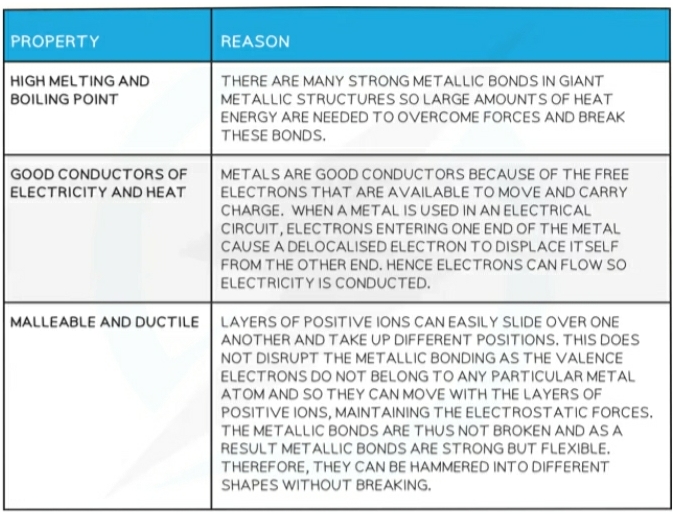
Metals
Metals are found in group 1, group II and the Transition Block of the periodic table.
As we go down the group there is an increase in metallic character.
Properties of Metals
Reactivity with water
metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
For example calcium: Ca (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Reactivity with acids
Fe (s) + 2HCl (aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Reactivity with oxygen
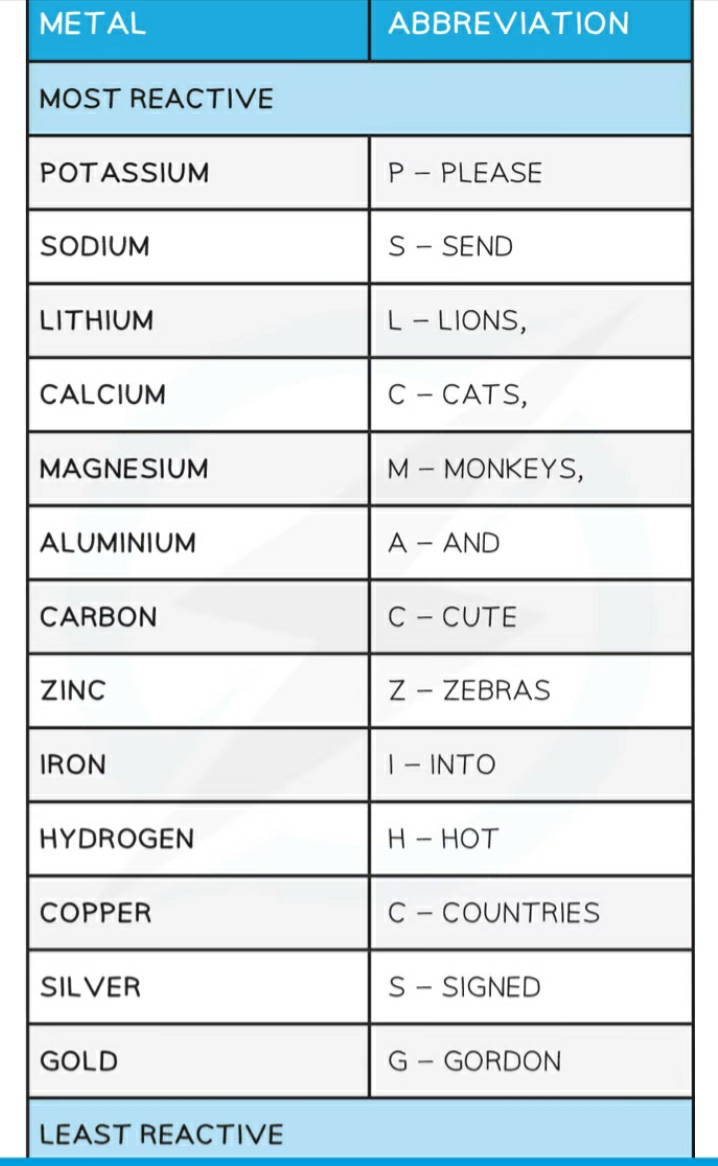
Reactivity series
Reactions with Aqueous Ions & Oxides
Magnesium is above copper in the reactivity series,
magnesium is more reactive so can displace copper from its oxide
The reducing agent in the reaction is magnesium: copper oxide + magnesium → copper + magnesium oxide
CuO (s) + Mg (s) → Cu (s) + MgO (s)
Displacement reactions
Any metal will displace another metal that is below it in the reactivity series from a solution of one of its salts
Magnesium + copper sulfate
Magnesium is a reactive metal and can displace copper from a copper sulfate solution
, more reactive metal slowly disappears from the solution, displacing the less reactive metal.
Decomposition reactions
Thermal decomposition reactions: Some compounds decompose or breakdown when they are heated to sufficiently high temperatures
These reactions are called thermal decomposition reactions.
metal hydroxide → metal oxide + water
Zn(OH)2 (s) → ZnO (s) + H2O (l)
MgCO3 (s) → MgO (s) + CO2 (g)
2NaNO3 (s) → 2NaNO2 (s) + O2 (g)
2Cu(NO3)2 (s) → 2CuO (s) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
 Note
Note Studied by 193 people
Studied by 193 people Note
Note Studied by 8 people
Studied by 8 people Note
Note Studied by 157 people
Studied by 157 people Note
Note Studied by 154 people
Studied by 154 people Note
Note Studied by 2 people
Studied by 2 people Note
Note Studied by 21 people
Studied by 21 people Knowt
Knowt


