Chemical Bonding
Definitions
electronegativity - the tendency of atoms in a molecule to attract a shared pair of electrons
intermolecular bonds - the bonds between molecules
valence electrons - the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom
covalent bond - a sharing of atleast one pair of electrons by two non-metal atoms
bond energy - energy required to completely seperate two covalently bonded atoms
bond length - distance between the nuclei of two covalently bonded atoms
pure covalent (non-polar) - equal sharing of electrons
polar covalent - unequal sharing causing dipole
dipole moment - measure of the polarity of a bond
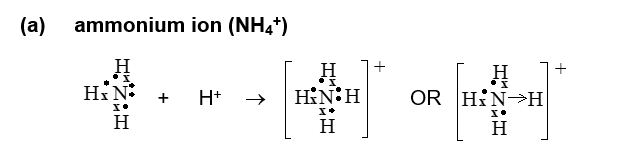
dative covalent - A dative covalent bond is a bond that is formed by the overlapping of orbitals and the sharing of an electron pair both of which belong to one atom
Dative Covalent Bonds
a molecule with a positive ion (needs electron) bonds to a molecule with a loan pair (donor atom).
overall charge becomes +.
Shape of Molecules
determined using VSEPR
Linear
bond angle 180
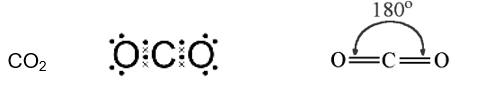
Angular
formed op 2 lone pairs
angle between bonded pairs - 104,5
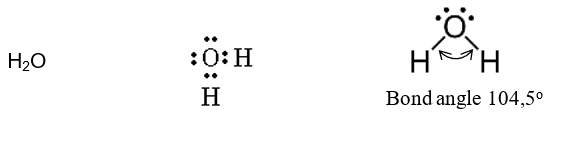
Trigonal Planar
120
no lone pair

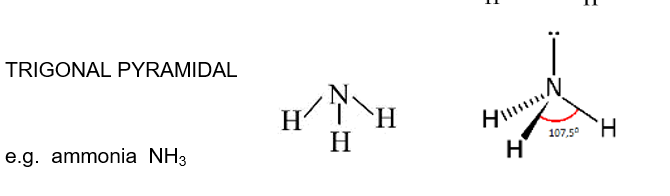
Trigonal Pyramidal
107,5 between bonded
single loan pair
Tetrahedral
109,5 between bonded
no lone pairs

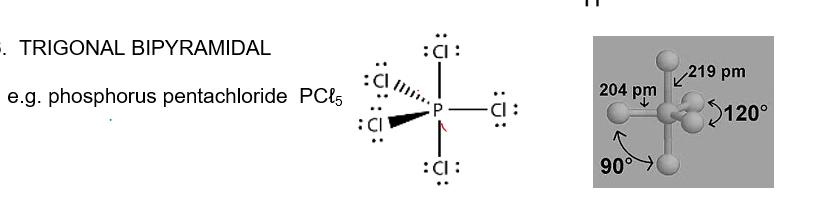
Trigonal Bipyramidal
120 horizontally, 90 vertically
Octahedral
90 all round

Polar Molecules
greater charge = more electronegative
size of atom - electrons closer to nuclei meaning stronger forces
non-polar bonds
no electronegativity dif
polar bonds
difference in electrongeativty pulls electron cloud one way = polar
If covalent

if the substance is ionic (nm → m), then becomes ionic with covalent characters at 1,7
if a molecule has polar bonds but is symetrical, the vector force equates to 0 and is therefore not a dipole (non-polar)