Bio Chapter 8 - Photosynthesis
Lesson 8.1 - Energy & Life
==Energy==
- Energy @@comes from food@@
- All living things need energy to live
- %%Food%% gets its energy %%from the sun%%
- Some ^^organisms^^ use ^^light to create energy^^
- Organims that ==make their own food== are called ==autotrophs==
- Organims that @@consume their energy@@ are called @@heterothrophs@@
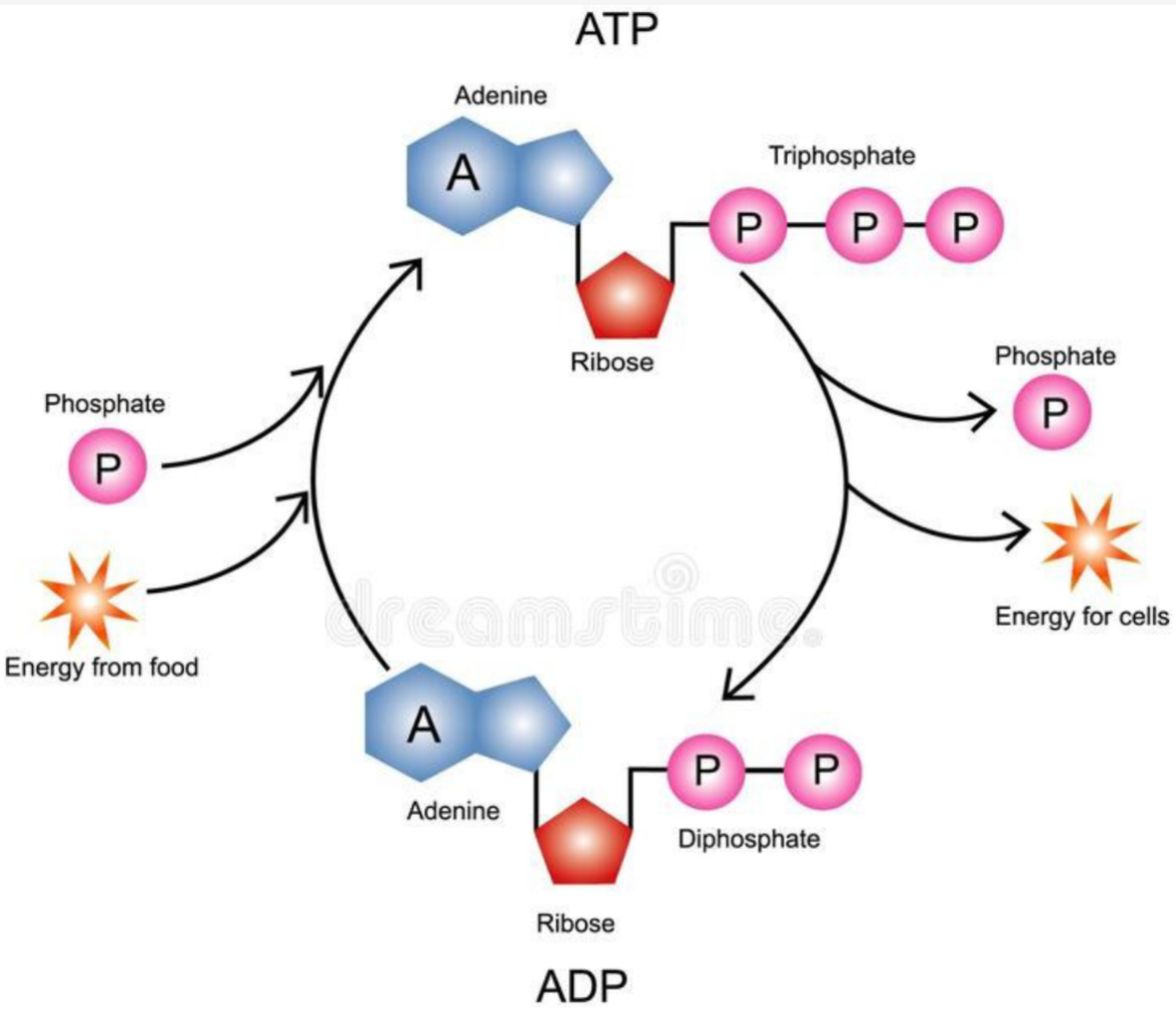
Chemical Energy + ATP
- %%Energy%% can come from %%light, heat, and electricity%%
- Can be ^^stored in chemical compounds^^
- Cells ==store and use ATP==
- ATP is @@made of@@:
- Adenine
- Ribose (5-sugar molecule)
- 3 phosphate groups
- The %%phosphate groups are the key to ATP use and recycling%%
^^Storing Energy^^
- ADP has ==2 phosphate groups instead of 3==
- A cell can @@store a small amount of energy@@ by @@adding one phosphate@@
Releasing Energy
- Energy is %%released by breaking one phosphate bond%%
- This bond must be between the ^^second and third bond^^
==Cellular Activites==
- Can be @@used for:@@
- Active transport across cell membranes
- %%Protein synthesis%%
- Muscle ^^contraction^^
- Most cells ==don’t store a lot of ATP== because it is ==not able to store large amounts of energy==
- Cells can @@regulate ATP from ADP@@ as needed by @@using the energy in foods like glucose@@
Lesson 8.2 - Photosynthesis Overview
- The Photosynthsis Equation
- Process in which %%green plants%% use the %%energy of sunligh%%t to %%convert water and carbon dioxide%% into %%high-energy carbs and oxygen%%
- ^^6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2^^
- Lights + ==Pigments==
- Photosynthesis also @@requires light and chlorophyll@@
- Plants absorb the sun’s energy with pigments
- %%Pigments%% are %%light-absobing%%
- The ^^main pigment^^ in plants is ^^chlorophyll^^
- Two ==main types of chlorophyll:==
- @@chlorophyll a@@
- @@chlorophyll b@@
- Chlorophyll absorbs light very well in the blue-violet and red regions
- This means that %%these colors are not visible%% to the naked eye on trees
- Chlorophyll does ^^not absorb light very well^^ in the ^^green and yellow regions^^
- This means that ==these colors are visible== to the naked eye on trees
- Light is a @@form of energy,@@ so @@when light is absorbed, so is energy@@
- When light is absorbed, much of the energy is moved directly to the electrons in the molecule, raising the energy levels of these electrons
- These electrons are %%what make photosynthesis work%%
- Electrons are ^^excited by light^^
- Factors ==Affecting Photosynthesis==
- Factors @@Affecting The Rate of Photosynthesis:@@
- Water
- Carbon D
- Temp
- Intensity of Light
- Ur Mom and Wooster The Rooster
- %%Enzymes%% do the %%physical work of making photosynthesis occur%%
- More ^^reactants, more enzymes, more work done^^
- You need ==more than just light for photosynthesis to be successful==
Lesson 8.3 - Reactions of Photosynthesis
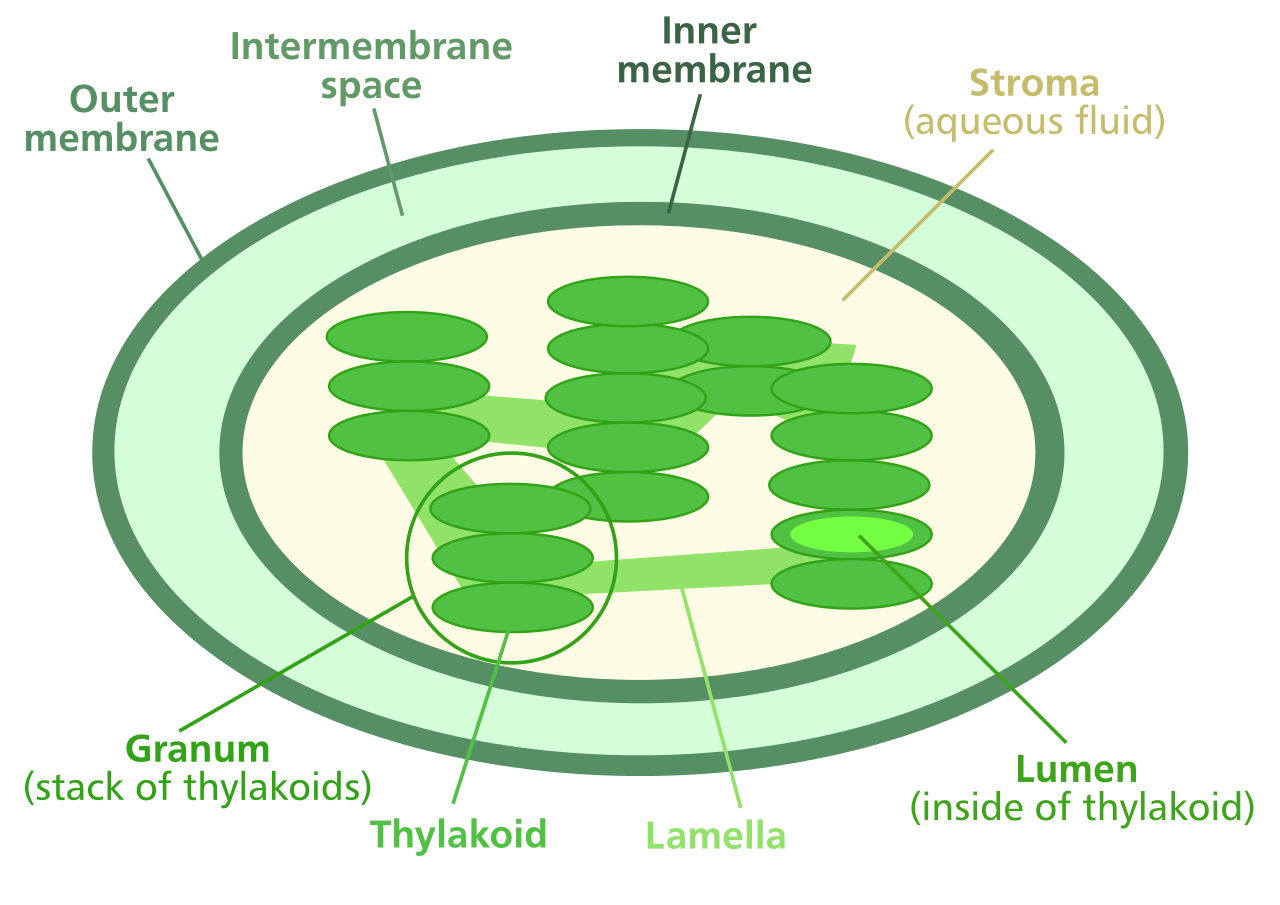
@@Inside a Chloroplast@@
- Photosynthsis occurs inside chloroplasts
- Chloroplasts %%contain thylakoids%%
- These are ^^saclike photosynthetic membranes^^
- Thylakoids are ==arranged in stacks known as grana==
- A @@singular stack is called a granum@@
- Proteins in the thylakoid membrane organize chlorophyll and other pigments into clusters called photosystems
- These are %%light-collecting units of the chloroplast%%
^^Steps to Photosynthesis^^
- There are ==2 steps to Photosynthesis:==
- @@Light-dependent@@ reactions
- These take place in the thylakoid membranes
- %%Light-independent%% reaction (also known as the %%Calvin Cycle%%)
- These ^^take place in the stroma^^, which is the ^^cytoplasm part of the chloroplast^^
==Electron Carriers==
- When electrons in @@chlorophyll absorb sunlight,@@ the @@electrons gain a great deal of energy@@
- Cells use electron carriers to transport these high-energy electrons to other molecules
- One carrier is called %%NADP+%%
- Transports ^^2 high-energy electrons along with a hydrogen ion (the parent)^^
- Convert ==NADP+ into NADPH==
- NADPH can store @@some of the energy from sunlight in chemical form@@
- The energy stored in NADPH can be used to build a variety of molecules including glucose (sugars) and carbs
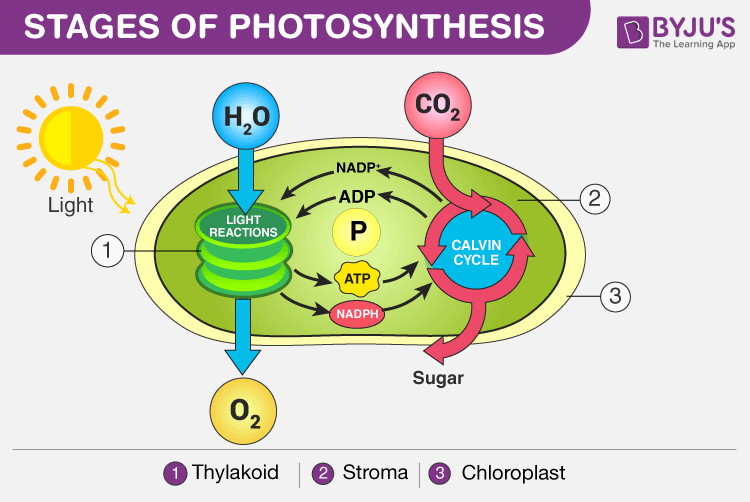
%%Light-Dependent%% Reactions
- ^^Require light^^
- ==Produce oxygen gas== and ==convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carries ATP and NADPH==
Inside A Thylakoid Processes:
Photosynthesis begins when pigments in photosystem II absorb light, increasing their energy level
These high-energy electrons are passed on to the electron transport chain
Enzymes on the thylakoid membrane break water molecules into:
hydrogen ions
oxygen atoms
energized electrons
The energized electrons from water replace the high-energy electrons that chlorophyll lost to the electron transport chain
As plants remove electrons from water, oxygen is left behind and is released into the air
The hydrogen ions left behind when water is broken apart are released inside the thylakoid membrane
Energy from the electrons moving down the electron transport chain (ETC) is used to transport H+ ions from the stroma into the inner thylakoid space
High-energy electrons move through the electron transport chain from photosystem II to photosystem I
Pigments in photosystem I use energy from light to re-energize the electrons
- NADP+ then picks up these high-energy electrons, along with H+ ions, and becomes NADPH
- As electrons are passed from chlorophyll to NADP+, more H+ ions are pumped across the membrane causing a concentration gradient
- The inside of the membrane has a high concentration of positively charged hydrogen ions, which makes the outside of the membrane negatively charged
- The difference in charges across the membrane provides the energy to make ATP
- H+ ions cannot cross the membrane directly, so the cell membrane contains a protein called ATP synthase that allows H+ ions to pass through it
- As it rotates, ATP synthase binds ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
- Because of this system, light-dependent electron transport produces not only high-energy electrons but ATP as well
Summary of Light-Dependent Reaction
- Light-dependent reaction use water, ADP, and NADP+
- Produce: Oxygen, ATP, and NADPH
- These provide the energy to build sugars from low-energy compounds
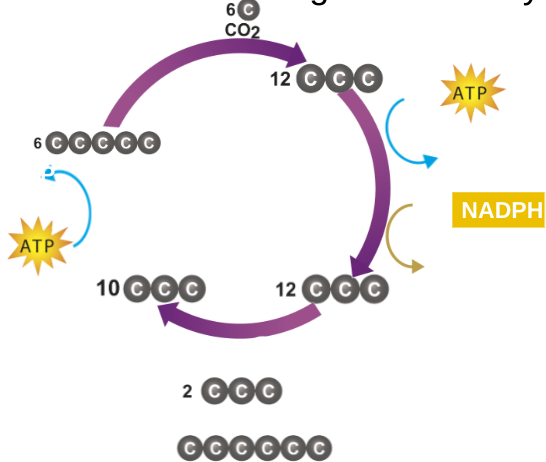
Calvin Cycle
- ATP and NADPH have a lot of chemical energy but are unstable to store energy for longer than a moment
- During this cycle, plants use the ATP and NADPH to build high-energy compounds that can be stored for a long time
- Uses ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to produce high-energy sugars
- These reactions are called light-independent
Summary:
- Two sets of photosynthetic reactions work together
- Light-dependent reactions trap sunlight in chemical form
- They use this energy to create stable, high-energy sugars from carbon and water