[FDNACCT] Unit 3: Financial Statements
Financial Statements
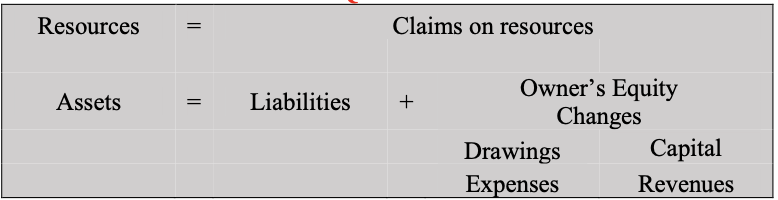
General purpose reports that provide financial information about the reporting entity’s [business] economic resources [assets], claims against the entity [liabilities and owner’s equity], and changes in those economic resources and claims [revenues, expenses, owner’s capital, owner’s drawings] that is useful to primary users in making decisions relating to providing resources to the entity
To provide financial information about the reporting entity’s assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses that is useful to users of financial statements in assessing the prospects for future net cash inflows to the reporting entity and in assessing management’s stewardship of the entity’s economic resources (includes protecting the company’s assets against price changes and technological changes as well as compliance with laws, regulations, and contracts)
only includes financial information about the reporting entity (scope)
records financial information from a specified period of time
Information about transactions and other events that have occurred after the end of the reporting period is provided if that information is necessary to meet the objective of financial statements
From the perspective of the reporting entity
Elements of Financial Statements
[FOUND IN THE BALANCE SHEET (STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION)]
Assets
Economic resource
the right that has the potential to produce economic benefits
Control
the present ability to direct the use of the economic resource and obtain the economic benefits that may flow from it
no other party controls that asset
the right to deploy that asset in its activities
ability to enforce legal rights on that asset
A present economic resource controlled by the entity as a result of past events
Liabilities
Claims of other entities
A present obligation of the entity to transfer an economic resource
as a result of past events
Obligation
a duty or responsibility that an entity has no practical ability to avoid and owed to another party/parties (e.g., person, another entity, a group of people / a group of entities, society at large)
Transfer an economic resource
pay cash
deliver goods or provide services
exchange economic resources with another party on unfavourable terms (E.g., Forwards; Options)
transfer an economic resource if a specified uncertain future event occurs
Issue a financial instrument if that financial instrument will oblige the entity to transfer an economic recourse
Result of past events
the entity has already obtained economic benefits or taken an action
the entity will or may have to transfer an economic resource that it would not otherwise have had to transfer
Owner’s Equity
Claims of owners
The residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities
Owner’s financial interest in a business
Net worth
[CHANGES IN ECONOMIC RESOURCES | FOUND IN INCOME STATEMENTS (STATEMENT OF PROFIT OR LOSS)]
Income/Revenue
Increases in assets, or decreases in liabilities, that result in increases in equity, other than those relating to contributions from holders of equity claims
Expenses
Decreases in assets, or increases in liabilities, that result in decreases in equity, other than those relating to distributions to holders of equity claims
*Other changes in economic resources and claims
Contributions from holder/s of equity claims, and distributions to them
Exchanges of assets or liabilities that do not result in increases or decreases in equity
Statement of Financial Position
A position statement that reports the financial condition (financial standing; financial strength) of an entity at the end of the period and presents an organized list of assets, liabilities, and equity
Provides information useful to assess the entity’s future cash flows, liquidity, and long-term solvency
limitations:
The entity's reported book value (assets minus liabilities) will not directly measure the company’s market value (in a public corporation, this is current market price x number of shares issued)
Many assets are measured at their historical costs rather than their fair values
Many aspects of a company may represent valuable resources but are not recorded as assets
Product knowledge
Experienced management team
Trained employees
Loyal customer relationships
FORMS:
Report Form

Account Form
*Operating Cycle
time between the acquisition of assets for processing and their realisation in cash or cash equivalents
Use cash to acquire inventory
Prepare inventory for sale to customers
(Including the production process for manufacturing business)
Deliver inventory to customer
Collect cash from customer
ELEMENTS:
Assets
Current Assets
assets that are expected to be realized (converted to cash) or intended to be sold or to be consumed within the entity’s normal operating cycle
held primarily for the purpose of trading
expected to be realized within twelve months after the reporting period
cash or cash equivalent unless the asset is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash
cash on hand and in banks that is available for use in the operations of the business
Cash equivalents
highly liquid investments that can be quickly converted into cash, not subject to significant risk of
changes in value, and must be held for the purpose of ‘meeting short-term cash commitments’
Examples include money market funds, such as:
Investment in treasury bills (short-term debt instruments of government)
Investment in commercial papers (short-term debt instruments of corporations)
Investment in certificate of deposits (short-term debt instruments of banks)
Trade and Other Receivables
Trade receivable / Accounts receivable
receivable resulting from a company’s normal trade, that is, providing services or selling goods on account [on credit; on charge account; on open-account credit]
Notes receivable
receivable with a written promissory note from another party from a company’s normal trade, usually requiring an additional receipt of explicit interest
Other receivables
Advances to employees
advances by the company to employees
Loans receivable
loans given by by the company to individuals and other entities
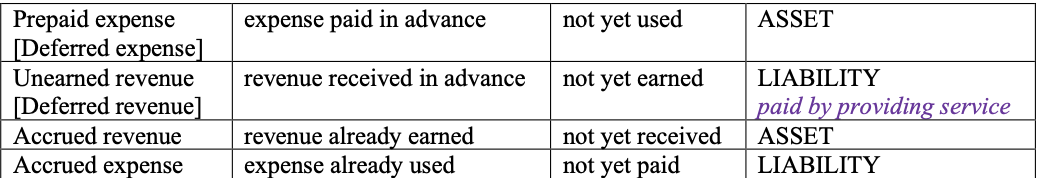
Accrued revenue
revenue already earned, but not yet received (recorded as part of adjusting entries at period-end)
Inventory
encompass goods that are:
purchased and held for resale
merchandise purchased by a retailer and held for resale [Merchandise Inventory]
land and other property held for resale
raw materials and factory supplies awaiting use in the production process
work in progress being produced by the entity
finished goods produced
Prepaid Expense [Deferred expense]
expense paid in advance, thus creating benefits, but not yet used
includes office supplies
Non-current Assets
residual by definition, an entity shall classify all other assets as non-current
Property, plant, and equipment
tangible items that are held for use in the production or supply of goods or services, for rental to others (except for land and building), or for administrative purposes
are expected to be used during more than one period
(e.g., Land, Land improvements, Building, Machinery, Vehicles, Furniture and fixtures, Fittings, Office equipment, Bearer plants)
Liabilities
Current Liabilities
liabilities that are expected to be settled in the entity’s normal operating cycle
owed primarily for the purpose of trading
are due to be settled within twelve months after the reporting period
do not have the right at the end of the reporting period to defer settlement of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period
Trade and other payables
Trade payable / Accounts payable
payable resulting from a company’s normal trade, that is, buying assets and goods on account [on credit; on charge account; on open-account credit]
Notes payable
payable with a written promise to pay cash at some future date (legal IOUs), usually requiring an additional payment of explicit interest
Other payables
Accrued expense
expense already used, but not yet paid (recorded as part of adjusting entries at period-end)
Loans payable – current portion
a portion of long-term Loans Payable that is payable within the next year
Unearned Revenue [Deferred revenue]
revenue received in advance, but not yet earned
Non-Current Liabilities
residual by definition, an entity shall classify all other liabilities that are not current as non-current
Loans payable – noncurrent portion
long-term Loans Payable that is not yet due within the next year
Long-term notes payable
long-term promissory notes that is not yet due within the next year
Mortgage payable
long-term promissory note secured by an asset whose title is pledged to the lender
Owner’s Equity
*Deferrals and Accruals
*Basic Accounting Equation

Statement of Profit & Loss
A change statement that summarizes the profit-generating transactions that changes the owner’s equity for the period and reports an entity’s financial performance, that is, its net profit or net loss, for the period
Provides information useful to assess the entity’s profitability, return on owner’s investment, its operations and various functions and predicting future expenses and cash outflows
FORMS:
Nature of expense method
Classifies expenses within profit or loss according to their nature
Function of expense method
Classifies expenses by their function within the entity
Cost of sales
cost of providing service/cost of goods sold
Distribution cost
expenses related to selling and distributing the goods to the customers
Administrative costs
expenses related to the general administration of the business
Finance costs
interest expense
ELEMENTS:
Income
Earnings of an entity
Inflow of resources resulting from services provided or goods sold to customers
Increases in assets, or decreases in liabilities, that result in increases in equity, other than those relating to
contributions from holders of equity claims
Service revenue/Professional fees
revenue from services provided to clients
Sales
revenue from sale of goods to customers
Other income
revenue from sources other than the main line of business
Interest income
Rent income
Commissions income
Income from investments
Gain on sale of plant, property, equipment item
Expenses
Outflow of resources incurred for generating revenues
Decreases in assets, or increases in liabilities, that result in decreases in equity, other than those relating to distributions to holders of equity claims
Delivery expense
Insurance expense
Interest expense
Marketing expense (advertising, promotion)
Office supplies expense
Professional fees (accounting, audit, legal)
Rent expense
Repair & maintenance expense
Representation & entertainment expense
Salaries & wages expense
Employee benefits
Taxes & licenses expense
Transportation & travel expense
Utilities expense
Miscellaneous expenses / Other expenses / Sundry expenses
Bad debts expense
Doubtful debts expense
Depreciation expense
Statement of Changes in Equity
A change statement that discloses the events that caused the owner’s equity to change for the period
Provides information useful to understand the transactions with owners in their capacity as owners, showing separately contributions by and distributions to owners
ITEMS AFFECTING EQUITY:
Income [revenues] and expenses
Contributions [investment] by owner
Owner’s capital
financial investment of the owner
Cash
Other assets
Recorded at its fair market value at the time of investment
Distributions to [withdrawal by] owner
Owner’s drawings
temporary withdrawal of the profit of the business
Capital
Capital / Owner’s capital
financial investment of the owner
Capital employed
the long-term source of financing, which includes both the capital of the owner and non-current liabilities
Working capital
refers to net current assets (Current assets minus Current liabilities)
Capital expenditures
expenditures for purchase of non-current assets
Capital budgeting
the process of investment appraisal
Expanded Accounting Equation
Statement of Cash Flows
A change statement disclosing the events that caused cash to change for the period
Provides information useful to assess the entity’s ability to generate cash and cash equivalents and to utilize those cash flows
Notes to Financial Statements
present information about the basis of preparation of the financial statements and the specific accounting policies used
disclose the information required by IFRSs that is not presented elsewhere in the financial statements
provide information that is not presented elsewhere in the financial statements, but is relevant to an understanding of any of them