
Unit 7: Economic Development and Industry Processes and Patterns
The Industrial Revolution:
1760-1840
Manual labor and craft production → machine-based
New technology: engine, power loom, railroads, metal and steel-making
Natural resources: coal & steam power as energy
Hearth: Britain
First diffused to: Rest of Europe, Japan
Better transportation: led to the diffusion and expansion of industrial activities
Effects of the Industrial Revolution:
Growing population: shift to stage 2 of the DTM/ lowered CDR
Increased food supply: 2nd Agricultural revolution
Rural to Urban migration: industrial jobs in cities
creation of the middle class
Investors needed more raw materials and new markets → rise of colonialism and imperialism in Africa and Asia.
Led to uneven geographic development today based on when different regions industrialized
Economic Sectors:
Primary: Extraction and production of raw materials
Farming, Coal mining
Secondary: Processing of raw materials into finished goods
manufacturing, factories
Tertiary: Service jobs
retail, server
Quaternary: Jobs requiring higher levels of knowledge and expertise
Doctor, IT, Nurse, Lawyer
Quinary: Decision-making and policy making jobs
CEO, President, Lawmaker
Weber’s Least Cost Theory:
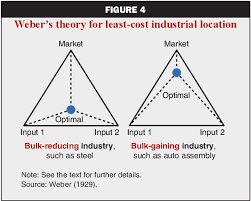
Shape: Location Triangle
Goal: Select location of industry based on lowest transportation & labor costs
Bulk Reducing Industry:
Locate manufacturing closer to the inputs: raw materials
copper mining, ethanol
Bulk Gaining Industry:
Locate manufacturing closer to market
Car production, bottling plants
Measures of Development:
Gross Domestic Product: The value of all goods & services made in a country’s borders regardless of who made it.
Gross National Product: The value of all goods & services made by a country’s citizens, regardless of where it was made
Gross National Income: The total income of a country’s residents & businesses, including investments and/or foreign investments
Per capita: divided by total population
Formal economy: work and income recorded by government
Informal: work and income not monitored or taxed (paid in cash)
Income distribution: assesses economic inequalities in a state
Use of fossil fuels and renewable energy:
Measures of Health and Social Development:
Access to healthcare
availability and affordability
Fertility Rates
Infant Mortality Rates
Literacy Rates
Women and Economic Development:
Role as countries develop economically:
less primary sector and informal sector jobs
Better family planning: lower TFR
Increase in education & higher income
Pay Parity:
No state has gender parity (equal pay)
the gap is shrinking
“Glass ceiling”: women less likely to be promoted to management jobs
Microloans: small loans to help a person start/expand a small business
Often given to women in LDCs by NGOs (non-government org.)
Used to invest in education, improve living conditions
Has risks
May not be able to pay off if not used well
Gender Inequality Index:
shows gender-based disadvantages
0-1 scale
lower score=less inequalities
Based on:
Reproductive health: MMR, adolescent birth
Empowerment: education, women in government
Labor market: jobs in formal economy
US: has a higher GII score due to high cost of healthcare and less women in legislature
Human Development Index:
Shows human development in a state
Scored on scale 0-1
higher score = more developed
Based on:
Health
Education
Income
Neoliberal policies:
favor free market economics & privatization rather than government ownership & control
Lower government barriers encourage trade
Free Trade Agreement: a treaty between two or more countries to reduce tariffs and promote foreign investment
EU: formed a single market & powerful economic bloc with the Euro
USMCA: More trade and economic prosperity
MERCOSUR: South American trade bloc; no tariffs to increase trade
World Trade Organization:
sets rules & standards for international trade
OPEC: Coordinates and unifies petroleum policies among countries
Globalization & Trade:
International Monetary Fund:
provides loans to member countries to help stabilize their economies
Complementary Advantage: How well a country’s export profile matches another’s import profile
Comparative Advantage: a state’s ability to produce a product much more efficiently than others
Economies of Scale
Outsourcing: when a company moves parts of its operations outside of the state where company is located
can lead to loss of jobs for core countries
Maquiladoras in Northern Mexico
Deindustrialization: shift in MDC urban areas from manufacturing to service sector
Manufacturing zones:
International division of labor: developing countries have lower-paying jobs
Special Economic Zones: areas within a country where the business & trade laws are different from the rest of the state
Free Trade Zone: Duty free areas for warehousing and redistribution of trade goods
Export Processing Zone: type of FTZ within developing countries that offer incentives to locate manufacturing there
Modern Economics:
Post Fordist Methods:
flexible, spatially dispersed production of goods
Multiplier Effects: creation of jobs in other industries due to investment in another
Agglomeration: clustering of related economic activities in a particular area or region
Growth pole: geographic areas organized around one major industry
Silicon Valley
Just in time delivery: production of small batches of goods based on customer demand
High tech industries: industries that use advanced technology and the highest level of R&D
Sustainable Development:
Resource depletion: using natural resources faster than they can be replenished
Solutions:
Pollution Control Laws:
US: Clean Air & Clean Water Act
Renewable Energy Production:
wind, solar, geothermal, hydropower
Carbon neutrality or carbon offsets
reforestation projects
Ecotourism: travel to natural areas to support conservation efforts & socially just economic development
Costa Rica, Africa
Pros:
creates local jobs and revenue
preserves natural landscape
educates tourists
Cons:
locals can be exploited for cheaper labor
companies can pay low wages
UN Sustainable Development Goals:
No poverty, zero hunger, good health and well being, quality education, gender equality, clean water, clean energy
10% of people in extreme poverty
poverty levels have decreased in recent decades
Food is unequally distributed
71 years is average life-expectancy
20% of adults cannot read or write
Almost 0 states have had more women in legislature than men
33% of people don’t have access to clean toilets
24% of greenhouse gases are from agriculture
Unit 7: Economic Development and Industry Processes and Patterns
The Industrial Revolution:
1760-1840
Manual labor and craft production → machine-based
New technology: engine, power loom, railroads, metal and steel-making
Natural resources: coal & steam power as energy
Hearth: Britain
First diffused to: Rest of Europe, Japan
Better transportation: led to the diffusion and expansion of industrial activities
Effects of the Industrial Revolution:
Growing population: shift to stage 2 of the DTM/ lowered CDR
Increased food supply: 2nd Agricultural revolution
Rural to Urban migration: industrial jobs in cities
creation of the middle class
Investors needed more raw materials and new markets → rise of colonialism and imperialism in Africa and Asia.
Led to uneven geographic development today based on when different regions industrialized
Economic Sectors:
Primary: Extraction and production of raw materials
Farming, Coal mining
Secondary: Processing of raw materials into finished goods
manufacturing, factories
Tertiary: Service jobs
retail, server
Quaternary: Jobs requiring higher levels of knowledge and expertise
Doctor, IT, Nurse, Lawyer
Quinary: Decision-making and policy making jobs
CEO, President, Lawmaker
Weber’s Least Cost Theory:

Shape: Location Triangle
Goal: Select location of industry based on lowest transportation & labor costs
Bulk Reducing Industry:
Locate manufacturing closer to the inputs: raw materials
copper mining, ethanol
Bulk Gaining Industry:
Locate manufacturing closer to market
Car production, bottling plants
Measures of Development:
Gross Domestic Product: The value of all goods & services made in a country’s borders regardless of who made it.
Gross National Product: The value of all goods & services made by a country’s citizens, regardless of where it was made
Gross National Income: The total income of a country’s residents & businesses, including investments and/or foreign investments
Per capita: divided by total population
Formal economy: work and income recorded by government
Informal: work and income not monitored or taxed (paid in cash)
Income distribution: assesses economic inequalities in a state
Use of fossil fuels and renewable energy:
Measures of Health and Social Development:
Access to healthcare
availability and affordability
Fertility Rates
Infant Mortality Rates
Literacy Rates
Women and Economic Development:
Role as countries develop economically:
less primary sector and informal sector jobs
Better family planning: lower TFR
Increase in education & higher income
Pay Parity:
No state has gender parity (equal pay)
the gap is shrinking
“Glass ceiling”: women less likely to be promoted to management jobs
Microloans: small loans to help a person start/expand a small business
Often given to women in LDCs by NGOs (non-government org.)
Used to invest in education, improve living conditions
Has risks
May not be able to pay off if not used well
Gender Inequality Index:
shows gender-based disadvantages
0-1 scale
lower score=less inequalities
Based on:
Reproductive health: MMR, adolescent birth
Empowerment: education, women in government
Labor market: jobs in formal economy
US: has a higher GII score due to high cost of healthcare and less women in legislature
Human Development Index:
Shows human development in a state
Scored on scale 0-1
higher score = more developed
Based on:
Health
Education
Income
Neoliberal policies:
favor free market economics & privatization rather than government ownership & control
Lower government barriers encourage trade
Free Trade Agreement: a treaty between two or more countries to reduce tariffs and promote foreign investment
EU: formed a single market & powerful economic bloc with the Euro
USMCA: More trade and economic prosperity
MERCOSUR: South American trade bloc; no tariffs to increase trade
World Trade Organization:
sets rules & standards for international trade
OPEC: Coordinates and unifies petroleum policies among countries
Globalization & Trade:
International Monetary Fund:
provides loans to member countries to help stabilize their economies
Complementary Advantage: How well a country’s export profile matches another’s import profile
Comparative Advantage: a state’s ability to produce a product much more efficiently than others
Economies of Scale
Outsourcing: when a company moves parts of its operations outside of the state where company is located
can lead to loss of jobs for core countries
Maquiladoras in Northern Mexico
Deindustrialization: shift in MDC urban areas from manufacturing to service sector
Manufacturing zones:
International division of labor: developing countries have lower-paying jobs
Special Economic Zones: areas within a country where the business & trade laws are different from the rest of the state
Free Trade Zone: Duty free areas for warehousing and redistribution of trade goods
Export Processing Zone: type of FTZ within developing countries that offer incentives to locate manufacturing there
Modern Economics:
Post Fordist Methods:
flexible, spatially dispersed production of goods
Multiplier Effects: creation of jobs in other industries due to investment in another
Agglomeration: clustering of related economic activities in a particular area or region
Growth pole: geographic areas organized around one major industry
Silicon Valley
Just in time delivery: production of small batches of goods based on customer demand
High tech industries: industries that use advanced technology and the highest level of R&D
Sustainable Development:
Resource depletion: using natural resources faster than they can be replenished
Solutions:
Pollution Control Laws:
US: Clean Air & Clean Water Act
Renewable Energy Production:
wind, solar, geothermal, hydropower
Carbon neutrality or carbon offsets
reforestation projects
Ecotourism: travel to natural areas to support conservation efforts & socially just economic development
Costa Rica, Africa
Pros:
creates local jobs and revenue
preserves natural landscape
educates tourists
Cons:
locals can be exploited for cheaper labor
companies can pay low wages
UN Sustainable Development Goals:
No poverty, zero hunger, good health and well being, quality education, gender equality, clean water, clean energy
10% of people in extreme poverty
poverty levels have decreased in recent decades
Food is unequally distributed
71 years is average life-expectancy
20% of adults cannot read or write
Almost 0 states have had more women in legislature than men
33% of people don’t have access to clean toilets
24% of greenhouse gases are from agriculture
 Knowt
Knowt