Copy of World War 1 Begins
Name:
Focus: How did total war alter the role of a civilian during World War 1?
The “Great War” Begins
In response to Austria’s declaration of war, Russia, Serbia’s ally, began moving its army toward the Russian-Austrian border. Expecting Germany to join Austria, Russia also mobilized along the German border. To Germany, Russia’s mobilization amounted to a declaration of war. On August 1, the German government declared war on Russia. Russia looked to its ally France for help. Germany, however, did not even wait for France to react. Two days after declaring war on Russia, Germany also declared war on France. Soon afterward, Great Britain declared war on Germany. Much of Europe was now locked in battle.
| Central Powers | Allies |
|---|---|
| These countries were known as the Central Powers because of their location in the heart of Europe. Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire would later join the Central Powers in the hopes of regaining lost territories. | Japan joined the Allies within weeks. Italy joined later. Italy had been a member of the Triple Alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary. However, the Italians joined the other side after accusing their former partners of unjustly starting the war. The U.S. had desperately tried to stay neutral, but ties to Britain, propaganda, the sinking of ships by German U-boats, and a German attempt in the Zimmermann Note to get Mexico to declare war on the U.S. pushed the U.S. to enter the war in 1917. |
| GermanyAustria-HungaryOttoman EmpireBulgaria (starting in 1915) | Great BritainFranceRussiaJapanItaly (starting in 1915)United States (starting in 1917) |
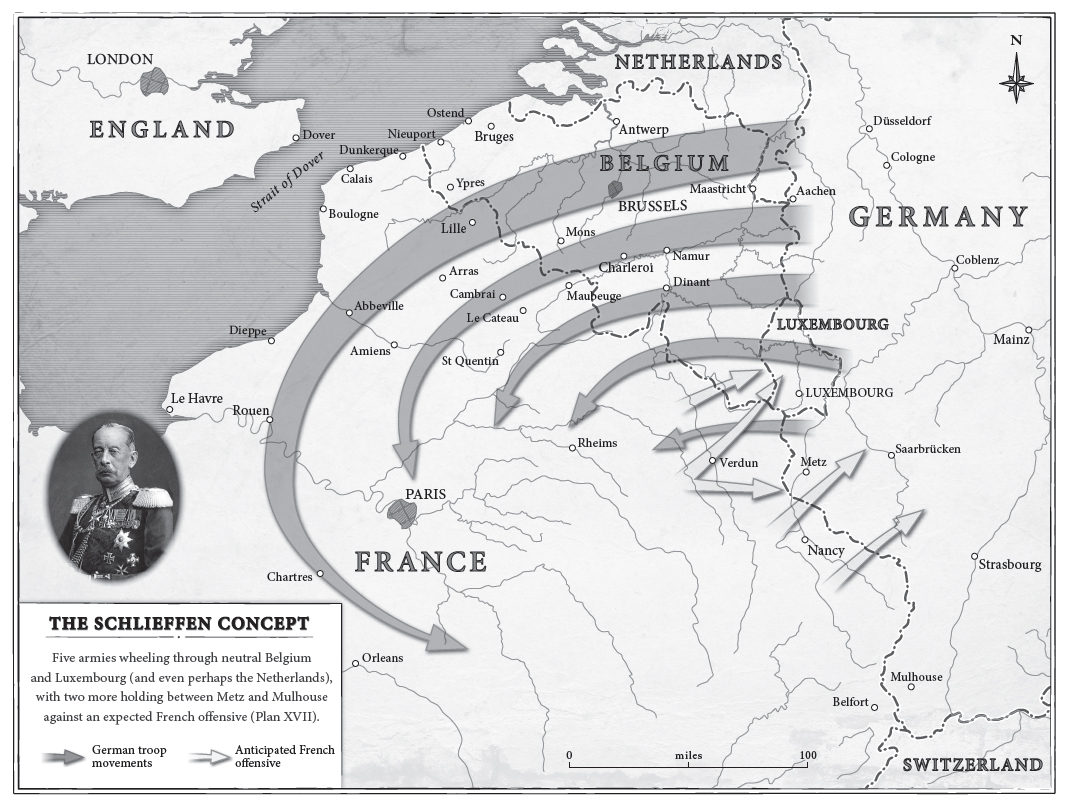
Schlieffen Plan
Facing a war on two fronts, Germany had developed a battle strategy known as the Schlieffen Plan, named after its designer, General Alfred Graf von Schlieffen. The plan called for attacking and defeating France in the west and then rushing east to fight Russia. The Germans felt they could carry out such a plan because Russia lagged behind the rest of Europe in its railroad system and thus would take longer to supply its front lines. Nonetheless, speed was vital to the Schlieffen Plan. German leaders knew they needed to win a quick victory over France.
Schlieffen Plan (MAP)
Please watch the video clip below in order to answer the questions that follow
Video Clip: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zuj4ccY78Nc
- Why did Germany decide to invade Belgium?-To avoid the French fortifications along the French-German border, the troops had to cross Belgium and attack the French Army by the north
- What was the obvious route for Germany to attack France? Why did Germany ultimately not choose this route to stage their initial attack on France?-Through Belgum
- Why was this plan politically unwise?-German Troops were too busy attacking france that they were not paying attention to other countries
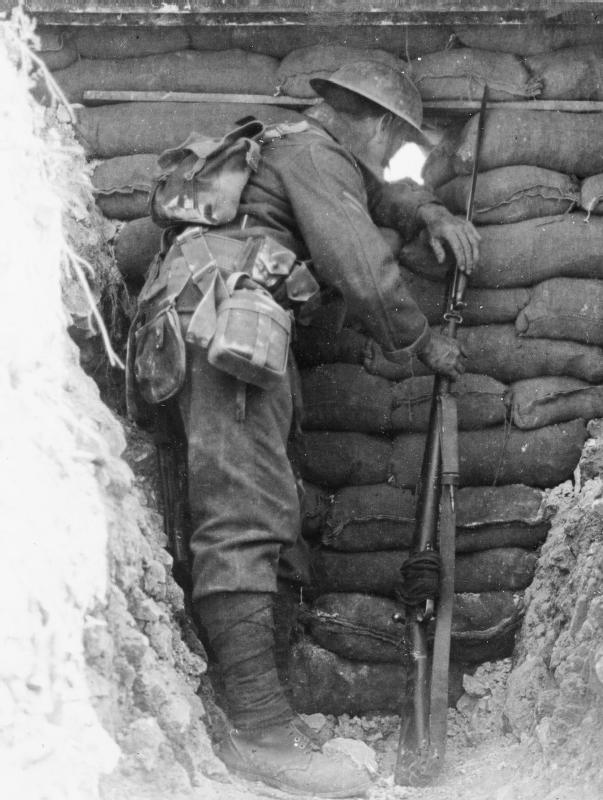
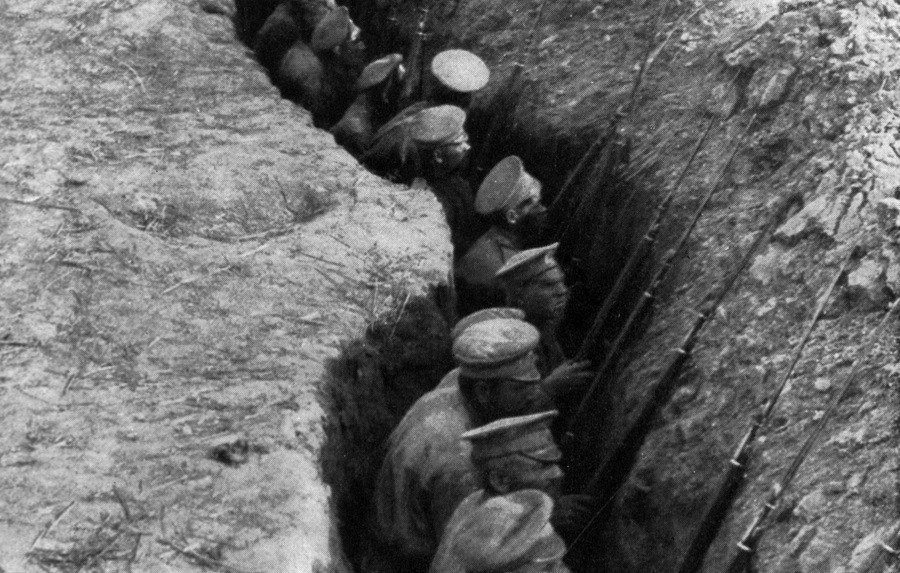
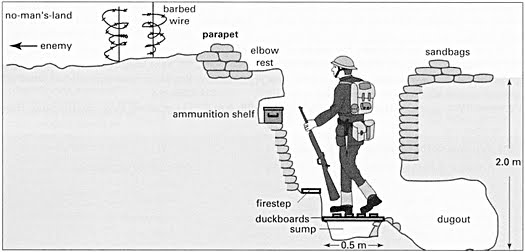
War in the Trenches
By early 1915, opposing armies on the Western Front had dug miles of parallel trenches to protect themselves from enemy fire. This set the stage for what became known as trench warfare. In this type of warfare, soldiers fought each other from trenches. And armies traded huge losses of human life for pitifully small land gains.
The space between the opposing trenches won the grim name “no man’s land.” When the officers ordered an attack, their men went over the top of their trenches into this bombed-out landscape. There, they usually met murderous rounds of machine-gun fire. Staying put, however, did not ensure one’s safety. Artillery fire brought death right into the trenches. “Shells of all calibers kept raining on our sector,” wrote one French soldier.
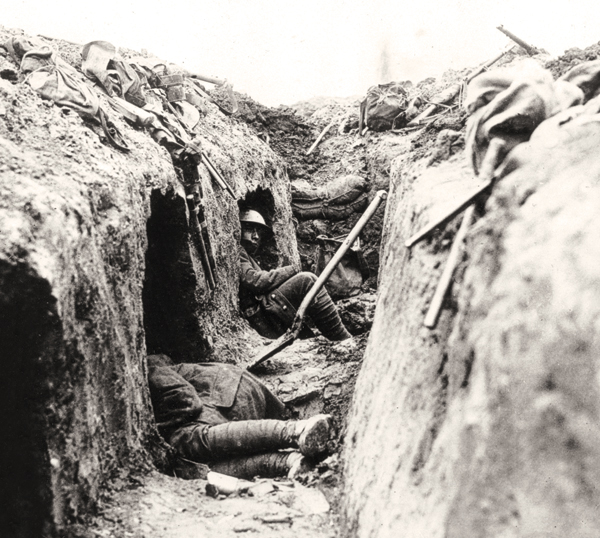

Trench Warfare: A Tour
Directions: Move through an immersive online tour at your own pace and get a close look into the realities of trench warfare!
As you move through the exhibit, jot down the most important points mentioned in each section of the virtual tour. Press the arrow on the right side of the site to move through each section of the virtual tour.
| Immersive Online Tour Link: https://artsandculture.google.com/exhibit/IQLS5svcf515Iw |
|---|
| Where did the trenches stretch from?-Stretched from the North Sea coast of Belgium southward through FranceHow did the introduction of advanced technology result in little progress along the trenches?-Perhaps the most significant technological advance during World War I was the improvement of the machine gun, a weapon originally developed by an American |
| German Trenches |
| Very Muddy and WetUncomfortable |
| What was life like for soldiers in the trenches on the Western Front?Trenches were long, narrow ditches dug into the ground where soldiers lived. They were very muddy, uncomfortable and the toilets overflowed. These conditions caused some soldiers to develop medical problems such as trench foot. |
| How can the effects of trench warfare still be seen in the landscape of Europe?Because of the Trenches built during WW1 The Eastern Front had front lines that moved widely, while the Western Front did not. |
Total War
World War I soon became a total war. This meant that countries devoted all their resources to the war effort. In Britain, Germany, Austria, Russia, and France, the entire force of government was dedicated to winning the conflict. In each country, the wartime government took control of the economy. Governments told factories what to produce and how much. Numerous facilities were converted to munitions factories. Nearly every able-bodied civilian was put to work. Unemployment in many European countries all but disappeared.
So many goods were in short supply that governments turned to rationing. Under this system, people could buy only small amounts of those items that were also needed for the war effort. Eventually, rationing covered a wide range of goods, from butter to shoe leather.
Governments also suppressed antiwar activity, sometimes forcibly. In addition, they censored news about the war. Many leaders feared that honest reporting of the war would turn people against it. Governments also used propaganda, one-sided information designed to persuade, to keep up morale and support for the war. \n
Total war meant that governments turned to help from women as never before. Thousands of women replaced men in factories, offices, and shops. Women built tanks and munitions, plowed fields, paved streets, and ran hospitals. They also kept troops supplied with food, clothing, and weapons. Women also saw the horrors of war firsthand, working on or near the front lines as nurses.
\n
Task!
We are now going to ask you to examine a series of propaganda posters. Your task is to figure out how each poster represented “total war”. If you get stuck, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the poster trying to encourage citizens of that nation to do something?
- If so, what exactly? \n
| Total War Poster AnalysisPlease visit the following Google Slides presentation to view the posters. |
|---|
| Poster 1Which country is this poster from? |
| Poster 2Which country is this poster from? |
| Poster 3Which country is this poster from? |
| Poster 4Which country is this poster from? |
| Poster 5Which country is this poster from? |
| Exit Slip/AttendancePlease answer the following question in the form of a claim on Google Classroom: How did total war alter the role of a civilian during World War 1? |
|---|