solutions, acids, and bases test review
vocabulary
soluble - capable of being dissolved
solute - substance that is dissolved (usually lesser amount)
solvent - substance that dissolves the solute (usually greater amount)
solution - homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in a single phase
- .01-1nm
- particles don’t settle
- doesn’t separate with filtration
- doesn’t scatter light
solubility - the amount of a substance of a solute required to form a saturated solution with a specific amount of solvent at a specified temperature
- g solute/100g solvent
- saturation point - the stage at which no more of a substance can be dissolved into a solution
electrolyte - substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that conducts electric current
non electrolyte - substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that does not conduct electric current
saturated solution - contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute
unsaturated solution - contains less solute than a saturated solution under the same conditions
supersaturated solution - contains more dissolved solute than a saturated solution contains under the same conditions
concentrated solution - contains a relatively high amount of dissolved solute
diluted concentration - contains a relatively low amount of dissolved solute
- M1V1=M2V2
aqueous - dissolved in water
molarity(M) - (moles solute)/(liters solution)
suspension - heterogeneous mixture in which the particles are so large that they settle out unless the mixture is constantly agitated
- particles settle out
- 1000nm
- separates with filtration
- may scatter light but not transparent
- ex oil in water, juice with pulp
colloid - heterogeneous mixture in which the particles are intermediate in size
- 1-1000nm
- particles don’t settle
- particles don’t separate with filtration
- scatter light -- Tyndall Effect: occurs when light is scattered by colloidal particles
- ex jello, fog, milk
miscible - two liquids are miscible if they dissolve in each other in all proportions
immiscible - liquids are not soluble in each other
effervescence - rapid escape of a gas from a liquid in which it is dissolved (soda)
factors that affect solubility
⋆⋆composition is the only factor that determines whether or not something dissolves⋆⋆
↳ like dissolves like - polar solute will dissolve polar+ionic solutes, etc for nonpolar
- temperature changes
- solids+liquids - ↑temp=↑solubility
- gases - ↑temp=↓solubility
- pressure - only affects gas - ↑pressure=↑solubility
- Henry’s Law - the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas on the surface of the liquid
- s1/p1=s2/p2
factors that affect rate of dissolution
- temperature
- surface area
- agitation - shaking, stirring
ways to express “strength”/concentration
- molarity M
- % by volume = (volume solute)/(volume solution) x100
- % by mass = (mass solute)/(mass solution) x100
properties of acids
- produce H+ ions in water (hydronium ion)
- taste sour
- corrodes metal
- weak/strong electrolytes
- react with bases to form salt and water
- pH less than 7
- turns blue litmus to red
- some acids react with active metals and release hydrogen gas H2
- nomenclature review
- -ide → hydro-ic acid
- -ite → -ous acid
- -ate → -ic acid
properties of bases
- produce OH- ions in water
- taste bitter, chalky
- electrolytes
- feel soapy, slippery
- react with acids to form salt and water
- pH greater than 7
- turns red litmus blue
Arrhenius Acids and Bases
- Arrhenius Acid - a chemical compound that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions H+ in an aqueous solution
- molecular compounds with ionizable hydrogen atoms
- strong acid ionizes completely in aqueous solution
- weak acid releases a few hydrogen ions in aqueous solution
- Arrhenius Base - a substance that increases the concentration of hydroxide ions OH- in an aqueous solution
- most bases are ionic compounds that contain metal cations and the hydroxide anion OH-
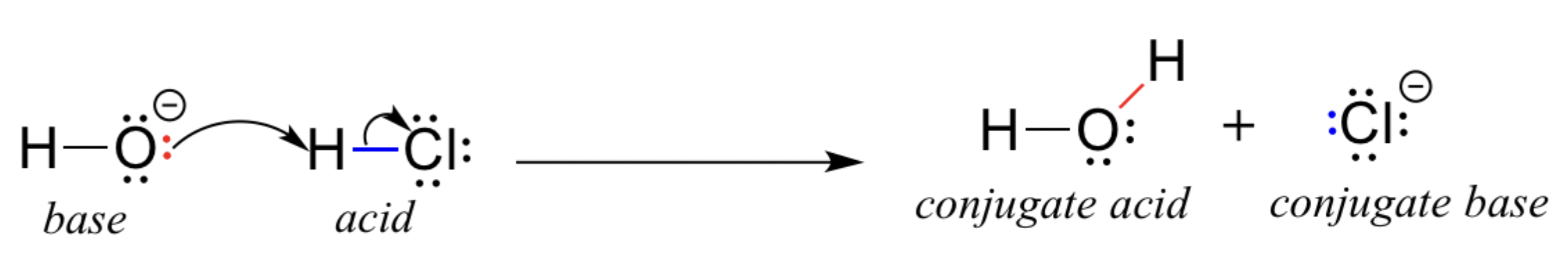
Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
Bronsted-Lowry Acid is a proton donor
- monoprotic - can only donate one hydrogen ion, ex HNO3
- polyprotic - can donate more than one hydrogen ion (one at a time) ex H2S
Bronsted-Lowry Base is a proton acceptor
the stronger an acid is, the weaker its conjugate base
the stronger a base is, the weaker its conjugate acid
Self Ionization of Water
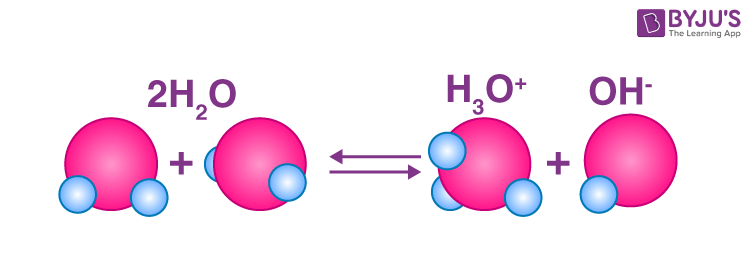
- in water at 25°C
- [H3O+]=1.0x10^-7M
- [OH-]=1.0x10^-7M
- ionization constant of water: [H3O+][OH-]=1x10^-14
pH
defined as the negative of the common logarithm of the hydronium ion concentration
- pH = -log[H+]
- pOH = -log[OH-]
- pH+pOH = 14
- [H+]M = 10^(-pH)
- [OH-]M = 10^(-pOH)
neutralization occurs when hydronium ions and hydroxide ions are supplied in equal numbers by reactants [H+]=[OH-]
titration - the controlled addition and measurement of the amount of known concentration required to react completely with a measured amount of a solution of unknown concentration
- equivalence point - point at which the two solutions used in a titration are present in chemically equivalent amounts
- end point of indicator - point at which an indicator changes color
- standard solution - contains the precisely known concentration of a solute
- primary standard - highly purified solid compound used to check the concentration of the know solution in a compound
- start with a balanced chemical equation
- determine moles of acid or base from the known solution used in the titration
- determine moles of solute of the unknown solution used during the titration
- determine molarity of unknown solution