L7 GERD
Objectives
Pathophysiologic mechanisms causing GERD
Common Risk Factors that influence GERD development, Symptom exacerbation, Complications
Differentiate Typical, Atypical, and ALARM symptoms
Notes
What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
when the reflux of the stomach contents
T/F: Heartburn is included under GERD
False due to it’s non-erosive symptom
What age is GERD more prominent in
40 +
What are the Risk Factors of GERD
Gender
FH
Smoking/Alcohol use
Medications
can affect LES pressure
Foods
Respiratory Diseases
Reflux Chest Pain Syndrome
Obesity
What are risk factors that may increase prevalence in females
Pregnancy and Nonerosive Reflux
What related disease states are more common in males
Erosive Esophagitis
Barrett’s Esophagus
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
What is the Esophagastric (EG) Junction
barrier that prevents gastric reflux into esophagus
What helps maintain the Esophagastric Junction
Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES)
What is the Lower Esophageal Spincter
muscular ring innervated by the vagus nerve → contraction (at rest) and relaxation (for swallowing)
Explain the pathophysiology of GERD
Excessive reflux → Breaks down Esophagus’ defense mechanisms over time → Irritation and Injury of Esophageal Mucosa
What are the different types of LES Pressure?
Spontaneous, Transient (short period) LES Relaxation
Intra-Abdominal Pressure
Atonic LES
When does Spontaneous, Transient LES Relaxation typically occur
Postprandial (after meals)
T/F: ST-LES is linked to abnormal LES pressure
False: more likely to occur with NORMAL LES pressure
What symptoms are typically seen with ST LES Relaxation
Esophageal Distention (enlargement/ballooning)
Vomiting, Belching, Retching
What factors can increase the probability of GERD
Degree of Sphincter Relaxation
Lower Esophageal Clearance
amount of time acid touches the esophageal mucosa
Position
Laying down
Increased Gastric Volume
Increased Intragastric Pressure
force exerted on the stomach walls by the contents within it, typically food, gas, or fluid
What are examples of Intra-Abdominal Pressure
Straining
Bending Over
Coughing
Eating
Pregnancy
What are other possible factors as to why pregnant women may experience GERD
Hormonal Effects on Esophageal Muscle
LES Tone
Explain what is Atonic LES
When the LES is continuously relaxed → no closure allows free reflux
T/F: Intra-Abdominal Pressure AND Atonic LES is more likely to occur with DECREASED LES pressures
True
What Anatomic factors can contribute to GERD
Hiatal Hernia
protrusion of the stomach through the diaphragm → may cause LES displacement and trapped gastric contents
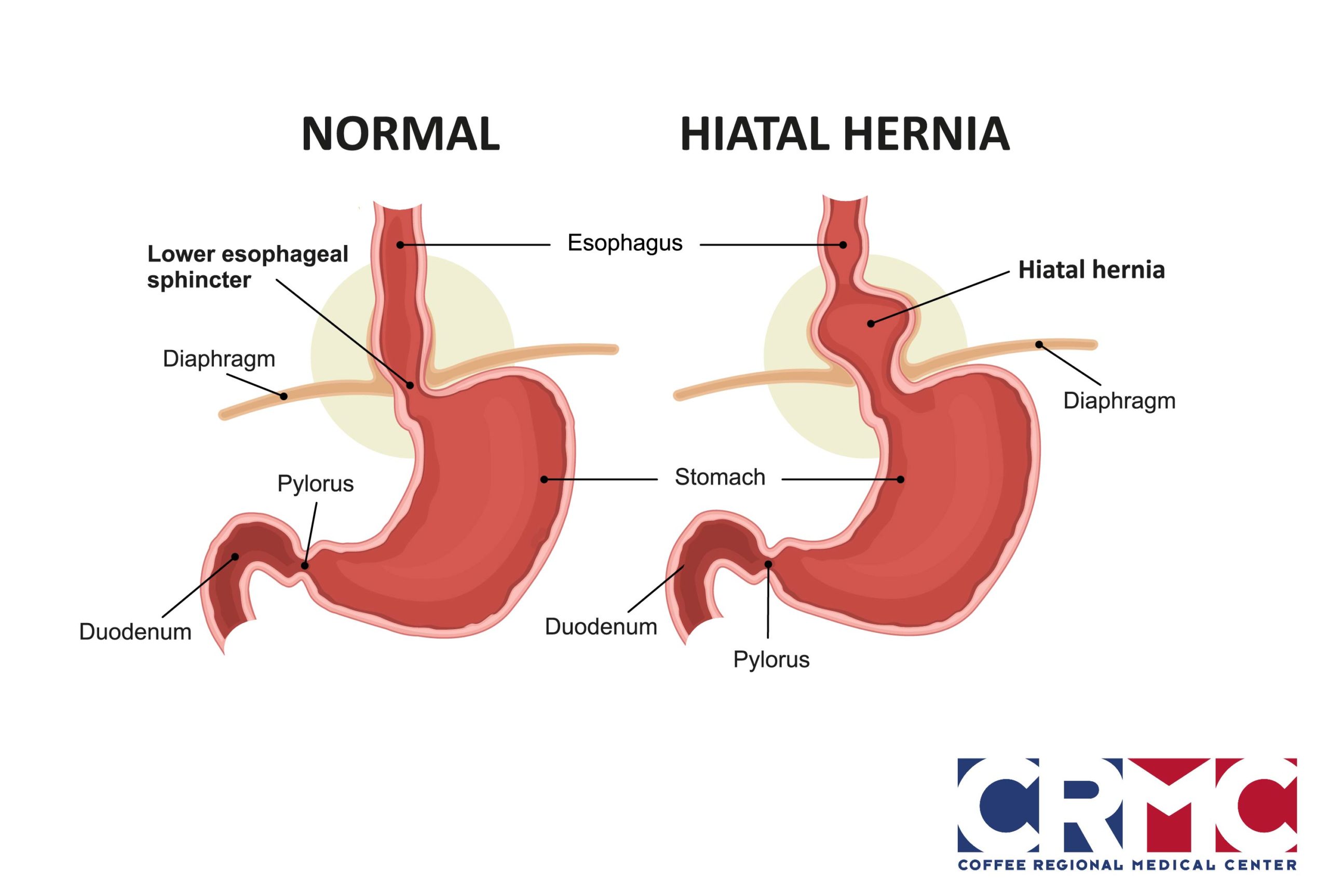
What factors are associated with Esophageal Clearance
Swallowing and Saliva
What factors may affect saliva production
Increased age and Sleep
What is the purpose of Mucus Secreting Glands
protects the esophagus
What happens when Mucus Secreting Glands interact with Acid
decreases protection and may result in inflammation (Esophagitis)
What reflux characteristic can lead to complications
(low) pH
What happens when Gastric Emptying is slowed down?
increased gastric volume, frequency and amount of reflux
What are contributing factors to slowed gastric emptying
DM, Smokers, high Fat meals
List examples that REDUCE LES Tone

What are examples that have direct irritant that could contribute to GERD
Medications (more acidic)
Bisphosphonates (ex. Alendronate, Risedronate, etc)
Chemotherapy
Iron
Aspirin and NSAIDs
inhibits prostaglandins which protect the GI tract
Potassium Chloride
Quinidine
Foods
Spice
Orange and Tomato Juice
Coffee
T/F: GERD has low morbidity
False, Significant morbidity
What are the possible complications with tissue injury of untreated GERD
Esophagitis
Esophageal Structures
Barrett’s Esophagus
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
Explain the components for the screening of Barrett’s Esophagus
MALE
Chronic GERD symptoms > 5 years
Weekly symptoms and 2+ related risk factors
What are the risk factors Barrett’s Esophagus
> 50
White
Central Obesity
Waist > 102 cm
Waist-Hip ratio > 0.9 cm
Tobacco
FH
Barrett’s or Adenocarcinoma
What is it when there are GERD symptoms but no tissue injury or erosion
Non-Erosive Reflux Disease (NERD)
T/F: symptom and tissue injury based syndromes are independent of each other
True
What are the symptoms of GERD
Pyrosis — heartburn
hallmark symptom
Hypersalivation
“acid brash”
sour or bitter
Belching
Regurgitation
Reflux Chest Pain
What are the ALARM Symptoms for GERD
Dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
Odynophagia
painful
GI Bleeding
Weight Loss
What are Extraesophageal Syndromes
(GERD) manifests outside the esophagus
Chronic Cough
Asthmatic symptoms
Laryngitis
Dental Erosion
Is Extraesophageal Syndromes common
no, atypical
What are the general components for a diagnosis of GERD
Clinical symptoms
Response to acid suppression therapy
Diagnostic tests for complicated GERD
Patient specific
When is an Endoscopy used for diagnosis?
complicated symptoms present, NOT for typical symptoms
Indications for endoscopy in patients with GERD
Persistent of progressive symptoms despite appropriate treatment
Dysphagia or odynophagia
Involuntary weight loss >5%
GI bleeding
Mass, stricture or ulcer
Suspected extra-esophageal symptoms
Screening for Barrett’s esophagus in high risk patients
Placement of wireless pH monitoring
Recurrent symptoms post-endoscopy or post-surgical anti-reflux procedures
What is a noninvasive endoscopic procedure
PillCam ESO
Eliminated in stool
can’t obtain biopsy
What is used to confirm reflux with persistent symptoms (excluding mucosal damage) or atypical symptoms
Ambulatory pH Monitoring
pH probe passed transnasally 5 cm above LES
Symptom diary used to correlate timing of symptoms to pH measurements
What is combined impedance monitoring
measuring both acid and non-acid reflux
What does a Radiotelemtry Capsule do?
wirelessly attached to mucosa to monitor pH
For pH monitoring, what should be discontinued a week prior to therapy?
PPI
What is a Manometry test
measures the pressure of organs or body systems to assess the function of the esophagus, stomach, or rectum
used for more complex situations
When is Manometry or High-Resolution Esophageal Pressure Topography (HREPT) used?
Failed twice daily PPI therapy
Normal endoscopy results
Identifying Motor Disorders
Evaluating Peristalsis for Antireflux Surgery
Finding pH probe placements
What is Impedance manometry used for
evaluates Esophageal Clearance, Retention through Bolus Transit, LES and Upper Esophageal Sphincter Pressures
Quiz
Question 1
1 / 1 pts
A patient (5’5”, 140 lbs.) with GERD and type 2 diabetes complains of heartburn, belching and regurgitation. The patient is a current smoker and denies alcohol use. Symptoms occur only after eating high fat meals and often feels full after eating a small amount of food. Which of the following pathophysiologic mechanisms of GERD is mostly likely occurring based on the patient’s presentation? (LO # 1, 4)
Atonic LES due to hormonal changes
Decreased esophageal clearance due to age
Delayed gastric emptying
Increased abdominal pressure
Question 2
1 / 1 pts
A patient is in her third trimester of pregnancy. Her PMH is noncontributory. She is not taking any medications. She reports frequent symptoms of pyrosis, which is causing significant discomfort. She would like to know why her symptoms have worsened over the past few months. What is the likely reason for her symptoms? (LO # 1, 2)
Hormonal changes during pregnancy decrease esophageal clearance
Hormonal changes increase gastric emptying
Pregnancy causes increased intra-abdominal pressure
Pregnancy increases the risk of hiatal hernias
Question 3
1 / 1 pts
A patient reports worsening symptoms of GERD, complaining of heartburn, belching, increased salivation and difficulty swallowing. Which of the following best characterizes the patient’s GERD based on symptom presentation? (LO # 3)
Increased risk for extraesophageal complications
Increased risk of tissue injury-based GERD syndromes
Typical GERD symptoms
Atypical GERD symptoms
Question 4
1 / 1 pts
Which of the following patients experiencing chronic GERD symptoms should be screened for Barrett's esophagus?
45-year-old Asian man with current tobacco use
55-year-old Caucasian man with central obesity
65-year-old African American woman with central obesity
40-year-old Caucasian woman with tobacco use
 Knowt
Knowt