IB BIO C3-C4- 3/2/25
Study Guide: C3 - C4 Interaction & Interdependence: Organisms & Ecosystems (HL Only)
C3.1 Integration of Body Systems
Importance of Integration of Body Systems: Ensure all systems (nervous, endocrine, etc.) work together harmoniously. Nutrition, respiration, excretion, reproduction and coordination are some of the physiological processes that are seen in all living organisms.
System Integration is how everything works together
The cardiovascular system: comprises the heart, blood vessels and blood that transport materials in the body, very much like the transportation system of a city with its roads and vehicles to transport people and goods. The circulatory system transports the nutrients and oxygen to cells.
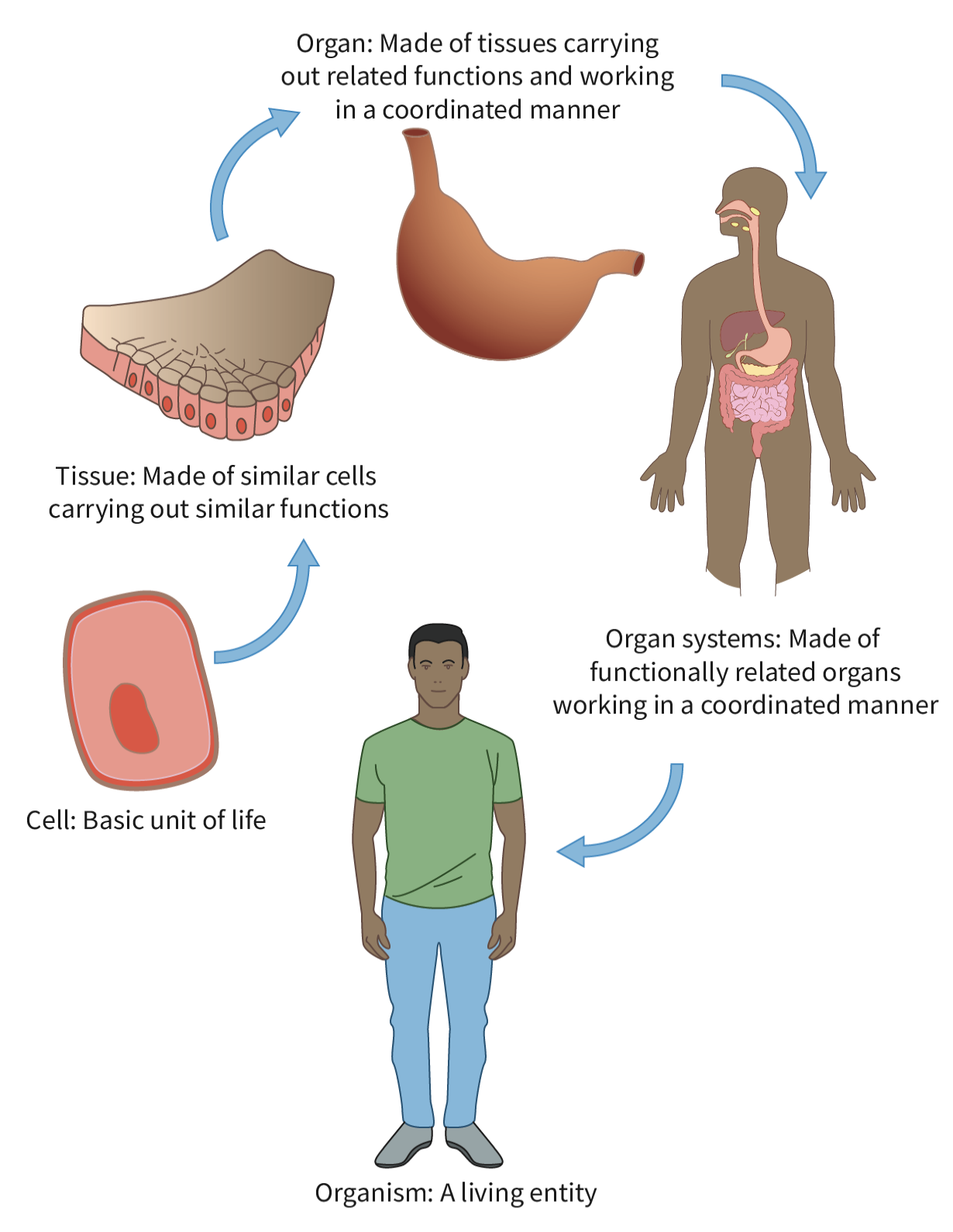
Hierarchy of Biological Organisation: Levels from cells to tissues, organs, and systems.
Roles of Nervous vs Endocrine Systems: The human nervous system is a complex system that includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, which control and coordinate other body systems. It operates by collecting, processing, and responding to information through electrical signals transmitted via specialized cells called neurons.
It is divided into two main parts:
Central Nervous System (CNS): Composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Links the CNS to the body's organs and consists of:
Somatic Nervous System: Manages voluntary movements.
Autonomic Nervous System: Regulates involuntary activities like heartbeat and breathing.
In contrast, the endocrine system also processes information but uses hormones, which are chemical signals secreted by endocrine glands into the bloodstream. These hormones reach target organs to control actions. The nervous system's responses are fast but short-lived, while the endocrine responses are slower but longer-lasting.
Brain and Spinal Cord Function: Process and relay information, essential for reflex actions and voluntary movements.
Cerebellum: Coordinates muscle movements and maintains posture, playing a crucial role in balance and motor control.
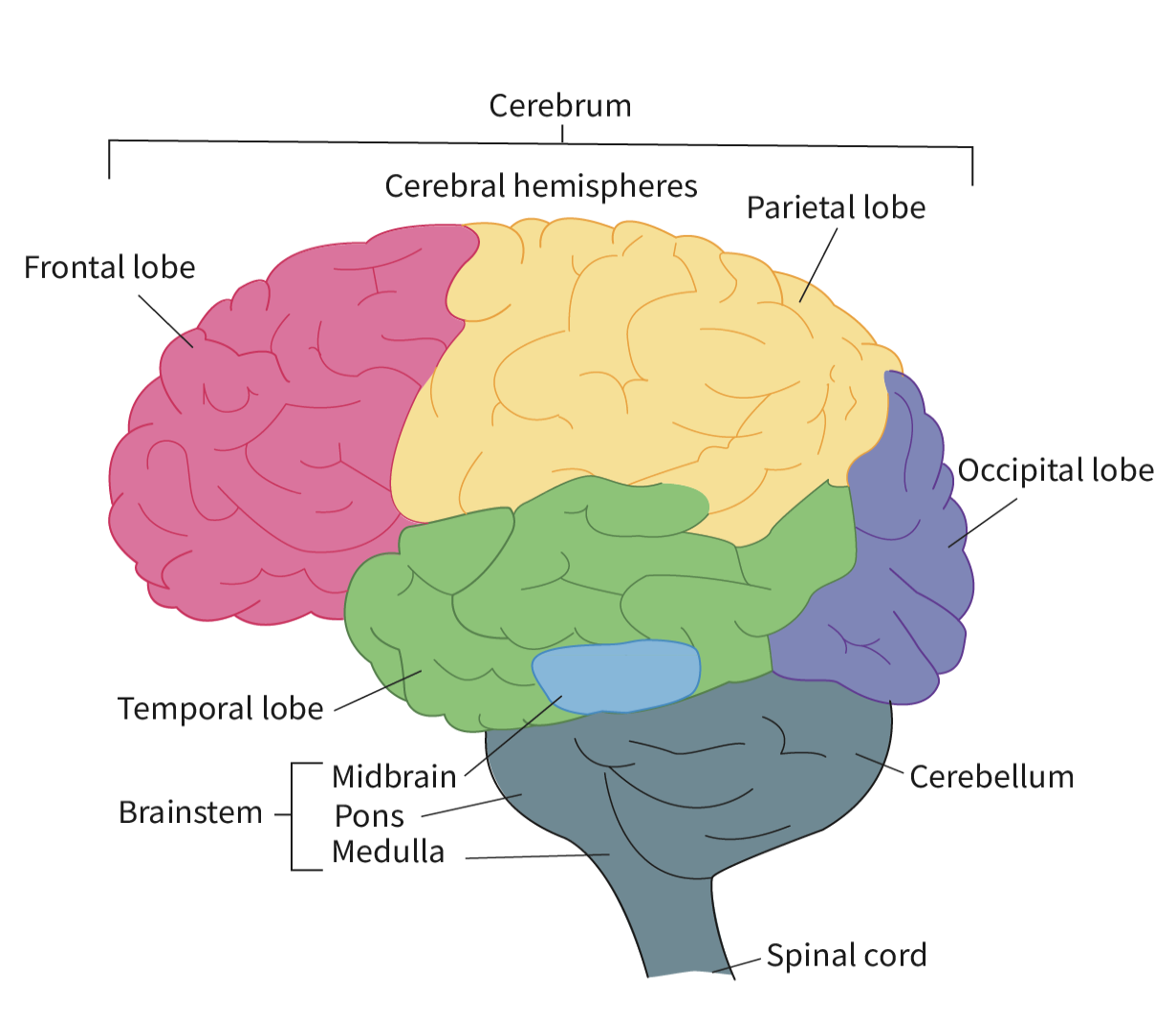
Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, responsible for higher brain functions such as thought, memory, and decision-making, as well as processing sensory information and controlling voluntary muscle movements.
Brain Stem: Controls basic life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure, serving as a vital connection between the brain and the spinal cord.
Midbrain- The middle portion of the developing brain
Pons- A mass of nerve fibres which connect the medulla and the cerebellum and controls unconscious functions such as sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, and posture.
Medulla Oblongata- Lowest part of the brain, regulates functions such as swallowing,breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Sensory vs Motor Neurons: Sensory neurons detect stimuli; motor neurons control muscle actions.
Myelinated Nerve Structure: Increases speed of nerve impulse transmission.
Pain Reflex Arc Structure: Components include sensory nerve, interneuron, and motor nerve for quick reflexes.
Nerve endings in the hand that respond to potentially damaging stimuli act as pain receptors (nociceptors) initiating a nerve impulse in the sensory (afferent) neuron.

Melatonin and Circadian Rhythms: Regulates sleep-wake cycles.
Effects of Epinephrine: Prepares body for 'fight or flight' response (increases heart rate, blood flow).
Endocrine Feedback Mechanisms: Maintain homeostasis (e.g., temperature regulation).
Baroreceptors and Chemoreceptors: Help control heart rate and respiration by detecting changes in blood pressure and gas levels.
CNS and ENS for Peristalsis: Central nervous system and enteric nervous system coordination for digestion.
C3.2 Defense Against Disease
Pathogen Categories:
Bacteria- Unicellular, prokaryotic organisms
viruses- responsible for a number of diseases such as a common cold, flu, measles, covid
fungi- unicellular or multicellular eukaryotic organisms, only a small percentage is pathogenic
parasites
Protist- host diseases such as malaria, and sleeping sickness
Primary Defense: Skin and mucous membranes act as barriers.
Mucous membranes line the body cavities and the parts that open to the outside. These membranes line the digestive, urogenital and respiratory tracts as well as the salivary ducts
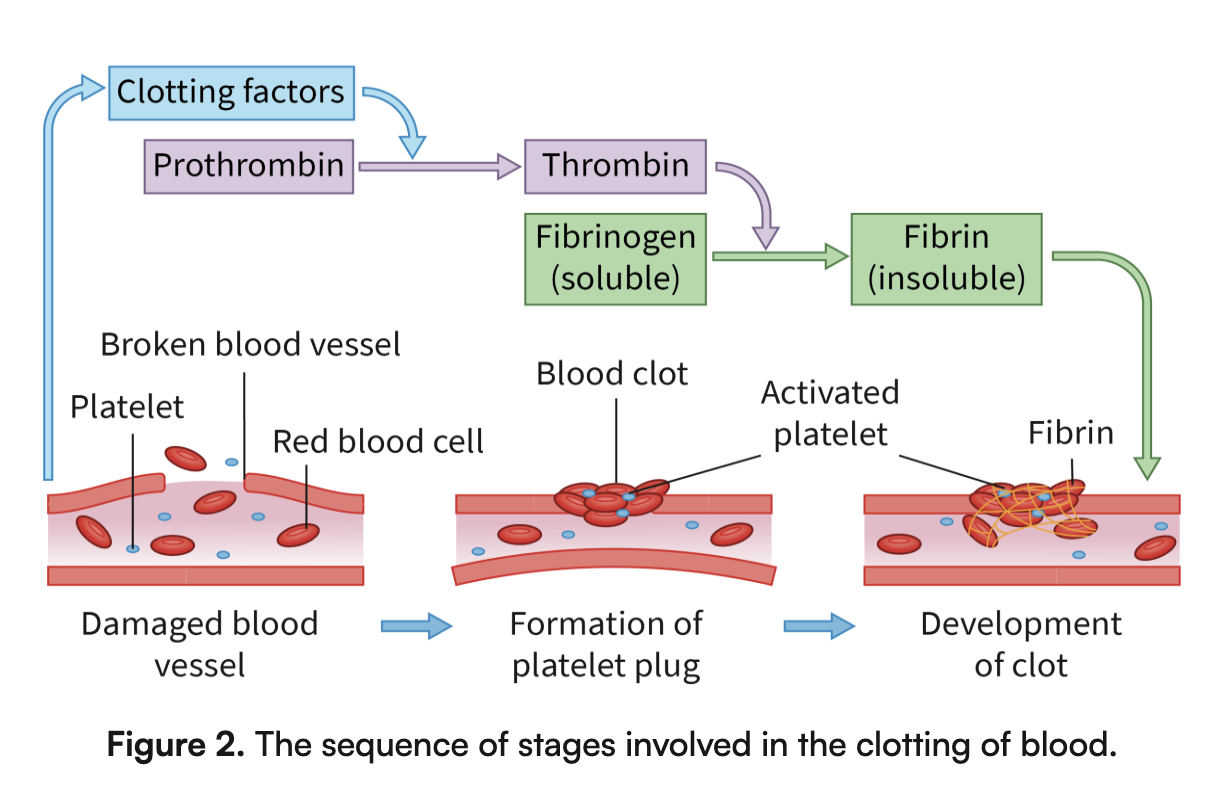
Blood Clotting Process: Involves platelets and clotting factors to prevent blood loss.
Innate vs Adaptive Immune Systems: Innate is immediate and non-specific; adaptive is slow but specific.
Role of Phagocytes: Engulf and destroy pathogens.
Lymphocytes and Antibodies: B-cells produce antibodies, T-cells help activate B-cells.
Memory Cells: Provide long-term immunity by remembering past infections.
HIV Transmission: The virus weakens the immune system, reducing the ability of the person to fight everyday diseases. In severe cases, this can result in AIDS, a spectrum of conditions.
sexual intercourse with an infected person
transfusion of infected blood
sharing needles or syringes
from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
Antibiotics Role: Treatment of bacterial infections but not viruses.
Bacterial Resistance: Develops due to overuse or misuse of antibiotics.
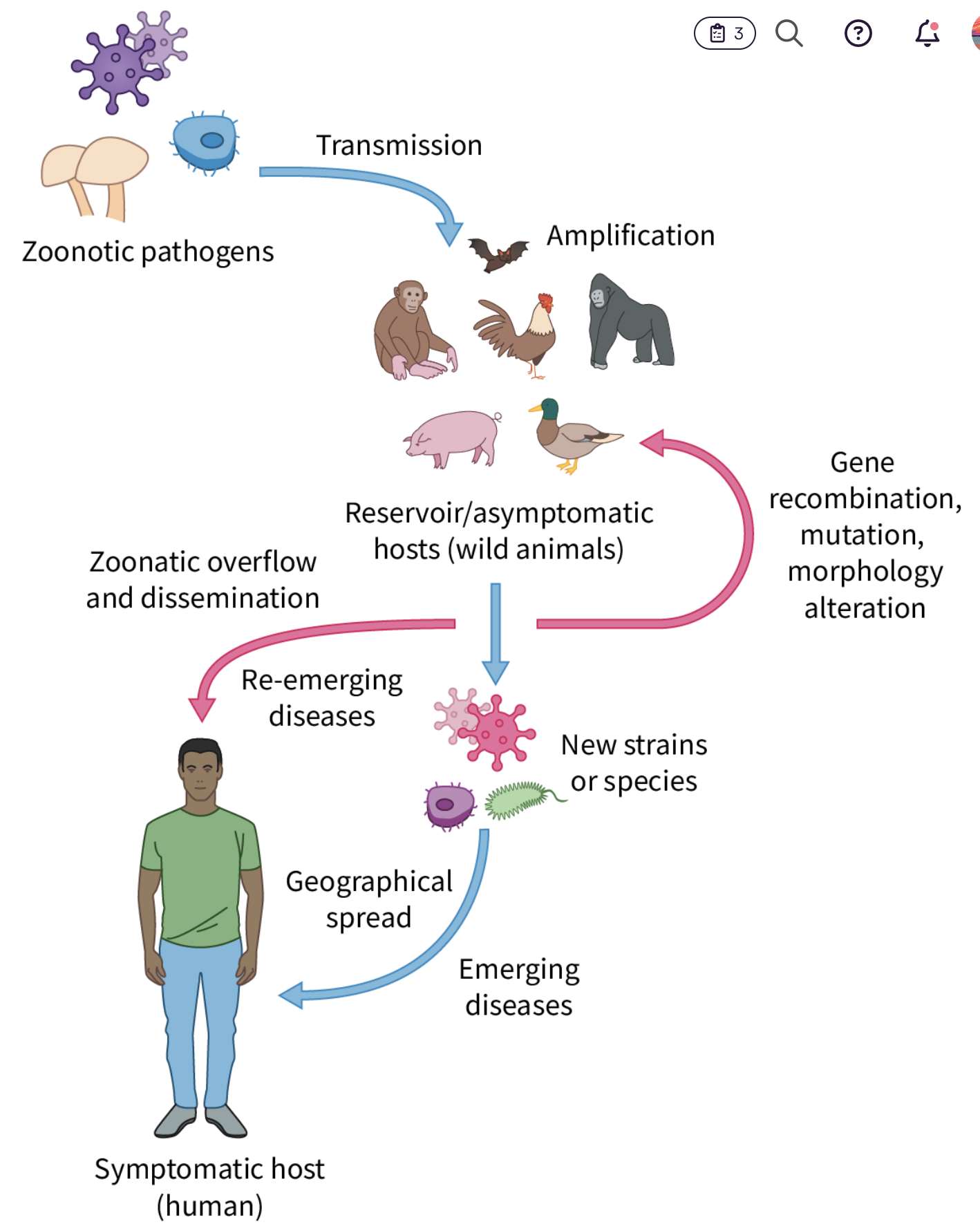
Zoonotic Disease Transmission: Spread of disease from animals to humans.
Vaccines: Stimulate immune response without causing disease.
Herd Immunity: Achieved when a significant portion of the population becomes immune.
COVID-19 Evaluation: Analyze data related to the pandemic and public health responses.
C4.1 Populations & Communities
Population Definition: Group of individuals of the same species in a given area.
Estimating Population Samples: Necessary for understanding species distribution and abundance. Also can help see recourses and lacks of necessary materials for different species.

Random Sampling Importance: Reduces bias in ecological studies.
Quadrat Sampling: Method for estimating sizes of stationary populations.

Capture-Mark-Release-Recapture: Technique for estimating populations of mobile species. (We did the lab on this, with the beads)
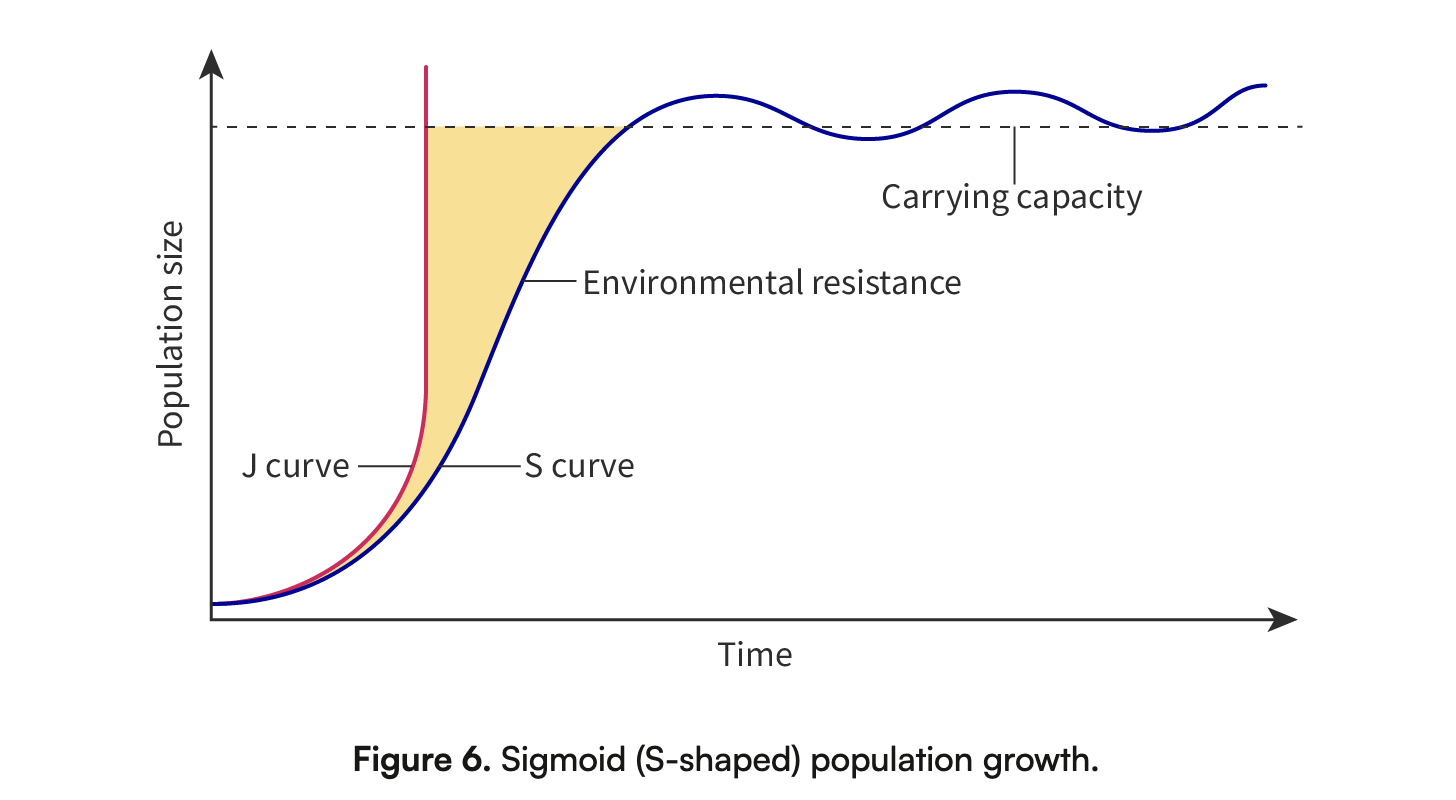
Carrying Capacity: Limit on population growth based on resources; growth slows as this limit is approached.
Density-Dependent vs Independent Factors: Factors that affect population growth based on density (food supply, disease) vs those that don’t (natural disasters).
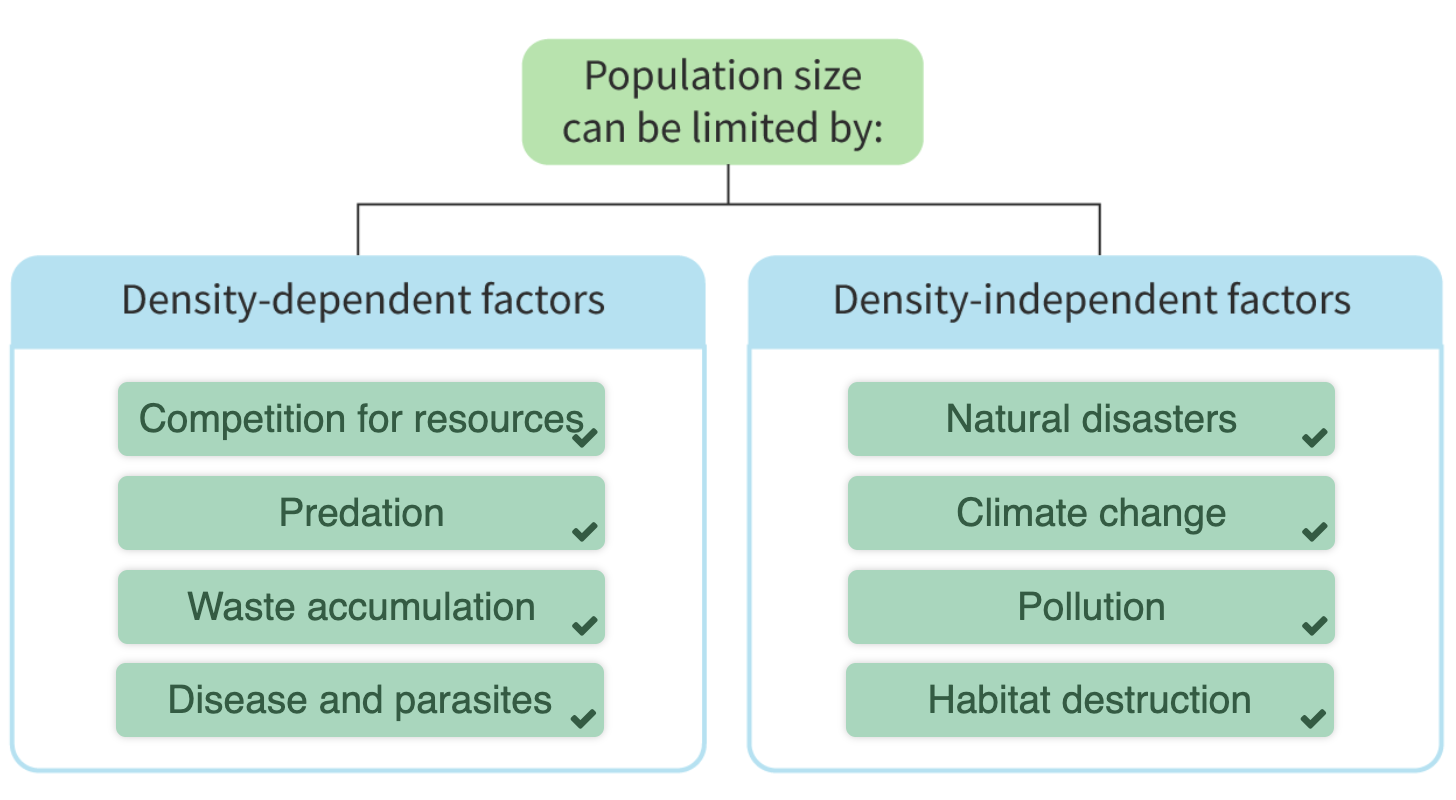
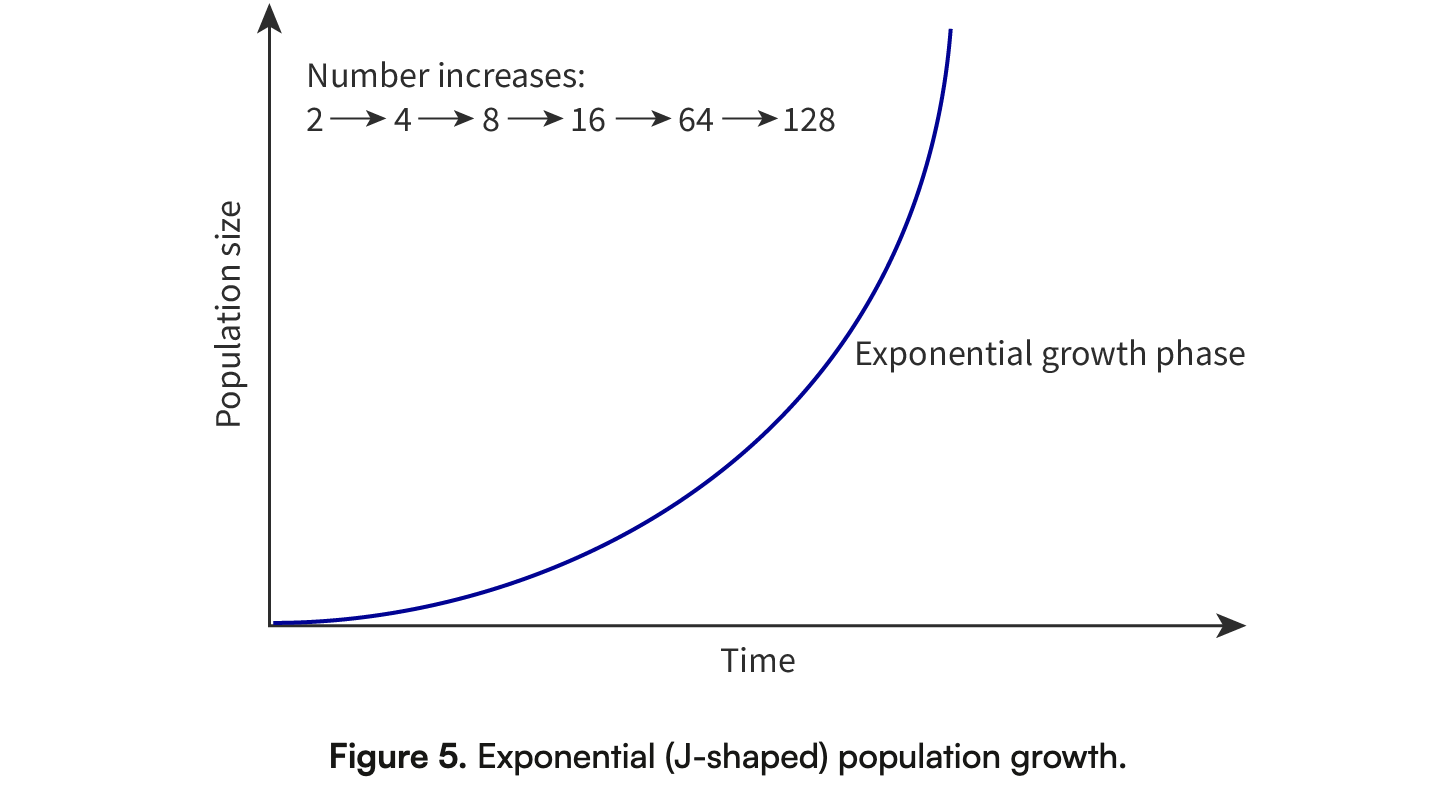
Exponential vs Sigmoidal Growth Models: Different patterns of population growth.
Exponential Growth- which is represented by a J-shaped curve, occurs in populations under ideal conditions where resources are unlimited and abiotic factors are favourable
Sigmoidal Growth- represented by an S-shaped curve, occurs in environments with a limited number of resources
Intraspecific Competition and Cooperation:
Intraspecific Relationships in Ecology Intraspecific relationships involve interactions among individuals of the same species and significantly influence population dynamics and resource utilization.
Intraspecific Competition: This occurs when members of a species compete for limited resources like food, water, and space. The outcomes of this competition can include:
Adaptation of individuals to different niches.
Displacement of less competitive individuals.
Regulation of population sizes.
Example: In a bird population, competition for nesting sites and territories can affect breeding success and overall population density.
Intraspecific Cooperation: Aside from competition, cooperation also plays a role in ecological communities where individuals collaborate to enhance their survival and reproductive prospects.
Example: The social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum demonstrates intraspecific cooperation; when starving, amoebas aggregate to form a multicellular structure for spore dispersal. The stalk formation is seen as altruistic since the cells in the stalk sacrifice themselves for the benefit of others.
Ecological Significance of Population Interactions: Including herbivory, predation, parasitism, etc.
Human Impact on Invasive Species: How activities lead to ecosystem changes. Invasive species can be brought into an environment by humans.
Chi-Squared Test: Analyze species associations; understand test validity.
The chi-squared test (χ2) is a statistical analysis used to determine whether there is a significant association between two categorical variables

.
Predator-Prey Dynamics: Study impacts using case studies.
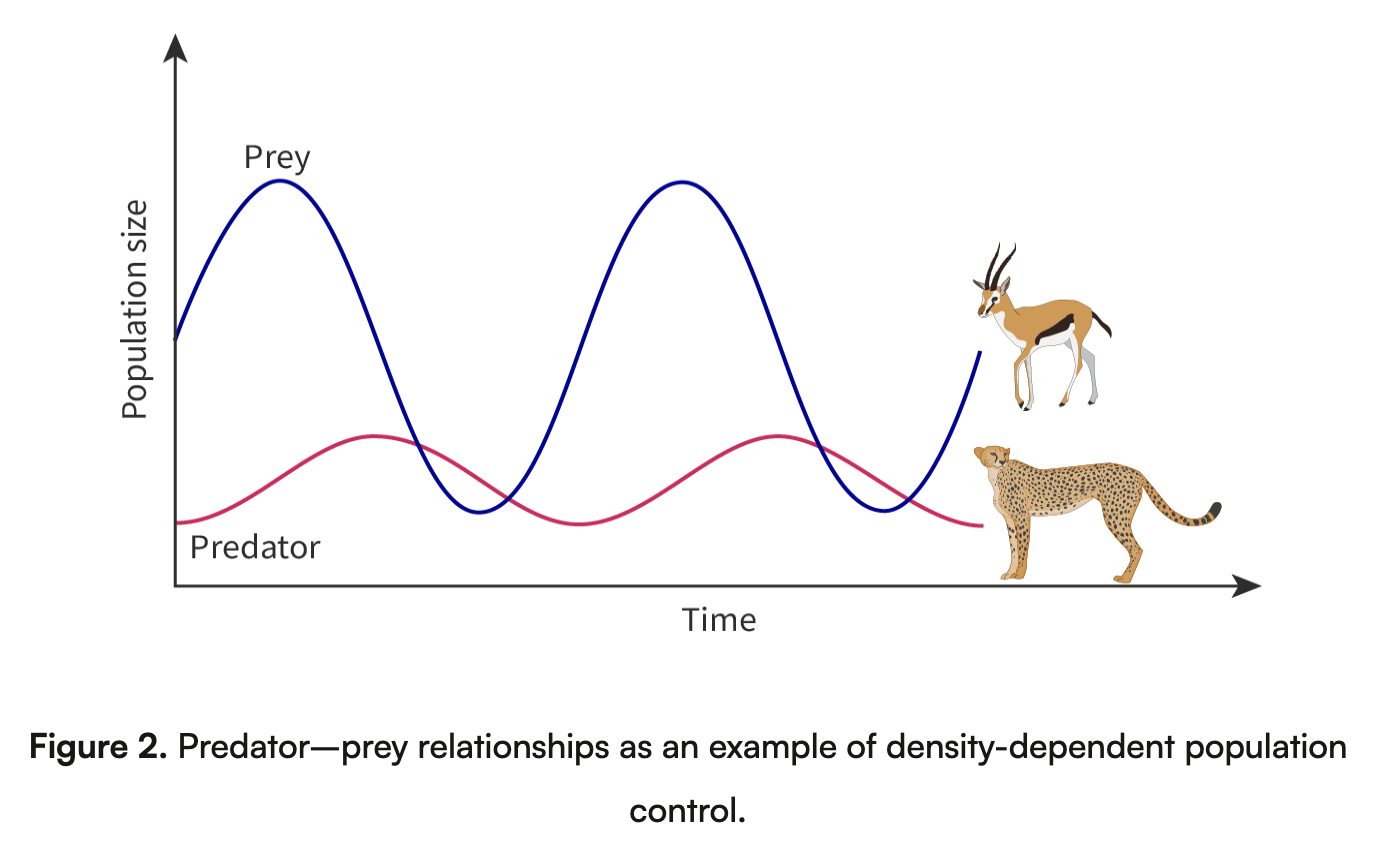
Top-Down and Bottom-Up Control: Concepts in regulating populations within communities.
Top-Down Control- The ecological control or regulation of a population or community by predation or other factors from higher trophic levels.
Bottom-up Control- The ecological control or regulation of a population or community by factors originating from lower trophic levels
Invasive Species: Species that are not native to a particular ecosystem and can cause harm to the environment, economy, or human health by disrupting local ecosystems and outcompeting native species.
C4.2 Transfer of Matter and Energy
Ecosystem as Open Systems: Interaction with surroundings for energy and matter.
Sunlight's Role: Primary energy source in ecosystems.
Energy Flow in Food Chains/Webs: Understand feeding relationships.
Decomposers' Role: Organisms known as decomposers play a crucial role in ecosystem processes by breaking down dead organisms and organic matter. Such organisms, which include bacteria, fungi, and invertebrates, can extract energy and nutrients from decaying materials such as leaf litter, wood, animal carcasses, and even animal faeces.
Autotrophic vs Heterotrophic Nutrition: Differences in nutritional modes. Autotroph- Make their own food Heterotroph- Consumes other food to get energy

Trophic Levels Classification: Based on food chain position. trophic levels represent an organism’s position in a food chain or a food web, defining its role in energy transfer.
Energy Pyramid: Visual representation of energy flow.
Energy Loss Factors: Includes metabolic processes and heat dissipation.
Trophic Levels Limitation: Energy loss restricts how many levels can exist.
Primary vs Secondary Productivity: Rates of production in ecosystems- Primary production refers to the rate at which producers, including plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, accumulate carbon compounds in their biomass.
Secondary production refers to the rate at which consumers accumulate carbon compounds as part of their own biomass
Effects on Primary Productivity: Environmental factors influencing rates.
Carbon Cycle: Important diagram illustrating carbon flow.
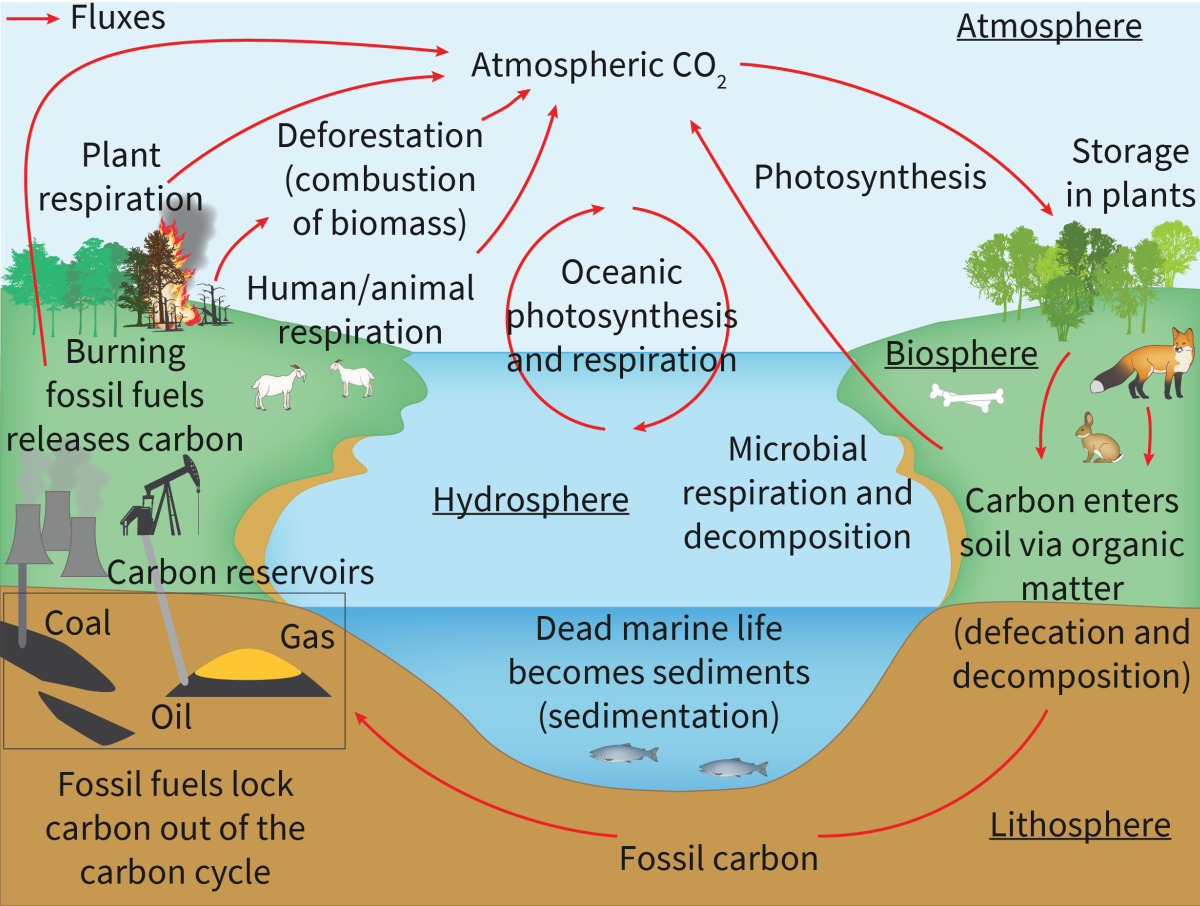
Fossil Fuel Combustion Effects: Impact on carbon cycle- Fossil Fuels bring back carbon which during the carbon cycle, the producers absorb CO2 and store it as a biomass.
Keeling Curve Trends: Analyze carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere- The Keeling Curve is a graph that shows the concentrations of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere over time
Photosynthesis & Aerobic Respiration: Importance for life sustenance-
The relationship between photosynthesis and aerobic respiration allows life on Earth to continue.
disrupting the natural balance of the carbon cycle.
Matter Cycles in Ecosystems: Essential for ecosystem functioning.