Check Payments Overview
Defining Payments Terms
Check Payments Definitions
Acronyms and terms defined in this section are grouped by:
Financial institutions
Industry rules
Regulations
Standards
Check Definitions
Check Payments Terminology: Financial Institutions
Depository Financial Institution (DFI)
State or nationally chartered bank, savings, and loan association, savings bank, or credit union
Bank of First Deposit (BOFD): Depositary Bank
First DFI to which check is transferred; may also be the Paying Bank or Payee
Collecting Bank
Bank handling an item for collection except the Payor Bank; subsequent bank in forward collection process
Example: FRBs are collecting bank
Intermediary Bank
Bank to which an item is transferred in course of collection
Except the Depositary Bank or Payor Bank
Presenting Bank
Bank presenting an item to the Payor Bank
Payor Bank
Bank that is the Drawee of a draft; see also Paying Bank definition in Reg CC
Terminology: Industry Rules
ECCHO Operating Rules & Commentary
ECCHO, a service of The Clearing House, maintains a national set of Rules for private sector image exchange
Rules apply only to exchanges between ECCHO members that agree to use the Rules
FRB OC3: Federal Reserve Operating Circular 3
Governs the collection of cash items and returned checks through the Federal Reserve Banks (FRBs)
References Regulation J for related warranties
Terminology: State Law
Uniform Commercial Code (UCC)
Model state law as adopted in a state
Provides general business law of a state regulating sale of goods, commercial paper (checks), bank collections, and secured transactions in personal property
Articles 3 and 4 relate to negotiable instruments and bank deposits and collections
Article 1 includes general provisions and definitions
Terminology: Regulations/Federal Laws
Reg CC or Regulation CC
Federal regulation that governs availability of funds deposited in transaction accounts (e.g., demand deposit accounts), the collection and return of checks and substitute checks
Reg J or Regulation J
Federal regulation that governs collection of checks/other items by FRBs
Establishes procedures, duties, and responsibilities among FRBs, senders and payors of checks and other items and senders and recipients of Fedwire fund transfers
Terminology: Standards:
Accredited Standards Committee X9
X9 is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (“ANSI”) to develop and maintain open consensus standards for the financial services industry in the US
Facilitates creation/administration of standards that improve payments, protect data and interoperability between exchange parties.
X9 standard related to payments in this training include:
X9.100-140: Specifications for Image Replacement Document - IRD
X9.100-160: Magnetic Ink Printing (MICR) Parts 1 and 2
X9.100-187: Electronic Exchange of Check and Image Data
X9.100-188: Return Reasons for Check Image Exchange and IRDs
X9.100-160: Magnetic Ink Printing (MICR) Parts 1 & 2
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR)
Descriptive information compromised of numbers and symbols printed at bottom of physical check
Generally printed in magnetic ink and designed to be recognized at high speed by automated processing equipment
Symbols printed in special font (E-13B)
Character set includes:

Terminology: Check - Negotiable Instrument
Written order
Written order directing a bank to pay money as instructed
Designed to transfer amount of money for which it is written on or after the date specified on the check and to specific payee (or to the bearer)
Promise to pay
An unconditional promise to pay
Includes a substitute check and an electronic check/electronic returned check
Defined by state & federal law
UCC definition:
Draft if it is an order to pay;
Within this definition it states check is a draft payable on demand
Reg CC definition:
Check covers several types of instruments including checks, money orders, etc.
Terminology: Checks
Remotely Created Check (RCC)
Defined by both UCC and Reg CC as check that is:
Not created by the Paying Bank; and
Does not bear signature applied, or purported to be applied, by person on whose account check is drawn
RCCs are considered unsigned drafts
Must be authorized by account holder;
Must be printed (a physical item) to meet Reg CC definition
RCCs are not created by a Paying Bank or agent of the Paying Bank
Negotiable Instrument
Negotiable Instrument - Draft/Check
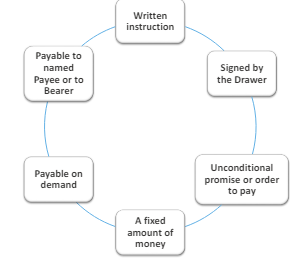
UCC 3-104 defines the check within the definition of a negotiable instrument as a draft that is:
Written instruction
Must be a writing/physical item
Signed by the drawer
Person giving the instruction
Order to pay fixed amount of money
Value of instrument
Payable on demand
Negotiable Instrument & Drafts
UCC divides instruments into two general categories:
Drafts and Notes
An instrument is a:
Note if it is a promise to pay; and
Draft if it is an order to pay
Draft is further defined in UCC as:
Written order signed by the drawer; an unconditional order to pay
Checks are drafts
Check: Demand Draft
Reg CC check definition covers several categories of instruments:
Negotiable demand draft drawn on:
Or payable through or at, an office of a bank;
Federal Reserve Bank or Federal Home Loan Bank;
US Treasury;
Demand draft drawn on:
State or unit of general local government not payable through or at a bank;
U.S. Postal Service money order;
Traveler’s check; and
An original check and a substitute check
Electronic check/electronic returned check defined as:
Electronic image of an electronic information derived from a paper check or paper returned check
Must conform with X9.100-187 standard
Must have agreement for exchange between sender and receiving bank
Summary
UCC and Reg CC define checks, electronic checks, returned checks, noncash items and electronically created items (ECIs)
Check: Defined as a negotiable demand draft
Checks include an original paper check and a substitute check
Electronic check and electronic returned check: Defined as
Electronic image of, and electronic information derived from paper check or paper returned check; that is sent to a receiving bank by agreement; and that conforms to X9.100-187 standard
Electronically-created Item
Electronic image that has all the attributes of an electronic check or electronic returned check but was created electronically and not derived from a paper check
ECI not considered a check under Reg CC
Currently not eligible for exchange under ECCHO Rules or Fed Operating Circular 3 (OC3)
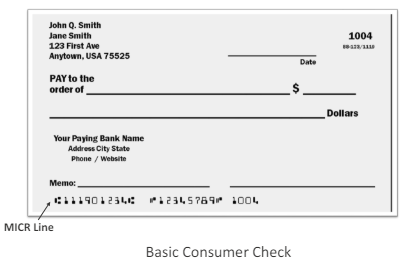
Parts of a Check
Blank Check Example
MICR and MICR Line
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR)
Common machine language for automated check handling
Descriptive info comprised of numbers and symbols designed to be recognized at high speed by automated processing equipment
Printed in magnetic ink according to standards
E-13B font
For magnetic ink printing in USA, Canada, others
Consists of ten numeric characters and four symbols
MICR line: Located at the bottom of the physical check; key fields include:
Amount: 10-digit field
On-Us: Includes drawer’s account number & check serial number
Routing Number: ABA assigned identifier
EPC: External processing code; optional, single-digit field
Definition of MICR also includes:
MICR line data in an electronic record
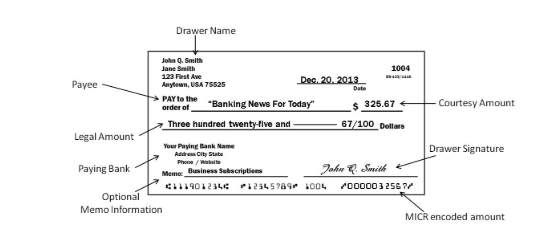
Processed Check Example
Consumer Check (6-inch check)
Processed check: completed and signed by drawer
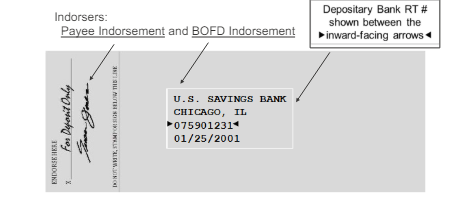
Note: In UCC and Reg CC, indorsement is spelled with an “I”
ECCHO incorporates UCC and Reg CC within the ECCHO rules and maintain that spelling
Endorsement with an “E” is a term generally used outside of banking laws and regulations
Drawer or Maker?
Usage of terms Drawer and Maker (see UCC and Reg CC)
Drawer: Person who signs or is identified in a draft as a person ordering payment (e.g., person who signs the check)
Maker: Person who signs or is identified in a note as a person undertaking to pay (e.g., person to pay on a note)
Other check terms:
Drawee: Person or bank ordered in a draft to make payment
Payor Bank: The bank that is the drawee of a draft
Note:
UCC defines person to mean an individual, public corporation, or any other legal or commercial entity
UCC defines bank as a person engaged in the business of banking
Paying Bank
Paying Bank: A Reg CC definition 229.2 (z)
Bank to which check is sent for payment or collection
May be designated as a payable-at bank or payable-through bank that is responsible for the expedited return of checks and notice of nonpayment requirements
If check is sent for forward collection based on the routing number, bank associated with that routing number in considered the Paying Bank under the regulation
Federal Reserve (FRB): Cash Items
Checks, including postdated checks
Government checks, postal money orders
Other demand items acceptable to Paying Bank’s FRB
Demand items payable outside of a State, acceptable to the last collecting FRB, that are accepted as cash items (foreign cash items)
Electronic checks that conform to Operating Circular 3 and FRB technical requirement
Substitute checks
Certain redeemed savings bond (see OC3 Appendix C)
Noncash items FRB has agreed to handle
Agreement or authorization required before sending noncash items
Noncash Items
Would otherwise be checks except for:
Attachments or special instructions
Printed on more than a single thickness of paper - don’t qualify for automated check processing
Not preprinted or post-encoded in magnetic ink with routing number of Paying Bank
Key takeaways:
Determining if item is a check or noncash item
Does the item qualify for handling by automated check processing equipment?
Does the item have the routing number of the Paying Bank pre-printed or post-encoded in magnetic ink?
Check Processing Overview
Level Set: General Processes
Cashing a check
Process by which check is negotiated by the holder for cash
Depositing a check
Process by which check is negotiated by the holder to the DFI for credit to the depositor’s account
Remote Deposit Capture (RDC)
Banking service which allows a user to scan checks and transmit the scanned images to a financial institution for posting and clearing
RDC described in FFIEC guidance as a transaction delivery system
Images may be created using a scanner or via a mobile device app
General Check Payment Processes
Clearing a Check
Process by which check moves through payment systems from DFI where it was deposited to Payor/Paying Bank (institution on which it’s drawn)
Note: May involve one or more collecting banks in the process
Collection of a Check
Process by which Depositary or Collecting Bank transfers a check to another collecting bank or presents it to the Paying Bank for payment
Presentment of a check:
Exchange of value for the amount of that check
Return of a Check
Process by which Paying Bank may determine not to pay for check presented due to NSF, Stop Pay, or other reasons
Must be returned timely to be a return
Return timing based on UCC and Reg CC requirements
Claim Adjustment
Process by which a bank may send/receive a claim to adjust settlement for a paid check
Must be for a valid reason
Adjustments are by agreement
Check Collection Process
Simple image exchange process (forward) with three banks
Depositary Bank (BOFD) = Bank A
Intermediary (Correspondent or FRB) = Bank B
Paying Bank = Bank C
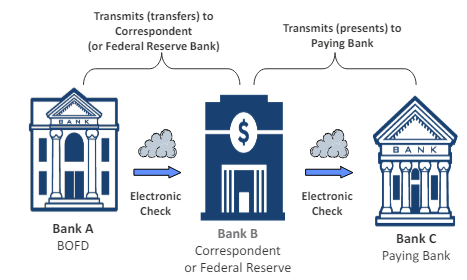
Check Processing
Detailed example with paper check then image exchange
Paper processes shown from individual/corporate Payor → Payee → Depositary Bank → through clearing network → Paying Bank
Overlay with image exchange: Medium changes (from paper check to electronic check) but general processes are the same
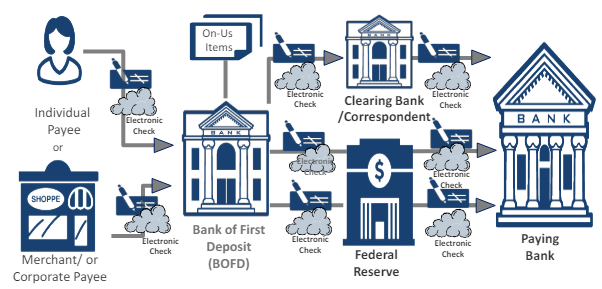
Daily cycle includes various steps - Processes and timing differ for:
Depositary Bank; Intermediary or Collecting Bank and Paying Bank
Sources of work: Where are checks cashed, deposited, or used for purchase or other payments?
ATM
Vault
Lockbox
Bank branch
Merchants
Capture process: Collecting check info via either physical or electronic (virtual) cycle
Reject/repair re-entry: Correcting errors (if possible) to get an item back into the processing cycle
Imaging: Create digital image of front and back of check
Required by standards to capture all info from both the front and back of the physical check to create an electronic check
Virtual (electronic process) to capture the check info
May also use some form of physical scanning of paper checks
Dispatch process: Sending out checks drawn on other banks for collection and final settlement
Majority sent electronically (no paper transportation today)
Clearing process: Process, prepare and release data files to move check data forward from point of deposit for collection
May go through intermediaries before final presentment to Payor/Paying Bank
Settlement process: Exchange of funds for the value of cash letters sent/received
May be net or gross settlement via clearinghouse, provider, or the FRB
Exception handling: Processing/resolution of returns or adjustments
Determine not to pay a check presented - based on timing
Return check with proper reason code or send as an adjustment
Exceptions and Check Fraud
Exceptions - Returns
Exception: An error or an exception to the normal operational process
Any paper or electronic check that requires further investigation before disposition can be determined
Exceptions deal with both returns and adjustments
Timing is a primary determining factor in whether an item is handled as a return or must be handled as an adjustment
Returns: Governed by statutory and regulatory requirements
UCC midnight deadline (UCC 4-301)
Reg CC expeditious return requirement (221.31(b))
Return of a check unpaid:
Items that are being sent back by the Paying Bank
Must state it is a return and the reason for the return
Must meet timing requirements or may be considered a late return
Exceptions - Adjustments
Adjustments: Handled by agreement of parties
FRB OC3; The Clearinghouse/ECCHO Rules
Errors that occur during item processing generally require some research to resolve; depending on timing and type of adjustment, may adjust settlement for a paid check either:
With entry (with financial settlement)
Without entry (without immediate financial settlement)
Must state specific adjustment type for each case
Adjustment types, timing and related requirements may differ depending on adjustment provider and adjustment rules:
FRB, Viewpointe, The Clearing House/ECCHO Rules, etc.
What is Fraud?
Fraud exists in all payment systems
Occurs when following elements exist:
Intentional untrue representation about an item, fact or event
Untrue representation is believed by the victim
Victim relies upon and acts upon the untrue representation
Victim suffers a loss of money and/or property as a result of reliance on untrue representation
Check fraud:
Refers to a category of criminal acts that involve making the unlawful use of checks in order to illegally acquire funds that do not exist within the account balance or account holder’s legal ownership
Other Payment Systems
Multiple Channels/Options
Checks can be cleared via multiple channels
Different channels (FRB vs. private sector): different rules may apply
Check can be cleared in different forms:
As a physical check
As an electronic check
As a substitute check (IRD)
As an ACH debit (if check is eligible for conversion) using appropriate SEC code:
ARC - Accounts Receivable entry
POP - Point of Purchase entry
BOC - Back Office Conversion entry
Automated Clearing House (ACH) - Simple Overview
Funds transfer system governed by Nacha Rules
Provides for interbank clearing of electronic entries for participating financial institutions
ACH transactions: Debits or credits
Examples include:
Direct deposit of payroll, government, and social security benefits
Scheduled payments for mortgage, insurance, or other bill payments
Participants in ACH exchange
Originator: Individual, corporation or another entity
Initiate either a deposit or payment transaction
ODFI: Originating Depository Financial Institution
RDFI: Receiving Depository Financial Institution
ACH Operators: Two central clearing facilities:
FRB
The Clearing House (EPN)
Sample ACH Process Example
ACH credits may be consumer or corporate payments:
Interest payments
Payrolls
Social security payments
Government vendor payments
Pensions
Dividends
State tax payments
Annuities
Originator initiates payment instructions to move funds into a Receiver’s account
Common use: Direct deposit of payroll
Other Payment Systems
Debit Card: May use term bank card or check card
Generally, uses shared ATM networks that offer payment services associated with a financial institution’s DDA system
Similar to a credit card, but unlike a credit card, the money comes directly from the user’s DDA account
Credit Card: Issued by a company to allow a user to purchase good/services from merchants who accept the card
Major networks include:
American Express, Discover, MasterCard, and Visa
Merchants generally pay fees to accept credit cards
Card-issuing banks receive part of the fees as revenue
Card Processing: When the card is used, card-holder is technically using the bank’s money instead of their own to pay for a product or service
Over time must repay with interest
Wire: Electronic payment service for transfer of funds
Characteristics of large dollar transactions, immediate availability, and irrevocable payments
To wire funds is to make a funds transfer from one bank to another with almost immediate availability
Credit transfer (crediting funds)
Contrast to checks which are debits
Funds transfer defined in UCC 4A-104 as:
Series of transaction, beginning with originator’s payment order, for purpose of making a payment to beneficiary of the order
Term includes payment order issued by originator’s bank, or an intermediary bank, intended to carry out originator’s payment order
Completed by acceptance of payment order by the beneficiary’s bank for the benefit of the beneficiary
Wires governed by provisions in UCC 4A and:
Regulation J for Fedwire
Rules and procedures for Clearing House Interbank Payment System (CHIPS)