
ch 5: the integumentary system
intro
made up of skin, sweat + oil glands, hair and nails
around 7% of body weight
role: protection from pathogens and dehydration
varies in thickness from 1.5-4.0 mm
3 layers: epidermis, dermis and hypodermis/superficial fascia
epidermis: outermost layer
composed of mainly keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
4 distinct cell types and 4-5 layers
cells of epidermis
keratinocytes: produce keratin (protein), connected by desmosomes
surface is dead
melanocytes: synthesize melanin, located at deepest level of epidermis
melanin → to keratinocytes, protects against uv damage
langerhans cells: arise from bone marrow, act as microphages that activate immune system
merkel cell: present at junction for epidermis and dermis, associated with sensory receptors
layers of the epidermis
thick skin (palms, fingertips and soles) have 5 strata
thin skin has 4 (missing stratum basale)
stratum basale: deepest layer, where mitosis takes place
also called stratum germinativum
stratum spinosum: several layers thick, has intermediate filaments, reduces tension
stratum granulosum: 3-5 layers thick, flattened keratinocytes
stratum lucidum: thin layer of dead keratinocytes, only in thick skin
stratum corneum: outermost layer, 20-30 layers thick, cornified cells, very tough
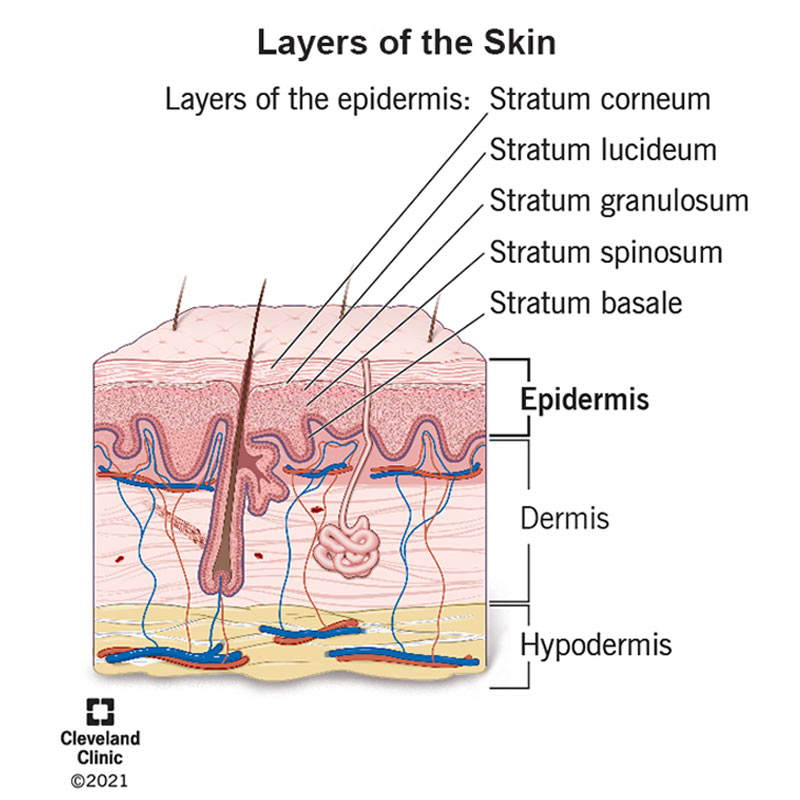
dermis: made up of connective tissue, rich innervated and vascularized
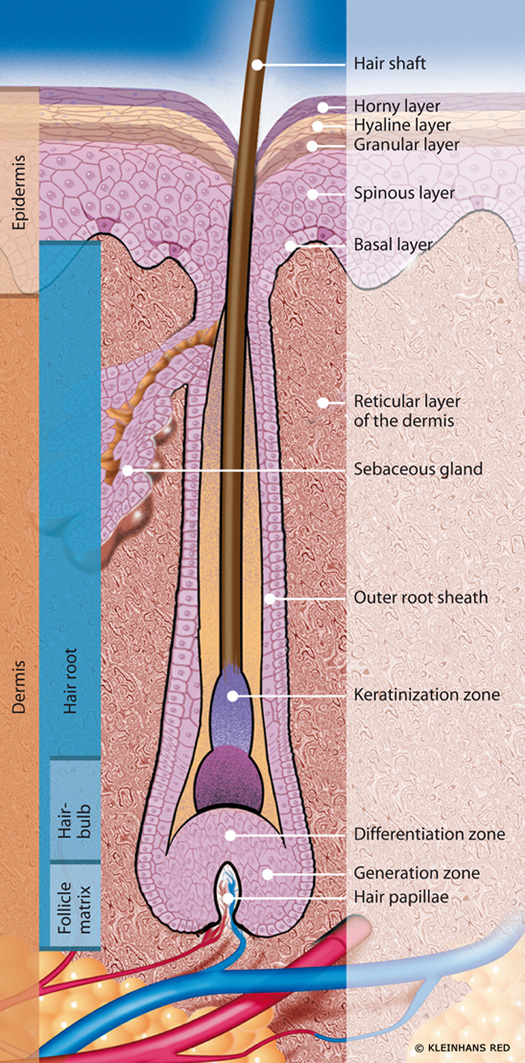
contains hair follicles, sweat and oil glands and much more
2 layers
papillary layer: areolar connective tissue, heavily vascularized
reticular layer: dense irregular connective tissue
skin appendages
sweat glands: more than 2.5 mil per person
eccrine sweat glands: cells in dermis, duct leads to pore on superficial surface
apocrine sweat glands: empty into hair follicles, no ducts
ceruminous glands: secrete earwax
mammary glands: secrete milk
sebaceous glands: oil glands, everywhere except palms
hair
ch 5: the integumentary system
intro
made up of skin, sweat + oil glands, hair and nails
around 7% of body weight
role: protection from pathogens and dehydration
varies in thickness from 1.5-4.0 mm
3 layers: epidermis, dermis and hypodermis/superficial fascia
epidermis: outermost layer
composed of mainly keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
4 distinct cell types and 4-5 layers
cells of epidermis
keratinocytes: produce keratin (protein), connected by desmosomes
surface is dead
melanocytes: synthesize melanin, located at deepest level of epidermis
melanin → to keratinocytes, protects against uv damage
langerhans cells: arise from bone marrow, act as microphages that activate immune system
merkel cell: present at junction for epidermis and dermis, associated with sensory receptors
layers of the epidermis
thick skin (palms, fingertips and soles) have 5 strata
thin skin has 4 (missing stratum basale)
stratum basale: deepest layer, where mitosis takes place
also called stratum germinativum
stratum spinosum: several layers thick, has intermediate filaments, reduces tension
stratum granulosum: 3-5 layers thick, flattened keratinocytes
stratum lucidum: thin layer of dead keratinocytes, only in thick skin
stratum corneum: outermost layer, 20-30 layers thick, cornified cells, very tough

dermis: made up of connective tissue, rich innervated and vascularized
contains hair follicles, sweat and oil glands and much more
2 layers
papillary layer: areolar connective tissue, heavily vascularized
reticular layer: dense irregular connective tissue
skin appendages
sweat glands: more than 2.5 mil per person
eccrine sweat glands: cells in dermis, duct leads to pore on superficial surface
apocrine sweat glands: empty into hair follicles, no ducts
ceruminous glands: secrete earwax
mammary glands: secrete milk
sebaceous glands: oil glands, everywhere except palms
hair

 Knowt
Knowt