GCSE Biology Revision "Respiration"
Introduction to Cellular Respiration
Energy is essential in biology for various functions:
Movement
Maintaining body temperature in mammals
Driving chemical reactions to synthesize/build larger molecules (e.g., proteins made from joining amino acids)
What is Respiration?
Definition: Respiration is an exothermic reaction that continually occurs in all living cells.
Purpose: It provides energy necessary for biological functions.
Photosynthesis is an exothermic reaction: because it releases energy
Types of Respiration
1. Aerobic Respiration
Definition: Occurs when glucose reacts with oxygen.
Products: Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) are produced, along with energy.
Word Equation: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
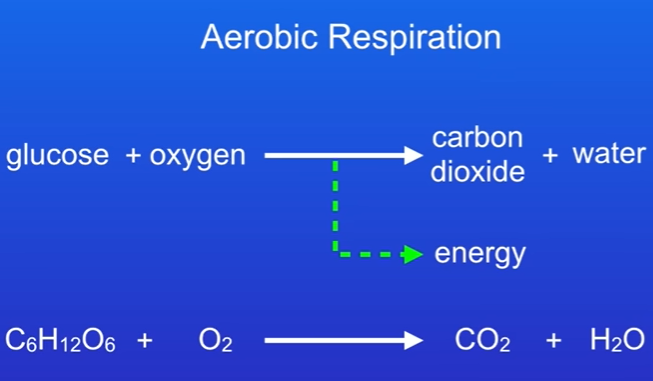
Chemical Symbols:
Glucose: C6H12O6
Oxygen: O2
Carbon Dioxide: CO2
Water: H2O
Key Fact:
Aerobic respiration releases a large amount of energy due to complete oxidation of glucose. (glucose molecule is fully oxidised)
if oxygen's present, then cells carry out aerobic respiration.
2. Anaerobic Respiration
Definition: Occurs when there is insufficient oxygen, such as during intense physical activity.
1st Situation: Muscle Cells
When there is a shortage of oxygen, muscle cells respire anaerobically for energy to contract. In anaerobic respiration in muscles, glucose is converted to lactic acid, and anaerobic respiration does not require any oxygen.
Anaerobic respiration releases much less energy than aerobic respiration because in anaerobic respiration, the oxidation of glucose is incomplete
Process: Glucose is converted to lactic acid.
Equation: Glucose → Lactic Acid + Energy
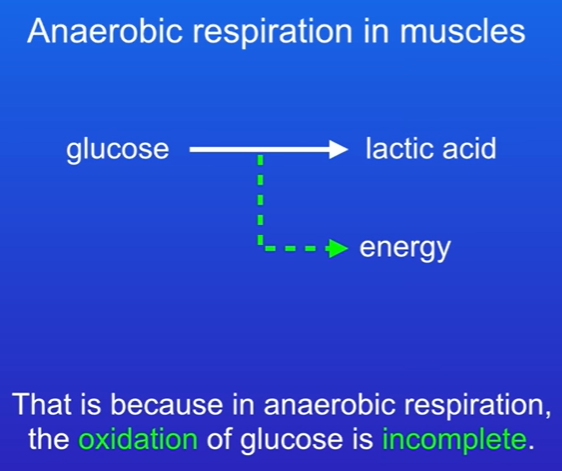
Key Fact: Releases much less energy than aerobic respiration due to incomplete oxidation of glucose.
2nd Situation: Plant Cells and Yeast Cells
Process: In these organisms, glucose is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Equation: Glucose → Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide + Energy
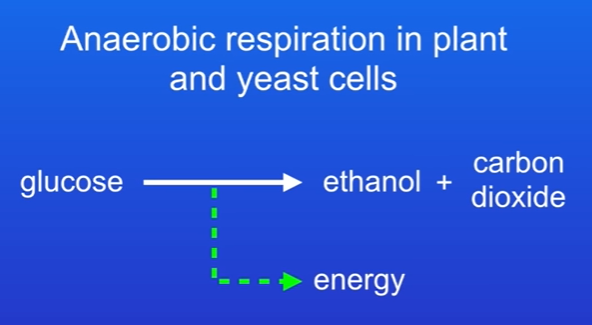
Key Fact: No oxygen is needed for this reaction.
Applications of Anaerobic Respiration
Fermentation:
Alcohol: Anaerobic respiration in yeast (fermentation) is used to produce alcohol (ethanol) in beverages such as beer.
(alcohol in drinks is called ethanol which is produced from fermentation)
Bread Making: Carbon dioxide produced by fermentation creates bubbles, causing dough to rise, which is essential for baking bread.
Key fact: Cells carry out anaerobic respiration when there is insufficient oxygen. Anaerobic repsiration carrys out less energy
 Knowt
Knowt