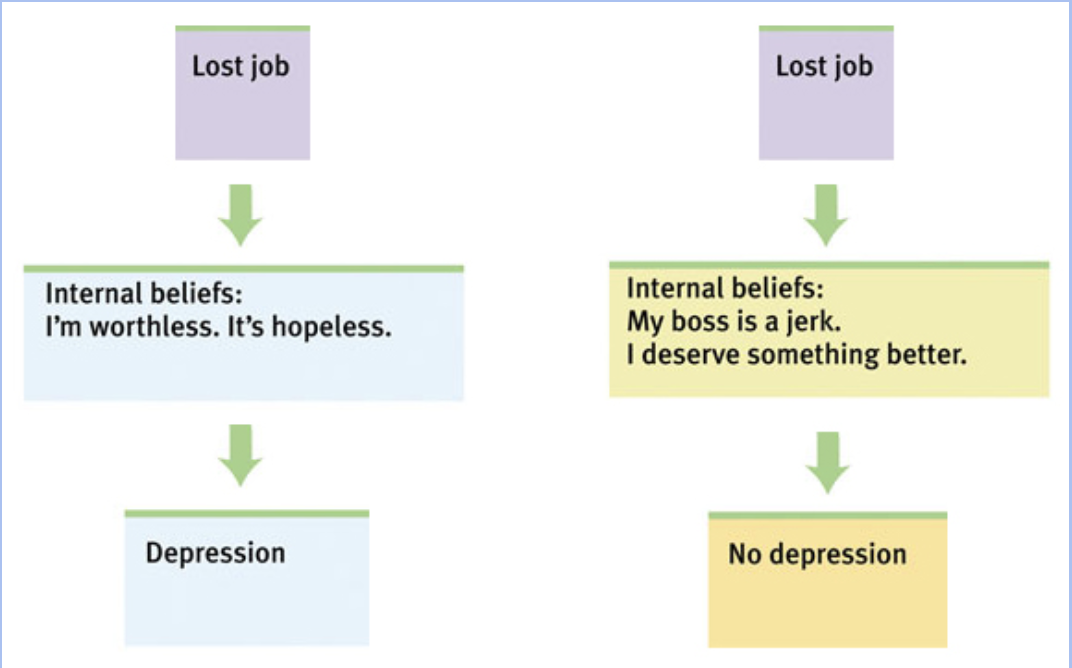
Beck’s Therapy For Depression:
- Aaron Beck suggests that depressed patients believe they can never be happy (thinking) and thus associate minor failings (failing a quiz) in life as major causes for their depression. “God never wants me happy, that’s why I failed this test. I’m hopeless. ;(“)
- Goal is to reverse catastrophizing beliefs. “I can never be happy” has to change to “This was just an obstacle to overcome so that I can be happy.”
- Criticisms: A link between negative thinking and depression does not mean that one has necessarily caused another - cause and effect can’t be established.
- It may be in fact that depression causes negative thinking and not the other way around.
Stress Inoculation Training
- Teaching coping skills to manage stress and anxiety: deep muscle relaxation, cognitive restructuring, breathing exercises, assertiveness skills, thought stopping, role playing, and guided self-dialogue.
Cognitive Behavior Therapy (generalized definition) - aims to alter the way people act (behavioral therapy) and alter the way they think (cognitive therapy) in response to certain situations.
Group therapy ~ normally consists of 6-9 people attending a 90-minute session that can help more people and costs less. Clients benefit from knowing others have similar problems.
Family therapy - treats the family as a system. Therapy guides family members toward positive relationships and improved communication.
The Criticisms of Psychotherapy
- Regression toward the mean~Can make natural variation in repeated data look like real change.
- Client’s perceptions - “the good participant role” in which the participant attempts to discern the experimenter’s hypotheses and to confirm them. The participant doesn’t want to “ruin” the experiment. Could the same be true in therapy?
- Clinician’s perceptions
- Outcome research - Randomize (are the results reliable?)
- Meta-analysis - a statistical procedure that combines the conclusions of a large number of different studies.
- Placebo treatments - a treatment that appears real, but is designed to have no therapeutic benefit.
Evaluating Alternative Therapies
- Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
- A mental health treatment technique. Involves moving your eyes in a specific way while you process traumatic memories. (APPARENTLY HELPS)
- Light exposure therapy for Seasonal affective disorder (SAD); can also cure major depression or depression during or after pregnancy (perinatal depression)
Counselors - marriage and family counselors specialize in problems arising from family relations. Pastoral counselors provide counseling to countless people. Abuse counselors work with substance abusers and with spouse and child abusers and their victims.
Clinical or psychiatric social workers - a two year master of social work graduate program plus postgraduate supervision prepares some social workers to offer psychotherapy, mostly to people with everyday personal and family problems. About half have earned the National Association of Social Workers’ designation of clinical social worker.
Clinical psychologists - most are psychologists with a Ph.D. or Psy.D. and expertise in research, assessment, and therapy, supplemented by a supervised internship and, often, post doctoral training. About half work in agencies and institutions, half in private practice ~ cannot prescribe medication.
Psychiatrists - They are physicians who specialize in the treatment of psychological disorders. Not all psychiatrists have extensive training in psychotherapy, but as MDs, they can prescribe medications.
Drugs - psychopharmacology
Psychopharmacology- the study of how drugs affect our behavior - initiation, implementation, and discontinuation.
- criticisms: over-prescription (dependence), side effects, placebo effects, poor clinical outcomes, decreased quality of life and health care costs of medications, needs comparison to normal rates of recovery of unmediated patient treatment success.
Antipsychotic drugs - reduce hallucinations, delusions and disordered thinking and can prevent symptoms from returning
- block dopamine receptors in brain, reduces flow of psychotic messages.
- Typically end in “azine, idone, spine.”
- General symptoms
Anti anxiety drugs - used to treat anxiety, such as panic attacks or extreme fear and worry and insomnia.
- depresses the CNS activity and tension by elevating the levels of GABA
Antidepressant drugs - used to treat depression and anxiety, bipolar depression, ocd, ptsd, social anxiety disorder, bulimia.
- regulate mood and behavior, affect by neurotransmission involving serotonin, norepinephrine by reducing uptake and increases neuroplasticity.
Antidepressants used a lot.
Mood stabilizing medications - used to treat bipolar disorders, mania and hypo mania, severe depression, schizoaffective disorder
Bring stability and calmness in brain
Increases serotonin and GABA
Electroconvulsive therapy- done under general anesthesia in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure.
Used to treat severe depression, treatment resistant depression, sever mania, catatonia, aggression in people with dementia.
Side effects: confusion, memory loss, etc.
Magnetic Stimulation - repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulations (rTMS) - uses a magnet to activate the brain. The electromagnetic painlessly delivers a magnetic pulse that stimulates nerve cells in the region of your brain involved in mood control and depression. It’s thought to activate regions of the brain that have decreased activity in depression.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) - surgerical procedure where electrodes are planted directly onto the brain. These treatments are mostly related to muscle disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor and epilepsy…also OCD?!? Also now apparently for multiple sclerosis, chronic pain, addiction, and depression.
Psychosurgery - lobotomy - used to treat mood disorders and schizophrenia. No longer performed in the United States since the late 1900s.
A surgeon drilled a hole in each side of the skull and cut through brain tissue.
Person no longer functional in society.
