1.3 Organizational Objectives
Vision Statements
- A statement outlining the desired position of a company in the distant future
- Example: “Where do we want to be?” “To be the leading sports brand in the world.”
Mission Statements
- A statement outlining the underlying purpose of an organization
- Example: “What is our business?” “Healthiest product provision”
Advantages for Both:
- Positive, ideal goals that direct the business in the right direction
- Parallel to business
- Customer-centric
- Sense of direction
Aims
- Long-term goals of what the organization wants to achieve
- Vague & unquantifiable
- “Provide high-quality education to all”
Objectives
- shorter-term goals that are specific and measurable
- “To achieve a 95% pass rate within two years.”
Advantages for Both:
- Provides a sense of direction & purpose
- Unifies management & workspace and motivates them
- Builds trust and goodwill
Strategies & Strategic Objectives
- Plans of action to achieve the organizational objectives
- Long-term goals of a business
- Profit maximization
- Growth
- Market standing
- Image & Reputation
Tactics & Tactical Objectives
- Actions taken to achieve the short-term objectives
- Short-term goals that affect a section of the organization
- Tend to refer to targets set up for up to 12 months:
- survival
- sales revenue maximization
The Need for Changing Objectives
Internal Factors
- Corporate Culture - should be a flexible and adaptable organizational culture
- Type & Size of Organization - various stakeholder objectives need to be considered
- Private vs. Public Sector - Private focus on profit maximization and public focus on providing a service
- Age of Business - newer businesses focus on breaking even and survival and established ones focus on growth and higher market share
- Finance - determine the scale of a firm’s objectives
- Risk Profile - managers who have a high ability to take risks to create more ambitious objectives
- Crisis Management - face internal crisis
External Factors
- State of the Economy - growth or recession
- Government Constraints - government rules & regulations limit what a business can do
- Pressure Groups - can force a business to review its approach to ethics
- New Technologies - create new business opportunities
Ethical Objectives
- Ethics - moral values and principles that guide the decision-making process
- Corporate Social Responsibility [CSR]
- organizations consider the interests of society and take responsibility for the impact of their activities on other stakeholders
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Improved Corporate Image | Compliance Costs |
| Increased Customer Loyalty | Lower Profits |
| Cost Cutting | Stakeholder Conflict |
| Improved staff morale & motivation | Ethics & CSR are subjective |
- Ethics have an evolving nature
- What is considered ‘right’ and ‘wrong’ is mainly dependent on public opinion which changes over time
- Forces firms to review their CSR frequently
- Media pressure in countries means that large multinationals must donate part of their profit to charity
SWOT Analysis
Internal Factors
STRENGTH - Internal advantages that can develop a competitive advantage against competitors
- strong brand loyalty
- skilled workers
WEAKNESSES - Negative internal factors that are unfavorable compared to rivals
- unskilled workplace
- obsolete equipment
External Factors
OPPORTUNITIES - External possibilities for future development and potential areas for expansion and rising future profits
- China has a large customer base. Opportunity for other firms
THREATS - External factors that hinder prospects for an organization. They cause problems for the business
- Changes in fashion
- Oil crisis
- Infectious diseases
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| simple & quick | doesn’t demand a detailed analysis |
| wide range of applications | model is static, whereas business is always changing |
| helps reduce the risks of decision-making | useful if decision-makers are open about the weaknesses |
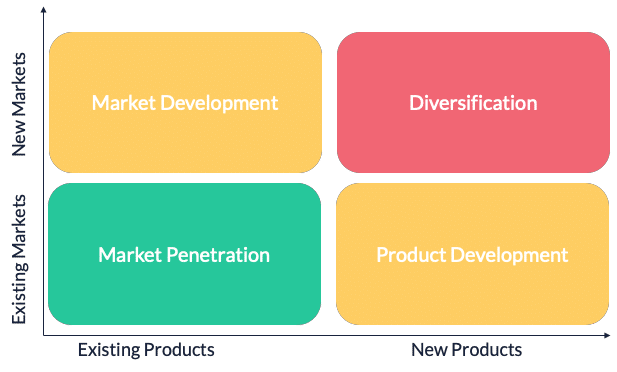
Ansoff Matric
- Analytical tool that helps managers choose and devise growth strategies for products and markets
Market Penetration
- low risk
- Existing products in an existing market
- Price adjustments, increases promotion, and minor product improvements
- Aims to increase market share
Product Development
- medium risk
- New products in an existing market
- Innovation to replace products
- Brand extension and larger product portfolio
- Customers may not like the new product
Market Development
- medium risk
- Existing products in a new market
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| new distribution channel | new customers may not like the product |
| geographical expansion | extensive market research required |
| attract new market segments |
Diversification
high risk
New product in a new market
Related Diversification = same industry
- Coca-Cola buying Bureau healthy drinks
Unrelated Diversification = different industry
- Coca-Cola making merchandise