3.4a - Storage Devices: Professor Messer
Hard disk drives (HDDs)

Non-volatile magnetic storage - function by using rapidly rotating platters.
Random-access - data can be retrieved from any part of the drive at any time.
Contains moving parts - spinner plates and a moving actuator arm. These components limit access speed, and can also break.
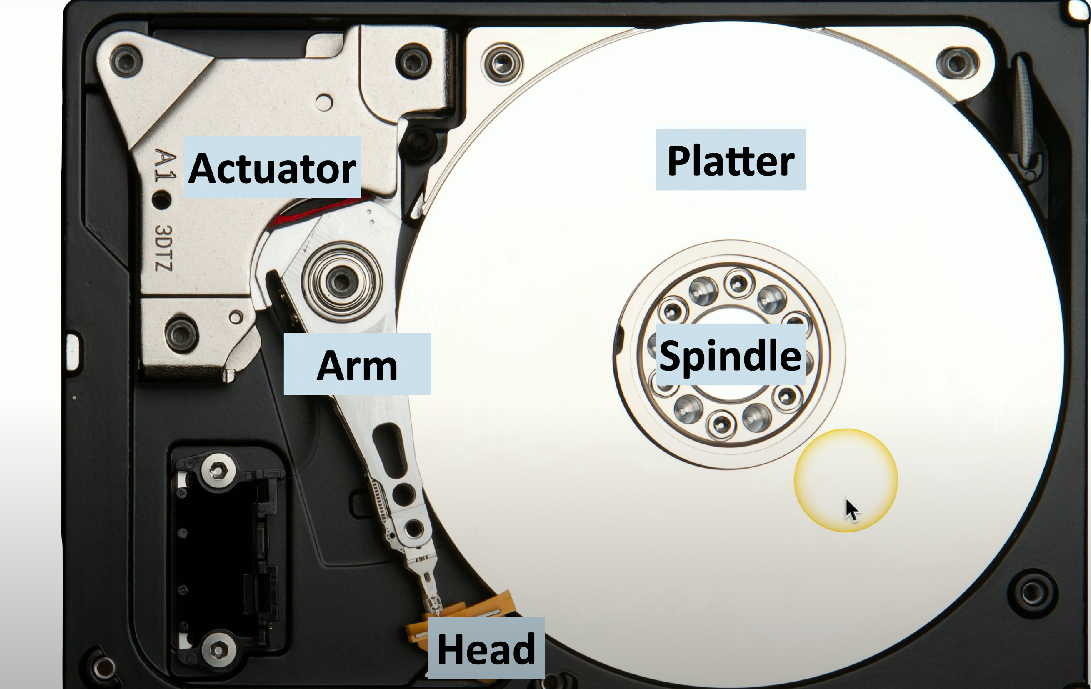
HDD arm: Responsible for moving back and forth to find data on the HDD.
HDD actuator: Mechanism that positions the read/write head over the correct track on the disk to read or write data efficiently.
HDD platter: Circular disks within the HDD, coated with magnetic material, where data is stored in concentric tracks.
HDD spindle: The rotating shaft that holds the HDD platters in place and enables them to spin at high speeds, allowing the read/write head to access data.
HDD head: Used to precisely locate, retrieve, and write data to spinning platters.
Spindle speeds
HDD spindle speed regulates how much latency (delay) for retrieving data from the HDD.
5,400 rpm
5,400 rpm: Spindle speed that provides about 5.55ms rotational latency.
7,200 rpm
7,200 rpm: Spindle speed that provides about 4.16ms rotational latency.
10,000 rpm
10,000 rpm: Spindle speed that provides about 3ms rotational latency.
15,000 rpm
15,000 rpm: Spindle speed that provides about 2ms rotational latency.
Form factors
HDD form factors: Different sizes for HDDs found in computer systems - vary between 3.5”, 2.5”, and M.2 size.
3.5 inch
Form factor commonly found on larger desktop
2.5 inch
Form factor commonly found on smaller laptops
M.2
Newer form factor that can be found on both laptops and desktops.
Solid-state drives (SSDs)
Non-volatile storage device that contains no moving parts and uses flash memory chips to store data.
Benefits of SSDs:
No moving parts: no risk of mechanical failure that can cause data read/write issues.
Very fast performance: no latency from spinning drive delays.
Communications interfaces
Communications interface: Used to access data from an SSD/storage device
Non-volatile memory express (NVMe)
Non-volatile memory express: Communication interface that is designed to match the throughput from an SSD - lower latency, and can use am M.2 form factor.
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe): Expansion bus standard used to connect external devices to a motherboard (e.g., network cards, graphics cards, storage devices).
Serial Attached SCSI [Small Computer System Interface] (SAS)
Form factors
SATA interfaces can be used with SSDs to improve data retrieval/performance.
M.2
Smaller form factor that doesn’t require SATA data or power cables - pulls power directly from the motherboard.
Can use a PCIe bus connection
4 GB/s throughput or faster when using NVMe PCIe x4.
Mini-serial Advanced Technology Attachment (mSATA)
Use of SSDs allows a decrease in the size of SATA drives - no spinning disk equipment.
Size typically less than <2 inches.
Removable storage
Flash drives
External storage devices that use EEPROM (Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory).
Non-volatile and no power is required to maintain the data.
Limited quantity of writes to the flash drive - once this threshold is surpassed, data is read-only.
Optical drives
Use laser technology to read and write data on discs such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-rays.
Data is stored in pits and lands on the optical disc surface.
Relatively slow - used for media that you don’t intend to change (e.g., archives).
Many different formats (CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, Blu-ray)