DTSC-620 Mod 1_ Intro to Cloud & AWS
Cloud computing defined- Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute power, database, storage, applications, and other IT resources via the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Infrastructure as software- Cloud computing enables you to stop thinking of your infrastructure as hardware, and instead think of it (and use it) as software.
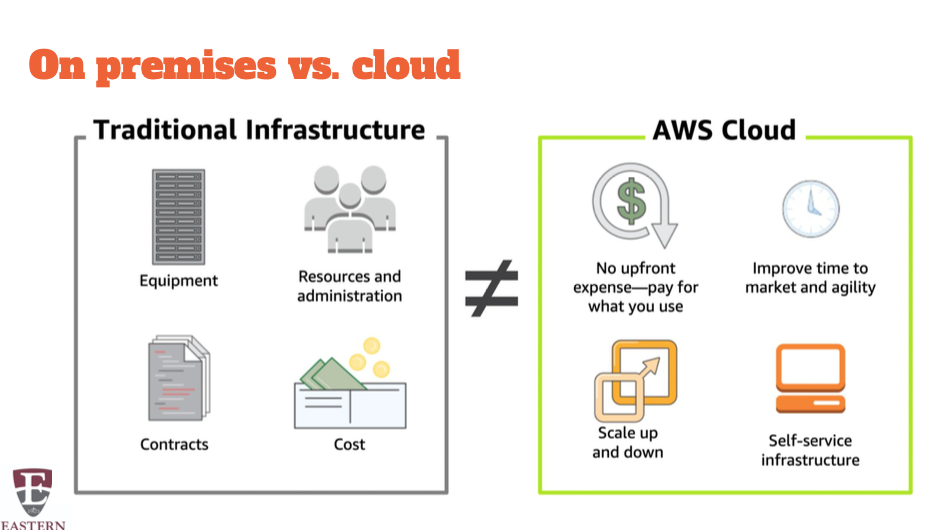
Traditional computing model Infrastructure as hardware
● Significant upfront investment and costs of maintaining
○ Requires space (and security)
○ Requires staff (and security)
● Requires capital expenditure (capex) and planning
● Has long hardware procurement cycles- adding a new person to system
Traditional computing model
Infrastructure as hardware
● Requires you to provision capacity by guessing maximum peaks
○ Problem of underestimating resource or storage needs
○ Problem of overestimating resource or storage needs
○ Needs change requiring more time, effort, money
Traditional computing model
Infrastructure as hardware
● Acquire, Provision, Maintain
Traditional computing model: example
New Website
● Buy the hardware
● Rack and stack servers
● Put it in a data center (Buy? Rent? Plus utilities)
● IT professional to manage it (or have someone else manage it)
● Secure it
● Replace servers
Cloud computing model
Infrastructure as software Software solutions
● Flexible
● Change more quickly, easily, cost-effectively
● Eliminate heavy-lifting tasks ○ Procurement
○ Maintenance
○ Capacity planning
Cloud computing model
Infrastructure as software Software solutions
● Elasticity
● Availability
● Automation
● Security
● Support
● Pay-as-you-go
Cloud service models
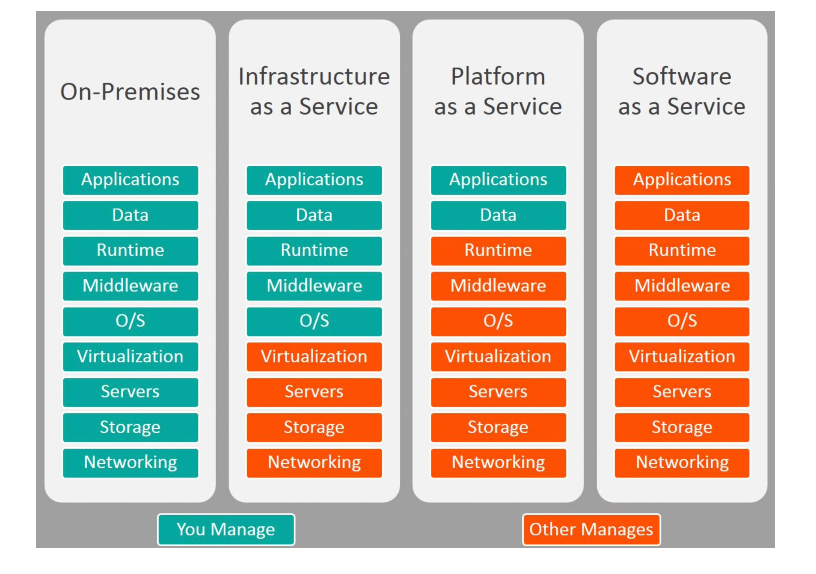
Cloud service models
Infrastructure as a Service- (IaaS) renting compute power but rest you do
-- Amazon EC2
- Most control over resources but most work
Platform as a Service- (PaaS)- you manage but cloud servers help
- Salesforce
- Heroku
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Amazon RDS
Software as a Service -(SaaS)- least manageable
- Microsoft Office 365
- Google Docs, Sheets, Calendar, Drive
- Netflix, Spotify
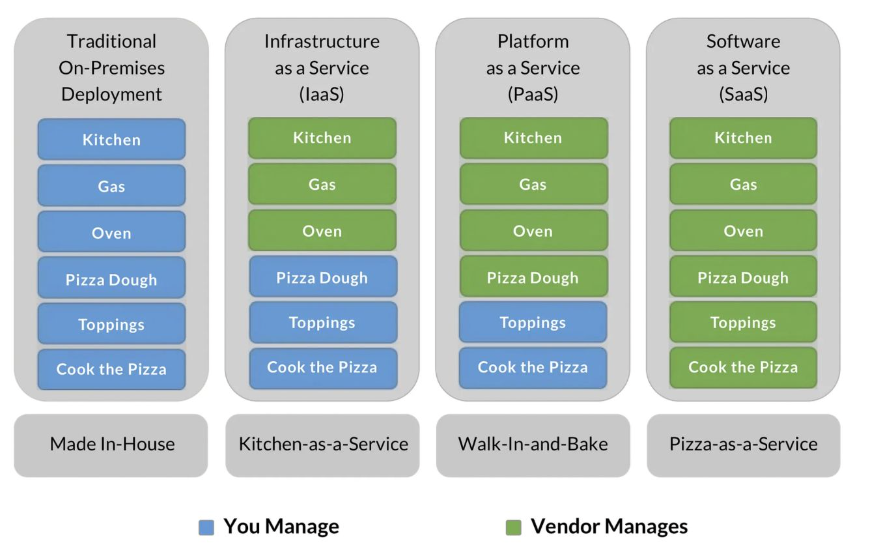
example of clouding Pizza as a Service
Cloud computing deployment models
Cloud full on the cloud
Hybrid
On-premises (private cloud)
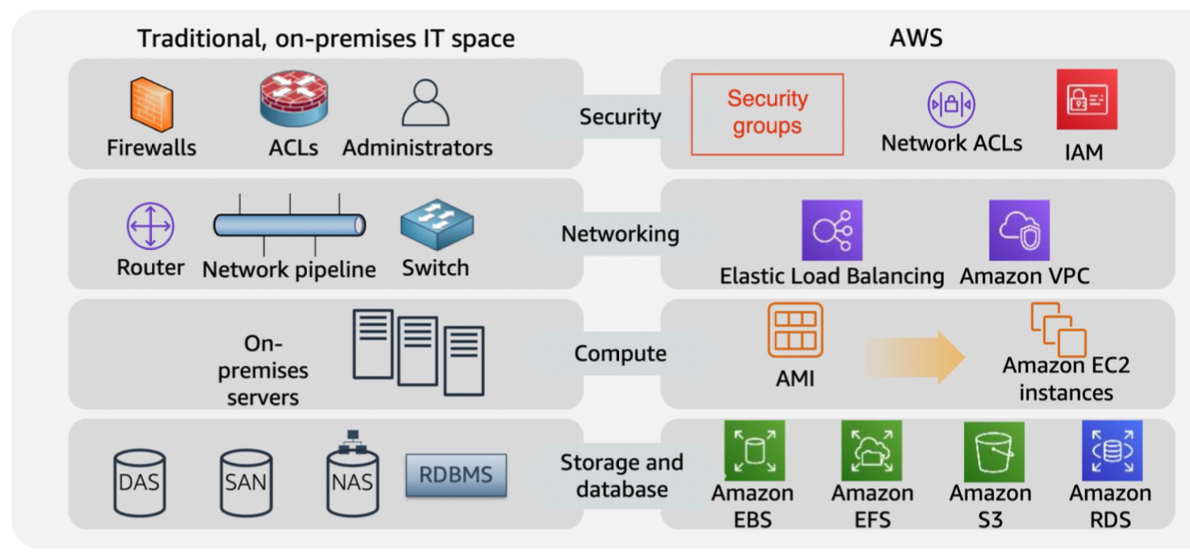
Similarities between AWS & traditional IT
Two kinds of cloud
Cloud Providers: FB, AWS, Google, etc. rent computers as a service
Cloud Services: performs a job for you in the cloud
FB Messenger, Amazon, Netflix, AirBnB, YouTube, Capital One, Google Drive
What does “stored in the cloud” mean?
Your data is stored on physical pieces of equipment in a datacenter.
Example from Facebook/Meta: Your profile, your likes, your viewing history, your friends, your groups, your messages (public and private), your preferences, ad information, etc. are stored on servers in FB data centers
What isn’t a cloud service?
On demand service, via the internet, pay-as-you-go
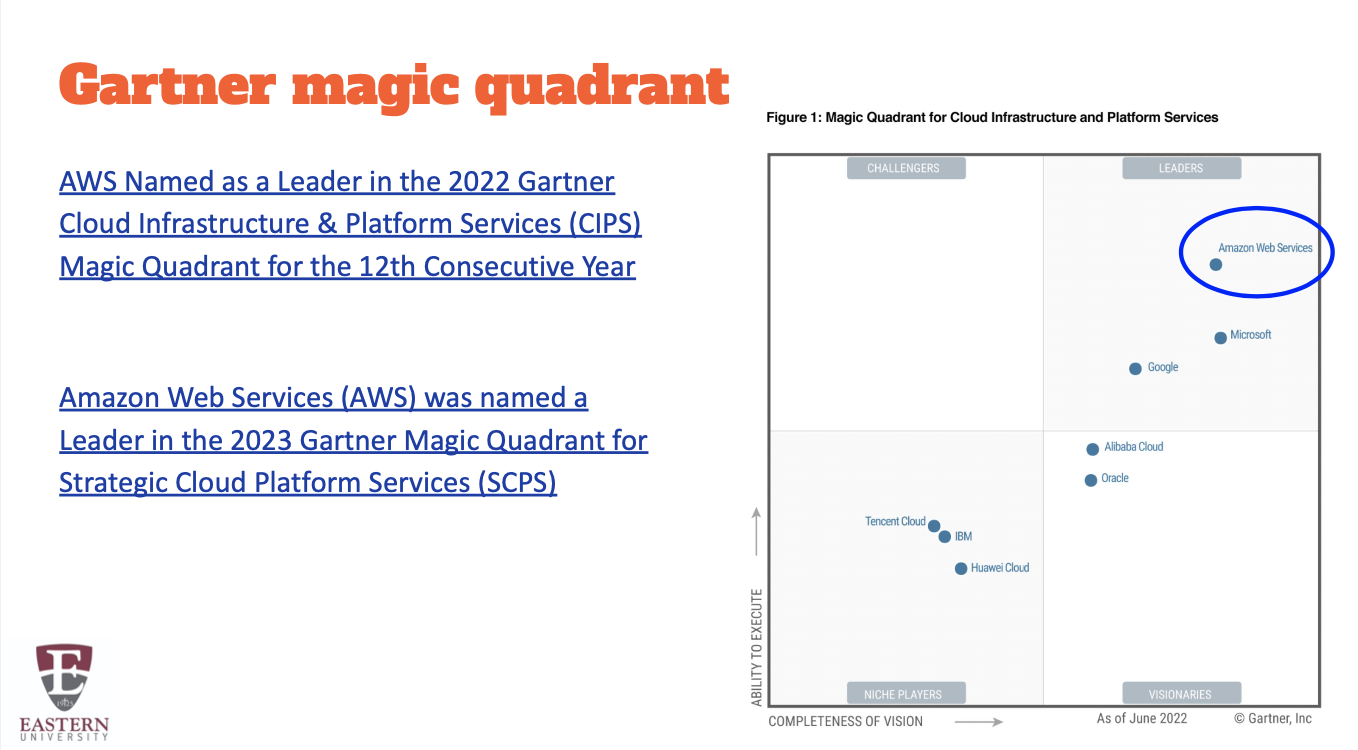
Cloud Providers
Top cloud providers
-IBM, AWS, MICROSOFT, GOOGLE. ORACLE
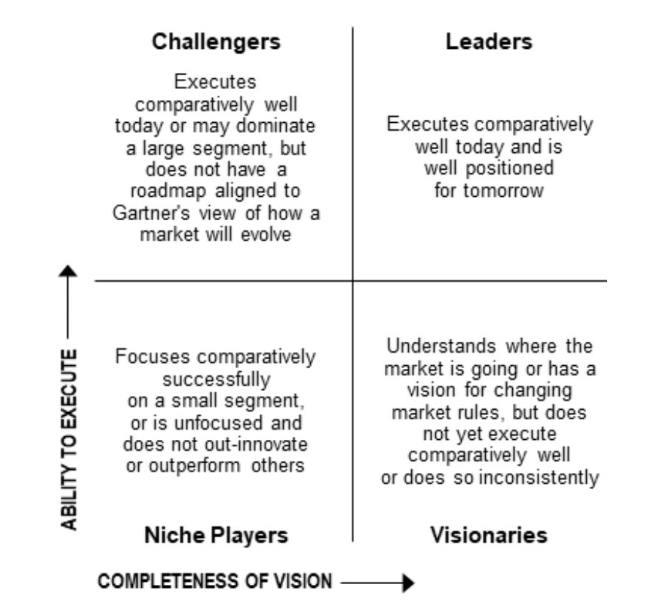
Cloud profile
Customer Orientation-Large or Small Organizations
Vision-Visionary or Fast Follower
Product Packaging - Integrated or Modular
End User Target-Business or IT
Cloud Focus-SaaS or IaaS
AWS is not the answer for every organization
Advantages of cloud computing
Advantage #1
Trade capital expense for variable expense - examples: Airbnb and hyundai
CAPEX: funds to acquire, provision, upgrade, maintain property & equipment
Pay for everything...whether you use it or not VAREX: expense that can be easily altered or avoided
Pay for only the resources you need and when (and how much) you use them
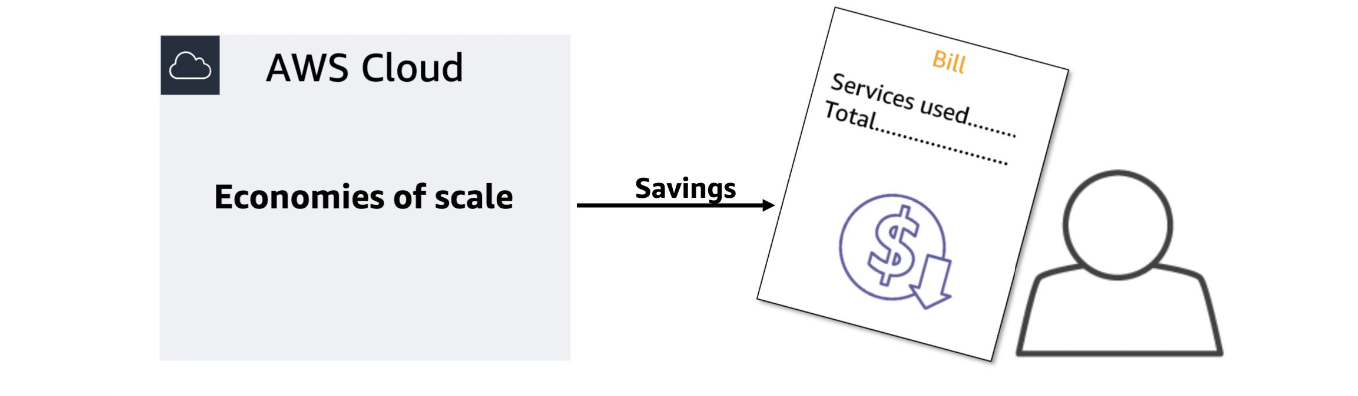
Advantage #2
Benefit from massive economies of scale
Advantage #3
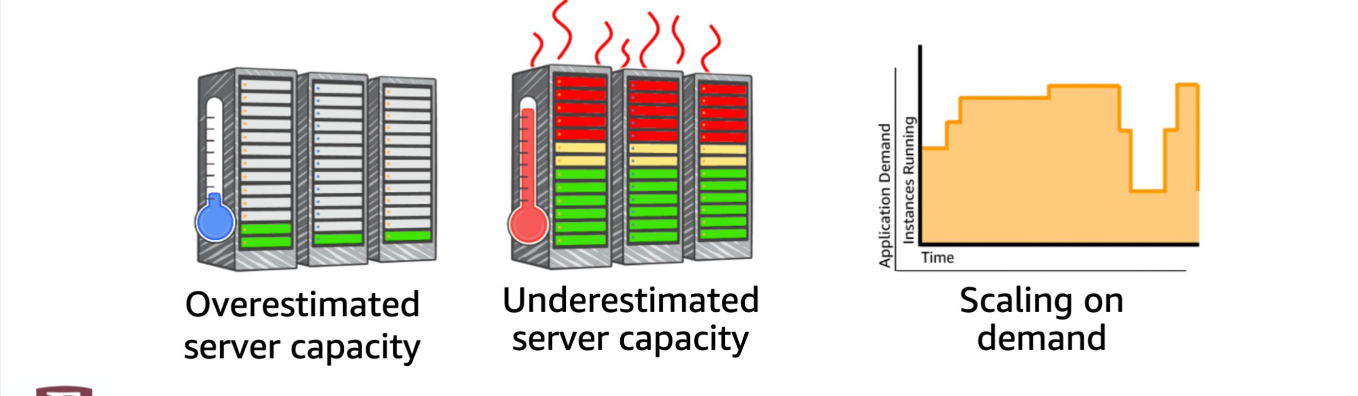
Stop guessing capacity
Advantage #4
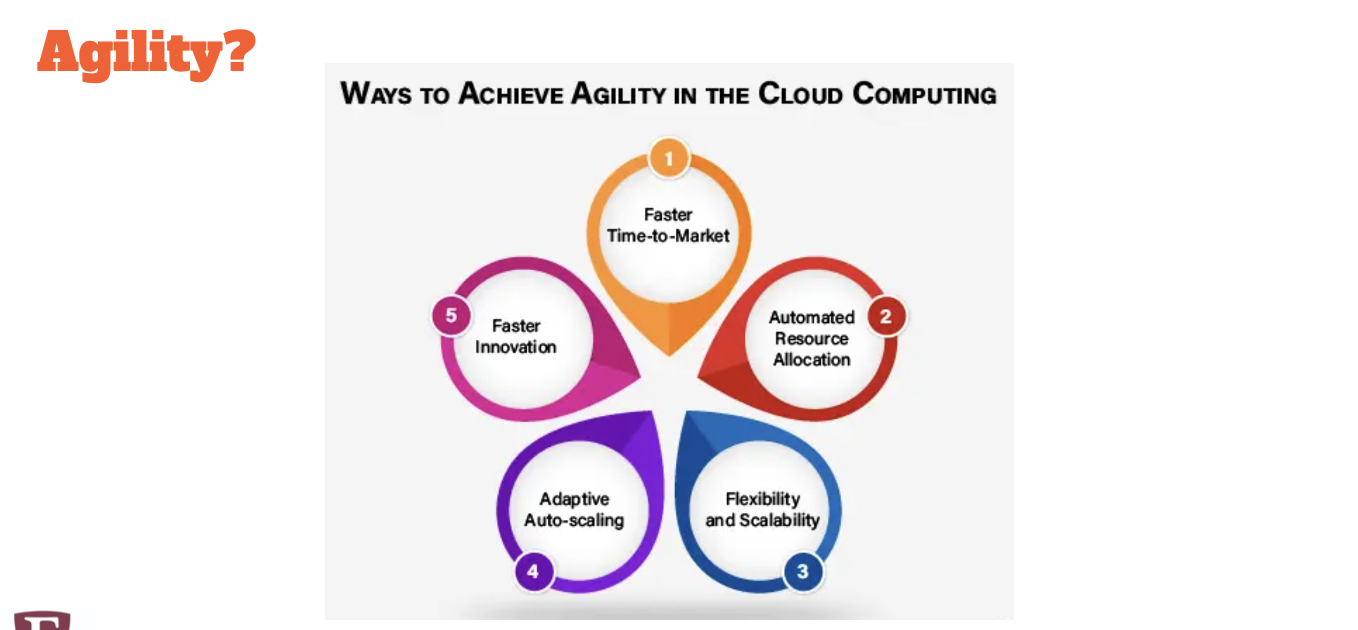
Increase speed and agility
From weeks (or months) to minutes——aka dont have to wait for tech support to get back to you
Advantage #5
Stop spending money on running and maintaining data centers
Advantage #6
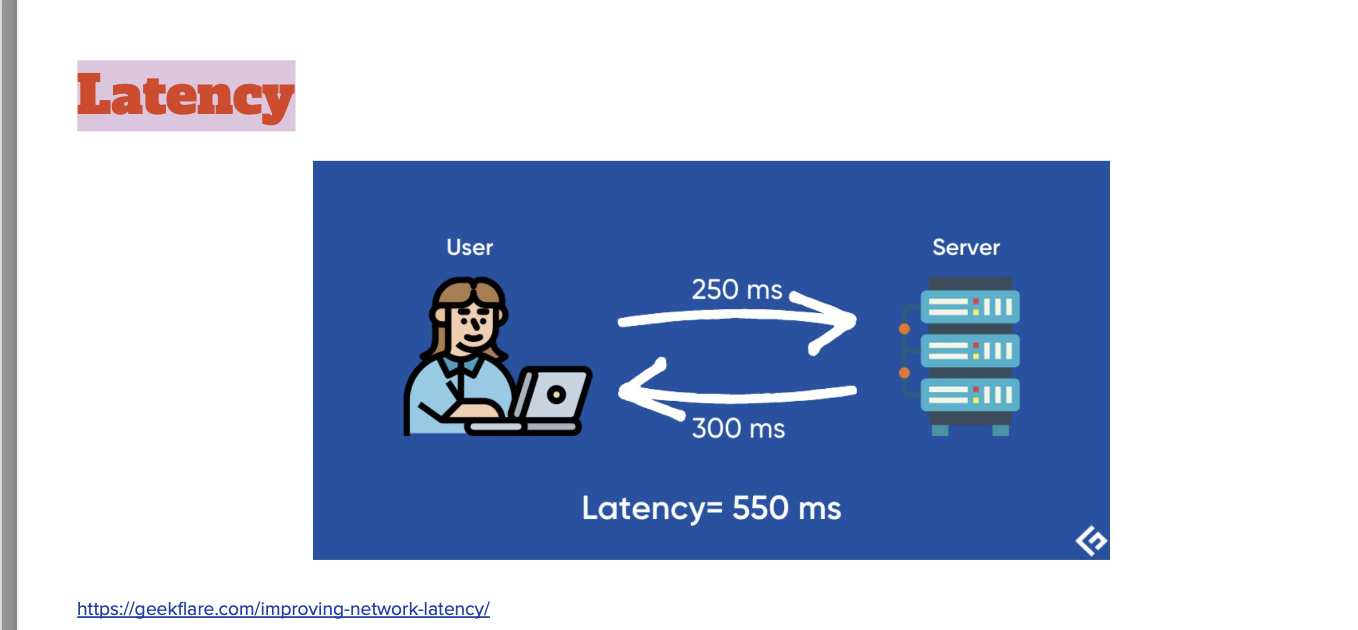
Go global in minutes
Deploy application in multiple regions Lower latency
Better customer experience
Latency
Right sizing
“Provisioning instances to match workload and control cloud costs”
Right sizing: continually analyzing instance performance and usage needs and patterns—and then turning off idle instances and right sizing instances that are either overprovisioned or poorly matched to the workload.
Because your resource needs are always changing, right sizing must become an ongoing process to continually achieve cost optimization.
Right Sizing
Introduction to Amazon Web Services (AWS)
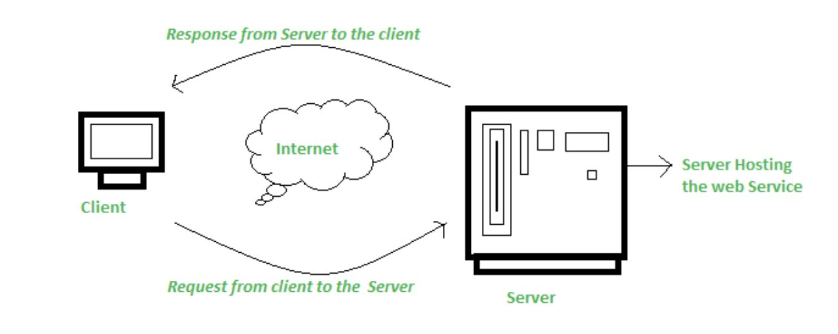
What are web services?
A web service is any piece of software that makes itself available over the internet and uses a standardized format – such as Extensible Markup Language (XML) or JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) – for the request and the response of an application programming interface (API) interaction.
What is AWS?
Not the online retailer!
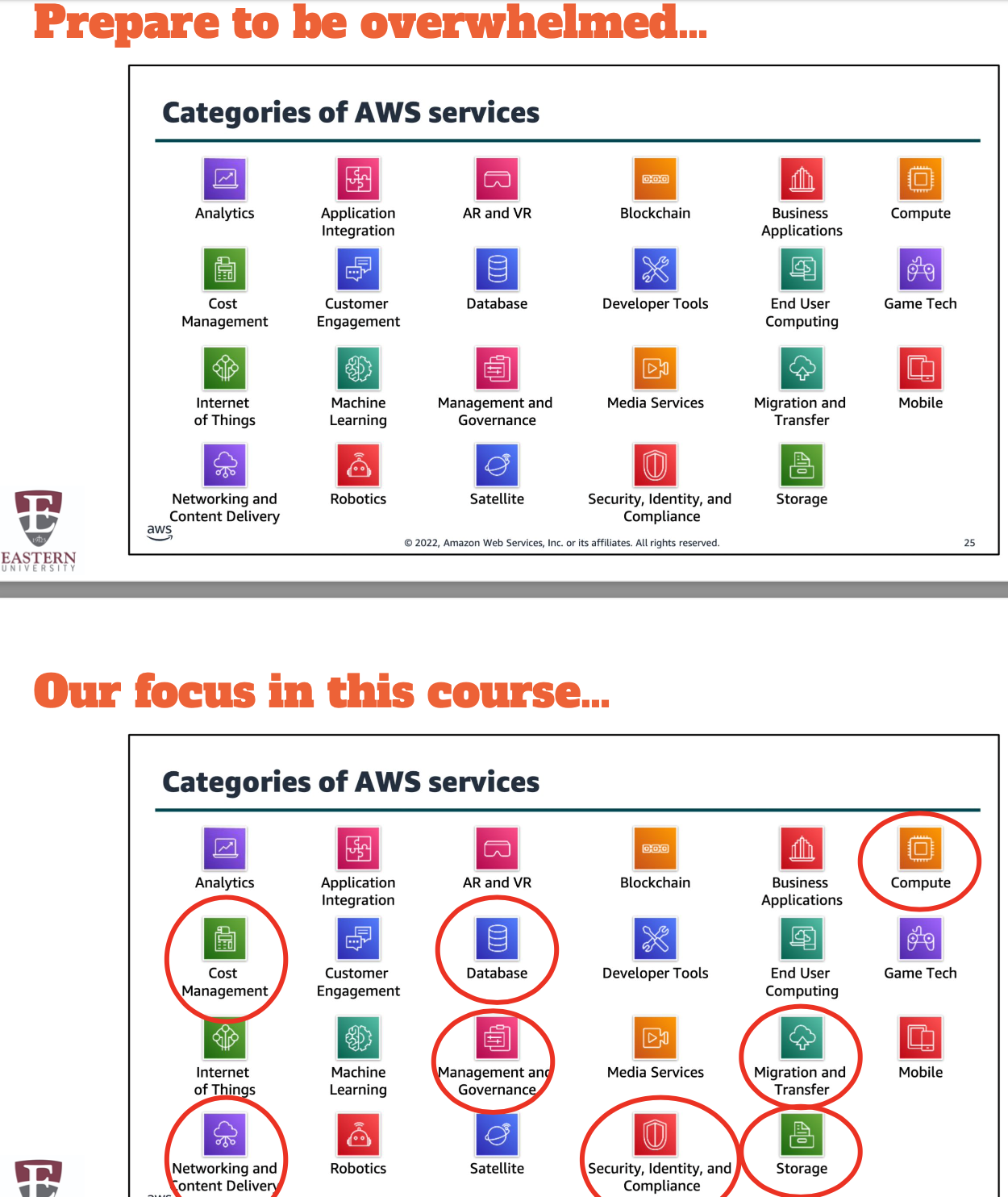
Secure cloud platform with broad set of global cloud-based products
● Provides on-demand access to compute, storage, network, database resources
● Offers flexibility: reconfig, update, scaled, shut down
● You pay only for the individual services you need
● Services: building blocks
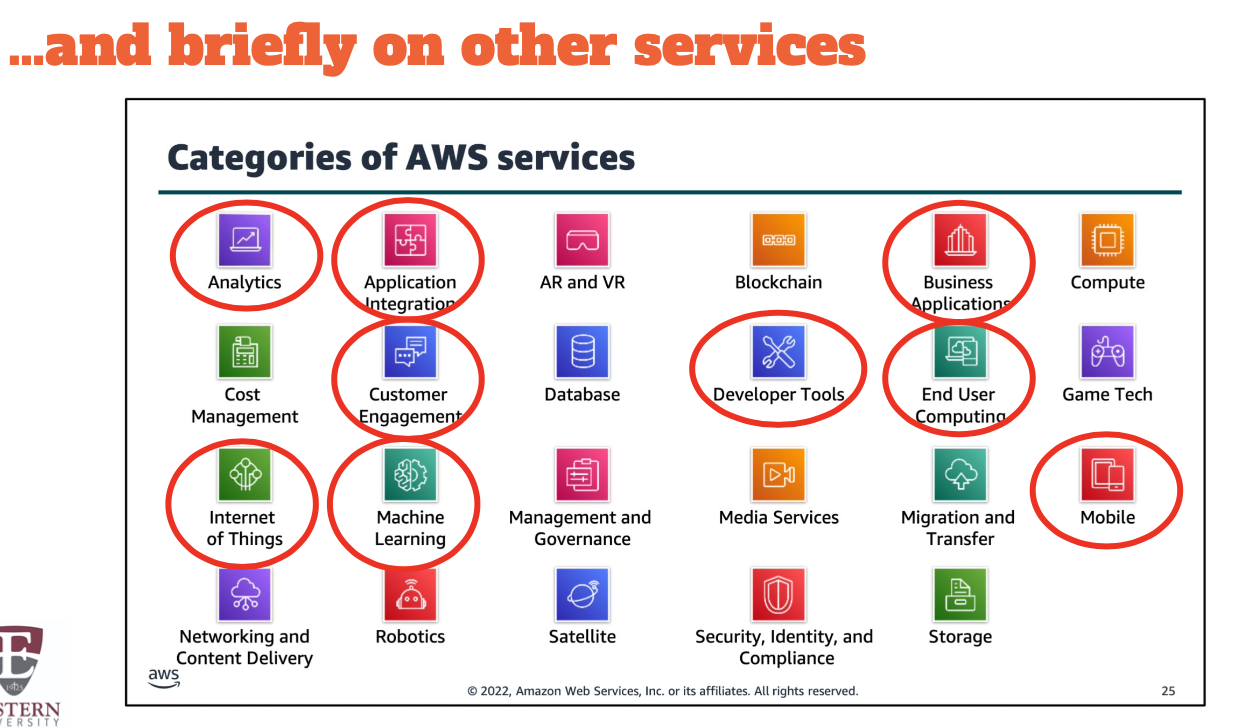
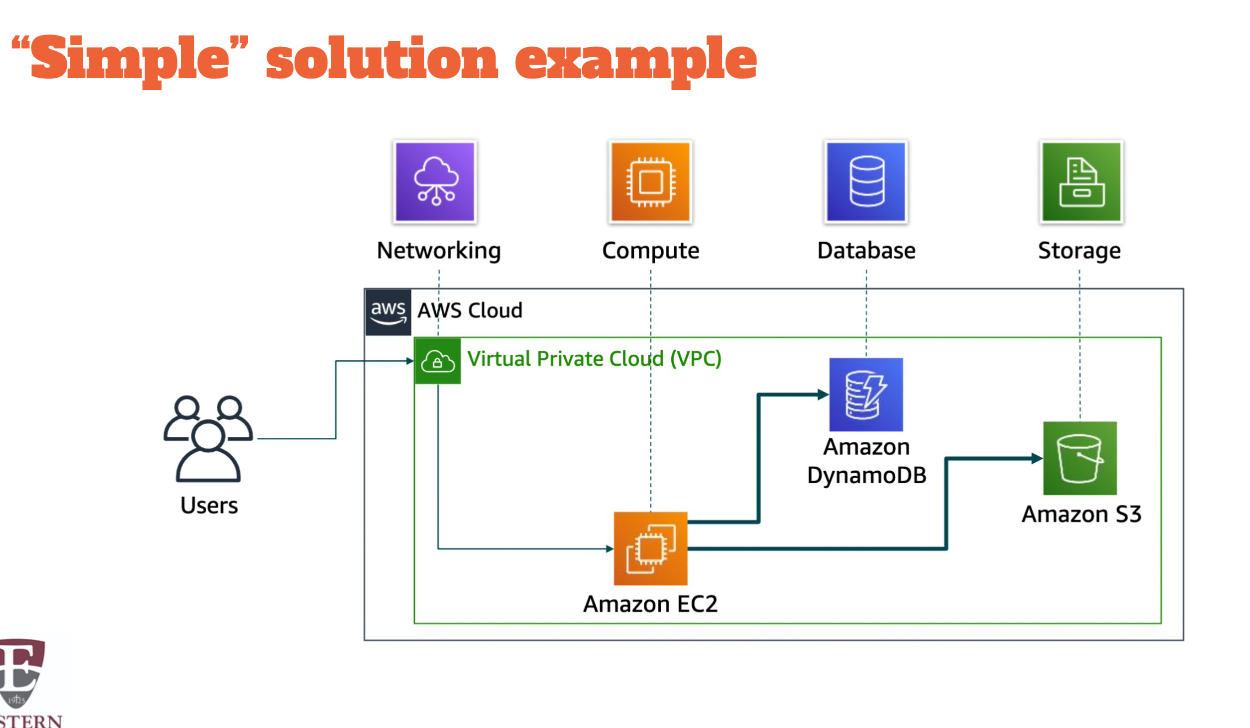
Choosing a service
The service you select depends on your business goals and technology requirements.
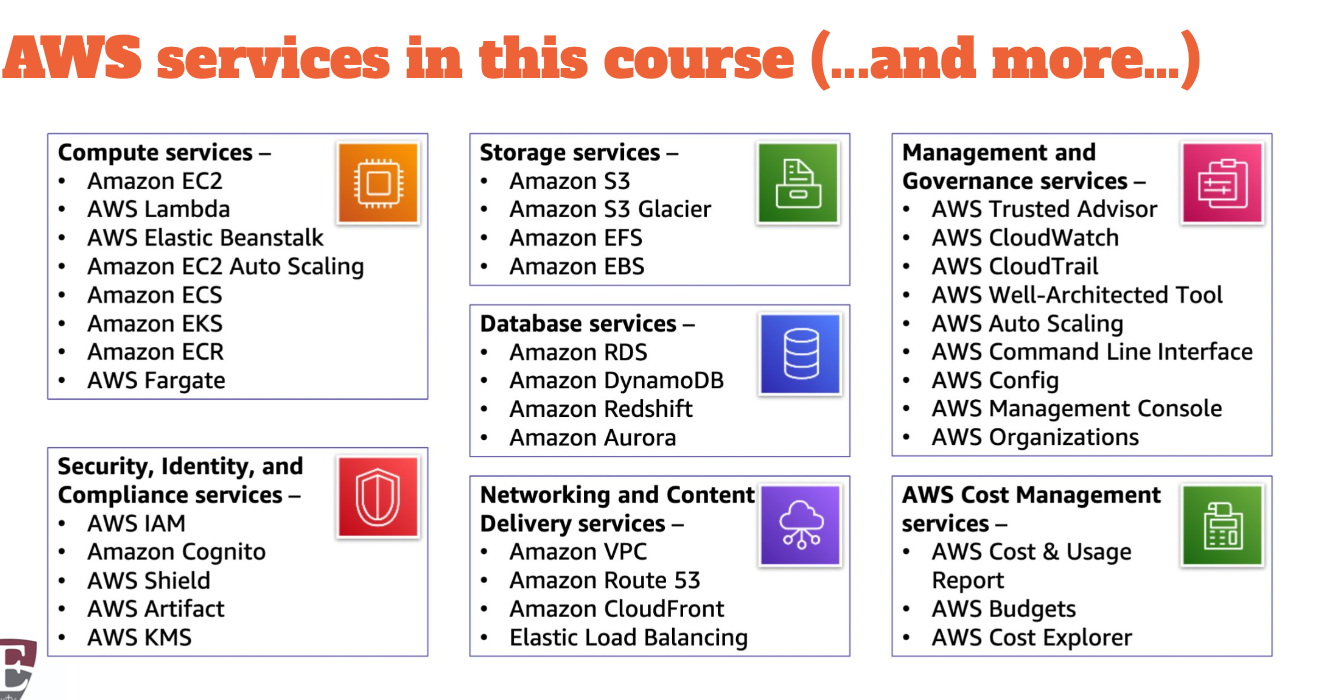
AWS Management console:
Three ways to interact with AWS
AWS Management Console
Command Line Interface (AWS CLI)
Software Development Kits (SDKs)
Accessing AWS services - Overview of Amazon Web Services
Tools to develop and manage applications:
AWS pricing model
1) Compute
a) Charged per hour or per second (Linux)
2) Storage
a) Charged typically per GB
3) Data transfer
a) Outbound is aggregated and charged
b) Inbound has no charge (with some expectations)
c) Charged typically per GB
How do you pay for AWS?
● Pay for what you use
● Pay less when you reserve
● Pay less when you use more
● Pay less as AWS grows
2 Pay less when you reserve
On Demand Reserved (up to 75%)
● No URI
● Partial URI
● All URI
...upfront reserved instances An instance is a server
Services to reserve
● Amazon EC2
● Amazon RDS
● Amazon ElastiCache
● OpenSearch Service
● Amazon Redshift
● Amazon DynamoDB
Not all services can be reserved (like S3)
3 Pay less by using more
Data transfer in is always free Tiered pricing by volume
● S3-Simple Storage Service
● EBS-Elastic Block Store
● EFS-Elastic File System
4 Pay less as AWS grows
● Economies of scale
● Since 2006, AWS has lowered pricing 75 times (as of Sept 2019)
● Future higher-performing resources replace current resources for no extra
charge
Customize
Custom pricing is available for high-volume projects with unique requirements
Which of the following services is not always free?
answer is Amazon EC2
Always free services
Amazon VPC
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Elastic Beanstalk**
Auto Scaling**
AWS CloudFormation**
- 10 custom monitoring metrics and 10 alarms on Amazon CloudWatch
- 62,000 outbound email messages with Amazon Simple Email Service (SES)
- One million requests and 3.2 million seconds of compute with AWS Lambda
AWS Organizations
Consolidated Billing
One bill for multiple accounts
Easily track the charges on each account
Decrease charges as results of volume pricing discounts from combined usage Consolidate all accounts and get tiered benefits
Show me the money!
Investigate pricing for each service you consider
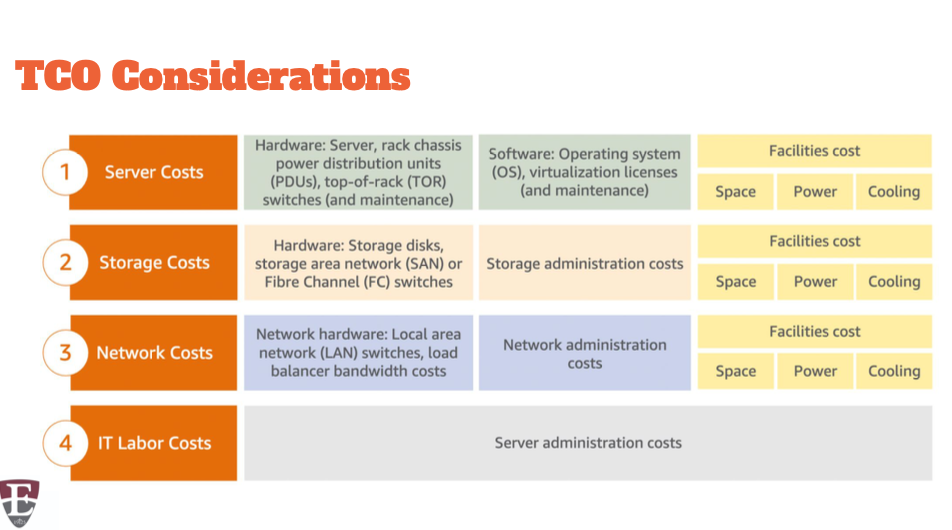
Total cost of ownership
TCO
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is a financial estimate to help identify direct and indirect costs of a system.
Entire infrastructure or specific workload Direct costs
Indirect costs
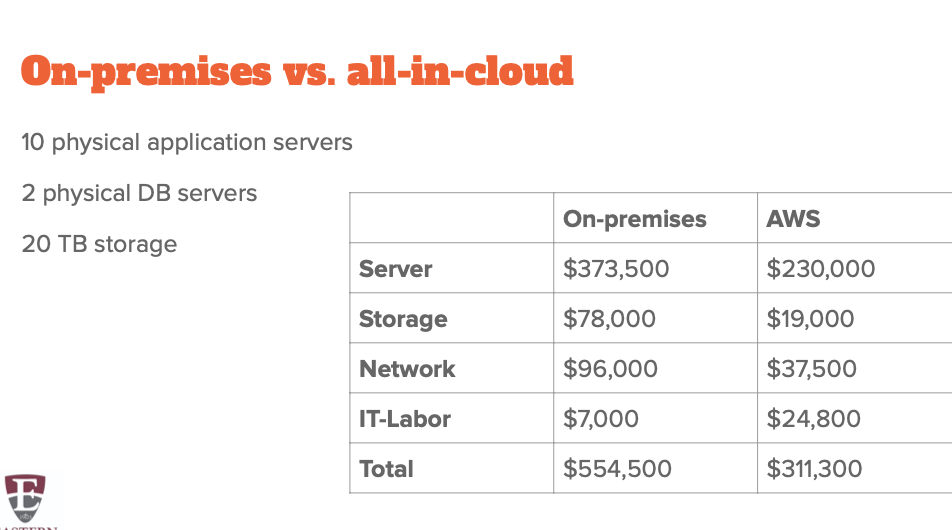
Additional considerations
Hard benefits
● Reduced spending on compute, storage, networking, security
● Reductions in hardware and software purchases (capex)
● Reductions in operation costs, disaster recovery
● Reduction in operations personnel
Additional considerations
Soft benefits
● Increased developer productivity
● Improved customer satisfaction
● Increase global reach
● Agile business processes that can quickly respond to new and emerging
opportunities
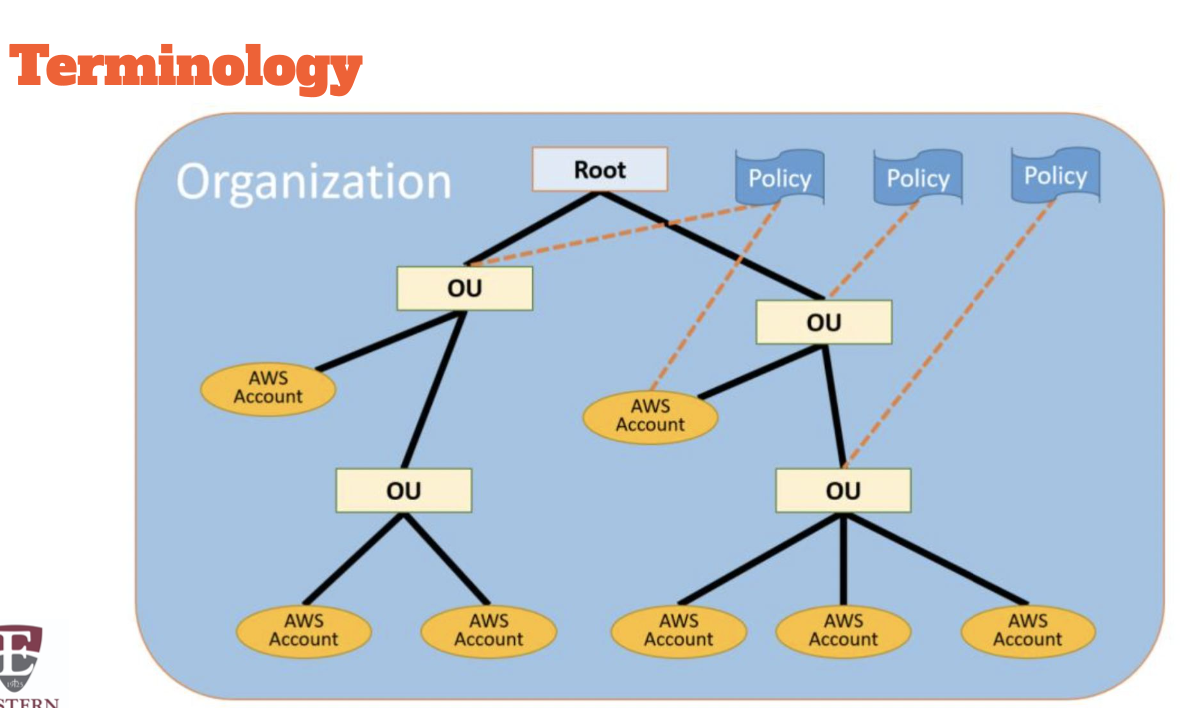
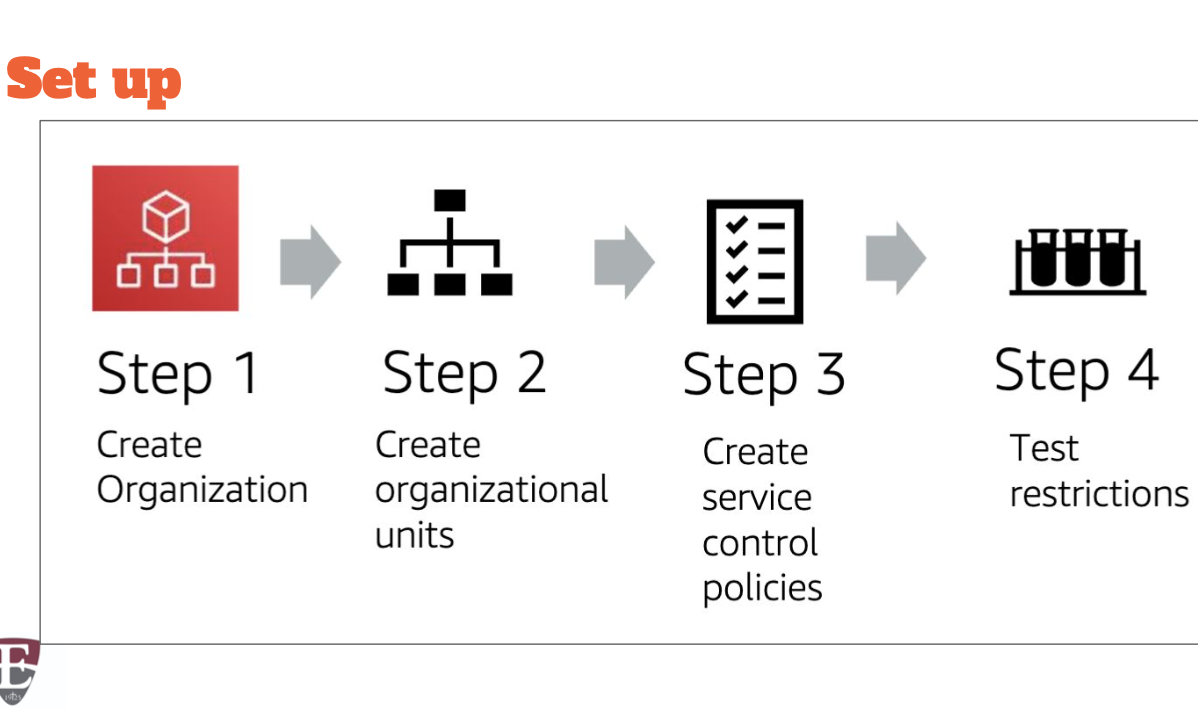
AWS Organizations
AWS Organizations
AWS Organizations is a free account management service that enables you to consolidate multiple AWS accounts into an organization that you create and centrally manage.
Features
What is AWS Organizations? - AWS Organizations
- Free, global service
- Consolidated billing (& discounts)
- Centralized management
- Hierarchical grouping to meet budgetary, security, or compliance needs
- Service Control Policies (SCP)
- IAM provides granular control over users and roles in individual accounts. AWS
Org expands that control to the account level
Not IAM vs. SCP
Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows or denies access to service, individual resources or API actions (applies to users, groups, roles, not root user)
SCPs allow or deny access to services for accounts or groups in an OU (affects all, even root user)
Service Control Policies
SCPs
● Specify the maximum permissions for member accounts in the organization.
● Restrict which AWS services, resources, and individual API actions the users
and roles in each member account can access.
● Define conditions for when to restrict access to AWS services, resources, and
API actions.
● These restrictions even override the administrators of member accounts in the
organization.

Quotas
Names have maximum 250 characters (Unicode) Maximum 1000 OUs
Maximum 1000 policies
Lots of other quota limits: Quotas for AWS Organizations
Accessing
AWS Management Console
Command Line Interface (CLI)
Software Development Kits (SDKs)
HTTPS Query APIs
AWS Billing & Cost Management - global service
Service to pay your AWS bill, monitor your usage, and budget your costs. Enables you to forecast your costs and usage
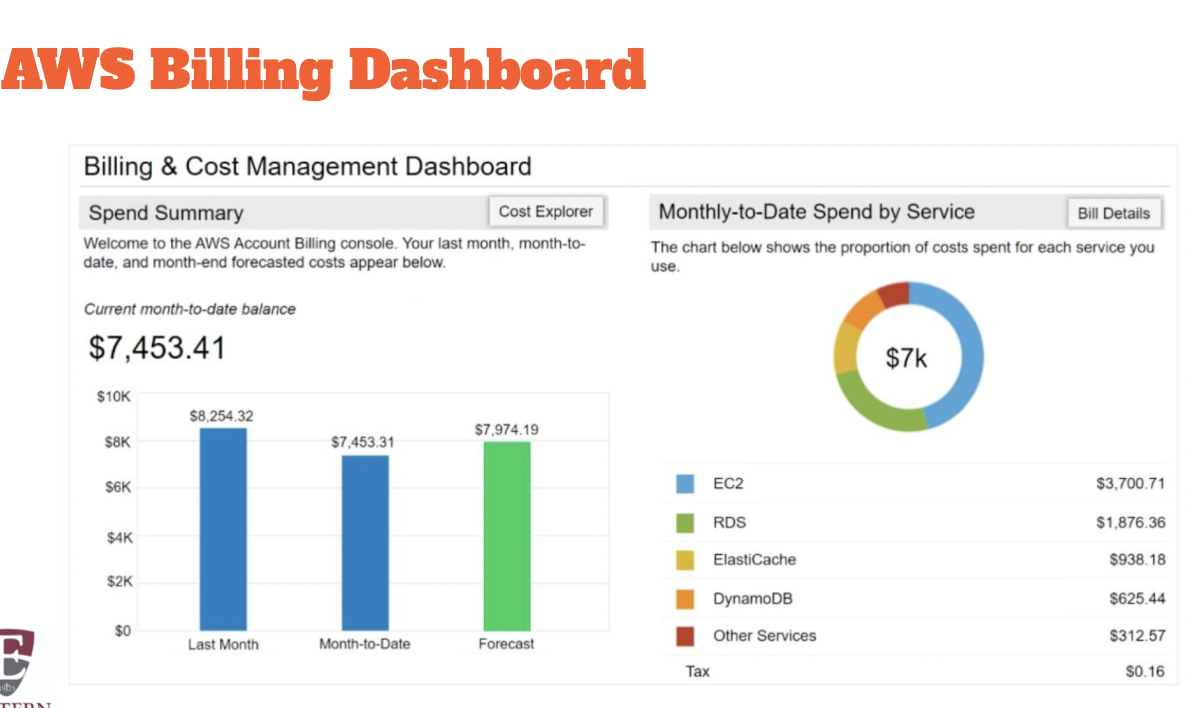

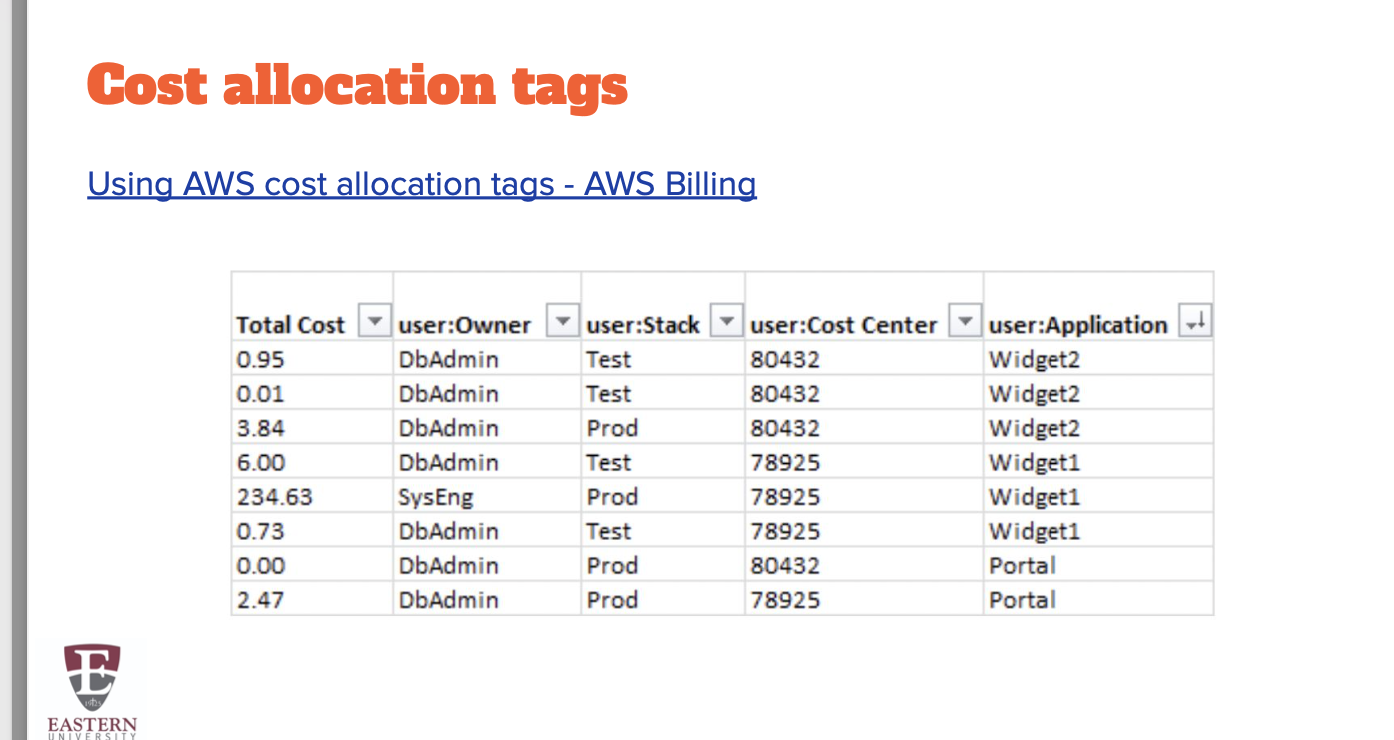
-get a csv with each cost monthly and breakdown and what application
-cost anomaly detection alerts random costs and it allows you to see hacks or other security features, and if anyone leaves things running.
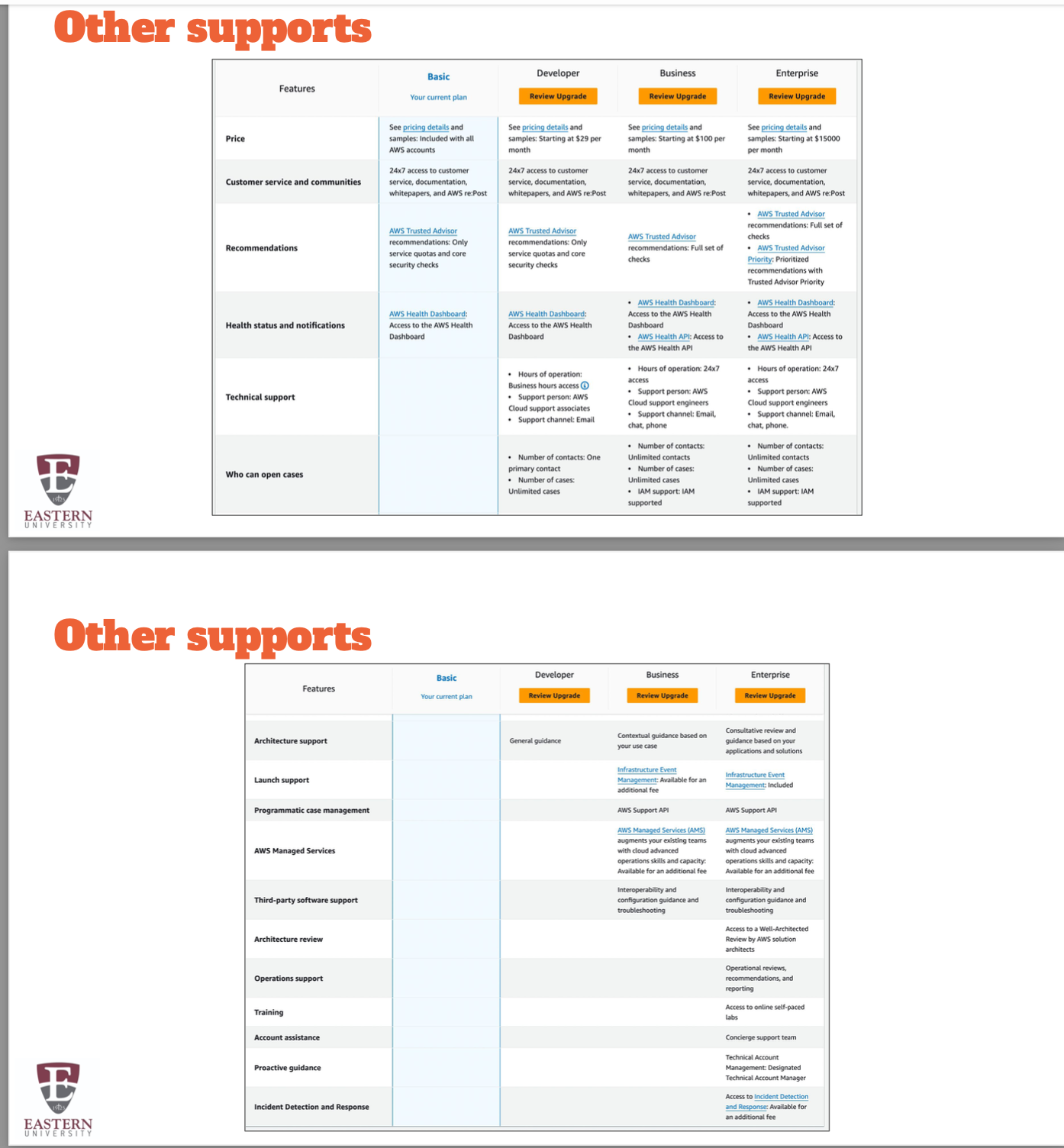
AWS Technical Support Plans
4 Support Plans
1. Basic- free
2. Developer - minimum $29
3. Business -minimum $100
4. Enterprise- minimum $15,000
Enterprise On-ramp (min. $5,500)
● Definitely choose “Basic” for your own personal use!

General Overview
Basic
Developer: Support for early development on AWS
Business: Customers that run production workloads
Enterprise: Customers that run business and mission-critical workloads


$15,000?
15-minute response
Technical Account Manager (TAM) - guide and advocate for your account, involved in planning, launch, proactive review of your architecture and account
Support Concierge – team to analyze account & billing analysis to help cut costs
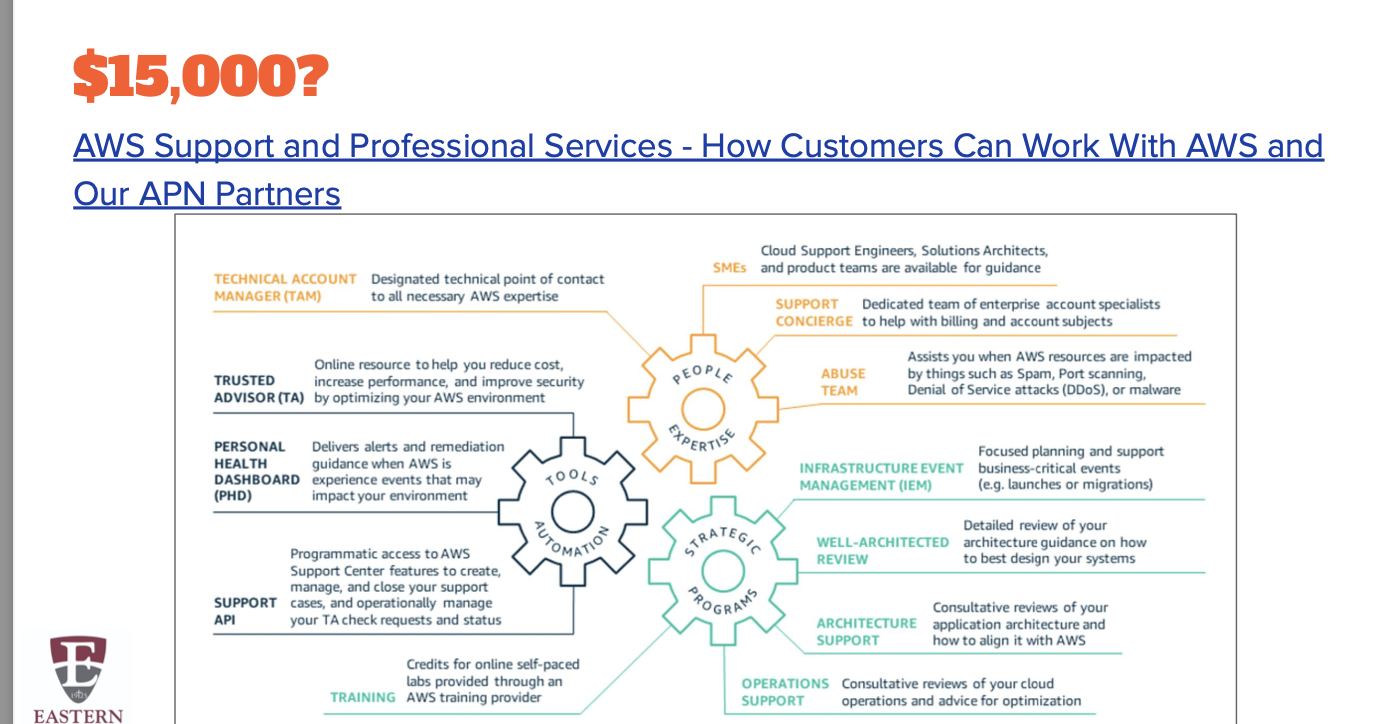
Other supports
Personal Health Dashboard (PHD)
Trusted Advisor Checks: 7 for Basic/Developer; All for Business/Enterprise AWS Partner Network (APN)
AWS Support Center
Self-Help
- Documentation
- AWS Knowledge Center (FAQ)
- Discussion forums
AWS Trusted Advisor
Trusted Advisor
Online tool that provides real-time guidance to help you provision your resources following AWS best practices by looking at your entire AWS environment and giving you real-time recommendations in six categories
Trusted Advisor
Trusted Advisor Checks:
● 7 for Basic/Developer
○ S3 Bucket Permissions
○ Security Groups – Specific Ports Unrestricted
○ IAM Use
○ MFA on Root Account
○ EBS Public Snapshots
○ RDS Public Snapshots
○ Service Limits
● All for Business/Enterprise
Trusted Advisor
False positives are possible
e.g., S3 bucket with public permissions



Multiple Choice
Why is AWS more economical than traditional data centers for applications with varying compute workloads?
A) Amazon EC2 costs are billed on a monthly basis
B) Customers retain full administrative access to their Amazon EC2 instances
C) Amazon EC2 instances can be launched on-demand when needed.
D) Customers can permanently run enough instance to handle peak workloads.
What is AWS Trusted Advisor?
answer: An AWS service that offers best practices and recommendations for optimizing AWS environments.
Moving to the Cloud (AWS CAF)
From traditional to cloud
Not automatic
Fundamental technological change: obtain, use, manage, purchase All stakeholders must be supportive
CAF
WS Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF)
AWS CAF provides guidance and best practices to help organizations build a comprehensive approach to cloud computing across the organization and through the IT lifecycle to accelerate successful cloud adoption.

people perspective capability:
we are going to focus on cloud fluency which is building the digital acumen to confidently and efficiently leverage the cloud to accelerate business outcomes.

Multiple Select
A company is investigating whether it should move to AWS with the Cloud Adoption Framework. Which of the following are components of the people perspective? (Select two.)
❏ Risk management
❏ Product management
❏ Culture evolution- this one
❏ Cloud fluency- this one
❏ Threat detection
What does AWS CAF (Cloud Adoption Framework) refer to in the context of cloud computing?
answer: A set of best practices and guidelines for planning and executing cloud adoption strategies.


Moving massive amounts of data
A 40 TB database migration with 1 Gbps (!) connection takes more than 4 days
It’s quicker to physically ship a large amount of data than it is to transfer it over a network



What is the primary purpose of AWS Migration Hub?
answer: To manage and orchestrate the migration of on-premises applications to the AWS cloud.
 Knowt
Knowt