Astronomy Midterm 1
Chapter 1: Science and the Universe
Cosmic Address
Earth ( 3rd planet )
Earth orbits our closest star the sun
The Sun is one of about 100 billion stars that make our galaxy ( Milky Way )
Local group group galaxies are part of the Virgo Supercluster of galaxies
What are the most abundant elements in the Universe?
Hydrogen ( 7,500 )
Helium ( 2,300 )
Oxygen ( 100 )
If the history of the universe was 1-year when would humans appear?
If the history of the Universe was 1 year humans would appear in the very last second of the very last day ( December 31 )
What does it mean to say that telescopes are time machines?
By looking farther away, we’re looking farther back in time. light moves at a finite speed hence light takes time to travel from one place to another so when we see an object we gather light from the object so we see it as it was when the light left the object and started traveling towards us.
Light moves at a finite speed of the universe.
Light moves at a finite speed, it takes time for the light from the distant objects to reach us.
Scientific Notation
Example: 500,000,000
answer: 5 X 10^8
( 8 zeros ) the first number is 5 hence it Is 5 times 10.
Chapter 2: Celestial Sphere
Celestial Sphere:
Zenith: the top of the dome, the point directly above your head is called the zenith.
Horizon: The astronomical horizon is a great circle 90° (ninety degrees) from the zenith or nadir r
.Celestial Poles: Points about which the celestial sphere appears to rotate, the intersection of the celestial sphere with the earth’s polar axis
Celestial Equator: Great circle on the celestial sphere 90 degrees from the celestial pole, where the celestial sphere intersects the plane of the earth’s equator.
System Astronomers use:
Altitude: Altitude is the point's angle above or below the horizon
Azimuth: The angle measured along the horizon from north around to the right (eastward) to a point on the horizon below the point in the sky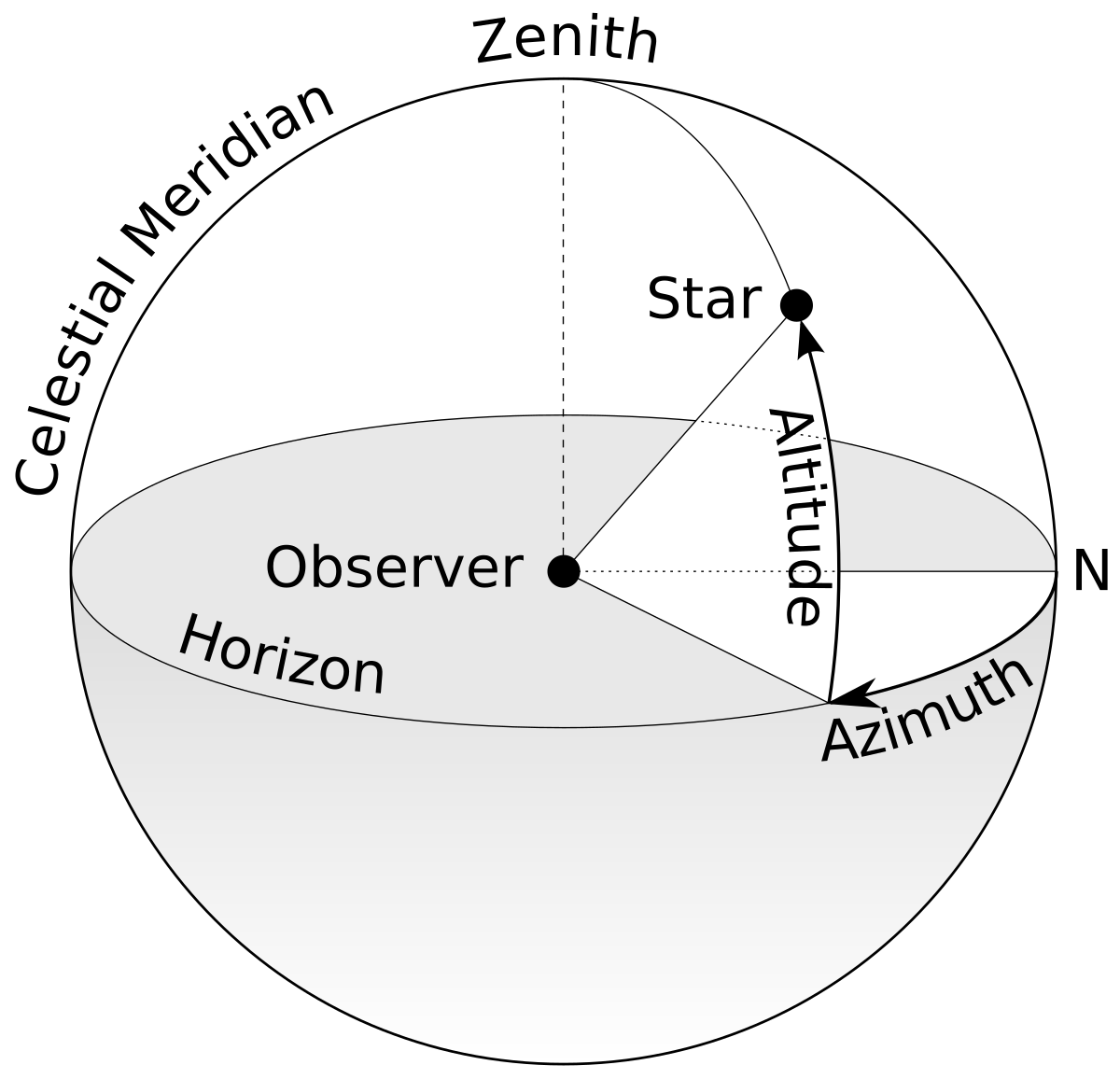
Equatorial System
z
⭐ ️Which system for describing the sky is Universal (all people at all locations on Earth would record the same position for a star) and which is specific to the observers’ location? Horizon System (measures the altitude and azimuth)
⭐ How do the stars move in the sky over a 24-hour period? Due to Earth’s rotation, however, the stars in our galaxy are all orbiting in a nearly circular path around the center of the galaxy.
⭐ Explain how the motion of the stars is different at the north pole, the equator, and intermediate latitude (like here in LA). 5
at the celestial equator, the stars are looking east or west, moving vertically (straight line).
At the North Pole stars circle the zenith ( circular motion).
At intermediate latitudes, the north celestial pole is at some position overhead and the horizon turns out to be equal to the observer’s latitude. stars rise and set at an angle to the horizon.
⭐ The sun moves along the ecliptic
 ⭐ Planets rise and set in the sky just like the sun and moon ⭐
⭐ Planets rise and set in the sky just like the sun and moon ⭐
ecliptic: the apparent annual path of the sun on the celestial sphere
Planets, the sun, moon move along the ecliptic because they trace the plane of our solar system in the sky.
Chapter 3: Orbits and Gravity
Kepler’s Three Laws of Planetary Motion
Law 1: Planetary orbits are ellipses (not perfect circles as we previously thought ) with the sun at one focus.
Law 2: Planets move faster when they are closer to the sun and slower when they are farther away.
Law 3: The larger the orbital path, the longer the orbital period.
Newton’s Three Laws of Motion
Law 1: Objects at rest stay at rest. Objects in motion stay in motion unless acted on by an outside force.
Law 2: A change in the motion of an object is proportional to and in the direction of the force applied to it. (force, mass, acceleration)
Law 3: For every motion, there is an equal and opposite reaction
MVD
Mass: Measure of the amount of material within an object
Volume: Measure of the amount of space an object or material occupies
Density: Mass divided by volume which equals the amount of material per unit volume
⭐ ️What is angular momentum? Based on angular momentum, as something collapses will its rotation speed up or slow down? Angular momentum is the measure of the rotation of a body as it revolves around a fixed point. When something collapses (distance from fixed point decreases) it starts spinning faster ( we will see this in how stars form)
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation?
He proposed that every planet (or mass) is kept in orbit by gravity ( a force attraction between all bodies in space)
increasing the mass = increasing the force of gravity.
increasing the distance = decreasing the force of gravity
formula: 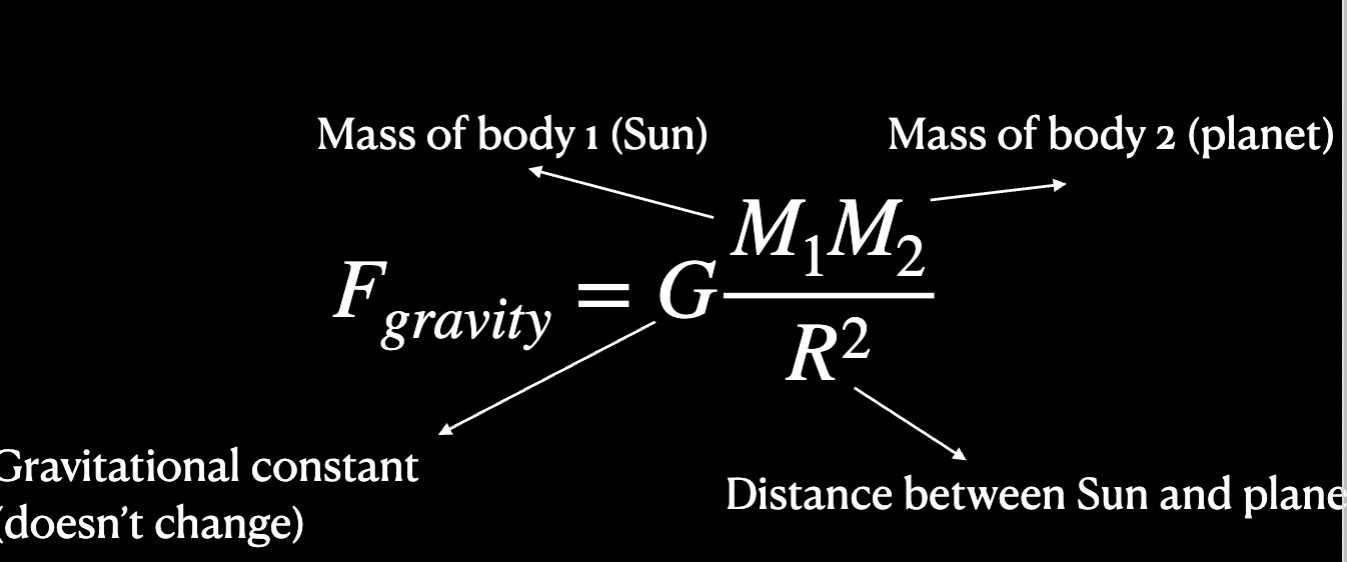 Prehelion: When the planet is closest to the sun in its orbit, moves faster
Prehelion: When the planet is closest to the sun in its orbit, moves faster
Aphelion: The planet is farthest to the sun in its orbit, moves slower
Perigee: Closest point
Apogee: The farthest point
Orbits
Planets and Asteroids: the orbits of all planets are on the same orbital plane, asteroids orbit the same orbital plane as the planets
Dwarf Planets: orbits are inclined with respect to the orbital plane
Comets: have larger, more eccentric ( less circular ) orbits than asteroids and planets
⭐ ️How fast must an object be moving to leave Earth’s gravitational pull?
Escape velocity, or escape speed, is the speed an object must be moving to overcome the earth’s gravitational pull.
more massive planets = faster escape speeds to escape their gravitational pull.
Chapter 4: Earth, Moon, Sky
The use of right ascension and declination to map the sky?
Ra and Dec are used to describe positions in the sky of all kinds of astronomical bodies.
⭐ ️How does the tilt of the earth’s axis cause the seasons?
Earth is tilted about 23.5 degrees, Caused by a change in the incidence angle of sunlight at different points in the earth’s orbit around the sun. the earth’s axis points towards the sun ( it is summer for that hemisphere ). When the earth’s axis points away it is winter.
⭐ Explain how/why seasonal variations on Earth differ with latitudes? are seasons more extreme at the equator? The poles? intermediate latitudes?
At the poles
summer solstice (the sun never sets)
the winter solstice (the sun never rises)
Equator
days are 12 hours round
Elsewhere (Intermediate latitudes)
Days longer in summer, shorter in winter
Extreme seasonal variation depends on proximity to poles.
⭐ ️Causes of the phase of the moon:
the changing positions of the Moon, Earth, and the Sun. As the Moon goes around the Earth, different parts of it are illuminated by the Sun. We see different phases from different perspectives as the moon orbits the Earth.
⭐ How long does it take the moon to rotate once on to axis? 27.32 days
⭐ How long does it take to revolve around the earth one time? 29.53 days
⭐ What is the dark side of the moon? explain how this relates to the time it takes for the moon to rotate once on its axis and revolve around the earth once.
The dark side of the moon Is the side of the moon facing away from the earth that doesn't get sunlight.
Causes of lunar and solar eclipses? It occurs when the moon passes directly between the Earth and the sun casting the moon's shadow on earth. In order for this to happen the moon needs to be in the new moon phase. However, it doesn’t happen at every new moon because the moon’s orbital plane is tilted with respect to the ecliptic.
Lunar eclipse: can occur during a full moon, the moon passes all or a portion of the earth’s shadow.
Why does the moon look red during a lunar eclipse? Sunlight reaching the moon passes through the earth’s atmosphere. The more dust or clouds in earth’s atmosphere during the eclipse the redder the moon will appear.
Chapter 5: Radiation and Spectra
Wavelength and Frequency
The distance between the crests of a wave (length). Frequency is related to wavelength, the number of waves per second.
frequency measures how far a wave or crest passes a particular point longer the wave → lower frequency shorter wave → higher frequency
(related to each other by the speed of light)
⭐ Light travels at a finite speed, the speed of light. What is the speed of light? 300,000,000 m/s
⭐ Is the light a particle or a wave? or both? Light is both a particle and a wave
⭐ How does light behave as a particle? what is the name of a light particle? The way light interacts with atoms (the photoelectric effect). A photon carries a specific amount of energy, related to the wavelength of the light Shorther wavelength= more energy Longer wavelength= less energy
Proportion of Light
⭐ How does the brightness of light we see from an object related to our distance from the object? Electromagnetic radiation from a source moves out isotropically or in all directions. The further you are from a source of light, the weaker the light will get.
Inverse Square Law: Intensity of light is proportional to 1 distance ² - Inverse square laws are common in physics.
Brightness 𝛼 1/distance ²
Types of Light
Radio Microwave Infrared Visible Ultrgaviolet X-ray Gamma ray
10 ^ 3 10^-2 10^-5 0.5×10^-6 10^-8. 10^-10 10^-12 Wavelength
10^4 10^8 10^12 10^15 10^16 10^18 10 ^ 20 Frequency
Wein’s Law
Hotter objects emit shorter wavelengths, more energetic, electromagnetic radiation. Cooler objects emit longer wavelength, less energetic, electromagnetic radiation. (red star/light = less hot —————- blue star/light= hotter)
Reflection: light reflects off smooth surfaces
Refraction: light bends when moving through different materials
Dispersion: white light can be separated into its constituent colors because different colors of light get bent differently.
Spectroscopy and why is it powerful? spectrometers are used to disperse light to form a spectrum. with this spectroscopy, we can identify the chemical composition of matter hence determining its physical structure.
Structure of an Atom
→ in the nucleus
protons (+)
neutrons ( no charge )
→ outside nucleus
electrons (-)
orbit nucleus in orbitals
The behavior of electrons within atoms, how do electrons interact with light to move among energy levels?
Each electron is in a specific energy level (how hard they are to unbid from an atom, the closer to the nucleus, the harder to unbid) electrons can be unbound if they absorb a photon with exactly the right amount of energy.
Emission vs. Absorption
Emission lines: are formed when electrons move down an energy level and emit a photon. Produced when specific elements emit photons or light
Absorption lines: are formed when an electron absorbs a photon and moves up an energy level. Caused when a continuous spectrum passes a hot thin cloud of gas and elements absorb specific wavelengths or colors of light.
Doppler Effect
Objects moving towards you will shift to shorter wavelengths of light so they will appear bluer or blueshift
Objects moving away from you will shift towards longer wavelengths so they will appear redder or redshift
* The faster the motion the larger the wavelength (change in color) *
Chapter 6: Astronomical Instruments
⭐ ️Aperture of a telescope?
The diameter of the opening of the telescope.
⭐ which one is best? larger or smaller aperture to observe really faint, far-away galaxy?
A bigger aperture = more light collecting area can make the image brighter, sharper, and able to produce more detail.
⭐ What factors should you take into account when choosing the ideal site to build an astronomical observatory?
Dark skies ( far from cities )
high elevation (less atmosphere to look through)
Good weather ( dry, infrequent cloud cover)
Low atmosphere turbulence ( less air motions)
⭐ What effect does the atmosphere have on astronomical observations?
Movements in the atmosphere can cause subtle variations in how a star appears and can cause them to appear to twinkle
⭐ define the technique of adaptive optics and explain how it?
A technique used to reduce the effects of atmosphere turbulence and create clearer images. Use a laser to produce a fake star. observe the star with a telescope and measure how the atmosphere distorts the star then you use computer algorithms to undo this effect in the real data
⭐ How is the resolution of a telescope defined?
Resolution is a numerical measure of how precise an image is
→ measured in angular size of smallest feature
→ depends on telescope aperture size and seeing
⭐ What is a Charge-coupled Device (CCD) and how are they used in astronomical imaging?
CCD records digital images.
Photons hit the CCD surface. CCD records where photons hit and how many hit each pixel. (more pixels-higher quality image)
⭐ How does a spectrometer work?
A spectrograph is an instrument attached to a telescope that splits light into many colors, the split light is then collected on a CCD for recording/analysis.
Light from an object enters the spectroscope through a slit, light goes to prism (disperses light into the spectrum), spectrum is focused onto CCD and recorded as a digital image
⭐ What are the advantages of putting telescopes in space?
above earth atmosphere = better seeing (no atmospheric turbulence)
Some types of light can only be observed from space because our atmosphere is opaque to light at those wavelengths
⭐ What types of light are only observable from space?
High energy ( ultraviolet, X-ray, Gamma-ray) and most infrared observing must be done from space
 Knowt
Knowt