Unit 2: Population and Migration Patterns and Processes
Population Distributions:
People move to areas that give them more opportunities and happiness
Larger urban areas offer economic and social opportunities
Rural areas have move dispersed housing with a quieter lifestyle
Population Density:
Arithmetic density: the population/ the amount of land
Physiological Density: The population/ the amount of arable land
Agricultural Density: The amount of farmers/ the amount of arable land
Important Population Vocabulary:
Crude Birth Rate: Number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive.
Crude Death Rate: Number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive
Natural Increase Rate: The percentage by which a population grows in a year
Total Fertility Rate: The average number of children a woman will have
Dependency Ratio: The number of working people in a country who support the people in a country who cannot work
Sex Ratio: The ratio of males to females in a population
Doubling time: The time it takes for a population to double in size
Child Policies:
Antinatalist: policies that restrict population growth and motivate people to have less children.
China One-Child Policy, Singapore
Pronatalist: policies that encourage people to have more children
Russia
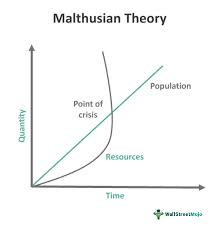
Malthusian Theory:
The population would grow exponentially until eventually reaching the Earth’s carrying capacity.
Human pop. grows exponentially
Food production grows arithmetically
Neo-Malthusians: People who believe that Thomas Malthus was right
Migration:
People move due to economic, political, social, or environmental reasons.
The number one reason for migration is economic
Ravenstein’s laws of migration:
Migrants move only a short distance
Migrants most likely move to cities
Migration is either forced or voluntary
Forced: When the migrant’s life or family’s life is in danger
Move to seek shelter and safety
Voluntary: the migrant chooses to migrate without fear of persecution or death
Intervening opportunities: Migrants can encounter a place on their journey that provides similar opportunities, causing them to stay.
Intervening obstacles: a barrier that interferes someone’s journey to their destination
ex: a mountain, border patrol