Dissection 2.1 - Superficial Thorax
Dissection guide
Articulated Skeleton
Costal groove: inferior border ribs 2-12
Costal margin: inferior border of rib cage
Sternum sections (superior → inferior)
Suprasternal notch → Manubrim → Sternalchondral ligamen → Body of sternum → Xiphoid process
Anterior Thoracic Wall
Cephalic vein: located between deltoid and pectoralis major (in deltopectoral groove)
Layer 1: Pectoralis major
3 bony attachments: ribs, sternum, clavicle
Innervated by lateral pectoral n. (superior to medial pectoral n.)
Layer 2: Pectoralis minor
Deep to pectoralis major
Innervated by medial pectoral n. (nerve pierces muscle and then enters pectoralis major)
Layer 3: External intercostal muscles
Fibers slant inferiorly and medially
Collagen fibers have same orientation
Medial part → External intercostal membrane (thin stretched out external intercostal m.)
Layer 4: Internal intercostal muscle
Lateral to sternum
Fibers slant inferiorly and laterally (perpendicular to external intercostal m.)
Intercostal VAN located in costal groove
Ventral rami of first 11 thoracic spinal n. → 11 intercostal n.
Ventral ramus T12 → Subcostal n.
Dermatomes
Cutaneous n. that innervate a region of skin
All SS cell bodies located in DRG of spinal n.
Clinically relevant for herpes zoster
Skinning the Neck
Layer 1: Platysma (embedded in superficial fascia)
SM innervated by cervical branch of CN VII
Other structures in the area include tributaries of anterior jugular v. and cutaneous branches of cervical plexus
Attaches onto the clavicle
Layer 2: SCM (not covered in this dissection)
Attaches onto the clavicle
Clavicle Removal
Clavicle is superficial to structures of the neck and thorax
Sternoclavicular joint: Joint between sternum and clavicle
Bolded terms
Acromion process
Flat, expanded projection at the outer end of the spine of the scapula (shoulder) and articulates with clavicle
Body of the sternum
Part of sternum between manubrium and xiphoid process
Manubrium is superior to the body (manubirosternal joint aka sternal angle in between, contain intraarticular sternochondral ligament)
Xiphoid process is inferior to the body
Cephalic vein
Located between deltoid and pectoralis major
Cephalic v. → Axillary v. → Subclavian v. → Brachiocephalic v. → Superior vena cava → Right atrium
Clavicle
Bone located superficial to structures of the neck and thorax but deep to muscles of the thorax
Attachment for SCM and platysma at superior border
Corpus (body) of the mandible
Section of mandible between mental protuberance and ramus
Costal cartilage
Hyaline cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum
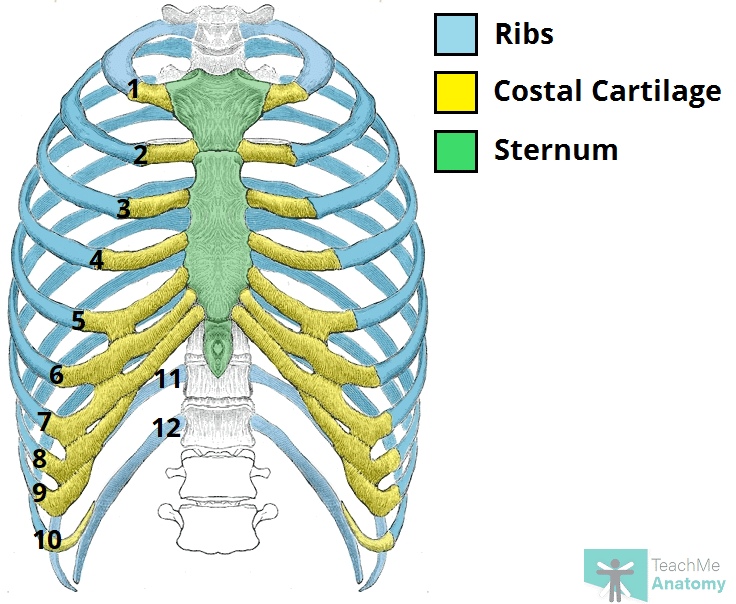
Costal groove
Groove located on the inferior border of ribs 2 to 12
Formed by pulsations of the intercostal artery
Holds the intercostal VAN
Costal margins
Inferior border of the ribcage
Costochondral joint
Short bar of costal cartilage located between the anterior end of the first rib
Articulates with the manubrium of the sternum (sternochostal joint)
Dermatome
Strip of skin innervated by dorsal and ventral cutaneous nerves from a single spinal nerve
External intercostal membrane
The most medial part of external intercostal muscle that is a semi-transparent membrane (under which we can see internal intercostal muscles)
External intercostal muscle
Seen lateral to the costochondral joint
Muscle fibers point inferior-medially
Elevate the ribs and expand the chest cavity
First rib
Most superior rib
Genu/symphysis of the mandible
The point of fusion where the two halves of the lower jaw (mandible) join together during development, forming a single bone
Located in midline - near chin
Gonial angle
Inferior angle of mandible (between body and rami)
Intercostal artery
Runs in intercostal groove
Subclavian a. → Costocervical trunk → Intercostal a.
Intercostal nerve
Runs in intercostal groove
Arises from ventral rami of 1st 11 thoracic spinal nerves
Intercostal vein
Runs in intercostal groove
Internal intercostal muscle
Located just lateral to the sternum and deep to external intercostal membrane
Fibers run inferiorly and laterally
Pulling the ribs downward and inward, effectively reducing the thoracic cavity volume and pushing air out of the lungs
Lateral pectoral nerve
Supplies innervation to pectoralis major (located medially)
Branch of lateral cord of brachial plexus
Manubrium
Superior portion of sternum
Medial pectoral nerve
Supplies innervation to pectoralis minor (located laterally - pierces into pectoralis minor and enters pectoralis major)
Branch of medial cord of the brachial plexus
Pectoralis major
Superficial muscle in thorax
Innervated by medial and lateral pectoral nerves
Pectoralis minor
Deep to pectoralis minor
Innervated by medial pectoral nerve
Platysma
Thin muscle embedded in the superficial fascia deep to the skin
Innervated by CN VII
Ribs
Second rib
Sternocostal joint
Joint between manubrium of the sternum and the costal cartilage which joins the anterior ends of the 1st rib
Sternum
Subcostal nerve
The ventral ramus of T12 that lies below the 12th rib
Suprasternal/jugular notch
Notch at the superior margin of the manubrium
Trapezius muscle
Large diamond shape muscle that spans the back
Ventral rami
Carry all 3 fiber types to the ventral side of the body (SM, SS, VS)
Xiphoid process
Inferior portion of the sternum