Lecture 14 - Microevolution
Key Concepts
Natural Selection
Definition: Process whereby individuals with traits more suited to their environment have a higher chance of survival and will most likely reproduce more successfully than others.
Significance: Primary mechanism of evolution.
Microevolution vs. Macroevolution
evolution is a change in allele frequency over time
Microevolution: occurs within species (in the allele frequencies)
Macroevolution: Evolutionary changes resulting in the formation of new species.
Mechanisms influencing allele frequency:
Natural selection
Genetic drift
Gene flow
Mutation
Allele Frequency
consider a population where gene A has 2 alleles (A1 and A2)
Example of Allele A with two variants, A1 and A2:
Initial Frequencies:
Freq A1 = 10/20 = 0.5
Freq A2 = 10/20 = 0.5
After 10 years:
Freq A1 = 4/20 = 0.2
Freq A2 = 16/20 = 0.8
Demonstrates alteration of genetic composition over time.
Origin of New Alleles
Methods for generating new alleles:
Mutation: Random, heritable changes in DNA that can introduce new alleles into a gene pool
mutation rates are generally low (e.g., humans ~1.1 x 10^-8 per site per generation)
Types of mutations:
Deleterious
Neutral
Beneficial
Only inherited mutations occur in germ line cells.
Horizontal Gene Transfer: Transfer of genes between organisms, particularly common in bacteria.
likely origin of eukaryotic chloroplasts and mitochondria
Mutation and Evolution
Discussion of the mutation rate in pathogens like COVID-19, highlighting higher than previously thought rates and potential implications for diversity among genomes:
Example from reports showing significant mutations in the COVID-19 genome over time.
deemed to be harmful, higher mutation rates = antibodies + immune system cannot keep up with new mutations/ variants
Types of Mutations
Point Mutation: Involves change in a single base pair affecting a single amino acid (e.g., normal vs. sickle-cell mutation).
example - Bird Flu
A single mutation with the virus can target humans + infect humans , leading to increased virulence and potential outbreaks. (no evidence of human transfer of the virus)
Gene duplication
if a gene is duplicated, the second copy can accumulate mutations freely
think: why would a duplicated gene accumulate mutations more quickly than a non-duplicated gene
This is because the original gene can maintain its essential function while the duplicate is free to evolve new functions or become non-functional without detrimental effects on the organism.
Genome Duplication
extra copies of all chromosomes above the diploid level
triploid, tetraploid etc.
mainly common in plants , where polyploidy can lead to increased genetic diversity and adaptability.
Polyploidy
can be induced artificially
agricultural plants often triploid - seedless, more vigorous
in trout and salmon - triploidy induces sterility
What affects allele frequency?
adaptive evolution results in a better fit between individuals and their environment —> natural selection
non-adaptive evolution is random and may have a positive, enutral or negative effect on fitness —> genetic drift + gene flow
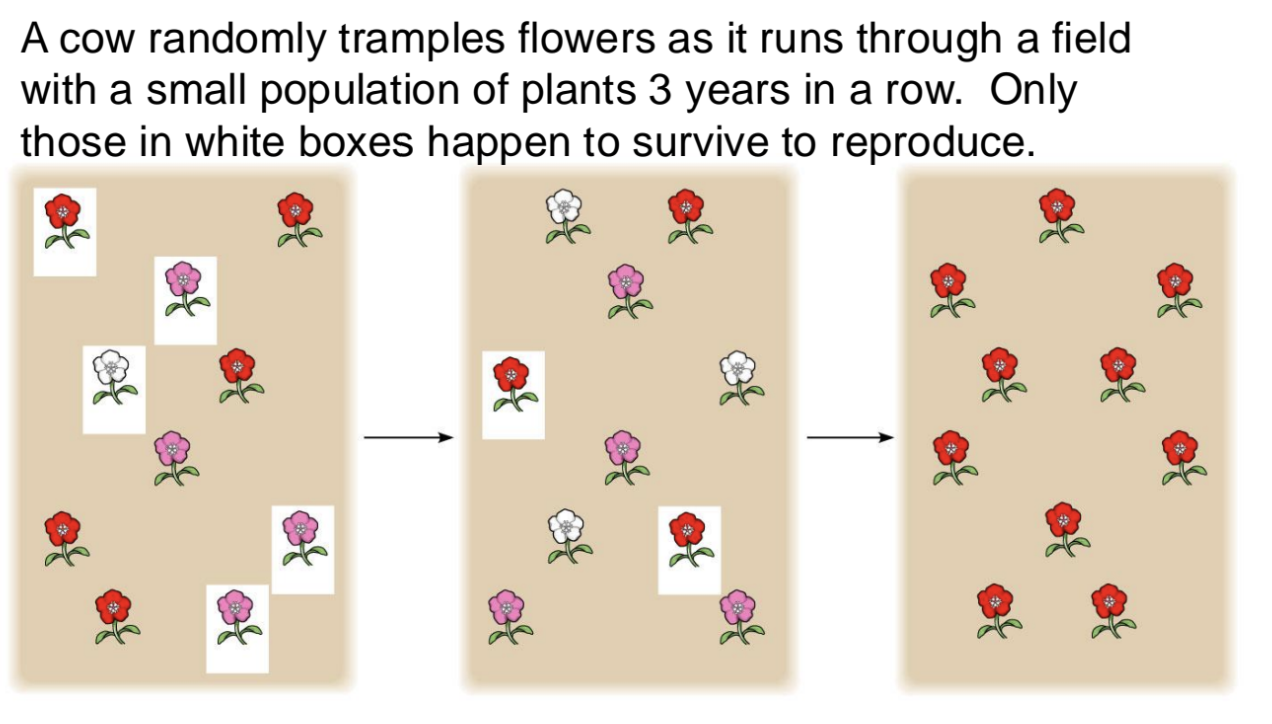
Genetic Drift
Definition: Random fluctuations in allele frequencies due to chance events, distinct from selection:
Most significant (larger effect) in small populations.
can fix alleles
an allele is fixed when it has a frequency of 1.0
Founder Effect: Example of limited genetic diversity arising from a small group founding a new population (e.g., Huntington's disease in Venezuela).
migrants are random sample of available alleles
new population may be over or under represented for some traits relative to the source population
Huntington’s disease example
frequency of disease, a degenerative nerve disease (autosomal dominant)
more common in Maracaibo Venezuela (700 infected per 100,000 people) compared to the US and Europe (6 infected per 100,000)
discovered that the villagers in Venezuela discovered the heritage led to a women who was infected by the disease who would then passed it down to her 10 kids
Bottleneck Effect: Example of genetic diversity loss due to a sudden reduction in population size (e.g., Northern elephant seals).
allele frequencies may change due to the chance event
effect can occur within populations (not because of migration)
North elephant seals
population reduced to 20 individuals in 1890
current population is 180,000
scientist examined 24 genes and found no allelic variation (each gene only had 1 allele) , indicating a significant reduction in genetic diversity due to the population bottleneck.
high homozygosity
Cheetahs
historic range: North America, Europe, Asia, Africa
Bottleneck effect occurred near the end of the last ice age (10,000 years ago)
90% homozygosity today
Gene Flow
Definition: Transfer of genetic material between populations through migration (immigration/emigration).
Impact: Helps maintain genetic similarity between populations and reduce divergence.
transfer of alleles from one population to another
immigration and emigration / accidental movement
important in mobile organisms
can reduce potential for genetic divergence
Types of Natural Selection
Directional Selection: Changes in phenotype favouring one extreme (e.g., size in salmon and coloration in guppies).
Disruptive Selection: Favors two or more extreme phenotypes over the average (e.g., beak size in Galapagos finches).
Stabilizing Selection: Favors average traits while extreme variants are removed (e.g., human birth weight).
Examples of Directional Selection
Trinidadian guppies: Differing phenotypes above and below waterfalls due to predation.
African Elephants: Tusked vs. tuskless females’ prevalence due to poaching.
Conclusion
Microevolution is influenced by various mechanisms including natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and mutation. Understanding these concepts is crucial for comprehending evolutionary processes. Next lecture: Phylogeny.
 Knowt
Knowt