PART 1 ANAT & PHYS REVIEW
What is anatomy? What is physiology?
Anatomy: the study of the form and composition of the body’s structures
Physiology: the study of the chemistry, biochemistry, and physics of the body’s functions
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis: the steady state of body systems that living organisms maintain
Describe negative feedback loop. Positive feedback loop. Give an example of both.
Negative Feedback Loop: A homeostasis mechanism that stabilizes an upset in the body by preventing excessive response to a stimulus; sweating
Positive Feedback Loop: a homeostasis mechanism that intensifies a change in the body in response to stimulus; birth
Describe the anatomical position.
Anatomical position: Standing upright, facing forward, each arm hanging on either side of the body, palms facing forward
Describe the body planes.
Midsagittal plane: Runs directly down the middle of the body (aka “medial plane”)
Transverse plane: Runs through the middle of the body horizontally, splits body superiorly and inferiorly
Frontal plane: runs along the side of the body and splits the posterior and anterior sides of the body (aka “coronal plane”)
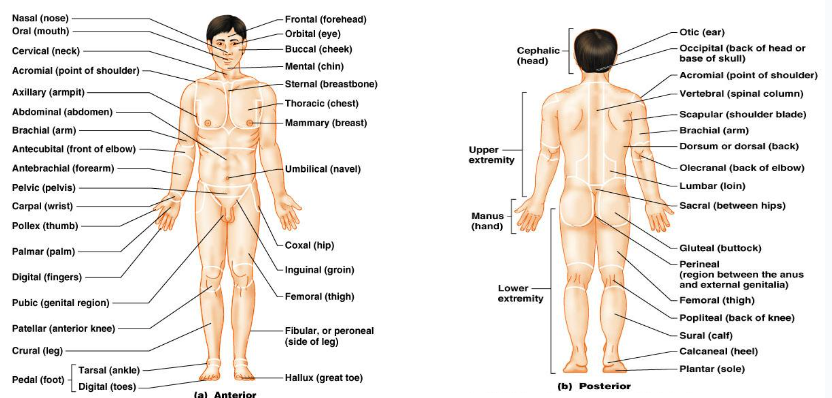
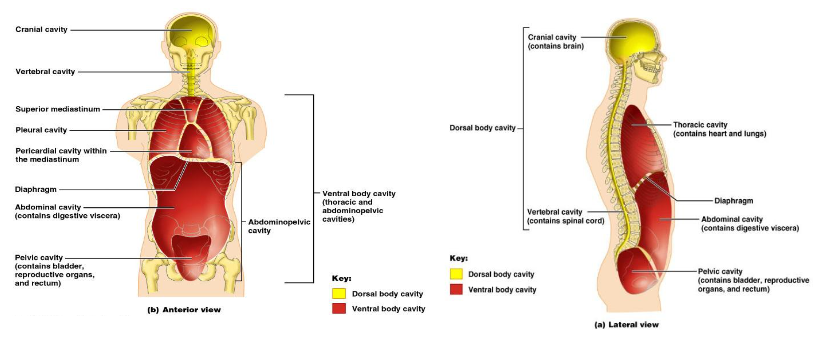
Know the anterior and posterior body landmarks and cavities.
What is protein conformation?
Protein Conformation: The three-dimensional shape or structure of a protein molecule
What is protein denaturation?
Protein Denaturation: The alteration of a protein's three-dimensional structure, leading to loss of its original shape and biological function
What is ATP and how does the body use the molecule?
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): used to fuel bodily functions and processes
What are the four primary organic molecules?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
What is an enzyme?
Enzyme: Protein or RNA that catalyzes chemical reactions
What are the functions of proteins?
Catalyze biochemical reactions
Structural support
Transport of substances
Cell signaling
Immune Defense
Storage
Gene Expression
Movement
Hormonal Regulation
Receptor Function
In what cellular organelle is most of the cellular ATP produced?
Mitochondrion
Describe exocytosis.
Exocytosis: export of a substance outside of the cell by a vesicle
Describe phagocytosis.
Phagocytosis: import of a substance via vesicle
What are the molecules that make up a cell membrane?
Phospholipids
What molecules in the cell membrane serve as receptors or binding sites for hormones or other chemical messengers?
Ligands
What is the function of microvilli? What kind of cells would they be found in and what are these cells specialized for?
Function of Microvilli: increase surface area
Found in epithelial cells, which specialize in absorption of nutrients
What are the three major components of cytoplasm?
Cytosol, organelles, inclusions
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Ribosomes on rough ER produce proteins for cell functions
In what type of cells would you expect to find numerous mitochondria?
Cells with high energy demands (especially if involved in aerobic respiration); Muscle cells, Liver cells, Neurons, Adipocytes
What would happen to a cell in a hypotonic solution? In a hypertonic solution?
Hypotonic: solution moves into the cell body and swells up/bursts
Hypertonic: solution moves out of cell body and shrivels up/shrinks
What are the nitrogen bases of DNA?
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
What is the base pair rule for DNA?
Adenine pairs with Thymine
Cytosine pairs with Guanine
What are the parts of a DNA nucleotide? Parts of a RNA nucleotide?
DNA nucleotide: Phosphate group, Pentose Sugar, Nitrogenous base
RNA nucleotide: Phosphate group, Ribose Sugar, Nitrogenous base (A, U, G, C)
What are the stages of mitosis? What happens in each stage?
Interphase; chromosomes make an exact copy then thicken and coil
Prophase; nucleolus disappears and chromosomes condense and become more visible
Metaphase; chromosomes line up with each sister chromatid attached to a spindle fiber
Anaphase; sister chromatids are pulled towards opposite poles
Telophase; chromosomes at opposite poles and a nuclear material envelopes the set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis; daughter cells separate
What are the two parts of protein synthesis and in what part of the cell do each occur in?
Transcription and translation; nucleus then cytoplasm
How many nitrogen bases (nucleotides) are needed to translate to an amino acid?
3
What does haploid mean? Give an example. What does diploid mean? Give an example?
Haploid: containing one set of chromosomes; sperm and egg cells
What kind of tissue is used for insulation?
Adipose tissue
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, reception
What kind of tissue is avascular?
Epithelial and cartilage tissue
What kind of epithelial tissue lines the stomach and intestines?
Simple columnar epithelium
What kind of tissue is composed of several layers of flat cells?
Stratified squamous epithelium
Describe serous, parietal, visceral and mucous membranes and where they might be found?
Serous: membrane that lines body cavities and covers organs to reduce friction; abdominal organs
Parietal: Outer layer of a serous membrane, covering cavity walls; also lines body cavities, ex. abdominal organs
Visceral: Inner layer of a serous membrane, covering organs; surrounds organs within body cavities, around the heart
Mucous: Moist membrane with epithelial layer, secreting mucus; Lines passages with external connections (e.g., digestive, respiratory tracts).
What are the layers of the skin?
Basale, Spinosum, Granulosum, Lucidum, Corneum
In what layer of the skin would you find the fastest rate of mitosis?
Basale
What is a hematoma? What is jaundice?
Hematoma: bruise, collection of blood outside of the blood vessel
Jaundice: skin, whites of eyes, and mucous membranes turn yellow due to build up of bilirubin in blood
What are sebaceous glands?
Sebaceous glands: oil gland in dermis that helps lubricate and waterproof skin and hair by secreting sebum
What are apocrine glands?
Apocrine glands: sweat gland typically in hair follicles in the armpits and genital regions
The biggest concern for a patient with severe burns is ______
Risk of infection
Describe the types of bones and where they would be found in the human skeleton.
Long; Elongated with a shaft and expanded ends.
Short; Cube-shaped, found in wrists and ankles.
Flat; Thin and flattened, protective role.
Irregular; Complex shape, various functions
Bones develop from –
Ossification
What layer of the skin contains areolar and adipose tissue, stores fat, and is the site for drug injections?
Hypodermis
What are the cells called that break down bone?
Osteoclasts
What are the cells called that produce bone?
Osterblasts
Compare the epiphyseal plate with the epiphyseal line in adults.
Epiphyseal Plate: sheet of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of an immature bone; replaced by bone tissue as the organ grows in length
Epiphyseal Line: Completely ossified remnant of the epiphyseal plate
What is the name of the cartilage at each epiphysis of the long bones?
Hyaline Cartilage
What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis: disease characterized by a decrease in bone mass; occurs when the rate of bone resorption exceeds the rate of bone formation, a common occurrence as the body ages
What kind of bone is found in the forearm?
Lone bone
How many thoracic vertebrae are there in the human skeleton?
12
What is the name of the bone that is between the chin and larynx and does not connect with another bone?
Hyoid bone
What is the periosteum?
Periosteum: fibrous membrane covering the outer surface of bone and continuous with ligaments
What is the function of red marrow? Yellow marrow?
Red marrow: connective tissue in the interior cavity of a bone where hematopoiesis takes place
Yellow marrow: connective tissue in the interior cavity of a bone where fat is stored
Describe compact bone? Describe spongy bone?
Compact bone: dense osseous tissue that can withstand compressive forces
Spongy bone: (also, cancellous bone) trabeculated osseous tissue that supports shifts in weight distribution
What is the name of the canal that runs through the center of bone tissue? What is its function?
Haversian canal: allows bone to get oxygen and nutrition without being highly vascular.
What is a foramen?
Foramen: an opening, hole, or passage, especially in a bone
What are lacunae?
Lacunae: small spaces in a bone or cartilage that cells (osteocytes) occupy
Describe pronation, abduction, and dorsiflexion.
Pronation: forearm motion that moves the palm of the hand from the palm forward to the palm backward position
Abduction: movement in the coronal plane that moves a limb laterally away from the body; spreading of the fingers
Dorsiflexion: movement at the ankle that brings the top of the foot toward the anterior leg
What is the joint called when two bones that are joined together cannot move?
Synarthroses/fibrous joint
Describe a tendon sheath.
Tendon sheath: connective tissue that surrounds a tendon at places where the tendon crosses a joint; contains a lubricating fluid to prevent friction and allow smooth movements of the tendon
A freely moveable joint is called –
synovial/diarthrosis
What is a bursa? A synovial membrane? A meniscus?
Bursa: connective tissue sac containing lubricating fluid that prevents friction between adjacent structures, such as skin and bone, tendons and bone, or between muscles
Synovial membrane: thin layer that lines the inner surface of the joint cavity at a synovial joint; produces the synovial fluid
Meniscus: articular disc